Nginx
Unix和Linux平台下的常见Web服务器有:
1. apache
2. nginx
3. lighttpd
4. tomcat
5. Ibm websphere
其中最广泛的是nginx,在windows平台上最常用的是微软的IIS(internet information server)是windows系统
默认的web服务程序。
Apache
apache是世界主流的web服务器,世界上大多著名网站都是apache搭建,优势在于开放源代码,开发维护团队
强大,支持跨平台(unix,linux,windows),强大的移植性等优点。
apache属于重量级产品,功能以模块化定制,消耗内存较高,性能稍弱于其他轻量级web服务器。
lighttpd
lighttpd是一款高安全性,快速,且灵活的web服务器产品,专为高性能环境而设计,相比其他web服务器,内存
占用量小,能够有效管理cpu负载,支持(FastCGI,SCGI,auth,输出压缩,url重写,别名)
等重要功能,是Nginx的重要对手之一。
Tomcat
Tomcat是一个开源,运行基于java的web应用软件的容器,Tomcat server根据sevlet和JSP规范执行,但是tomcat
对于平台文件,高并发处理较弱,要使用tomcat需要对java的应用部署有足够的了解。
IBM WebSphere Application Server
IBM WebSphere Application Server 是一种强大的Web应用服务器,基于Java的应用环境,建立,部署和管理网站应用。
Microsoft IIS
微软的IIS是一种灵活,安全易管理的web服务器,从流媒体到web应用程序,IIS提供了图形化的管理界面,用于配置
和管理网络服务。
IIS 是一整套web组件,包含了web服务器,FTP服务器,SMTP服务器等常用的网页浏览,文件传输,邮件新闻等功能。
缺点是只能运行在Windows平台,还得购买商业化的操作系统。
Nginx
Nginx以高效的epoll,kqueue,eventport作为网络IO模型,在高并发场景下,Nginx能够轻松支持5W并发连接数,
并且消耗的服务器内存,CPU等系统资源却很低,运行非常稳定。
国内著名站点,新浪微博,网易,淘宝,豆瓣,迅雷,等大型网站都在使用Nginx作为Web服务器,或者反向代理服务器。
Nginx资源消耗低/性能强
apache使用的是网络I/O模型中传统的select模型,nginx使用的是epoll模型。
nginx成本低
nginx优势:
1. 配置文件简单易读。
2. 支持rewrite重写,根据域名,url不同,转发http请求到不同的后端服务器组。
3. 高可用性,稳定性,宕机几率很低。
4. 节省资源,支持GZIP压缩静态资源。
5. 支持热部署,可以7*24小时不间断运行,数月时间可不重启,在不kill进程的情况下对软件修改。
网络I/O模型
http://book.luffycity.com/linux-book/%E4%BC%81%E4%B8%9A%E7%BA%A7%E8%B4%9F%E8%BD%BD%E5%9D%87%E8%A1%A1%E5%AE%9E%E6%88%98/Nginx.html#%E7%BD%91%E7%BB%9Cio%E6%A6%82%E5%BF%B5%E8%AF%B4%E6%98%8E
Nginx架构组成
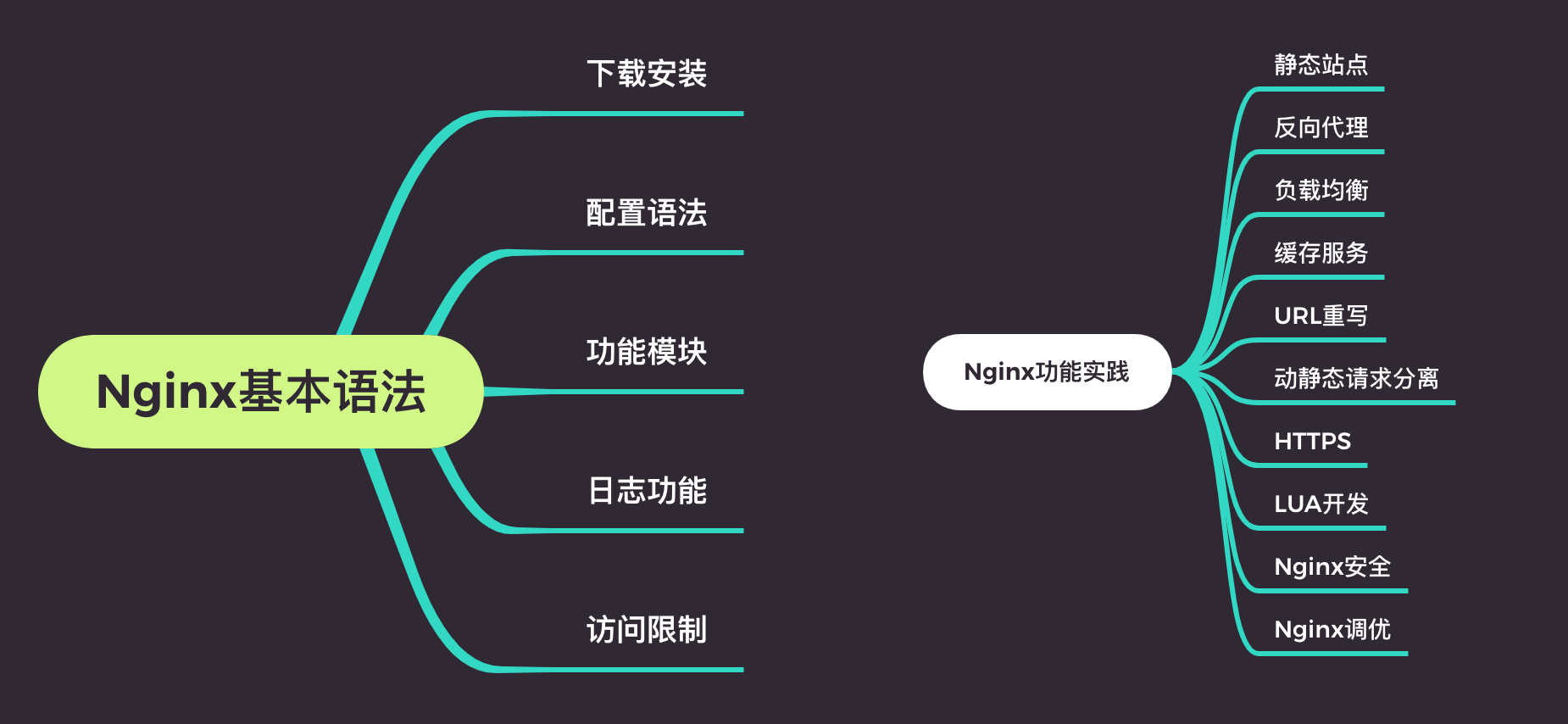
Nginx安装配置
nginx.com 商业版 nginx.org 开源版 https://tengine.taobao.org/
【环境准备】
操作系统:CentOS Linux release 7.3.1611 (Core) GCC编译环境:yum install -y gcc gcc-c++ autoconf automake make 模块依赖性:Nginx支持的功能模块需要有第三方的库支持,例如gzip的zlib库,rewrite重写 需要的pcre库,HTTPS需要的openssl库等等。 yum install zlib zlib-devel openssl openssl-devel pcre pcre-devel wget httpd-tools vim 系统基础开发环境:yum groupinstall "Development Tools" "Basic Web Server" 确保防火墙关闭 iptables -F 关闭selinux yum源配置正确 网络连接状态正常
【Nginx下载】
