关于netty 一些使用细节
netty 的客户端通常是websoket 但是为了演示也可以用netty做客户端,
- Channel:可以被理解为数据传输的通道。
- Pipeline:可以被视为一个由多个工序组成的流水线,负责将数据(事件)传递给流水线上的每个处理工序(handler)。
- Msg:指的是在流水线上流动的数据。最初输入的数据通常是
ByteBuf类型,但当它经过流水线上的各个处理工序后,可能会被转换成其他类型的数据对象,然后再变回ByteBuf进行输出。 - Handler:可以被理解为流水线上的各个处理工序。每个工序负责对数据进行特定的处理(通过重写相应的事件处理方法)。
- Inbound and Outbound Handler:入站(Inbound)和出站(Outbound)两类处理工序。入站处理工序负责处理进入的数据,而出站处理工序负责处理发送的数据。
- EventLoop:可以理解为负责处理数据的工人。每个工人可以管理多个通道的读写操作,并且一旦负责了某个通道,就会一直负责到底(绑定)。工人既可以执行IO操作,也可以执行任务处理。
- Worker:每位工人都有一个任务队列,队列中可以存放多个通道的待处理任务。任务分为普通任务和定时任务。
- Processing Order:工人按照流水线的顺序,根据每个处理工序(handler)的规划(代码)依次处理数据。可以为流水线上的每道工序指定不同的工人来负责。
- 每个流水只对自己流水一部份感 兴趣,比如 channelRead 这儿就对处理读的管道
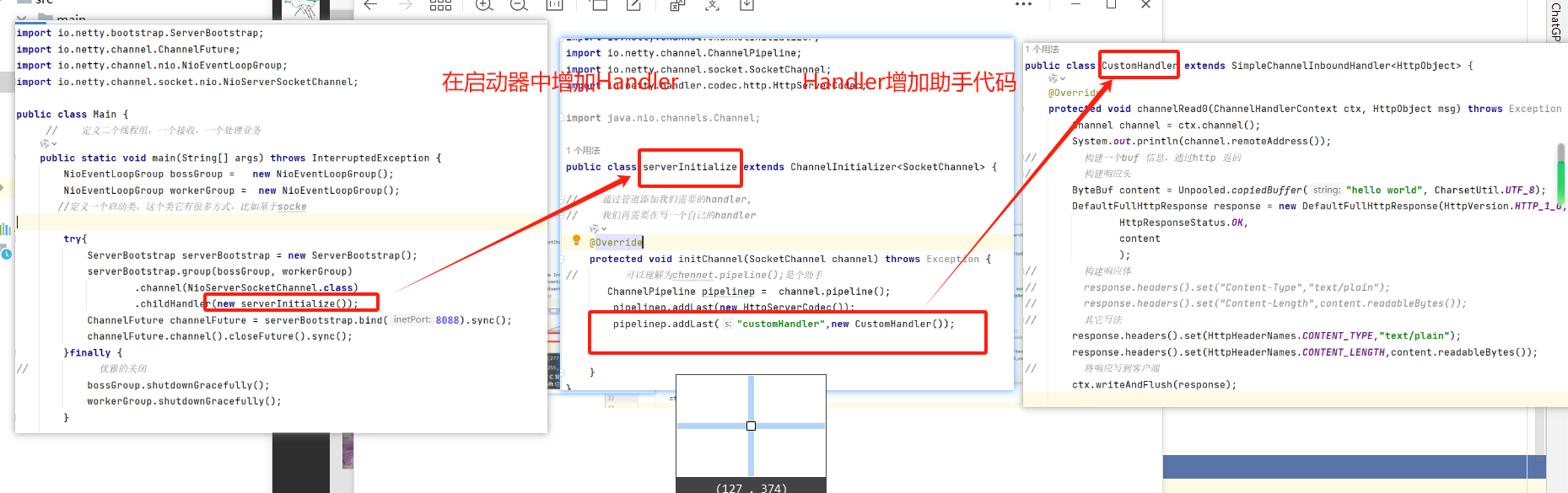
整 体使用netty 流程 ‘ 以下是一个完整 示例代码流程,浏览器运行locallost:8088 将会看到hello word
