Android中IntentService详解
简单说,IntentService是继承于Service并处理异步请求的一个类,在IntentService内有一个工作线程来处理耗时操作,启动IntentService的方式和启动传统Service一样,同时,当任务执行完后,IntentService会自动停止,而不需要我们去手动控制。另外,可以启动IntentService多次,而每一个耗时操作会以工作队列的方式在IntentService的onHandleIntent回调方法中执行,并且,每次只会执行一个工作线程,执行完第一个再执行第二个,以此类推。
而且,所有请求都在一个单线程中,不会阻塞应用程序的主线程(UI Thread),同一时间只处理一个请求。
那么,用IntentService有什么好处呢?首先,我们省去了在Service中手动开线程的麻烦,第二,当操作完成时,我们不用手动停止Service。
接下来让我们来看看如何使用,写一个Demo来模拟两个耗时操作,Operation1与Operation2,先执行1,2必须等1执行完才能执行:
新建工程,新建一个继承IntentService的类,我这里是IntentServiceDemo.java
public class IntentServiceDemo extends IntentService {
public IntentServiceDemo() {
//必须实现父类的构造方法
super("IntentServiceDemo");
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
System.out.println("onBind");
return super.onBind(intent);
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
System.out.println("onCreate");
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
System.out.println("onStart");
super.onStart(intent, startId);
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
System.out.println("onStartCommand");
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
@Override
public void setIntentRedelivery(boolean enabled) {
super.setIntentRedelivery(enabled);
System.out.println("setIntentRedelivery");
}
@Override
protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) {
//Intent是从Activity发过来的,携带识别参数,根据参数不同执行不同的任务
String action = intent.getExtras().getString("param");
if (action.equals("oper1")) {
System.out.println("Operation1");
}else if (action.equals("oper2")) {
System.out.println("Operation2");
}
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
System.out.println("onDestroy");
super.onDestroy();
}
}
我把生命周期方法全打印出来了,待会我们来看看它执行的过程是怎样的。接下来是Activity,在Activity中来启动IntentService:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
public class TestActivity extends Activity { /** Called when the activity is first created. */ @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); //可以启动多次,每启动一次,就会新建一个work thread,但IntentService的实例始终只有一个 //Operation 1 Intent startServiceIntent = new Intent("com.test.intentservice"); Bundle bundle = new Bundle(); bundle.putString("param", "oper1"); startServiceIntent.putExtras(bundle); startService(startServiceIntent); //Operation 2 Intent startServiceIntent2 = new Intent("com.test.intentservice"); Bundle bundle2 = new Bundle(); bundle2.putString("param", "oper2"); startServiceIntent2.putExtras(bundle2); startService(startServiceIntent2); }} |
最后,别忘了配置Service,因为它继承于Service,所以,它还是一个Service,一定要配置,否则是不起作用的,开始我就是忘了,结果半天没反应。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<service android:name=".IntentServiceDemo"> <intent-filter > <action android:name="com.test.intentservice"/> </intent-filter></service> |
ok,最后来看看执行结果:
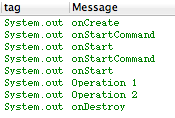
从结果可以看到,onCreate方法只执行了一次,而onStartCommand和onStart方法执行了两次,开启了两个Work Thread,这就证实了之前所说的,启动多次,但IntentService的实例只有一个,这跟传统的Service是一样的。Operation1也是先于Operation2打印,并且我让两个操作间停顿了2s,最后是onDestroy销毁了IntentService。
这就是IntentService,一个方便我们处理业务流程的类,它是一个Service,但是比Service更智能。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号