[Atcoder] ABC245

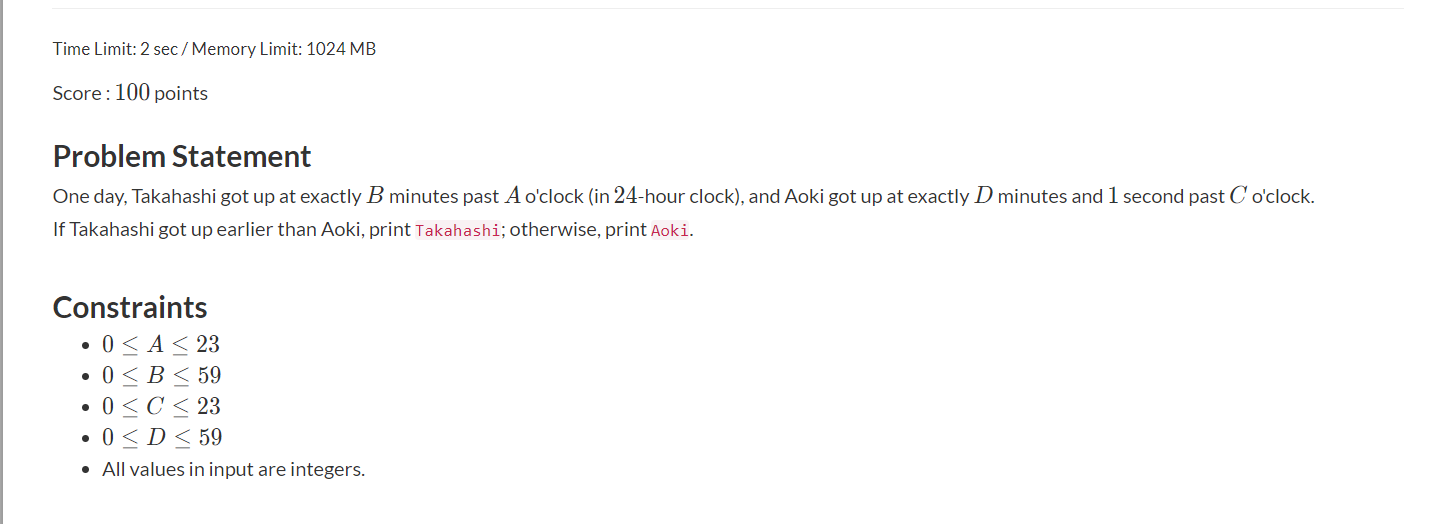
A - Good morning
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
//==========================================
const int N = 2e5+5;
typedef long long ll;
signed main(signed argc, char const *argv[])
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
//======================================
int a, b, c, d;
cin >> a >> b >> c >> d;
if(a < c) cout << "Takahashi" << endl;
else if(a == c) {
if(b <= d) cout << "Takahashi" << endl;
else cout << "Aoki" << endl;
}
else cout << "Aoki" << endl;
//======================================
return 0;
}
B - Mex

思路
暴力,数据范围只有2000,把每个出现过数字的标记一下,暴力在0~2000里找第一个没出现的数字
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
//==========================================
const int N = 2e5+5;
typedef long long ll;
int t[2010], a[2010];
signed main(signed argc, char const *argv[])
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
//======================================
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
cin >> a[i];
t[a[i]] ++;
}
for(int i = 0; i <= 2000; i ++) {
if(!t[i]) {
cout << i << endl;
return 0;
}
}
//======================================
return 0;
}
C - Choose Elements
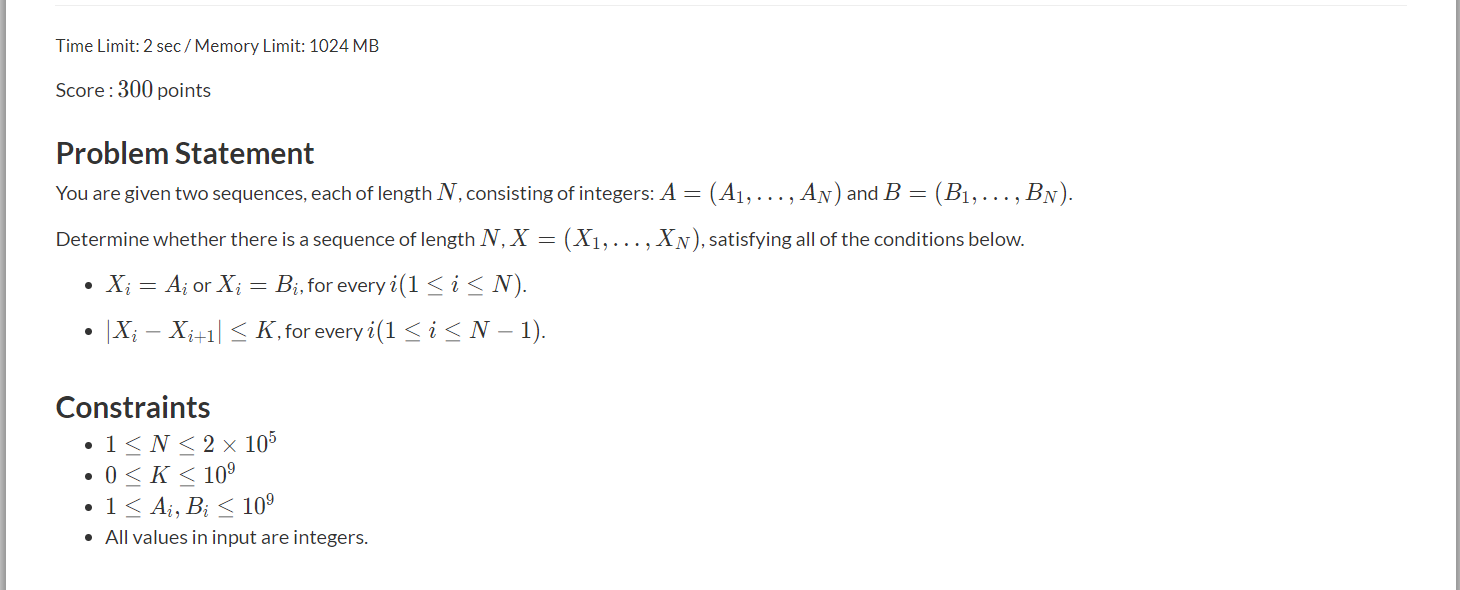
给出A、B两个序列,问能否构成一个X序列,满足Xi = Ai或者Xi = Bi,且|Xi - Xi+1|<=K
思路
dp,dp(i,j)表示为遍历到第i个数时,j=1为当前取ai,j=2为当前取bi
首先对于Xn我们是可以直接确定的,所以dp的起始条件为dp(n,1)=an,dp(n,2)=bn
对于Xi,Xi+1只有三种情况,一种是取ai+1,一种是取bi+1,还有就是两个都取不了
而我们的Xi如果要取ai的话,就需要满足|ai - dp(i+1,1)|<=k或者|ai - dp(i+1,2)|<=k
dp初始化时直接正无穷,这样无解的话在dp时就不会产生影响
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
//==========================================
const int N = 2e5+5;
typedef long long ll;
int a[N], b[N];
int dp[N][4];
signed main(signed argc, char const *argv[])
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
//======================================
int n;
int k;
cin >> n;
cin >> k;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cin >> b[i];
bool fg = false;
ll tmp = a[n];
memset(dp, 0x3f, sizeof dp);
dp[n][1] = a[n], dp[n][2] = b[n];
for(int i = n - 1; i >= 1; i --) {
if(abs(a[i] - dp[i + 1][1]) <= k && dp[i + 1][1] != 0x3f3f3f3f) dp[i][1] = a[i];
else if(abs(a[i] - dp[i + 1][2]) <= k && dp[i + 1][2] != 0x3f3f3f3f) dp[i][1] = a[i];
