Python
Python
是一种面向对象的动态类型语言,最初被设计用于编写自动化脚本(shell),随着版本的不断更新和语言新功能的添加,越来越多被用于独立的、大型项目的开发。
Python在执行时,首先会将.py文件中的源代码编译成Python的byte code(字节码),然后再由Python Virtual Machine(Python虚拟机)来执行这些编译好的byte code。
Python安装
https://www.python.org/下载安装包进行安装(猜测和java的JDK一样)
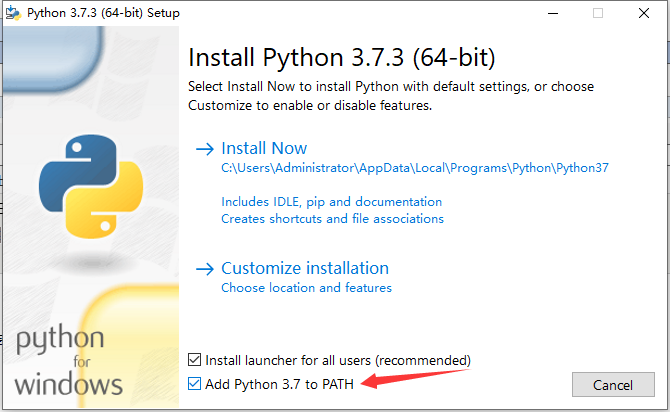
下载完成后安装,这里点击Add Python 3.7 to PATH添加到环境变量(3.5以下没有自动加入环境变量要自己配置),选择自定义安装。
测试Python是否安装成功
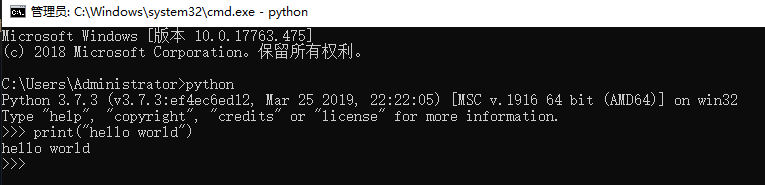
安装完成后,用cmd命令执行python命令,测试hello world
配置环境变量
在环境变量Path中加入%PYTHON_HOME%\Python37\和%PYTHON_HOME%\Python37\Scripts这两个路径

使用python
写python可以使用三种方式编辑,cmd、Python命令框、IDLE工具,前两种都是交互式,IDLE是文本编辑工具。
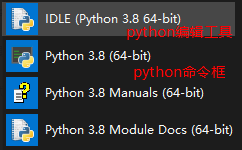
三种如下图

专业人员还是需要使用专业的工具,例如pycharm.
开发工具Pycharm
下载
去jetbrains的官网下载http://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/,可以下载专业版然后激活

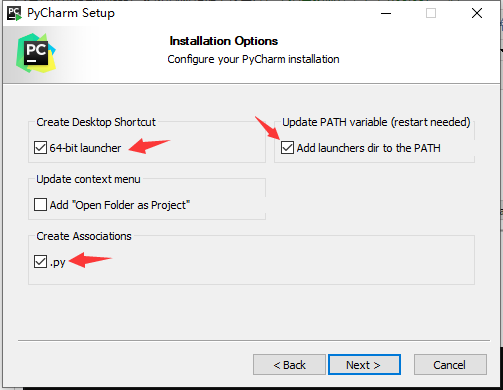
勾选如下的框
激活
进入到C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc文件夹下,修改hosts.txt
在最下面加
0.0.0.0 account.jetbrains.com
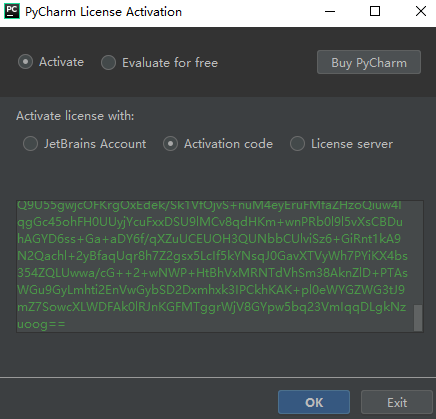
打开软件,弹出如下框,选择Activation Code,网上搜pycharm激活码
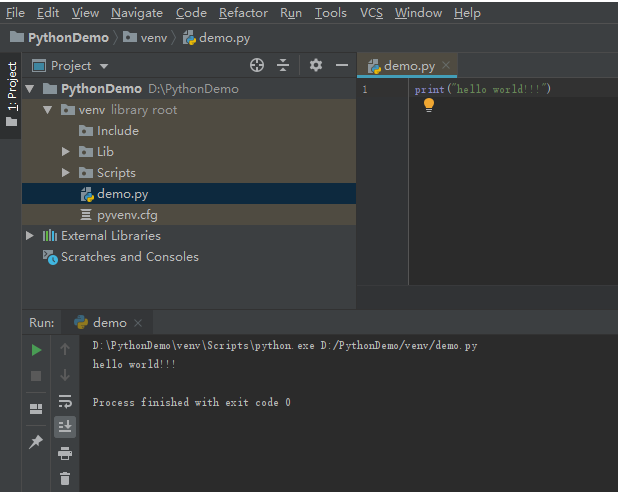
新建Pure Python项目,新建Python File,测试pycharm
数据类型
Python 中数据类型分为数字型和非数字型:
- Number(数字)
- int(整型)
- float(浮点型)
- bool(布尔型)
- complex(复数型)
非数字型
- String(字符串)
- List(列表)
- Tuple(元组)
- Dictionary(字典)
所有非数字型变量都支持以下特点:
- 都是一个序列sequence,可以理解为容器
- 取值[]
- 遍历for in
- 计算长度、最大/最小值、比较、删除
- 链接+和重复*
- 切片
列表
''' 列表最频繁的数据类型 用[]来定义list,数据之间由,分割 长度可变 索引从0开始 ''' #定义一个列表 name_list = [1,2,3,4,5,6] #末位添加数据 name_list.append('python') #指定位置插入数据 name_list.insert(2,'python') #将列表二添加到列表一 age_list = [7,8,9] name_list.extend(age_list) #修改指定索引的数据 name_list[0] = 'first' #删除指定索引的的数据 (不赞同使用,从内存中删除变量) del name_list[4] #删除第一个出现的指定数据 name_list.remove(8) #删除末尾的数据,默认是弹出最后一个 name_list.pop() #列表长度 print(len(name_list)) #数据在列表中出现的次数 print(name_list.count('python')) #排序 name_list2 = [1,2,3,4,5,6] name_list2.sort() #升序 print(name_list2) name_list2.sort(reverse=True) #降序 print(name_list2) print(name_list)
元组
''' 元组:tuple 和列表类似 不同的是元组元素不能修改 多个元素组成 定义:小括号() 索引从0开始 ''' info_tuple = (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,1) print(info_tuple) #打印元组() #数据类型的转换 元组转list list_data = list(info_tuple) print(list_data) #打印列表[] #如果在元素中只有一个元素 需要加, #info_tuple1 = (1) 这样写类型返回为int info_tuple1 = (1,) print(type(info_tuple1)) #查看元素出现的次数 print(info_tuple.count(1)) #查看元素的索引 print(info_tuple.index(2)) #遍历 print('遍历元组') for i in info_tuple: print(i)
字典
''' 字典(dictionary):无序 定义:{} 键值对 ,分割 键key是索引 值value数据 键:值 键是唯一的 值是任何数据类型 但是键只能是字符串 数组 或者元素 ''' IronMan = { 'name':'stack', 'age':36, 'gender':True, 'height':1.80 } #通过键来取值 print(IronMan['name']) print(IronMan.get('age')) # 取到字典的所有键 for i in IronMan.keys(): print(i) # 取到字典的所有值 for i in IronMan.values(): print(i) #取到键值对\ for i,v in IronMan.items(): print(i,v) #删除 del IronMan['name'] IronMan.pop('height') #修改 IronMan['age'] = 40 #合并 ,键重复则覆盖 SpiderMan = { 'age':20, 'height1':180 } IronMan.update(SpiderMan)
