1. 程序为什么能识别模块
Ansible 能识别模块,主要因为以下几个原因:
root@jJkJOt1054298:~# ansible --version
ansible [core 2.17.3]
config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
configured module search path = ['/root/.ansible/plugins/modules', '/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules']
ansible python module location = /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/ansible
ansible collection location = /root/.ansible/collections:/usr/share/ansible/collections
executable location = /usr/local/bin/ansible
python version = 3.10.14 (main, Apr 6 2024, 18:45:05) [GCC 9.4.0] (/usr/bin/python3.10)
jinja version = 3.1.4
libyaml = True
configured module search path 是ansible的模块搜索路径,分别是上述列表中的元素,第一个元素/root/.ansible/plugins/modules是用户的本地模块目录,/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules是系统级别的模块目录,本地模块目录中对应的优先级更高.这两个路径表明ansible运行时,查找模块的位置
也就是如果自定义模块,可以将模块入到/root/.ansible/plugins/modules或/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules,以供ansible到这两个目录中加载模块
ansible python module location 表示ansible python模块位置,指向/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/ansible,表明ansible使用的python版本,及ansible的安装位置
ansible collection location表明ansible collection(集合)的目录路径,集合是一种打包和分发ansible内容包括(模块,插件,角色)的方式./root/.ansible/collections 拥有较高优先级,ansible会首先查询家目录下的集合./usr/share/ansible/collections是系统级别的集合目录
a. 模块是独立的脚本
Ansible 模块是 Python、Shell 或其他可执行脚本。Ansible 调用模块时,会在控制节点上将模块传输到目标主机,并在目标主机上执行。模块可以是 Python 文件(默认)或任何其他脚本语言,只要目标主机能够执行该语言。
b. 模块的路径与目录结构
Ansible 会在安装目录(如 /usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules/)中查找模块。此外,Ansible 还支持自定义模块,用户可以将自定义模块放在 library 目录下,Ansible 会自动识别这些模块并加载它们。
2. 模块的工作特性
a. ansible模块执行任务,会ssh到远程主机
b. ansible.module_utils.basic
它简化了模块的开发流程,提供了参数解析、结果处理、错误处理和跨平台兼容性等核心功能,帮助开发者编写模块时更专注于具体业务逻辑
c. 核心模块(Core Modules)与插件(Plugins)的区别
核心模块用于执行常见的自动化任务,如文件操作、软件包管理、服务管理、系统配置等
-
系统级模块路径:
/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules//usr/lib/pythonX.X/site-packages/ansible/modules//usr/local/lib/pythonX.X/dist-packages/ansible/modules/(取决于 Python 环境)
-
用户级模块路径:
~/.ansible/plugins/modules/(用户本地自定义模块目录)
-
自定义模块路径:
如果你定义了自己的模块,可以将其放在自定义路径中,并在ansible.cfg中通过library选项指定:[defaults] library = /path/to/custom/modules
插件是扩展 Ansible 功能的组件,它们可以执行各种辅助任务,如连接到远程主机、处理数据、过滤结果等.而是影响 Ansible 的执行方式。插件按类型分类,如 callback、lookup、connection 等,并存放在对应的插件路径下
-
系统级插件路径:
/usr/share/ansible/plugins//usr/lib/pythonX.X/site-packages/ansible/plugins//usr/local/lib/pythonX.X/dist-packages/ansible/plugins/(取决于 Python 环境)
-
用户级插件路径:
~/.ansible/plugins/
-
自定义插件路径:
用户可以自定义插件路径,并通过ansible.cfg中的plugin相关选项来指定。例如:[defaults] callback_plugins = /path/to/callback_plugins lookup_plugins = /path/to/lookup_plugins filter_plugins = /path/to/filter_plugins
3.构建简单模块
#创建目录
mkdir -p /root/.ansible/plugins/modules
cd /root/.ansible/plugins/modules
vim my_module.py
a.模块功能
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
DOCUMENTATION = '''
---
module: my_module
short_description: This is a test module
description:
- This module prints a hello message.
options:
name:
description:
- The name to greet.
required: true
type: str
author:
- Your Name (@yourgithubhandle)
'''
EXAMPLES = '''
# Greet Ansible
- name: Test custom module
my_module:
name: "Ansible"
'''
RETURN = '''
message:
description: The greeting message.
type: str
returned: always
'''
from ansible.module_utils.basic import AnsibleModule
def main():
module = AnsibleModule(
argument_spec=dict(
name=dict(type='str', required=True),
)
)
name = module.params['name']
result = dict(
changed=False,
message=f"Hello, {name}!"