if(abs(b[i] - dp[i + 1][1]) <= k && dp[i + 1][1] != 0x3f3f3f3f) dp[i][2] = b[i];
else if(abs(b[i] - dp[i + 1][2]) <= k && dp[i + 1][2] != 0x3f3f3f3f) dp[i][2] = b[i];
//cout << dp[i][1] << " " << dp[i][2] << endl;
}
//cout << dp[1][1] << endl;
if(dp[1][1] != 0x3f3f3f3f || dp[1][2] != 0x3f3f3f3f) cout << "Yes" << endl;
else cout << "No" << endl;
//======================================
return 0;
}
D - Polynomial division

给出C(x)和A(x)每项的系数,求B(x)的每项的系数
思路
首先推一下式子Cn+m=AnBm,Cn+m-1=AnBm-1+An-1Bm,Cn+m-2=AnBm-2+An-2Bm+An-1Bm-1等,以此类推,可以发现只要求了Bm,那后面的所有受Bm影响的C都可以减掉这一项,所有受Bm-1影响的同理,
那最后每一个C只受当前要求的B和An影响
不管是从前往后还是从后往前推式子,都可以发现求每一项的时候,只要把之前求的影响去掉即可
首先题目给出的是An!=0和Cn+m!=0,所以这题要反着求Bi
因为正着求会出现如果A0是0的话,那后面Bi全是0的情况(喜提RE)
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
//==========================================
const int N = 2e5+5;
typedef long long ll;
ll a[N], b[N], c[N];
signed main(signed argc, char const *argv[])
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
//======================================
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i ++) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 0; i <= n + m; i ++) cin >> c[i];
//b[0] = c[0] / a[0];
int k = 0;
for(int i = m; i >= 0; i --) {
int tmp = c[n + m - k];
if(!c[n + m - k]) b[i] = 0;
else b[i] = tmp / a[n];
for(int j = 0; j <= n; j ++) c[i + j] -= b[i] * a[j];
//tmp -= a[i] * b[0];
k ++;
}
for(int i = 0; i <= m; i ++) {
cout << b[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//======================================
return 0;
}
E - Wrapping Chocolate
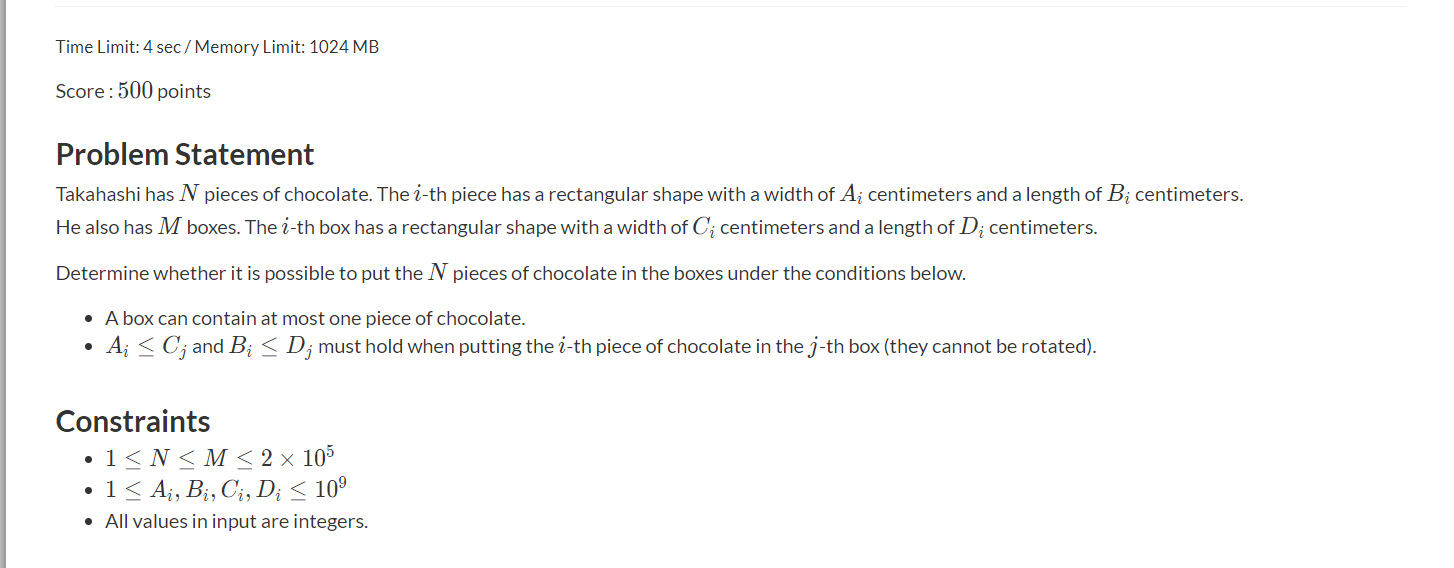
有巧克力长和宽x, y,盒子长和宽x, y,问是否把每个巧克力装到盒子里,每个盒子只能装一个
思路
二维排序转化为一维,对全部的元素按x进行排序,那么对于每个i,j,他们的x肯定符合条件i.x <= i.y,那么就可以在符合x的条件的盒子里,找一个最小的满足y条件的盒子,二分+multiset找
如果找不到的话,那么肯定就是装不下了,否则的话肯定是最优的
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
//==========================================
const int N = 2e5+5;
typedef long long ll;
struct Node {
int x, y, fg;
}B[N], C[N];
bool cmp(Node a, Node b) {
if(a.x == b.x) return a.fg > b.fg; //这里相等时候将盒子放前面,这样能多出一个选择
return a.x > b.x;
}
signed main(signed argc, char const *argv[])
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
//======================================
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