print(IronMan)
顺序选择循环
if语句
if 条件1: 语句1…… elif 条件2: 语句2…… else: 执行语句3……
while语句
while 条件: 语句……
石头剪刀布
''' 引入random函数 ''' import random while 1==1: #将输入转为int player = int(input("请出: (1)石头 (2)剪刀 (3)布")) computer = random.randint(1,3) print(computer) if(player== 0): #当为0时跳出循环 print("退出") break; if(player ==1 and computer==2) or (player == 2 and computer == 3) or (player == 3 and computer == 1): print("you win") elif player == computer: print("平局") else: print("你输了")
函数
''' def 函数名(): 函数封装的代码 函数名() 调用函数 def define 缩写 函数名称 可以表达函数封装代码的功能 符合标志符 命名规则 字母 数组 下划线 不能以数字开头 不能与关键字重名 ''' #定义一个无参函数 #python的解释器 知道我们定义了一个函数 def sayHello(): print('hello world') print('hello!!!') #调用函数 sayHello() #定义一个有参函数 #定义时,小括号里的参数为形参 def num_sum(num1,num2): result = num1+num2 print('{}+{}+{}'.format(num1,num2,result)) #调用时,小括号里的参数为实参 num_sum(50,60) ''' 函数的返回值:一个函数执行结束后 告诉调用者一个结果 返回值是函数完成工作后 最后给调用者的一个结果 在函数内部使用return关键字可以返回结果 调用的一方需要用变量来进行接收 ''' #定义一个有参函数 def num_sum2(num1,num2): result = num1+num2 return result #使用一个变量来接收参数 result = num_sum2(50, 70) print(result)
不定参数
''' *args表示任何多个无名参数,它是一个tuple;**kwargs表示键值对参数,它是一个dict 同时使用*args和**kwargs时,必须*args参数列要在**kwargs前 *args:元组 **kwargs:字典 ''' def test(a,*args,**kwargs): print(a) print(args) print(kwargs) #打印tuple和dictionary中的值 print(args[0]) #根据下标取元组中值 print(kwargs['d']) #根据键取字典中值 test(1,'2',3,d='4',e=5)
@装饰函数
和面向对象的装饰模式有异曲同工之妙,第一次被python这门语言震撼到。
无参装饰函数
#装饰函数 def funA(fn): #@装饰函数会在原函数声明时就开始装饰原函数,所以这里的print在原函数声明时就开始执行 print("before ...") fn() print("after ...") return '装饰器函数结果'; #原函数 #这里@funA相当于funB = funA(funB),因为funA返回的是一个字符串,所以此时funB为funA返回的字符串 @funA def funB(): print("func was called") #funB函数经过装饰funB已经变字符串类型,打印装饰函数返回的字符串 print(funB);
带参数装饰模式
#装饰函数 def funA(fn): # 定义一个嵌套函数,arc即为原函数fn的参数,这里把原函数包装成新的函数 def new_funB(arc): #fn(arc) print("装饰函数:",arc) #把原本的函数包装为一个新的函数并返回 return new_funB #原函数,使用@表示被funA函数装饰 @funA def funB(arc): print("funA函数执行",arc) #调用funB实际为被funA装饰后的函数funB = funA(funB) funB("参数")
类
类定义
类定义及_init_构造函数,参数self代表实例。
#!/usr/bin/python3 #类定义 class people: #定义基本属性 name = '' age = 0 #定义私有属性,私有属性在类外部无法直接进行访问 __weight = 0 #定义构造方法 def __init__(self,n,a,w): self.name = n self.age = a self.__weight = w def speak(self): print("%s 说: 我 %d 岁。" %(self.name,self.age)) # 实例化类 p = people('runoob',10,30) p.speak()
单继承
#单继承示例 class student(people): grade = '' def __init__(self,n,a,w,g): #调用父类的构函 people.__init__(self,n,a,w) self.grade = g #覆写父类的方法 def speak(self): print("%s 说: 我 %d 岁了,我在读 %d 年级"%(self.name,self.age,self.grade))
多继承
#另一个类,多重继承之前的准备 class speaker(): topic = '' name = '' def __init__(self,n,t): self.name = n self.topic = t def speak(self): print("我叫 %s,我是一个演说家,我演讲的主题是 %s"%(self.name,self.topic)) #多重继承 class sample(speaker,student): a ='' def __init__(self,n,a,w,g,t): student.__init__(self,n,a,w,g) speaker.__init__(self,n,t) test = sample("Tim",25,80,4,"Python") test.speak() #方法名同,默认调用的是在括号中排前地父类的方法