1.下载Nginx源代码 nginx.org官网 [root@chaogelinux Learn_Nginx]# wget nginx.org/download/nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz 2.解压缩Nginx源代码 [root@chaogelinux Learn_Nginx]# tar -zxf nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz 3.复制Nginx默认提供的vim语法插件 [root@chaogelinux nginx-1.14.0]# mkdir ~/.vim [root@chaogelinux nginx-1.14.0]# cp -r contrib/vim/* ~/.vim/ 4.Nginx源代码目录介绍 auto 检测系统模块 CHANGES nginx更改记录文件 conf 存放nginx配置文件 configure 释放编译文件的定制脚本 contrib 提供了perl与vim插件 html 存放标准html页面语法 src 存放nginx源码 5.开始编译Nginx,扩展编译模块 #列出Nginx的编译选项,如制定安装路径,配置文件、日志文件等路径,指定开启模块功 能等 [root@chaogelinux nginx-1.14.0]# ./configure --help #编译Nginx初步, [root@chaogelinux nginx-1.14.0]# ./configure -- prefix=/home/Learn_Nginx/nginx/ --with-http_ssl_module --with- http_flv_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with- http_stub_status_module --with-threads --with-file-aio 6.执行make编译 make 7.首次编译安装,生成Nginx的可执行命令 make install 8.检查Prefix指定的安装目录 [root@chaogelinux nginx-1.14.0]# ls /home/Learn_Nginx/ nginx nginx-1.14.0 nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz 9.Nginx的程序目录 [root@chaogelinux nginx]# pwd /home/Learn_Nginx/nginx [root@chaogelinux nginx]# ls conf html logs sbin 依次是配置文件,静态文件,日志,二进制命令目录 10.创建nginx的环境变量文件,修改如下,创建/etc/profile.d/nginx.sh脚本文件便于以 后维护 [root@chaogelinux ~]# cat /etc/profile.d/nginx.sh export PATH=/home/Learn_Nginx/nginx/sbin:$PATH 11.退出会话,重新登录终端,此时可以正常使用nginx [root@chaogelinux ~]# echo $PATH /home/Learn_Nginx/nginx/sbin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin :/root/bin 12.检查nginx的编译模块信息 [root@chaogelinux ~]# nginx -V nginx version: nginx/1.14.0 built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-39) (GCC) built with OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017 TLS SNI support enabled configure arguments: --prefix=/home/Learn_Nginx/nginx114/ --with- http_ssl_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_gzip_static_module -- with-http_stub_status_module --with-threads --with-file-aio
【nginx.conf指令注释】
######Nginx配置文件nginx.conf中文详解#####
#定义Nginx运行的用户和用户组
user www www;
#nginx进程数,建议设置为等于CPU总核心数。
worker_processes 8;
#全局错误日志定义类型,[ debug | info | notice | warn | error | crit ]
error_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/error.log info;
#进程pid文件
pid /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid;
#指定进程可以打开的最大描述符:数目
#工作模式与连接数上限