以下代码只是演示一个最简单的 使用,所以使用了HttpHandler ,我们还能用来处理json 的,不过这些我们在下面在示例
以下示例用来buffer的示例,直接显示hello ,这个例子更直接。

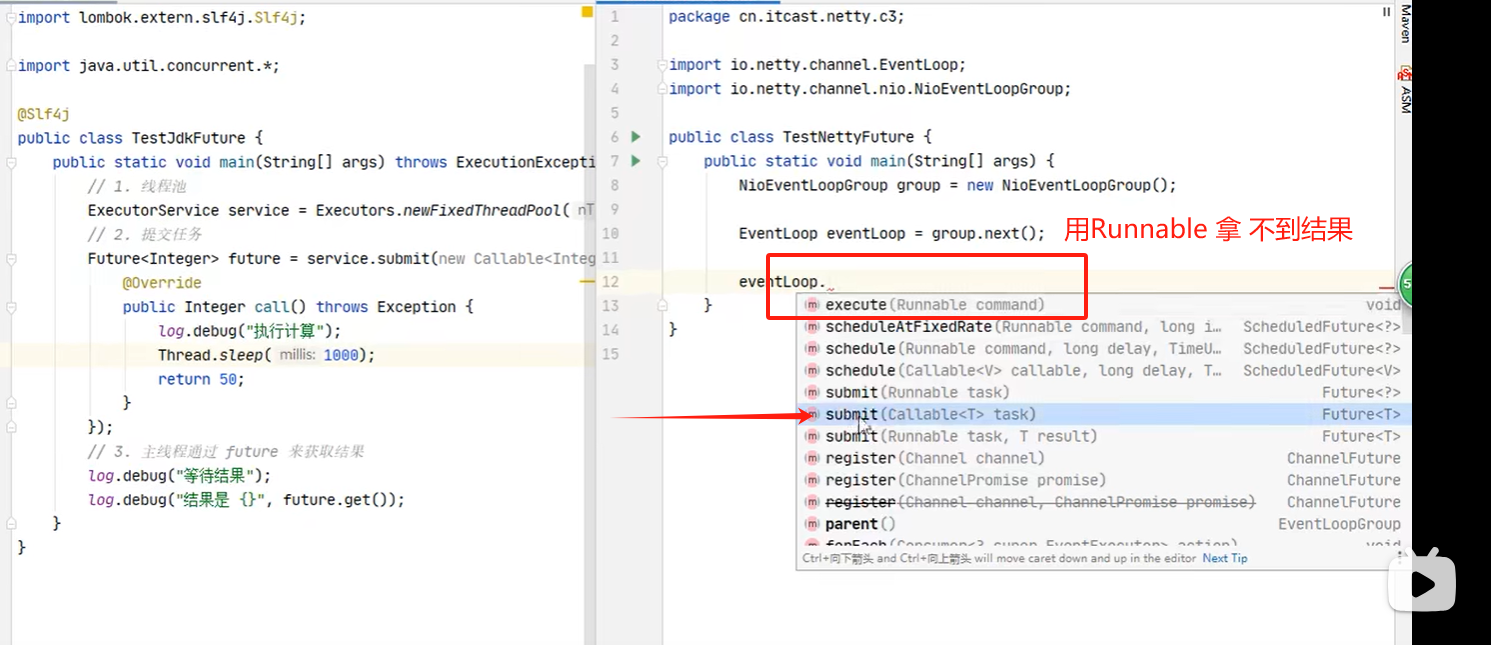
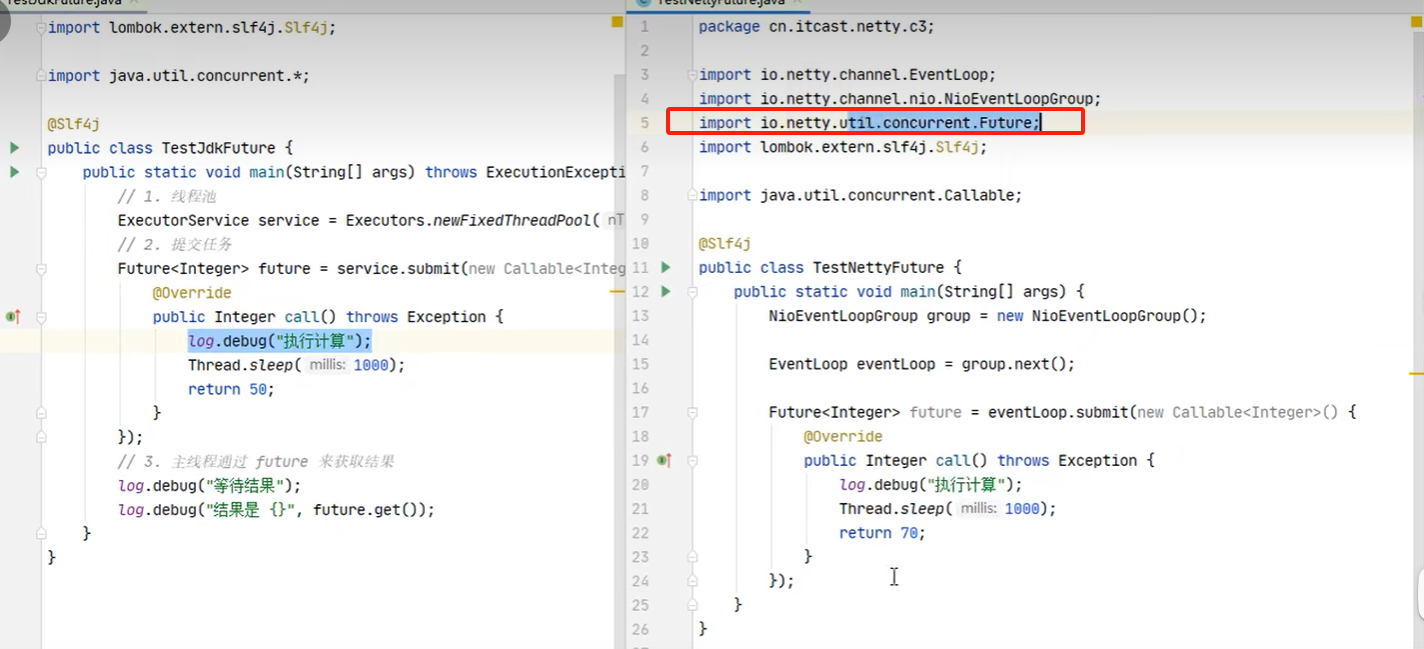
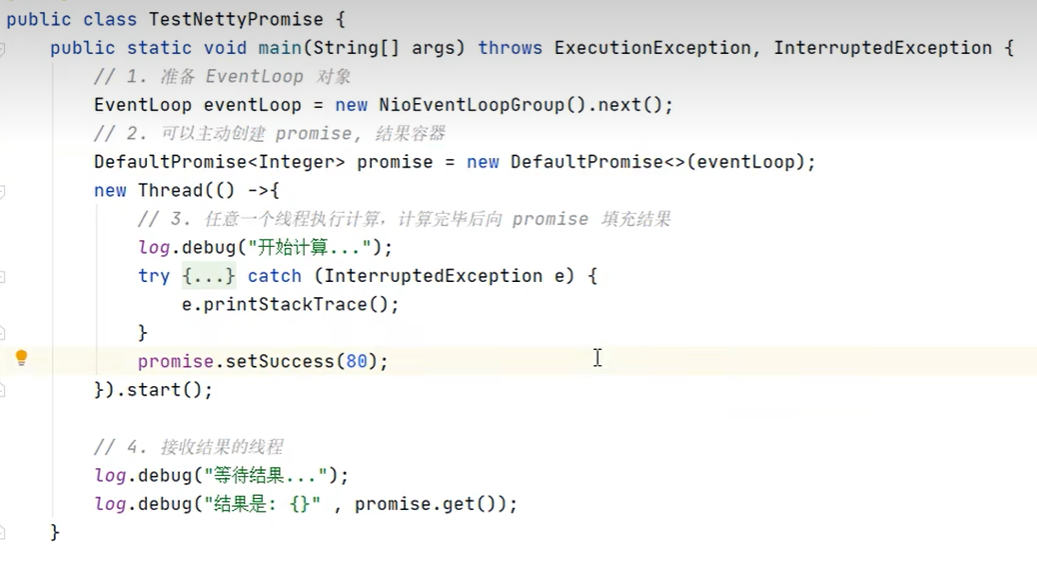
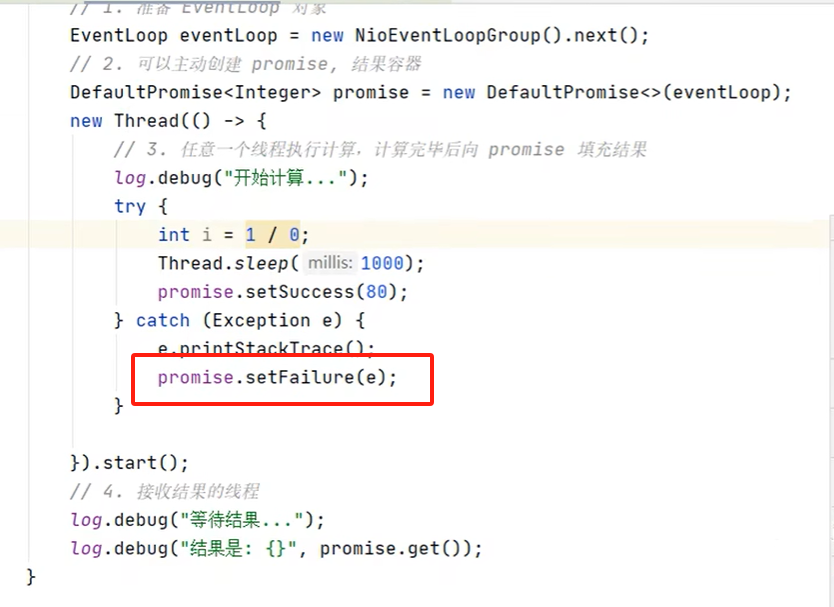
拿 到输出句柄最常用有二种方式,以下是关于future拿 结果的二种方式,最后一种是promect,就是拿到鉴听的句柄,用来调关闭或监听那个方法,
这个包是
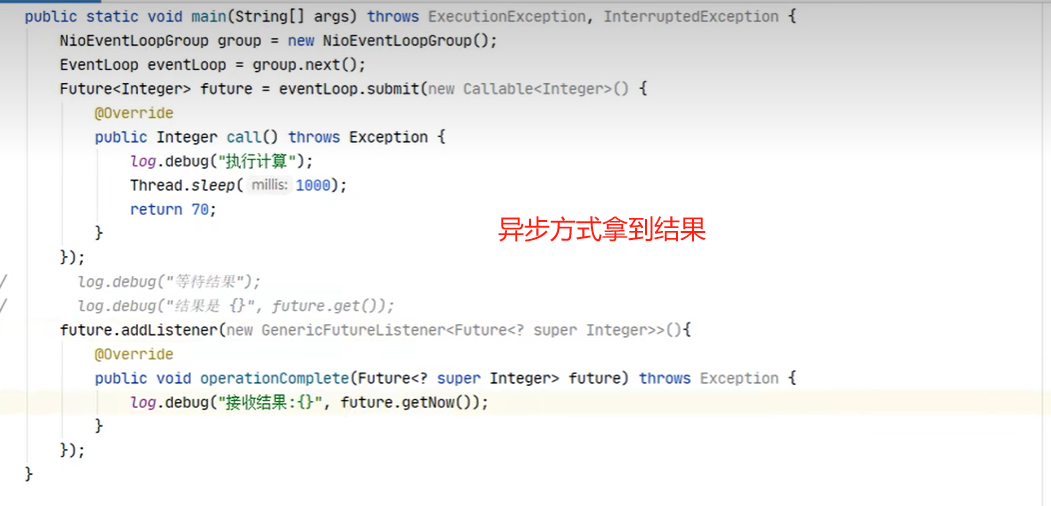
promise 结果
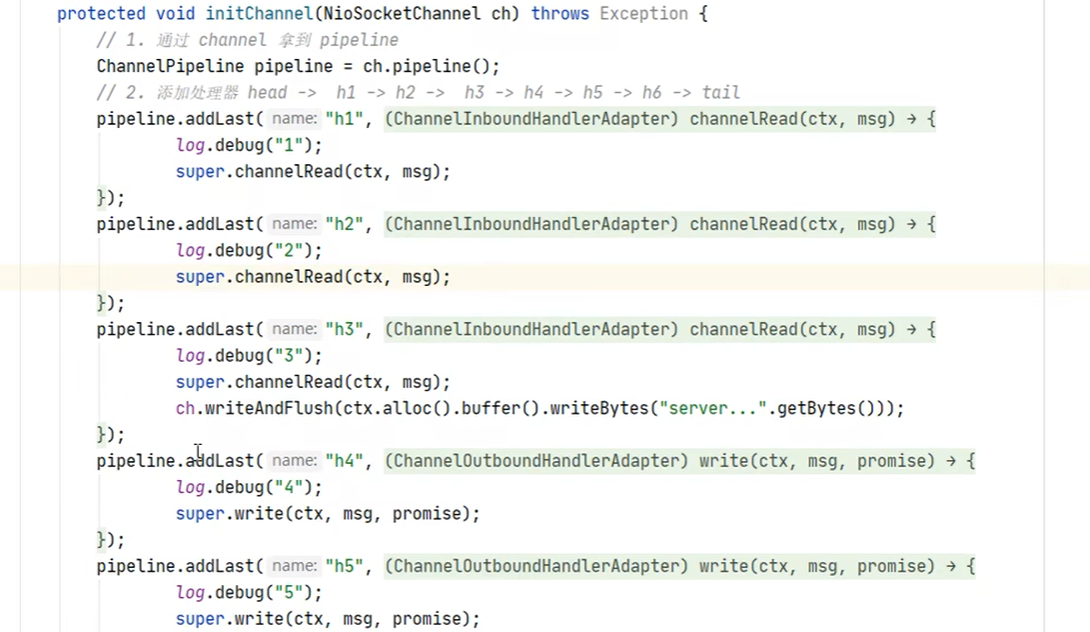
Handerl 有很多种,处理编吗,响应的啊,字节啊,好多好多,都 是一条管理依次顺序来运行
各种handel
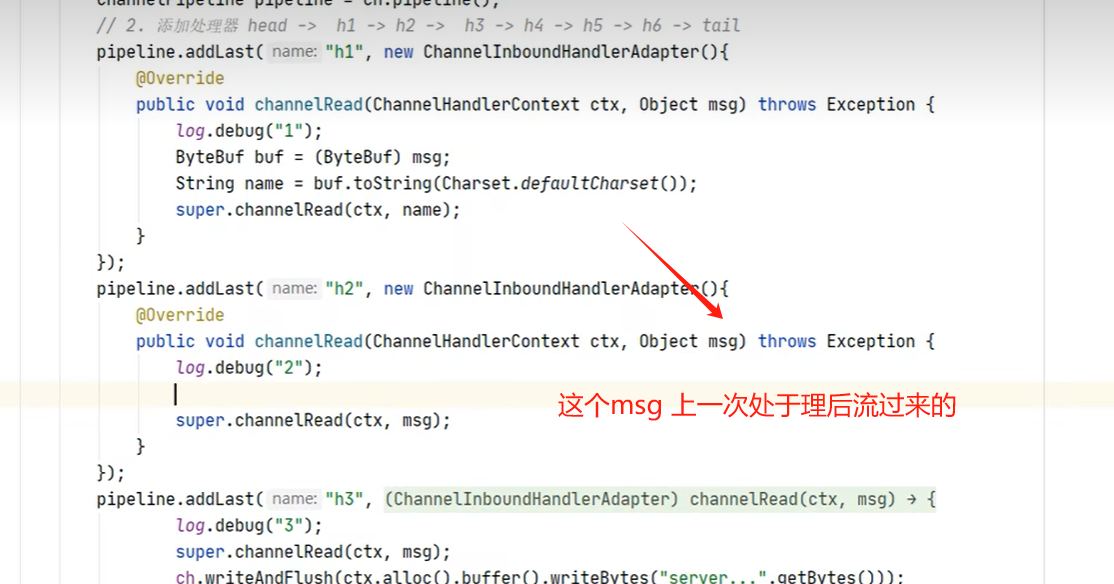
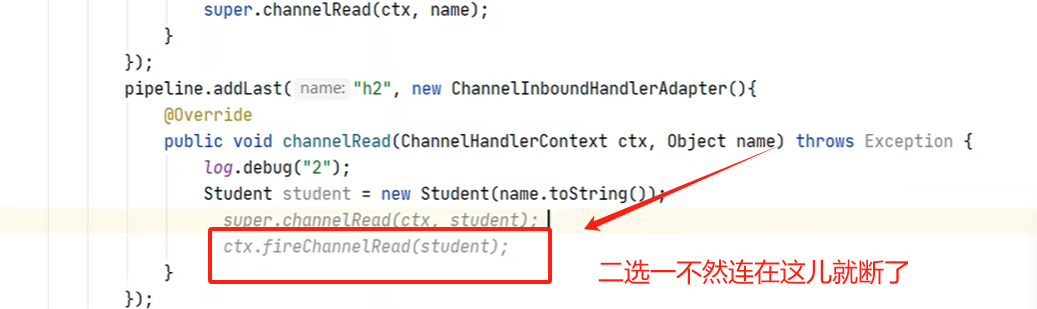
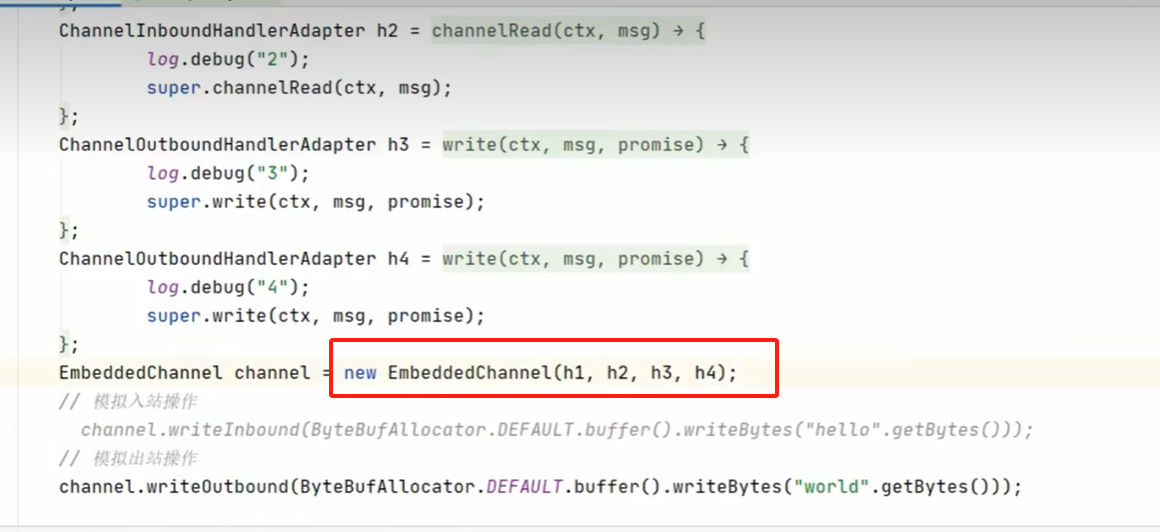
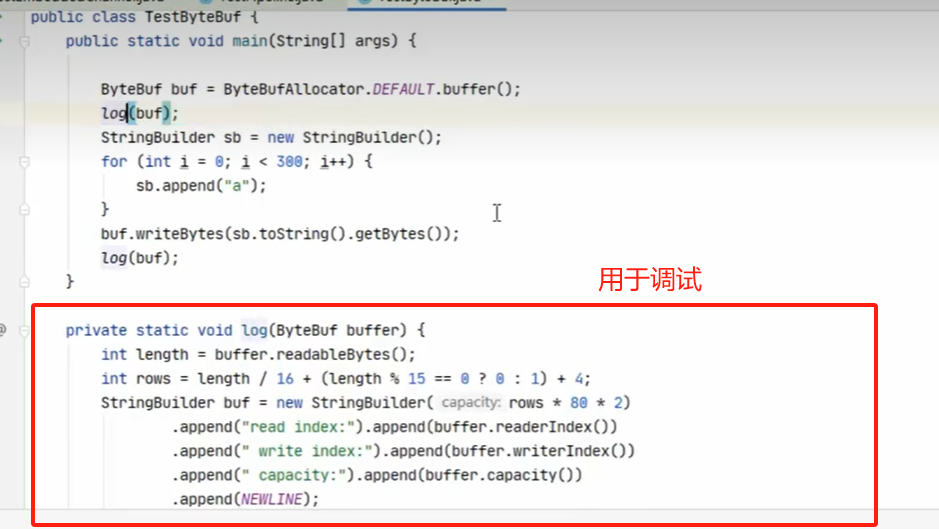
用于测度的andel
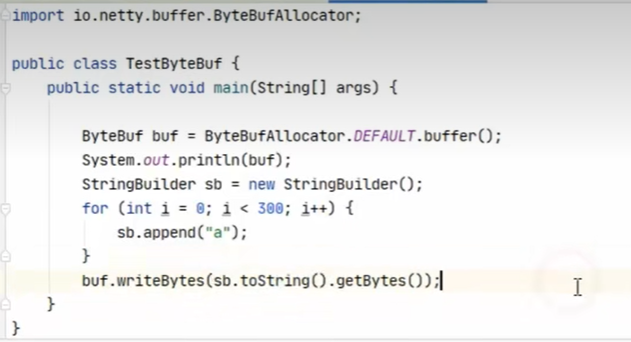
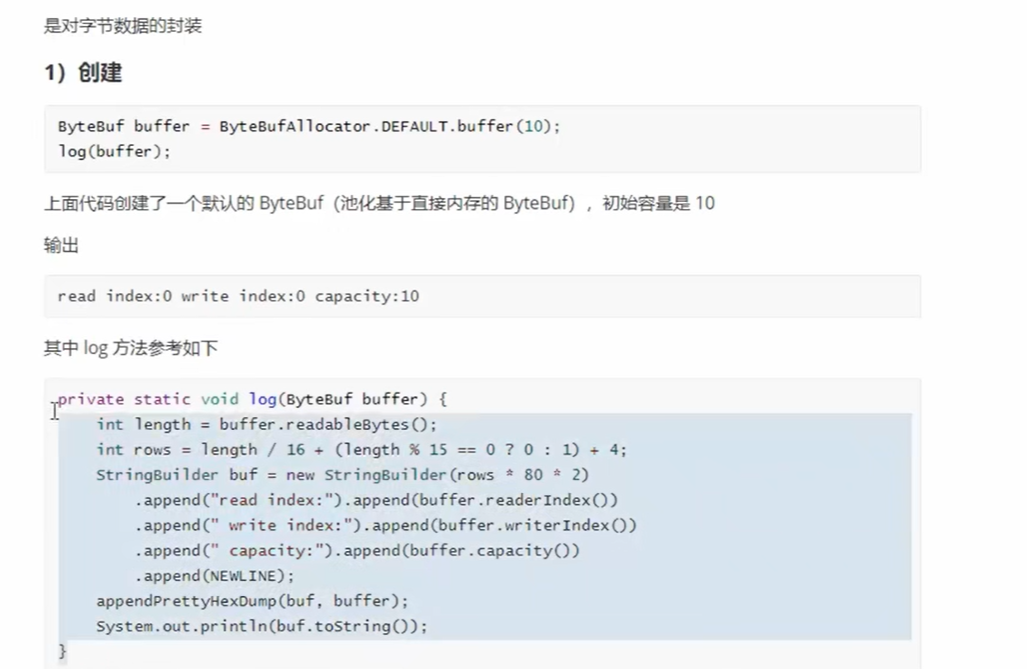