方法重写
#!/usr/bin/python3 class Parent: # 定义父类 def myMethod(self): print ('调用父类方法') class Child(Parent): # 定义子类,重写myMethod方法 def myMethod(self): print ('调用子类方法') c = Child() # 子类实例 c.myMethod() # 子类调用重写方法 #super(类,对象实例) super(Child,c).myMethod() #用子类对象调用父类已被覆盖的方法
config.ini配置读取
config.py模块代码如下
import os import configparser #声明一个类,集成object类 class Config(object): #定义构造函数,self代表实例本身,config_file形参赋初值,config.ini必须在config.py同目录下 def __init__(self, config_file='config.ini'): #通过os库获取目录join拼接成文件全路径 self._path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), config_file) #检测是否存在文件 if not os.path.exists(self._path): #抛出FileNotFound异常 raise FileNotFoundError("No such file: config.ini") #configRaw self._config = configparser.ConfigParser() self._config.read(self._path, encoding='utf-8-sig') #获取configRaw self._configRaw = configparser.RawConfigParser() self._configRaw.read(self._path, encoding='utf-8-sig') def get(self, section, name): return self._config.get(section, name) def getRaw(self, section, name): return self._configRaw.get(section, name) #实例化一个变量,其他module需要导入时可以用from config import global_config直接导入这个实例 global_config = Config() #测试,读取config.ini配置文件中[config]段的键为fp的值 ip=global_config.getRaw("config","ip"); print(ip);
其他模块引用
#引入config模块中的global_config实例变量 from config import global_config #直接使用global_config这个实例即可 ip=global_config.getRaw("config","ip"); print(ip);
自定义异常
exception.py
#自定义一个异常 class AutException(Exception): #构造函数 def __init__(self, message): super().__init__(message) #测试 raise AutException('自定义异常');
日志模块
Aut_logger.py
import logging import logging.handlers ''' 日志模块 ''' LOG_FILENAME = 'autumn.log' #获取日志实例 logger = logging.getLogger() #设置日志模板方法 def set_logger(): logger.setLevel(logging.INFO) formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(process)d-%(threadName)s - ' '%(pathname)s[line:%(lineno)d] - %(levelname)s: %(message)s') console_handler = logging.StreamHandler() console_handler.setFormatter(formatter) logger.addHandler(console_handler) file_handler = logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler( LOG_FILENAME, maxBytes=10485760, backupCount=5, encoding="utf-8") file_handler.setFormatter(formatter) logger.addHandler(file_handler) #设置日志模板 set_logger() #测试,其他模块引入from logger import logger后直接调用logger的方法 logger.info('信息展示'); logger.error('结果异常')
Request请求
import requests; url = 'http://www.xxx.com/name.png'; response_data = requests.get(url) #判断是否请求成功,返回true/false def getresponse_status(resp): if resp.status_code != requests.codes.OK: print('Status: %u, Url: %s' % (resp.status_code, resp.url)) return False return True #打印是否成功 print(getresponse_status(response_data))
图片保存
requests下载保存图片,pillow打开图片