#这个指令是指当一个nginx进程打开的最多文件描述符数目,理论值应该是最多打开文件
数(ulimit -n)与nginx进程数相除,但是nginx分配请求并不是那么均匀,所以最好与
ulimit -n 的值保持一致。
#现在在linux 2.6内核下开启文件打开数为65535,worker_rlimit_nofile就相应应该填
写65535。
#这是因为nginx调度时分配请求到进程并不是那么的均衡,所以假如填写10240,总并发
量达到3-4万时就有进程可能超过10240了,这时会返回502错误。
[root@m01 ~]# tail -5 /etc/security/limits.conf
* soft nofile 65535 # open file
* hard nofile 65535
* soft nproc 65535 # open user processes
* hard nproc 65535
worker_rlimit_nofile 65535;
events
{
#参考事件模型,use [ kqueue | rtsig | epoll | /dev/poll | select | poll ]; epoll
模型
#是Linux 2.6以上版本内核中的高性能网络I/O模型,linux建议epoll,如果跑在
FreeBSD上面,就用kqueue模型。
#补充说明:
#与apache相类,nginx针对不同的操作系统,有不同的事件模型
#A)标准事件模型
#Select、poll属于标准事件模型,如果当前系统不存在更有效的方法,nginx会选择
select或poll
#B)高效事件模型
#Kqueue:使用于FreeBSD 4.1+, OpenBSD 2.9+, NetBSD 2.0 和 MacOS X.使
用双处理器的MacOS X系统使用kqueue可能会造成内核崩溃。
#Epoll:使用于Linux内核2.6版本及以后的系统。
#/dev/poll:使用于Solaris 7 11/99+,HP/UX 11.22+ (eventport),IRIX
6.5.15+ 和 Tru64 UNIX 5.1A+。
#Eventport:使用于Solaris 10。 为了防止出现内核崩溃的问题, 有必要安装安全补
丁。
use epoll;
#单个进程最大连接数(最大连接数=连接数*进程数)
#根据硬件调整,和前面工作进程配合起来用,尽量大,但是别把cpu跑到100%就行。
每个进程允许的最多连接数,理论上每台nginx服务器的最大连接数为。
worker_connections 65535;
#keepalive超时时间。
keepalive_timeout 60;
#客户端请求头部的缓冲区大小。这个可以根据你的系统分页大小来设置,一般一个请求
头的大小不会超过1k,不过由于一般系统分页都要大于1k,所以这里设置为分页大小。
#分页大小可以用命令getconf PAGESIZE 取得。
#[root@web001 ~]# getconf PAGESIZE
#4096
#但也有client_header_buffer_size超过4k的情况,但是client_header_buffer_size该值必须设置为“系统分页大小”的整倍数。
client_header_buffer_size 4k;
#这个将为打开文件指定缓存,默认是没有启用的,max指定缓存数量,建议和打开文
件数一致,inactive是指经过多长时间文件没被请求后删除缓存。
open_file_cache max=65535 inactive=60s;
#这个是指多长时间检查一次缓存的有效信息。
#语法:open_file_cache_valid time 默认值:open_file_cache_valid 60 使用字
段:http, server, location 这个指令指定了何时需要检查open_file_cache中缓存项目的
有效信息.
open_file_cache_valid 80s;
#open_file_cache指令中的inactive参数时间内文件的最少使用次数,如果超过这个数
字,文件描述符一直是在缓存中打开的,如上例,如果有一个文件在inactive时间内一次没
被使用,它将被移除。
#语法:open_file_cache_min_uses number 默认值:open_file_cache_min_uses
1 使用字段:http, server, location 这个指令指定了在open_file_cache指令无效的参数
中一定的时间范围内可以使用的最小文件数,如果使用更大的值,文件描述符在cache中总是打开状态.
open_file_cache_min_uses 1;
#语法:open_file_cache_errors on | off 默认值:open_file_cache_errors off 使用
字段:http, server, location 这个指令指定是否在搜索一个文件是记录cache错误.