multiset<int> st;
vector<Node> v;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cin >> C[i].x;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cin >> C[i].y;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) cin >> B[i].x;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) cin >> B[i].y;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) v.push_back({C[i].x, C[i].y, 0});
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) v.push_back({B[i].x, B[i].y, 1});
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), cmp);
for(auto i : v) {
if(i.fg == 1) st.insert(i.y);
else {
auto it = st.lower_bound(i.y);
if(it == st.end()) {cout << "No" << endl; return 0;}
else {
st.erase(it);
}
}
}
cout << "Yes" << endl;
//======================================
return 0;
}
F - Endless Walk

题意是给出一个有向图,问有多少个点是可以无限走下去的
即从一个点出发可以到达一个环
思路
画一下图,会发现如果有一个出度为0的点,那这个点肯定是不能到达其他点的,自然也就不能到达一个环,按这个结论的话就可以想到拓扑排序,拓扑排序每轮将所有入度为0的点都删除了,同时拓扑排序也可以用来简单的判是否存在环。那反向建图,将原本的出度作为入度进行拓扑排序就可以在每轮将原图上所有出度为0的点都删除
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
//==========================================
const int N = 2e5+5, M = 2 * N;
typedef long long ll;
int e[M], ne[M], h[N], idx;
int d[N];
bool st[N];
void add(int x, int y) {
e[idx] = y, ne[idx] = h[x], h[x] = idx ++;
}
signed main(signed argc, char const *argv[])
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
//======================================
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
int x, y;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) {
cin >> x >> y;
add(y, x);
d[x] ++;
}
queue<int> q;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if(!d[i]) q.push(i), st[i] = true;
}
int ans = n;
while(q.size()) {
int tmp = q.front();
if(!st[tmp]) st[tmp] = true;
ans --;
q.pop();
for(int i = h[tmp]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
if(!(-- d[j])) {
q.push(j);
}
}
}
/*
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if(st[i]) cout << i << endl;
} */
cout << ans << endl;
//======================================
return 0;
}
这里在贴一下我一开始的代码,一开始直接想到缩点去了。。。虽然也能做,但是还是要加上反向建图进行拓扑排序,麻烦很多,当做是复习tarjan缩点了
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
//==========================================
const int maxn = 2e5+5;