import requests; #pip install pillow安装,可以展示图片 from PIL import Image #url地址 url = 'http://www.xxx.com/name.png'; #响应内容 response_data = requests.get(url) #打印内容,content - 字节 print(response_data.content) #数据保存 #with open('文件名','文件读写方式','文本编码格式') as f: # f.write() #w 有则写入无则创建,b进制文件的读写方式 with open("img.jpg","wb") as f: #把字节写入文件 f.write(response_data.content) #打开图片 im = Image.open("img.jpg") #展示图片 im.show() #关闭 im.close()
大图片下载
requests下载保存图片,os打开图片
import requests; import os; #保存大图片 def save_image(resp, image_file): with open(image_file, 'wb') as f: for chunk in resp.iter_content(chunk_size=1024): f.write(chunk) #定义打开图片方法 def open_image(image_file): if os.name == "nt": os.system('start ' + image_file) # for Windows else: if os.uname()[0] == "Linux": if "deepin" in os.uname()[2]: os.system("deepin-image-viewer " + image_file) # for deepin else: os.system("eog " + image_file) # for Linux else: os.system("open " + image_file) # for Mac #请求图片 url = 'http://www.xxx.com/name.png'; response_data = requests.get(url) #保存打开 save_image(response_data,"bigimg.jpg") open_image("bigimg.jpg")
禁用安全请求警告
import urllib3 from urllib3.exceptions import InsecureRequestWarning #禁用安全请求警告 urllib3.disable_warnings(InsecureRequestWarning)
随机请求头
import random USER_AGENTS = [ "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/41.0.2228.0 Safari/537.36", "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/41.0.2227.1 Safari/537.36", "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/41.0.2227.0 Safari/537.36", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/41.0.2227.0 Safari/537.36", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.3; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/41.0.2226.0 Safari/537.36", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.4; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/41.0.2225.0 Safari/537.36", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.3; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/41.0.2225.0 Safari/537.36", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 5.1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/41.0.2224.3 Safari/537.36", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/40.0.2214.93 Safari/537.36" ] #随机选择列表中的一个值 def get_random_useragent(): return random.choice(USER_AGENTS)
带Header&Param请求
import requests def send_withParam(message): #url,{}为字符串占位符 url = 'http://www.xxxx.com/{}/send'.format("restful") #http参数 payload = { "param1":'参数一', "param2": message } #http请求头 headers = { 'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/41.0.2228.0 Safari/537.36' } #发送请求 res = requests.get(url, params=payload, headers=headers)
return res.text;
Json解析
import json def parse_json(s): #可以直接json.loads(s),加个s[begin:end]截取首个{和尾个}可以排除首位的非json数据 begin = s.find('{') end = s.rfind('}') + 1 return json.loads(s[begin:end]) #测试 if __name__ == "__main__": str = '干扰数据1{"total":2,"rows":[{"startStamp":"1610007480","startTime":"2021-01-07 16:18"},{"startStamp":"1610007480","startTime":"2021-01-07 16:18"}]}干扰数据2' #解析并取出键为total的值 t = parse_json(str)['total'] print(t) #解析并取出键为rows的值 r = parse_json(str)['rows'] print(r)