open_file_cache_errors on;
}
#设定http服务器,利用它的反向代理功能提供负载均衡支持
http
{
#文件扩展名与文件类型映射表
include mime.types;
#默认文件类型
default_type application/octet-stream;
#默认编码
#charset utf-8;
#服务器名字的hash表大小
#保存服务器名字的hash表是由指令server_names_hash_max_size 和
server_names_hash_bucket_size所控制的。参数hash bucket size总是等于hash表
的大小,并且是一路处理器缓存大小的倍数。在减少了在内存中的存取次数后,使在处理器
中加速查找hash表键值成为可能。如果hash bucket size等于一路处理器缓存的大小,那
么在查找键的时候,最坏的情况下在内存中查找的次数为2。第一次是确定存储单元的地
址,第二次是在存储单元中查找键 值。因此,如果Nginx给出需要增大hash max size 或
hash bucket size的提示,那么首要的是增大前一个参数的大小.
server_names_hash_bucket_size 128;
#客户端请求头部的缓冲区大小。这个可以根据你的系统分页大小来设置,一般一个请求
的头部大小不会超过1k,不过由于一般系统分页都要大于1k,所以这里设置为分页大小。
分页大小可以用命令getconf PAGESIZE取得。
client_header_buffer_size 32k;
#客户请求头缓冲大小。nginx默认会用client_header_buffer_size这个buffer来读取
header值,如果header过大,它会使用large_client_header_buffers来读取。
large_client_header_buffers 4 64k;
#设定通过nginx上传文件的大小
client_max_body_size 8m;
#开启高效文件传输模式,sendfile指令指定nginx是否调用sendfile函数来输出文件,
对于普通应用设为 on,如果用来进行下载等应用磁盘IO重负载应用,可设置为off,以平衡
磁盘与网络I/O处理速度,降低系统的负载。注意:如果图片显示不正常把这个改成off。
#sendfile指令指定 nginx 是否调用sendfile 函数(zero copy 方式)来输出文件,对
于普通应用,必须设为on。如果用来进行下载等应用磁盘IO重负载应用,可设置为off,以
平衡磁盘与网络IO处理速度,降低系统uptime。
sendfile on;
#开启目录列表访问,合适下载服务器,默认关闭。
autoindex on;
#此选项允许或禁止使用socke的TCP_CORK的选项,此选项仅在使用sendfile的时候
使用
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
#长连接超时时间,单位是秒
keepalive_timeout 120;
#FastCGI相关参数是为了改善网站的性能:减少资源占用,提高访问速度。下面参数看
字面意思都能理解。
fastcgi_connect_timeout 300;
fastcgi_send_timeout 300;
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
fastcgi_buffer_size 64k;
fastcgi_buffers 4 64k;
fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 128k;
fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 128k;
#gzip模块设置
gzip on; #开启gzip压缩输出
gzip_min_length 1k; #最小压缩文件大小
gzip_buffers 4 16k; #压缩缓冲区
gzip_http_version 1.0; #压缩版本(默认1.1,前端如果是squid2.5请使用1.0)
gzip_comp_level 2; #压缩等级
gzip_types text/plain application/x-javascript text/css application/xml; #压
缩类型,默认就已经包含textml,所以下面就不用再写了,写上去也不会有问题,但是会有
一个warn。
gzip_vary on;
#开启限制IP连接数的时候需要使用
#limit_zone crawler $binary_remote_addr 10m;
#负载均衡配置
upstream pythonav.cn {
#upstream的负载均衡,weight是权重,可以根据机器配置定义权重。weigth参数
表示权值,权值越高被分配到的几率越大。
server 192.168.80.121:80 weight=3;
server 192.168.80.122:80 weight=2;
server 192.168.80.123:80 weight=3;
#nginx的upstream目前支持4种方式的分配
#1、轮询(默认)
#每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器,如果后端服务器down掉,能
自动剔除。
#2、weight
#指定轮询几率,weight和访问比率成正比,用于后端服务器性能不均的情况。
#例如:
#upstream bakend {
# server 192.168.0.14 weight=10;
# server 192.168.0.15 weight=10;
#}
#2、ip_hash
#每个请求按访问ip的hash结果分配,这样每个访客固定访问一个后端服务器,可以
解决session的问题。
#例如:
#upstream bakend {
# ip_hash;
# server 192.168.0.14:88;
# server 192.168.0.15:80;
#}
#3、fair(第三方)
#按后端服务器的响应时间来分配请求,响应时间短的优先分配。
#upstream backend {
# server server1;
# server server2;
# fair;
#}
#4、url_hash(第三方)
#按访问url的hash结果来分配请求,使每个url定向到同一个后端服务器,后端服务
器为缓存时比较有效。
#例:在upstream中加入hash语句,server语句中不能写入weight等其他的参数,
hash_method是使用的hash算法
#upstream backend {
# server squid1:3128;
# server squid2:3128;
# hash $request_uri;
# hash_method crc32;
#}
#tips:
#upstream bakend{#定义负载均衡设备的Ip及设备状态}{
# ip_hash;
# server 127.0.0.1:9090 down;
# server 127.0.0.1:8080 weight=2;
# server 127.0.0.1:6060;
# server 127.0.0.1:7070 backup;
#}
#在需要使用负载均衡的server中增加 proxy_pass http://bakend/;
