实验六
3.1.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <array> #define N 5 int main() { using namespace std; array<int, N> x {97, 98, 99, 100, 101}; ofstream out; out.open("data1.dat", ios::binary); if(!out.is_open()) { cout << "fail to open data1.dat\n"; return 1; } out.write(reinterpret_cast<char *>(&x), sizeof(x)); out.close(); }
3.2.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <array> #define N 5 int main() { using namespace std; array<char, N> x; ifstream in; in.open("data1.dat", ios::binary); if (!in.is_open()) { cout << "fail to open data1.dat\n"; return 1; } in.read(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&x), sizeof(x)); in.close(); for (auto i = 0; i < N; ++i) cout << x[i] << ", "; cout << "\b\b \n"; }
(1)read函数原型为:
istream& read (char* s, streamsize n); //用来暂存内容的数组(必须是char*型),以及流的长度
(2)reinterpret_cast:是四种强制转换中功能最为强大的,它可以暴力完成两个完全无关类型的指针之间或指针和数之间的互转,比如用char类型指针指向double值。它对原始对象的位模式提供较低层次上的重新解释(即reinterpret),完全复制二进制比特位到目标对象,转换后的值与原始对象无关但比特位一致,前后无精度损失。int型是4个字节,char型式1个字节,所以int型转成char型时多余的三个字节转成空格。
(3)data1.dat里面的内容有空格,将文件内容读入时,会将空格读入,导致上面的运行结果。
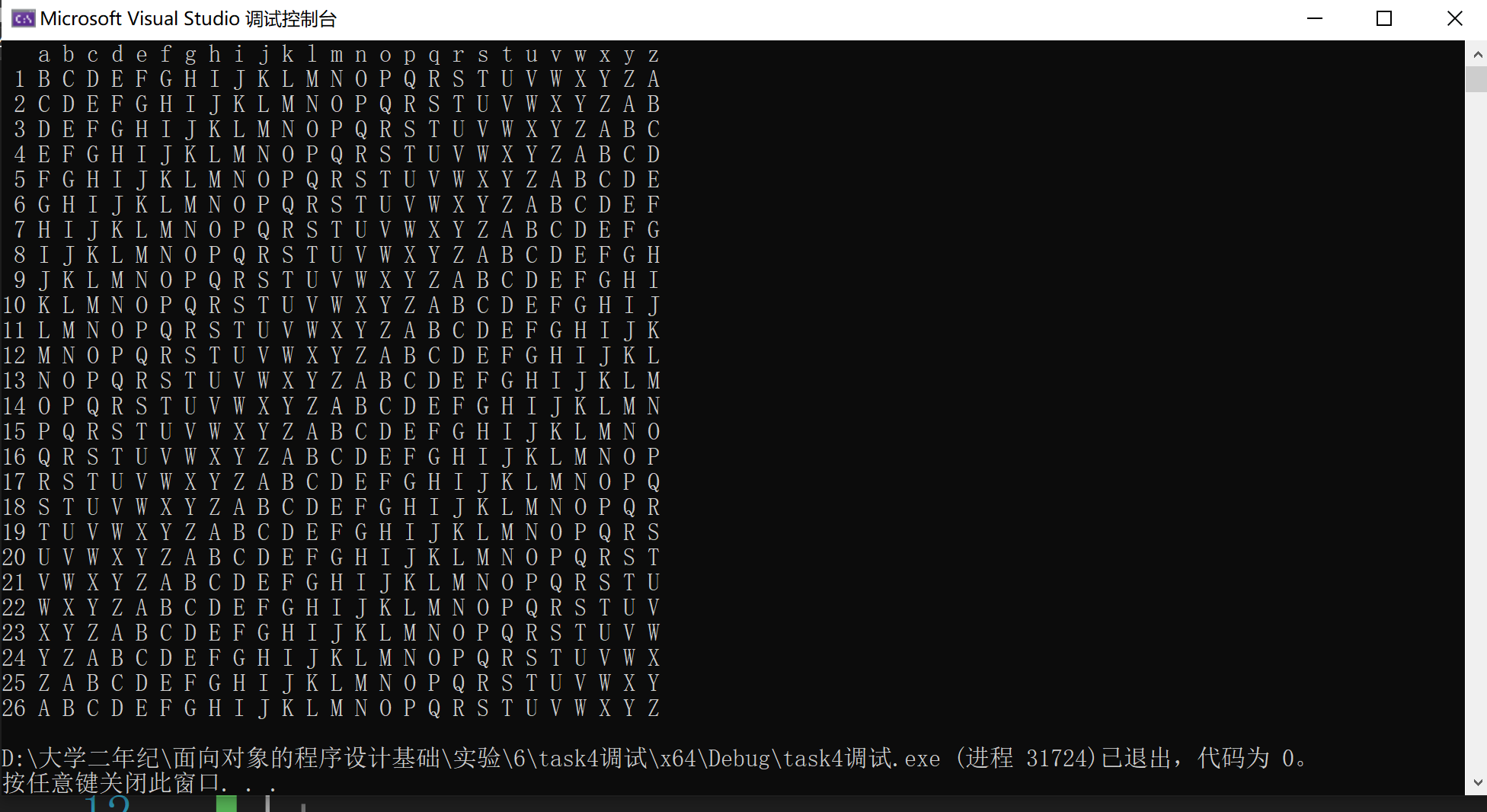
(4):将data1.dat里的空格删掉,得到运行结果如上图3:
4.cpp
#include <iostream> #include "Vector.hpp" void test() { using namespace std; int n; cin >> n; Vector<double> x1(n); for (auto i = 0; i < n; ++i) x1.at(i) = i * 0.7; output(x1); Vector<int> x2(n, 42); Vector<int> x3(x2); output(x2); output(x3); x2.at(0) = 77; output(x2); x3[0] = 999; output(x3); } int main() { test(); }
Vector.hpp:
#pragma once #include<iostream> #include<cassert> using std::cout; using std::cin; template<typename T> class Vector { public: Vector(int n) :size{ n } { p = new T[n]; } Vector(int n, T value) { size = n; p = new T[n](); for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) { p[i] = value; } } Vector(const Vector<T>& v); ~Vector() { delete[]p; } int get_size()const { return size; } T& at(int index) { assert(index >= 0 && index < size); return p[index]; } T& operator[](int index) { return p[index]; } template<typename T1> friend void output(const Vector<T1>& v); private: int size; T* p; }; template <typename T> Vector<T>::Vector (const Vector<T>& v) { size = v.size; p = new T[v.size]; for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) p[i] = v.p[i]; } template<typename T1> void output(const Vector<T1>& v) { for (int i = 0; i < v.size; ++i) cout << v.p[i] << ", "; cout << "\b\b \n"; }
5.cpp
#include<fstream> #include<iostream> #include<iomanip> using std::endl; using std::setw; using std::ofstream; void output(std::ostream& out) { out << " "; char n = 'a'; for (int i = 1; i <= 26; ++i, ++n) { out << setw(2) << n; } out << endl; for (int i = 1; i <= 26; ++i) { out << setw(2) << i; if (n == 'Z') n = 'A'; else n = i + 'A'; for (int j = 1; j <= 26; ++j, ++n) { out << setw(2) << n; if (n == 'Z') n = 'A' - 1; } out << endl; } } int main() { output(std::cout); ofstream out; out.open("cipher_key.txt"); if (!out.is_open()) { std::cout << "fail to open file cipher_key.txt.\n"; return 1; } output(out); out.close(); }