大模型MCP实战
背景和价值
MCP解决什么问题?MCP是Function Call的企业级实现.
Function calling有些缺点?MCP解决了什么问题
1 需要冗长的代码描述
2 要实现高并发,好的容错能力门槛高
3 (关键) 函数复用能力差。 一个团队开发的函数,其他团队要用只能拷贝过去用。不可复用的本质:大模型 Function Call 的代码通常与上下文管理、动态参数解析、模型交互等逻辑强耦合。
MCP的作用:将功能分解为模型(业务逻辑)、控制器(流程控制)、展示层(接口适配),解耦各层,使得每个部分可以独立复用。
具体解决方案:通过MCP架构,将Function Call的业务逻辑封装在Model层,控制器处理与模型的交互和参数解析,Presenter处理输入输出的适配,这样各部分可以独立变化和复用。
MCP C/S架构
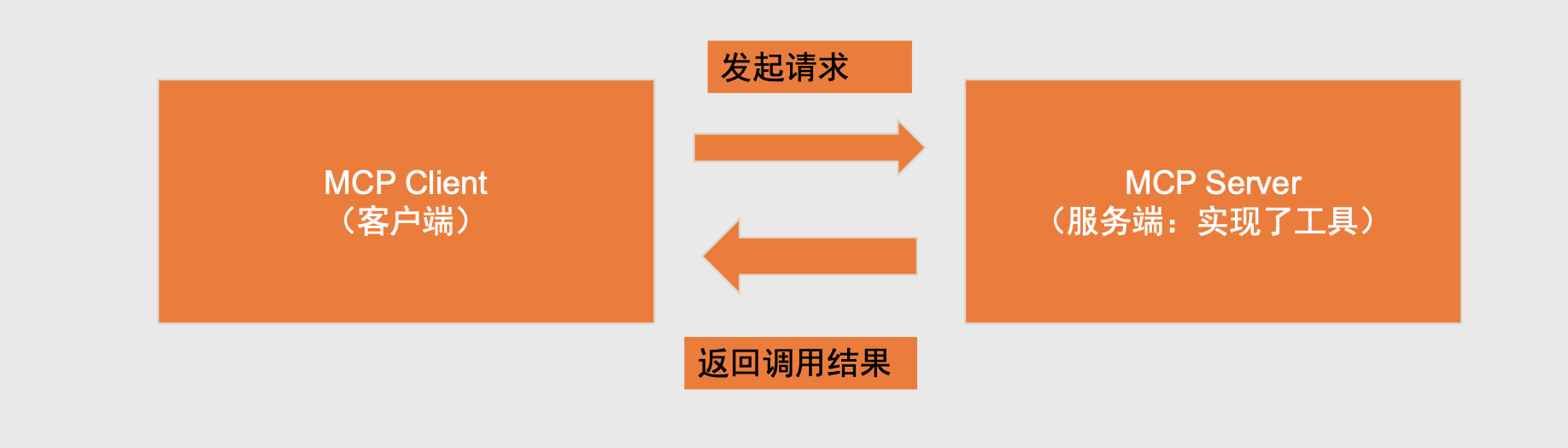
MCP 客户端和服务器端可以在一个服务器上,也可以在不同的服务器上。
MCP服务端可以调用 别人发布的server(生态),也可以自己实现MCP server
基于MCP开发最基本要实现客户端。
MCP Server通讯机制
Model Context Protocol(MCP)由Anthropic开源,用于将大型语言模型直接连接数据源。它支持标准输入输出(stdio) 和 基于HTTP的服务器推送事件(SSE) 两种传输方式。Stdio模式适用于本地通信,通过启动服务器作为子进程实现高效低延迟的数据交换,适合快速响应的本地应用。而基于HTTP和SSE的方式则适用于分布式或远程场景,实现客户端与服务器间实时数据推送。
-
本地通讯:使用了stdio传输数据,具体流程Client启动Server程序作为子进程,其消息通讯是通过stdin/stdout进行的,消息格式为JSON-RPC 2.0。
-
远程通讯:Client与Server可以部署在任何地方,Client使用SSE与Server进行通讯,消息的格式为JSON-RPC 2.0,Server定义了/see与/messages接口用于推送与接收数据
流程
服务端实现
初始化 MCP 服务器
mcp = FastMCP("WeatherServer")
实现外部函数
跟Function calling没什么区别,
注意事项
1 但是要定义为异步函数 (函数前 async),
2 函数注释要清晰
注册到MCP
使用 @mcp.tool() 装饰费
客户端事项
客户端端实现
连接到服务端
- 连接到服务端。 可以选择 标准输入输出或者网络的方式
- 向 MCP 服务器请求所有已注册的工具(用 @mcp.tool() 标记)
工具调用
获取所有的调用对象
获取所有的调用对象,把每个工具信息存到 列表
调用大模型(附上提示词和 工具信息列表)
如果大模型返回结果需要调用外部函数,需要处理调用外部函数
调用外部函数使用 MCP的API实现
result = await self.session.call_tool(tool_name, tool_args)
实例代码
客户端代码
import asyncio
import os
import json
from typing import Optional
from contextlib import AsyncExitStack
from openai import OpenAI
from openai import AsyncOpenAI
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from mcp import ClientSession, StdioServerParameters
from mcp.client.stdio import stdio_client
load_dotenv()
class MCPClient:
def __init__(self):
"""初始化 MCP 客户端"""
self.exit_stack = AsyncExitStack()
self.openai_api_key = os.getenv("DASHSCOPE_API_KEY") # 读取Key
self.model = os.getenv("MODEL") # 读取 model
if not self.openai_api_key:
raise ValueError("未找到 OpenAI API Key")
self.client = AsyncOpenAI(
api_key=os.getenv("DASHSCOPE_API_KEY"),
base_url="https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1"
)
# 关键信息存储
self.session: Optional[ClientSession] = None
self.exit_stack = AsyncExitStack()
async def connect_to_server(self, server_script_path: str):
"""连接到 MCP 服务器并列出可用工具"""
# 使用标准输入输出方式 客户端何服务端传递。 服务端脚本作为客户端参数,通过客户端启动服务端
is_python = server_script_path.endswith('.py')
is_js = server_script_path.endswith('.js')
## 判断服务器脚本是 Python 还是 Node.js,选择对应的运行命令
if not (is_python or is_js):
raise ValueError("服务器脚本必须是 .py 或 .js 文件")