#每个设备的状态设置为:
#1.down表示单前的server暂时不参与负载
#2.weight为weight越大,负载的权重就越大。
#3.max_fails:允许请求失败的次数默认为1.当超过最大次数时,返回
proxy_next_upstream模块定义的错误
#4.fail_timeout:max_fails次失败后,暂停的时间。
#5.backup: 其它所有的非backup机器down或者忙的时候,请求backup机器。
所以这台机器压力会最轻。
#nginx支持同时设置多组的负载均衡,用来给不用的server来使用。
#client_body_in_file_only设置为On 可以讲client post过来的数据记录到文件中
用来做debug
#client_body_temp_path设置记录文件的目录 可以设置最多3层目录
#location对URL进行匹配.可以进行重定向或者进行新的代理 负载均衡
}
#虚拟主机的配置
server
{
#监听端口
listen 80;
#域名可以有多个,用空格隔开
server_name www.w3cschool.cn w3cschool.cn;
index index.html index.htm index.php;
root /data/www/w3cschool;
#对******进行负载均衡
location ~ .*.(php|php5)?$
{
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi.conf;
}
#图片缓存时间设置
location ~ .*.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf)$
{
expires 10d;
}
#JS和CSS缓存时间设置
location ~ .*.(js|css)?$
{
expires 1h;
}
#日志格式设定
#$remote_addr与$http_x_forwarded_for用以记录客户端的ip地址;
#$remote_user:用来记录客户端用户名称;
#$time_local: 用来记录访问时间与时区;
#$request: 用来记录请求的url与http协议;
#$status: 用来记录请求状态;成功是200,
#$body_bytes_sent :记录发送给客户端文件主体内容大小;
#$http_referer:用来记录从那个页面链接访问过来的;
#$http_user_agent:记录客户浏览器的相关信息;
#通常web服务器放在反向代理的后面,这样就不能获取到客户的IP地址了,通过
$remote_add拿到的IP地址是反向代理服务器的iP地址。反向代理服务器在转发请求的
http头信息中,可以增加x_forwarded_for信息,用以记录原有客户端的IP地址和原来客
户端的请求的服务器地址。
log_format access '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" $http_x_forwarded_for';
#定义本虚拟主机的访问日志
access_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/host.access.log main;
access_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/host.access.404.log log404;
#对 "/" 启用反向代理
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:88;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
#后端的Web服务器可以通过X-Forwarded-For获取用户真实IP
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
#以下是一些反向代理的配置,可选。
proxy_set_header Host $host;
#允许客户端请求的最大单文件字节数
client_max_body_size 10m;
#缓冲区代理缓冲用户端请求的最大字节数,
#如果把它设置为比较大的数值,例如256k,那么,无论使用firefox还是IE浏览
器,来提交任意小于256k的图片,都很正常。如果注释该指令,使用默认的client_body_buffer_size设置,也就是操作系统页面大小的两倍,8k或者16k,问题就出
现了。
#无论使用firefox4.0还是IE8.0,提交一个比较大,200k左右的图片,都返回
500 Internal Server Error错误
client_body_buffer_size 128k;
#表示使nginx阻止HTTP应答代码为400或者更高的应答。
proxy_intercept_errors on;
#后端服务器连接的超时时间_发起握手等候响应超时时间
#nginx跟后端服务器连接超时时间(代理连接超时)
proxy_connect_timeout 90;
#后端服务器数据回传时间(代理发送超时)
#后端服务器数据回传时间_就是在规定时间之内后端服务器必须传完所有的数据
proxy_send_timeout 90;
#连接成功后,后端服务器响应时间(代理接收超时)
#连接成功后_等候后端服务器响应时间_其实已经进入后端的排队之中等候处理
(也可以说是后端服务器处理请求的时间)
proxy_read_timeout 90;
#设置代理服务器(nginx)保存用户头信息的缓冲区大小
#设置从被代理服务器读取的第一部分应答的缓冲区大小,通常情况下这部分应答
中包含一个小的应答头,默认情况下这个值的大小为指令proxy_buffers中指定的一个缓冲
区的大小,不过可以将其设置为更小
proxy_buffer_size 4k;
#proxy_buffers缓冲区,网页平均在32k以下的设置
#设置用于读取应答(来自被代理服务器)的缓冲区数目和大小,默认情况也为分
页大小,根据操作系统的不同可能是4k或者8k
proxy_buffers 4 32k;
#高负荷下缓冲大小(proxy_buffers*2)
proxy_busy_buffers_size 64k;
#设置在写入proxy_temp_path时数据的大小,预防一个工作进程在传递文件时
阻塞太长
#设定缓存文件夹大小,大于这个值,将从upstream服务器传
proxy_temp_file_write_size 64k;
}
#设定查看Nginx状态的地址
location /NginxStatus {
stub_status on;
access_log on;
auth_basic "NginxStatus";
auth_basic_user_file confpasswd;
#htpasswd文件的内容可以用apache提供的htpasswd工具来产生。
}
#本地动静分离反向代理配置
#所有jsp的页面均交由tomcat或resin处理
location ~ .(jsp|jspx|do)?$ {
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080;
}
#所有静态文件由nginx直接读取不经过tomcat或resin
location ~ .*.