Sleep随机时间
睡眠0.1s~0.3s
import random import time #等待0.1s~0.3s def wait_some_time(): time.sleep(random.randint(100, 300) / 1000)
时间
import time import requests import json from datetime import datetime from Aut_logger import logger from config import global_config class Timer(object): def __init__(self, sleep_interval=0.5): #获取购买时间 self.buy_time = datetime.strptime(global_config.getRaw('config','buy_time'), "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f") #购买时间转换为购买时间毫秒数 self.buy_time_ms = int(time.mktime(self.buy_time.timetuple()) * 1000.0 + self.buy_time.microsecond / 1000) #等待间隔 self.sleep_interval = sleep_interval #时间区别 self.diff_time = self.local_jd_time_diff() #获取服务器时间 def jd_time(self): """ 从京东服务器获取时间毫秒 :return: """ url = 'https://a.jd.com//ajax/queryServerData.html' #接口 ret = requests.get(url).text #请求接口返回json字符串 js = json.loads(ret) #json字符串转换为json return int(js["serverTime"]) #根据json的key获取值 #获取本地时间戳 def local_time(self): """ 获取本地毫秒时间 :return: """ return int(round(time.time() * 1000)) #获取时间差 def local_jd_time_diff(self): """ 计算本地与京东服务器时间差 :return: """ return self.local_time() - self.jd_time() #当大于某时间点时跳出循环 def start(self): logger.info('正在等待到达设定时间:{},检测本地时间与京东服务器时间误差为【{}】毫秒'.format(self.buy_time, self.diff_time)) while True: # 本地时间减去与京东的时间差,能够将时间误差提升到0.1秒附近 # 具体精度依赖获取京东服务器时间的网络时间损耗 if self.local_time() - self.diff_time >= self.buy_time_ms: logger.info('时间到达,开始执行……') break else: time.sleep(self.sleep_interval)
Session对象带cookie
import requests import os import pickle from config import global_config class SpiderSession: """ Session初始化相关操作,设置cookie目录,设置带header的session """ def __init__(self): self.cookies_dir_path = "./cookies/" self.user_agent = global_config.getRaw('config', 'DEFAULT_USER_AGENT') self.session = self._init_session() #获取session函数 - 初始化用 def _init_session(self): session = requests.session() session.headers = self.get_headers() return session #获取请求头函数 - 初始化用 def get_headers(self): return {"User-Agent": self.user_agent, "Accept": "text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;" "q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;" "q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;" "v=b3", "Connection": "keep-alive"} #获取请求头 def get_user_agent(self): return self.user_agent #获取session def get_session(self): """ 获取当前Session :return: """ return self.session #从session中获取cookie def get_cookies(self): """ 获取当前Cookies :return: """ return self.get_session().cookies #设置session中的cookie def set_cookies(self, cookies): self.session.cookies.update(cookies) #从本地文件中获取cookie,并放入session.cookie中 def load_cookies_from_local(self): """ 从本地加载Cookie :return: """ cookies_file = '' if not os.path.exists(self.cookies_dir_path): #判断cookies文件夹是否存在 