netty 中的bybuffer 是对nio 的buffer 增强自动扩容,
生命 周期
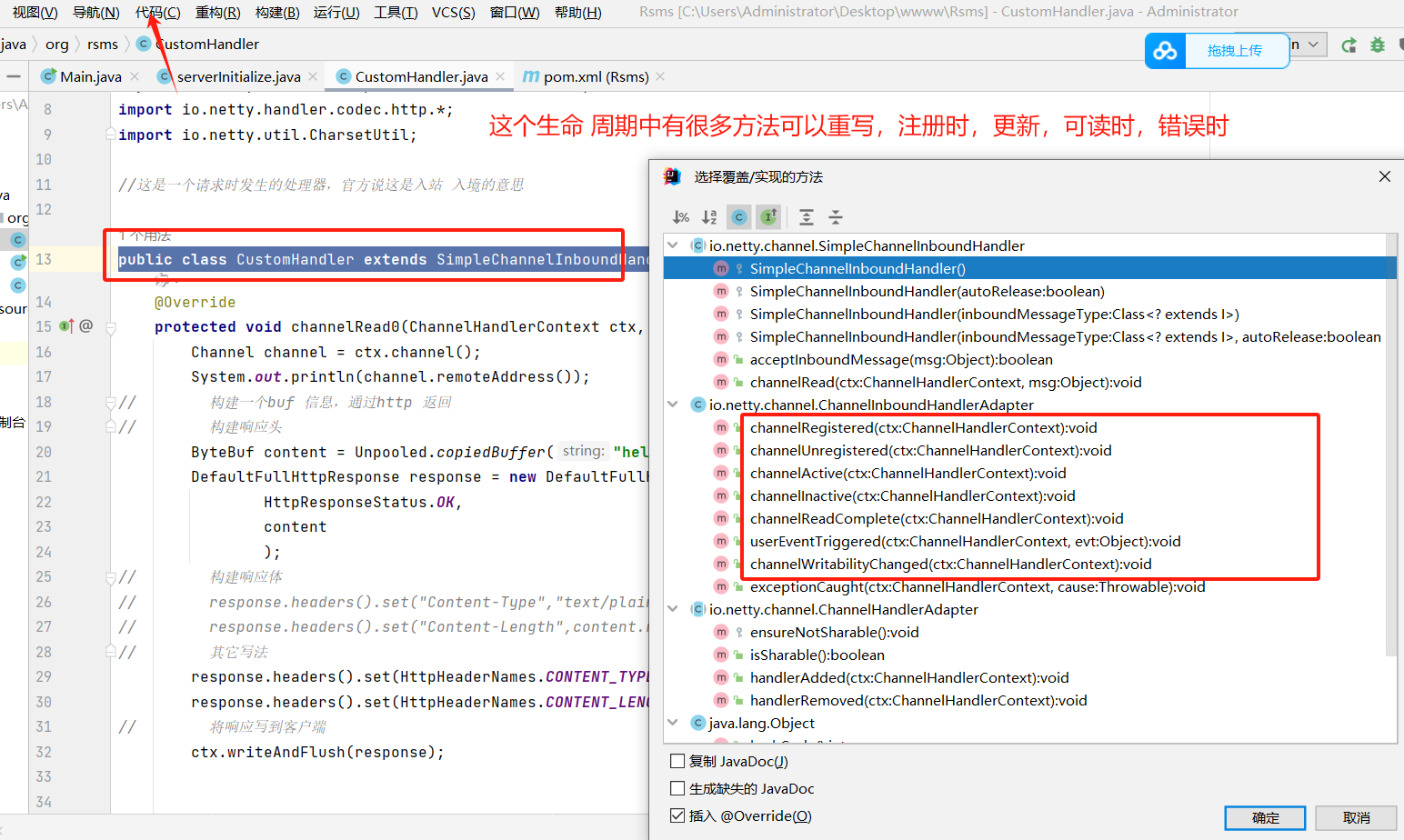
channelRegisterd注册
chanetlUnregisterdd 移除
channelActive 活跃
excetptionCaught 捕获异常
handlerAdded 助手添加
handlerRemoved 助手移除
示例二 netty 用于websockkect的例子,说例说初充一下websocket 的用法 先建一个入口文件
package org.rsms.websocjet;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
public class WSServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
NioEventLoopGroup mainGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup subGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
// 启动服务器
ServerBootstrap server = new ServerBootstrap();
server.group(mainGroup, subGroup)
.channel(io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new WSServerInitialzer());
ChannelFuture future = server.bind(8089).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