(htm|html|gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf|ioc|rar|zip|txt|flv|mid|doc|ppt|
pdf|xls|mp3|wma)$
{
expires 15d;
}
location ~ .*.(js|css)?$
{
expires 1h;
}
}
}
######Nginx配置文件nginx.conf中文详解#####
nginx.conf详解
【Nginx 命令行】
nginx -s stop
nginx -s reload
nginx
nginx帮助命令
[root@chaogelinux nginx114]# nginx -h nginx version: nginx/1.14.0 Usage: nginx [-?hvVtTq] [-s signal] [-c filename] [-p prefix] [-g directives] Options: -?,-h : this help #帮助信息 -v : show version and exit #显示版本 -V : show version and configure options then exit #显示编译信息与版本 -t : test configuration and exit #测试配置文件语法 -T : test configuration, dump it and exit #测试语法且输出内容 -q : suppress non-error messages during configuration testing -s signal : send signal to a master process: stop, quit, reopen, reload #发送信 号,stop立即停止,quit优雅停止,reload重读配置文件,reopen重新记录日志 -p prefix : set prefix path (default: /home/Learn_Nginx/nginx114//) -c filename : set configuration file (default: conf/nginx.conf) #使用指定配置文件 -g directives : set global directives out of configuration file #覆盖默认参数
【配置文件重读】
在不停止服务的情况下,更新配置文件。
1.修改nginx.conf worker_processes 3; #定义nginx工作进程数的 2.重载配置文件 nginx -s reload 3.检查linux进程 [root@chaogelinux nginx114]# vim conf/nginx.conf [root@chaogelinux nginx114]# [root@chaogelinux nginx114]# ps -ef|grep nginx root 6191 1 0 10:33 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process nginx nobody 6213 6191 0 10:33 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process nobody 6214 6191 0 10:33 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process nobody 6215 6191 0 10:33 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 6345 5283 0 10:38 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
【nginx-master信号】
信号由ngx_signal_hander函数处理
1.master不处理请求,而是分配worker进程,负责重启,热部署,重载等功能。 2.master根据worker_processes 定义开始的workers数量 3.worker运行后,master处于挂起状态,等待信号 4.可以发送kill,或者nginx -s 参数发出信号
【信号集】
| nginx -s 对应参数 | 信号 | 含义 | English |
| stop | TERM | 强制关闭整个服务 | Shut down quickly |
| null | INT | 强制关闭整个服务 | Shut down quickly |
| quit | QUIT | 优雅地关闭整个服务 | Shut down gracefully |
| reopen | USR1 | 重新打开日志记录 | Reopen log files |
| reload | HUP | 重新读取配置文件,并且优雅地退出老worker | Reload configuration,start the new worker process with a new configuration,and gracefully shut down old worker processes |
| null | USR2 | 平滑升级到新版本 |
Upgrade the nginx executable on the fly |
| null | WINCH | 优雅地关闭worker(在热更新的时候必用) | Shut down worker processes gracefully |
【热部署】
热部署指的是在不重启或关闭进程情况下,新应用直接替换掉旧应用
热部署大致流程 1.备份旧的二进制文件 2.编译安装新的二进制文件,覆盖旧的二进制文件 3.发送USR2信号给旧master进程 4.发送WINCH信号给旧master进程 5.发送QUIT信号给旧master进程
【热部署时的坑】
nginx必须使用绝对路径启动,
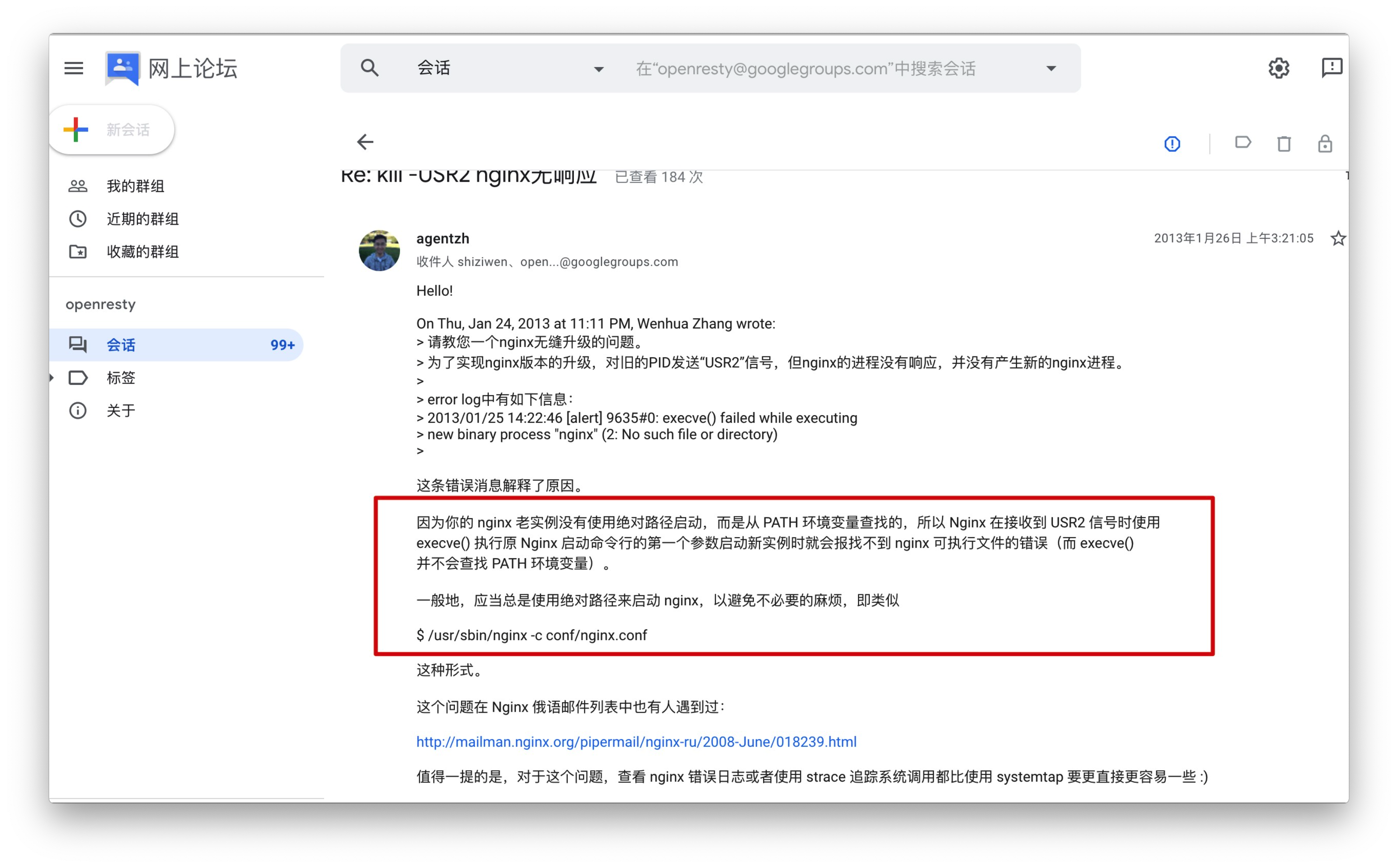
nginx支持reload重载仅仅时nginx的master进程,检查配置文件发育是否正确,错则返回错误,正确也不会改变
已经建立连接的worker,只得等待worker处理完毕请求之后,杀死旧配置文件的worker,启动新配置文件的worker。
但是nginx这里提供了热部署功能,就是在不影响用户体验下,进行软件版本升级,也就是不主动杀死worker,替换
软件的二进制文件。