command = "python" if is_python else "node"
## 告诉 MCP 客户端如何启动服务器
server_params = StdioServerParameters(
command=command,
args=[server_script_path],
env=None
)
# 启动 MCP 服务器并建立通信
stdio_transport = await self.exit_stack.enter_async_context(stdio_client(server_params))
self.stdio, self.write = stdio_transport
self.session = await self.exit_stack.enter_async_context(ClientSession(self.stdio, self.write))
await self.session.initialize()
# 向 MCP 服务器请求所有已注册的工具(用 @mcp.tool() 标记)
response = await self.session.list_tools()
tools = response.tools
print("\n已连接到服务器,支持以下工具:", [tool.name for tool in tools])
## 这个本质就是Function call
async def process_query(self, query: str) -> str:
"""
使用大模型处理查询并调用可用的 MCP 工具 (Function Calling)
"""
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": query}]
# 获取所有的调用对象
response = await self.session.list_tools()
# 获取所有的调用对象,把每个工具信息存到 available_tools
available_tools = [{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": tool.name,
"description": tool.description,
"input_schema": tool.inputSchema
}
} for tool in response.tools]
# print(available_tools)
response = await self.client.chat.completions.create(
model=self.model,
messages=messages,
tools=available_tools)
# 处理返回的内容
content = response.choices[0]
if content.finish_reason == "tool_calls":
# 如何是需要使用工具,就解析工具
tool_call = content.message.tool_calls[0]
tool_name = tool_call.function.name
tool_args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
# 执行工具
result = await self.session.call_tool(tool_name, tool_args)
print(f"\n\n[Calling tool {tool_name} with args {tool_args}]\n\n")
# 将模型返回的调用哪个工具数据和工具执行完成后的数据都存入messages中
messages.append(content.message.model_dump())
messages.append({
"role": "tool",
"content": result.content[0].text,
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id, })
# 将上面的结果再返回给大模型用于生产最终的结果
response = await self.client.chat.completions.create(
model=self.model,
messages=messages,
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
return content.message.content
async def chat_loop(self):
"""运行交互式聊天循环"""
print("\n 智能助手客户端已启动!输入 'quit' 退出")
while True:
try:
query = input("\n用户: ").strip()
if query.lower() == 'quit':
break
response = await self.process_query(query) # 发送用户输入到 OpenAIAPI
print(f"\n天气预报智能助手: {response}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"\n发生错误: {str(e)}")
async def cleanup(self):
"""清理资源"""
await self.exit_stack.aclose()
async def main():
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