mainGroup.shutdownGracefully();
subGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
然后编写初始化管道 ,这儿主要是增加大在文件读写
package org.rsms.websocjet;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpObjectAggregator;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpServerCodec;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.WebSocketServerProtocolHandler;
import io.netty.handler.stream.ChunkedWriteHandler;
public class WSServerInitialzer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
// 我们要处理大数据和http协议的channelPipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
// 对大文件读写
pipeline.addLast(new ChunkedWriteHandler());
// 封装http 相关,聚合请求和响应。几乎netty 都 要用一下
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(1024 * 64));
// 以上是用于http 协议支持
// 以下的websocketw会帮我处理一些复杂的事,比如close ping pong 等等,心跳处理
// 对于websocket来讲,都是以frames进行传输的,不同的数据对应的frames 也不同
pipeline.addLast(new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/ws"));
pipeline.addLast(new ChatHandler());
}
}
第三步就是编写自己的业务软件
这一步比较重要:
- 定义
ChatHandler类并继承SimpleChannelInboundHandler<TextWebSocketFrame>: - 定义一个静态的
ChannelGroup变量clinets,用于存储所有连接的Channel: - 重写
channelRead0方法,用于处理接收到的文本WebSocket帧: - 重写
handlerAdded方法,当有新的Channel添加到ChannelPipeline时调用: - 重写
handlerRemoved方法,当有Channel从ChannelPipeline中移除时调用:
package org.rsms.websocjet; import io.netty.channel.Channel; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; import io.netty.channel.group.ChannelGroup; import