1.目前运行的是旧的nginx版本,如下检查 [root@chaogelinux sbin]# ps -ef|grep nginx root 20311 1 0 15:12 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process nginx nobody 20312 20311 0 15:12 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 20314 13589 0 15:12 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx [root@chaogelinux sbin]# [root@chaogelinux sbin]# [root@chaogelinux sbin]# curl 127.0.0.1/123 #访问错误页面,返回nginx版本了 <html> <head><title>404 Not Found</title></head> <body bgcolor="white"> <center><h1>404 Not Found</h1></center> <hr><center>nginx/1.14.0</center> </body> </html>
【热部署具体操作】
1.备份旧版本的nginx二进制文件 [root@chaogelinux sbin]# pwd /home/Learn_Nginx/nginx/sbin [root@chaogelinux sbin]# mv nginx nginx.old [root@chaogelinux sbin]# ls nginx.old 2.检查旧版本nginx的编译参数 [root@chaogelinux Learn_Nginx]# nginx.old -V nginx version: nginx/1.14.0 built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-39) (GCC) built with OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017 TLS SNI support enabled configure arguments: --prefix=/home/Learn_Nginx/nginx/ --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-threads --with-file-aio 3.编译安装新版本nginx #下载新nginx源码 [root@chaogelinux Learn_Nginx]# wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.17.8.tar.gz #编译安装新版本nginx [root@chaogelinux Learn_Nginx]# tar -zxf nginx-1.17.8.tar.gz #开始编译 [root@chaogelinux Learn_Nginx]# cd nginx-1.17.8/ [root@chaogelinux nginx-1.17.8]# [root@chaogelinux nginx-1.17.8]# ./configure --prefix=/home/Learn_Nginx/nginx/ --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-threads --with-file-aio #编译安装 [root@chaogelinux nginx-1.17.8]# make && make install 4.此时发现已存在2个版本nginx程序 [root@chaogelinux sbin]# ls nginx nginx.old 5.替换旧的nginx可执行文件 [root@chaogelinux sbin]# cp -a /home/Learn_Nginx/nginx-1.17.8/objs/nginx /home/Learn_Nginx/nginx/sbin/ cp:是否覆盖"/home/Learn_Nginx/nginx/sbin/nginx"? y 5.1检查旧的nginx进程,请注意,这里用绝对路径启动nginx 请注意,这里用绝对路径启动nginx 请注意,这里用绝对路径启动nginx 例如 /home/Learn_Nginx/nginx/sbin/nginx 注意这里的PID和PPID(pid是当前进程的id号,ppid是启动该进程的pid,也就是父ID,可知该pid由谁启动) [root@chaogelinux sbin]# ps -ef|grep nginx root 20311 1 0 15:12 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process nginx nobody 20312 20311 0 15:12 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 20314 13589 0 15:12 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx 6.发送USR2信号给旧版本主进程,使得nginx旧版本停止接收请求,切换为新nginx版本 [root@chaogelinux sbin]# kill -USR2 `cat ../logs/nginx.pid ` 7.检查此时的nginx进程 nginx-master首先会重命名pid文件,在文件后面添加.oldbin后缀 然后会再启动一个新的master进程以及worker,且使用的是新版Nginx nginx能够自动将新来的请求,过度到新版master进程下,实现平滑过度 #可以发现新的master进程由旧master启动,由PPID可看出 [root@chaogelinux sbin]# ps -ef|grep nginx root 20311 1 0 15:12 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process nginx nobody 20312 20311 0 15:12 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 20335 20311 0 15:13 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process nginx nobody 20336 20335 0 15:13 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 20338 13589 0 15:13 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx [root@chaogelinux sbin]# ls ../logs/ access.log error.log nginx.pid nginx.pid.oldbin 8.