print("Usage: python client.py <path_to_server_script>")
sys.exit(1)
client = MCPClient()
try:
await client.connect_to_server(sys.argv[1])
await client.chat_loop()
finally:
await client.cleanup()
if __name__ == "__main__":
import sys
asyncio.run(main())
服务端代码
import json
import httpx
from typing import Any
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
# 初始化 MCP 服务器
mcp = FastMCP("WeatherServer")
# OpenWeather API 配置
OPENWEATHER_API_BASE = "https://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather"
API_KEY = "5c939a7cc59eb8696fxxx75c5a9a" # 请替换为你自己的 OpenWeather API Key
USER_AGENT = "weather-app/1.0"
async def fetch_weather(city: str) -> dict[str, Any] | None:
"""
从 OpenWeather API 获取天气信息。
:param city: 城市名称(需使用英文,如 Beijing)
:return: 天气数据字典;若出错返回包含 error 信息的字典
"""
params = {
"q": city,
"appid": API_KEY,
"units": "metric",
"lang": "zh_cn"
}
headers = {"User-Agent": USER_AGENT}
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
try:
response = await client.get(OPENWEATHER_API_BASE, params=params,
headers=headers, timeout=30.0)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json() # 返回字典类型
except httpx.HTTPStatusError as e:
return {"error": f"HTTP 错误: {e.response.status_code}"}
except Exception as e:
return {"error": f"请求失败: {str(e)}"}
def format_weather(data: dict[str, Any] | str) -> str:
"""
将天气数据格式化为易读文本。
:param data: 天气数据(可以是字典或 JSON 字符串)
:return: 格式化后的天气信息字符串
"""
# 如果传入的是字符串,则先转换为字典
if isinstance(data, str):
try:
data = json.loads(data)
except Exception as e:
return f"无法解析天气数据: {e}"
# 如果数据中包含错误信息,直接返回错误提示
if "error" in data:
return f"{data['error']}"
# 提取数据时做容错处理
city = data.get("name", "未知")
country = data.get("sys", {}).get("country", "未知")
temp = data.get("main", {}).get("temp", "N/A")
humidity = data.get("main", {}).get("humidity", "N/A")
wind_speed = data.get("wind", {}).get("speed", "N/A")
# weather 可能为空列表,因此用 [0] 前先提供默认字典
weather_list = data.get("weather", [{}])
description = weather_list[0].get("description", "未知")
return (
f"城市{city}, {country}\n"
f"温度: {temp}°C\n"
f"湿度: {humidity}%\n"
f"风速: {wind_speed} m/s\n"
f"天气: {description}\n")
@mcp.tool()
async def query_weather(city: str) -> str:
"""
输入指定城市的英文名称,返回今日天气查询结果。
:param city: 城市名称(需使用英文)
:return: 格式化后的天气信息
"""
data = await fetch_weather(city)
return format_weather(data)
if __name__ == "__main__":
mcp.run(transport='stdio')
参考资料
agent API往MCP迁移
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/nQF-bUcmODpqo_SGPSxfbg




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号