io.netty.channel.group.DefaultChannelGroup; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.TextWebSocketFrame; import io.netty.util.concurrent.GlobalEventExecutor; import java.time.LocalDate; public class ChatHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<TextWebSocketFrame> { // 这个是可以保存所有连接的channel private static ChannelGroup clinets = new DefaultChannelGroup(GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE); @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, TextWebSocketFrame msg) throws Exception { String content = msg.text(); System.out.println("收到的消息"); System.out.println("received:" + msg.text()); // 这儿channel.writeAndFlush是不能接传字符串的,除了for 可以对clinet遍历, // 其实clients.writeAndFlush(content)也是可以打印结果 for(Channel channel : clinets){ channel.writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame("服务器收到消息:" + content)); channel.writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame("服务器收到消息:" + LocalDate.now())); } } @Override public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { System.out.println("有人来了添加一个channel"); clinets.add(ctx.channel()); } @Override public void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { System.out.println("有人走了删除一个channel"); System.out.println("客户id 长整型"+ ctx.channel().id().asLongText()); System.out.println("客户,短整型" + ctx.channel().id().asShortText()); // clinets.remove(ctx.channel()); } }
websocket api 介结
WebSocket API 是一种在单个 TCP 连接上进行全双工通信的协议。它允许服务器与客户端之间进行实时双向通信。下面是如何使用 WebSocket API 的详细步骤:
-
创建 WebSocket 对象
使用
new WebSocket(url)来创建一个新的 WebSocket 对象,其中url是 WebSocket 服务器的地址。例如:var socket = new WebSocket("ws://example.com:8080"); -
监听 WebSocket 生命周期事件
WebSocket 对象有四个重要的生命周期事件:
open,message,error, 和close。你可以通过设置这些事件的on属性来添加事件处理函数。onopen: 当连接建立时触发。onmessage: 当从服务器接收到消息时触发。onerror: 当发生错误时触发。onclose: 当连接关闭时触发。
示例如下:
// 创建 WebSocket 对象 var socket = new WebSocket("ws://example.com:8080"); // 监听打开事件 socket.onopen = function(event) { console.log("WebSocket 连接已打开", event); // 发送一条消息到服务器 socket.send("Hello, Server!"); }; // 监听消息事件 socket.onmessage = function(event) { console.log("从服务器接收到数据", event.data); // 关闭连接 socket.close(); }; // 监听错误事件 socket.onerror = function(error) { console.error("WebSocket 发生错误", error); }; // 监听关闭事件 socket.onclose = function(event) { console.log("WebSocket 连接已关闭", event); };






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号