发送WINCH信号给旧master进程,优雅的关闭旧worker进程 [root@chaogelinux sbin]# kill -WINCH `cat ../logs/nginx.pid.oldbin` #再次检查进程情况,旧master的worker已经关闭了,旧master不会自己退出,用作版本回退:kill -HUP 拉起进程, [root@chaogelinux sbin]# ps -ef|grep nginx root 20311 1 0 15:12 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process nginx root 20335 20311 0 15:13 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process nginx nobody 20336 20335 0 15:13 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 20607 13589 0 15:25 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx 9.如果你觉得没问题了,可以关闭旧master进程 [root@chaogelinux sbin]# ps -ef|grep nginx root 20335 1 0 15:13 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process nginx nobody 20336 20335 0 15:13 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 20665 13589 0 15:28 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
【日志切割】
1.查看当前nginx日志 [root@chaogelinux logs]# ll 总用量 12 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1645 2月 11 15:30 access.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2370 2月 11 15:30 error.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6 2月 11 15:13 nginx.pid #大致看下日志内容 [root@chaogelinux logs]# tail -2 access.log 192.168.178.12 - - [11/Feb/2020:15:32:22 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 304 0 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_3) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/79.0.3945.130 Safari/537.36" 192.168.178.12 - - [11/Feb/2020:15:32:23 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 304 0 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_3) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/79.0.3945.130 Safari/537.36" 2.给文件重命名,注意用mv而不是cp(涉及到文件inode知识) [root@chaogelinux logs]# mv access.log access.log$(date +"%Y-%m-%d--%H:%M:%S") [root@chaogelinux logs]# ll 总用量 16 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4630 2月 11 15:32 access.log2020-02-11--15:43:49 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2370 2月 11 15:30 error.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6 2月 11 15:13 nginx.pid 3.发送USR1信号给nginx-master,重新打开日志记录,生成新的日志文件 nginx -s reopen #等同于 Kill -USR1 nginx.pid 4.注意,在以上的nginx重命名日志切割,不要着急立即对文件修改,且要sleep 等待1秒 由于nginx的工作模式,master下发指令给worker只是做了标记,当业务量大的时候,这个修改操作可能会慢一点,不会理解生效 5.在生产环境下,主要以crontab形式,执行cut_nginx_log.sh脚本的 [root@bogon sbin]# pwd /opt/nginx/sbin [root@bogon sbin]# cat cut_nginx_log.sh #!/bin/bash # 脚本写入crontab,每天0点执行,这是一个nginx日志切割脚本 #nginx日志存放点 logs_path="/opt/tngx232/logs/" mkdir -p ${logs_path}$(date -d "yesterday" +"%Y")/$(date -d "yesterday" +"%m") mv ${logs_path}access.log ${logs_path}$(date -d "yesterday" +"%Y")/$(date -d "yesterday" +"%m")/access_$(date -d "yesterday" +"%Y-%m-%d").log kill -USR1 `cat /opt/tngx232/logs/nginx.pid` 6.写入crontab crontab -l 0 0 * * * /bin/bash /opt/nginx/sbin/cut_nginx_log.sh


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号