return False #没有则直接返回false for name in os.listdir(self.cookies_dir_path): #遍历cookies文件夹下面的文件 if name.endswith(".cookies"): #判断文件是否以cookies结尾 cookies_file = '{}{}'.format(self.cookies_dir_path, name) #把./cookies/路径和文件(cookies结尾)连接 break if cookies_file == '': return False with open(cookies_file, 'rb') as f: #打开cookies结尾的文件 local_cookies = pickle.load(f) #pickle库读取文件中的内容(cookie) self.set_cookies(local_cookies) #把文件中的cookie放入session中 #保存cookie到本地 def save_cookies_to_local(self, cookie_file_name): """ 保存Cookie到本地 :param cookie_file_name: 存放Cookie的文件名称 :return: """ cookies_file = '{}{}.cookies'.format(self.cookies_dir_path, cookie_file_name) #获取cookie文件全路径 directory = os.path.dirname(cookies_file) #返回文件的目录路径 if not os.path.exists(directory): #如果目录不存在 os.makedirs(directory) #则创建目录 with open(cookies_file, 'wb') as f: #打开文件 pickle.dump(self.get_cookies(), f) #将cookie对象保存到文件中
二维码登录
import random import time import requests import json from Aut_logger import logger from timer import Timer from config import global_config from exception import AutException from util import ( parse_json, send_wechat, wait_some_time, response_status, save_image, open_image ) #二维码扫码 class QrLogin: """ 扫码登录 """ def __init__(self, spider_session: SpiderSession): """ 初始化扫码登录 大致流程: 1、访问登录二维码页面,获取Token 2、使用Token获取票据 3、校验票据 :param spider_session: """ self.qrcode_img_file = 'qr_code.png' #文件名 self.spider_session = spider_session #获取带cookie的session对象 self.session = self.spider_session.get_session() #获取session self.is_login = False #是否登录 self.refresh_login_status() #验证 #刷新是否登录状态 def refresh_login_status(self): """ 刷新是否登录状态 :return: """ self.is_login = self._validate_cookies() #验证cookie是否有效 def _validate_cookies(self): """ 验证cookies是否有效(是否登陆) 通过访问用户订单列表页进行判断:若未登录,将会重定向到登陆页面。 :return: cookies是否有效 True/False """ url = 'https://order.jd.com/center/list.action' payload = { 'rid': str(int(time.time() * 1000)), } try: resp = self.session.get(url=url, params=payload, allow_redirects=False) #禁止重定向 if resp.status_code == requests.codes.OK: return True except Exception as e: logger.error("验证cookies是否有效发生异常", e) return False #获取登录页面,此时 def _get_login_page(self): """ 获取PC端登录页面 :return: """ url = "https://passport.jd.com/new/login.aspx" page = self.session.get(url, headers=self.spider_session.get_headers()) return page #获取二维码并自动打开 def _get_qrcode(self): """ 缓存并展示登录二维码 :return: """ url = 'https://qr.m.jd.com/show' payload = { 'appid': 133, 'size': 147, 't': str(int(time.time() * 1000)), } headers = { 'User-Agent': self.spider_session.get_user_agent(), 'Referer': 'https://passport.jd.com/new/login.aspx', } resp = self.session.get(url=url, headers=headers, params=payload) if not response_status(resp): logger.info('获取二维码失败') return False save_image(resp, self.qrcode_img_file) logger.info('二维码获取成功,请打开京东APP扫描') open_image(self.qrcode_img_file) return