)
module.exit_json(**result)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
b.模块文档
ansible-doc -M /root/.ansible/plugins/modules/ my_module
> MODULE my_module (/root/.ansible/plugins/modules/my_module.py)
This module prints a hello message.
OPTIONS (red indicates it is required):
name The name to greet.
type: str
AUTHOR: Your Name (@yourgithubhandle)
EXAMPLES:
# Greet Ansible
- name: Test custom module
my_module:
name: "Ansible"
RETURN VALUES:
message The greeting message.
returned: always
type: str
DOCUMENTATION:
这是模块的文档块,使用 YAML 格式来定义模块的名称、简短描述、选项参数及其要求等信息。Ansible 会根据这个块生成模块的帮助文档。
EXAMPLES:
这是示例块,展示如何在 playbook 中调用这个模块。它通常包含最常见的用法。
RETURN:
这个部分定义模块的返回值,以及每个字段的类型和描述。这样,使用者就可以清楚知道模块会返回哪些数据。
c.验证模块功能
ansible all -m my_module -a "name=Ansible"
localhost | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python3.10"
},
"changed": false,
"message": "Hello, Ansible!"
}
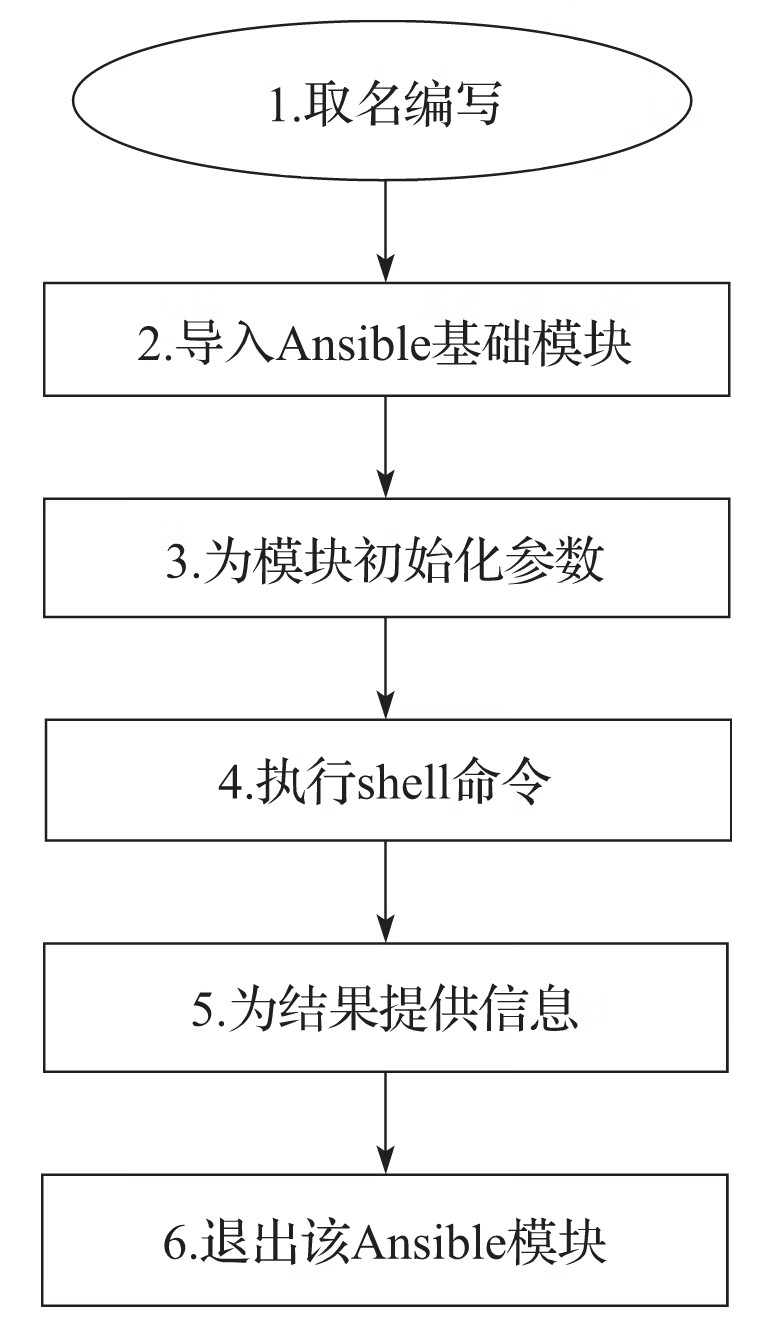
my_module.py
#!/usr/bin/python #指定python解析器
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- #指定文件编码
from ansible.module_utils.basic import AnsibleModule #引入AnsibleModule类
def main(): #定义main 函数
module = AnsibleModule(
argument_spec=dict(
name=dict(type='str', required=True),
)
)
name = module.params['name']
result = dict(
changed=False,
message=f"Hello, {name}!"
)
module.exit_json(**result)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
AnsibleModule是一个类名称,快速构建ansible模块
arguments_spec是AnsibleModule的一个参数,是一个是一个字典类型{}
name是arguments_spec下的参数名称,要求必须指定参数,name参数值类型为str,此名称与其值,皆可自定义
module.params['name']获取name参数
使用命令方式为
root@test:~# ansible all -m my_module -a "name=test"
elk1 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python3"
},
"changed": false,
"message": "Hello, test!"
}
使用剧本方式为
root@test:~# cat test.yaml
---
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: use my_module
my_module:
name: "test"
register: my_test
- name: debug my_module
debug:
msg: "{{ my_test }}"
root@test:~# ansible-playbook test.yaml
PLAY [all] *********************************************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************************************************************************
ok: [elk1]
TASK [use my_module] ***********************************************************************************************************************
ok: [elk1]