struct EDGE {
int from, to, next;
}edge[maxn * 10], ed[maxn * 10];
int n;
int h[maxn], idx, idx2, h2[maxn];
int dfn[maxn], low[maxn], tim, vis[maxn];
int a[maxn], belo[maxn], in[maxn], dist[maxn];
int siz[maxn], vs[maxn];
stack<int> stk;
void add(int x,int y)
{
edge[++idx].next=h[x];
edge[idx].from=x;
edge[idx].to=y;
h[x]=idx;
}
void tarjan(int x) { //tarjan缩点,将环都缩成点,这题里不必要
dfn[x] = low[x] = ++ tim;
stk.push(x), vis[x] = 1;
for(int i = h[x]; i != 0; i = edge[i].next) {
int j = edge[i].to;
if(!dfn[j]) {
tarjan(j);
low[x] = min(low[x], low[j]);
}
else if(vis[j]) {
low[x] = min(low[x], dfn[j]);
}
}
if(dfn[x] == low[x]) {
int cnt = 0;
while(1) {
int tmp = stk.top();
belo[tmp] = x;
stk.pop();
cnt ++;
siz[x] ++;
vis[tmp] = 0;
if(tmp == x) break;
a[x] += a[tmp];
}
}
}
int topu() {
queue<int> q;
int tot = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) { //注意遍历的时候点的范围应该是无所谓的,但是最好是改成重建的图的点范围,对结果不会产生影响
if(belo[i] == i && !in[i]) {
q.push(i);
dist[i] = a[i];
}
vs[i] = (siz[i] > 1);
}
while(!q.empty()) {
int k = q.front();
q.pop();
if(siz[k] > 1) vs[k] = 1; //因为有缩点,如果点的大小大于等于2,代表存在环,那这个点肯定是可行的
for(int i = h2[k]; i != 0; i = ed[i].next) {
int j = ed[i].to;
vs[j] |= vs[k]; //因为是反向建的图,所以只要可达,那就代表在原图中,可以通过j点抵达k点
dist[j] = max(dist[j], dist[k] + a[j]);
in[j] --;
if(in[j] == 0) q.push(j);
}
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) if(vs[i]) ans += siz[i]; //因为tarjan缩了点,所以ans加的时候要加上缩的点的大小
return ans;
}
signed main(signed argc, char const *argv[])
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
//======================================
int m;
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
dist[i] = 0;
//h[i] = -1;
}
int x, y;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) {
cin >> x >> y;
add(x, y);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if(!dfn[i]) tarjan(i);
}
//cout << a[1] << endl;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) {
int u = belo[edge[i].from], v = belo[edge[i].to];
if(u != v) { //这里要反向建图,因为要将出度为0的点通过拓扑排序删除
//cout << u << v << endl;
ed[++ idx2].next = h2[v];
ed[idx2].to = u;
ed[idx2].from = v;
h2[v] = idx2;
in[u] ++;
}
}
cout << topu() << endl;
//======================================
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号