True #扫码后接口获取token def _get_qrcode_ticket(self): """ 通过 token 获取票据 :return: """ url = 'https://qr.m.jd.com/check' payload = { 'appid': '133', 'callback': 'jQuery{}'.format(random.randint(1000000, 9999999)), 'token': self.session.cookies.get('wlfstk_smdl'), '_': str(int(time.time() * 1000)), } headers = { 'User-Agent': self.spider_session.get_user_agent(), 'Referer': 'https://passport.jd.com/new/login.aspx', } resp = self.session.get(url=url, headers=headers, params=payload) if not response_status(resp): logger.error('获取二维码扫描结果异常') return False resp_json = parse_json(resp.text) #解析返回的文本 if resp_json['code'] != 200: logger.info('Code: %s, Message: %s', resp_json['code'], resp_json['msg']) return None else: logger.info('已完成手机客户端确认') return resp_json['ticket'] #返回接口中ticket部分 #验证票据 def _validate_qrcode_ticket(self, ticket): """ 通过已获取的票据进行校验 :param ticket: 已获取的票据 :return: """ url = 'https://passport.jd.com/uc/qrCodeTicketValidation' headers = { 'User-Agent': self.spider_session.get_user_agent(), 'Referer': 'https://passport.jd.com/uc/login?ltype=logout', } resp = self.session.get(url=url, headers=headers, params={'t': ticket}) if not response_status(resp): return False resp_json = json.loads(resp.text) if resp_json['returnCode'] == 0: return True else: logger.info(resp_json) return False #通过二维码登录 def login_by_qrcode(self): #session请求登录页 self._get_login_page() # 下载二维码 if not self._get_qrcode(): raise AutException('二维码下载失败') # 获取票据 ticket = None retry_times = 85 for _ in range(retry_times): #循环85次 ticket = self._get_qrcode_ticket() #获取ticket if ticket: #如果请求到ticket则退出 break time.sleep(2) #每次睡眠2秒 else: raise AutException('二维码过期,请重新获取扫描') # 验证ticket有效 if not self._validate_qrcode_ticket(ticket): raise AutException('二维码信息校验失败') #再次验证是否登录成功 self.refresh_login_status() logger.info('二维码登录成功')
安装其他模块
在线安装
pip线上安装库
pip install requests

安装时指定源
pip install packageNmae -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
packageNmae: 需要安装的第三方库的名字
-i: 选项 --index-url 的缩写
中国境内常用的源
阿里云:http://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
清华:https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
中科大:https://pypi.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/simple/
配置永久国内的源
# 命令会生成一个名为pi 的文件夹,并在该文件夹内生成一个名为 pip.ini 的文件, # 路径C:\Users\your_username\AppData\Roaming\pip\pip.ini # 使用 --global 选项时,pip.ini 文件位于 C:\ProgramData\pip\pip.ini pip config set global.index-url https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple # 直接使用记事本打开 pip.ini pip config --editor notepad edit --user # 或 pip config --editor notepad edit --global # 查看配置项 pip config list # 查看指定配置项 pip config get global.index-url
离线包安装
pypi网站:https://pypi.python.org/pypi/
国内网站:https://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/
下载好whl压缩包,然后用命令安装
pip install ***.whl





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号