TASK [debug my_module] *********************************************************************************************************************
ok: [elk1] => {
"msg": {
"changed": false,
"failed": false,
"message": "Hello, test!"
}
}
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************************************************************************
elk1 : ok=3 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
result = dict(changed=False, message=f"Hello, {name}!" ): result用于存储模块执行后的结果信息.返回类型为字典,changed表示是否修改了主机状态,message表示反馈信息,使用了python语言中的插值方式将变量与字符串拼接
module.exit_json(**result): 用于获取返回结果,返回给ansible引擎,主要做清理和格式化输出工作,并退出任务
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
DOCUMENTATION = '''
---
module: my_module
short_description: This is a test module
description:
- This module prints a hello message.
options:
name:
description:
- The name to greet.
required: true
type: str
author:
- anyux (@anyux)
'''
EXAMPLES = '''
# Greet Ansible
- name: Test custom module
my_module:
name: "Ansible"
'''
RETURN = '''
message:
description: The greeting message.
type: str
returned: always
'''
from ansible.module_utils.basic import AnsibleModule
def main():
module = AnsibleModule(
argument_spec=dict(
name=dict(type='str', required=True),
)
)
name = module.params['name']
result = dict(
changed=False,
message=f"Hello, {name}!",
pass_code=0
)
module.exit_json(**result)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
test.yaml
---
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: use my_module
my_module:
name: "test"
register: my_test
- name: debug my_module
debug:
msg: "ok"
when: my_test.pass_code == 0
在剧本中可以通过when: my_test.pass_code == 0,判断条件执行结果
root@test:~# ansible-playbook test.yaml
PLAY [all] *********************************************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************************************************************************
ok: [elk1]
TASK [use my_module] ***********************************************************************************************************************
ok: [elk1]
TASK [debug my_module] *********************************************************************************************************************
ok: [elk1] => {
"msg": "ok"
}
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************************************************************************
elk1 : ok=3 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号