java编程基础(四)----容器
JCF
JCF(Java Collection Framework)
容器:能存放数据的空间结构(数组、树)
容器框架:为表示和操作容器而规定的一种标准体系结构(C++中的STL、java中的JCF)
- 对外的接口:容器中能存放抽象的数据类型
- 接口的实现:可复用的数据结构
- 算法:对数据的查找和排序
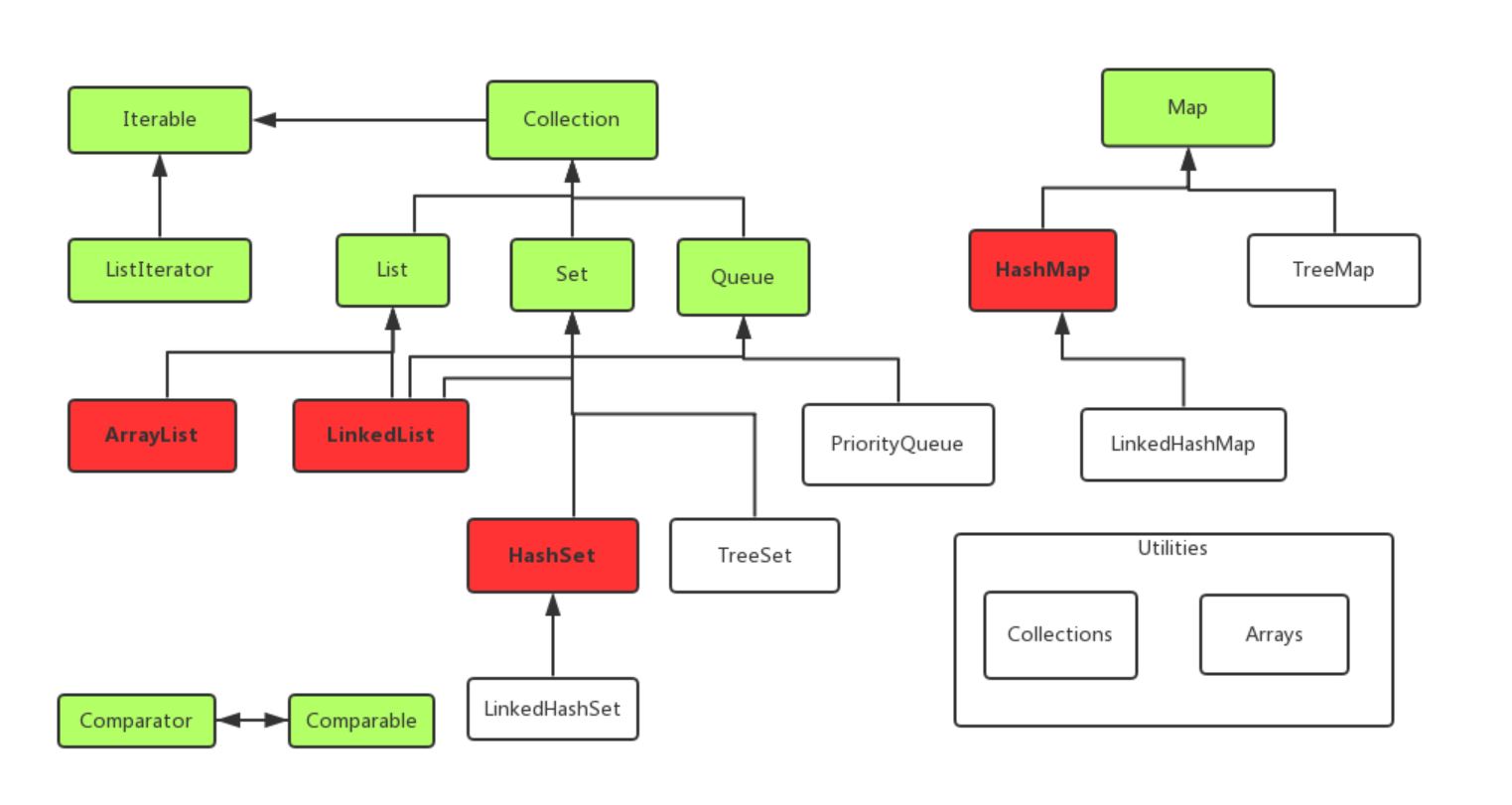
JCF主要数据结构实现类:
- 列表(List、Arraylist、LinkedList)
- 集合(Set、HashSet、TreeSet、LinkedHashSet)
- 映射(HashMap、TreeMap、LinkedHashMap)
JCF主要的算法类:
- Arrays:对数组进行查找和排序等操作
- Collections:对Collection及其子类进行排序和查找操作
Colletction接口定义的方法:
| 返回类型 | 方法名(参数类型,参数) | 描述 |
| int | Size() | 容器中对象的数目 |
| boolean | isEmpty() | 是否为空 |
| void | clear() | 清空 |
| boolean | contains(Object element) | 是不是包含element对象 |
| boolean | add(Object element) | 添加element的对象 |
| boolean | remove(Object element) | 移除element对象 |
| iterator | iterator() | 返回一个Iterator对象,用于遍历容器中的对象 |
| boolean | containsAll(Collection c) | 是否包含c容器中的所有对象 |
| boolean | addAll(Collection c) | 把c容器中的所有对象添加到容器中 |
| boolean | removeAll(Collection c) | 从容器中移除C容器中存在的所有对象 |
| boolean | retainAll(Collection c) | 求当前的集合类与C容器的交集 |
| Object[] | toArray() | 把容器中的所有对象转换到对应的数组中 |
List(列表)
list的两个特征:
- 有序的Collections
- 允许重复的元素
List主要实现的三种类:
- ArrayList(非同步的)
- LinkedList(非同步的)
- Vector(用的比较少)
ArrayList
- 以数组实现的列表,但不支持同步。
- 利用索引位置可以快速定位访问
- 不适合指定位置的插入、删除操作。
- 和java数组相比,其容量可以动态调整的。
- Arraylist在元素填满容器时会自动扩充容器大小的50%
命名原则:
例如:ArrayList<Integer> al=new ArrayList<Integer>();其中<>是泛型表示al这个数据结构里只能容纳Integer的对象,其他对象无法放入。
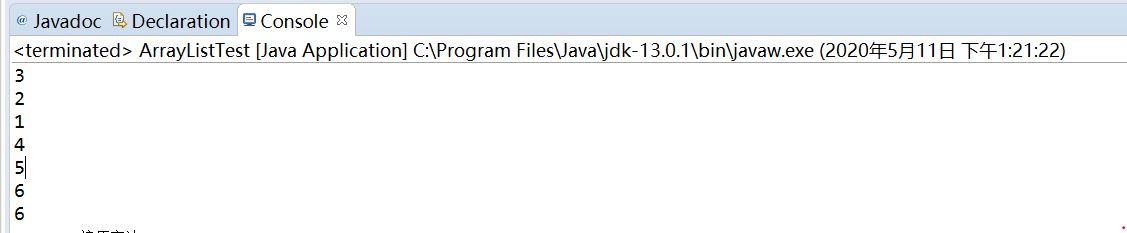
public class ArrayListTest { public static void main(String[] a) { ArrayList<Integer> al = new ArrayList<Integer>(); al.add(3); al.add(2); al.add(1); al.add(4); al.add(5); al.add(6); al.add(new Integer(6)); for(Integer i:al) { System.out.println(i); }
自动装箱:
尽管ArrayList只能装对象,但是上面代码中有add(3)会将普通的int变量3自动装箱为Integer(3)的对象放入;
所以上面al.add(6)和al.add(new Integer(6))其实是一样的效果。
LinkedList
- 以双向链表实现的列表,不支持同步
- 可以被当作堆栈、队列、双端队列进行操作
- 随机访问较差,中间插入删除高效
- 适合经常变化的数据
命名规则和自动装箱机制与Arraylist一样不做过多介绍
集合(Set)
集合的三大特性:
- 确定性:对任意对象都能判定是否属于某一个集合
- 互异性:集合内每个元素都是不相同的
- 无序性:集合内顺序无关
java中的集合类:
- HashSet(基于散列函数的集合,无序,不支持同步)
- TreeSet(基于树结构,可排序,不支持同步)
- LinkedHashSet(基于散列函数和双向链表的集合,可排序,不支持同步)
HashSet
示例代码:
public class HashSetTest { public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet<Integer> hs = new HashSet<Integer>(); hs.add(null); hs.add(1000); hs.add(20); hs.add(3); hs.add(40000); hs.add(5000000); hs.add(3); //3 重复 hs.add(null); //null重复 System.out.println(hs.size()); //6 for(Integer i:hs) { System.out.print(i+" "); }
可以看出来,重复的元素不会被放入容器中,容器中的元素顺序也跟放入顺序无关是无序的。(ArrayList容器跟元素放入顺序一样的)
TreeSet
- 基于TreeMap实现,不可以容纳null元素,不支持同步
- 方法(add、clear、contains、remove、size)
- 根据compareTo方法或者指定所存储对象大小升序输出
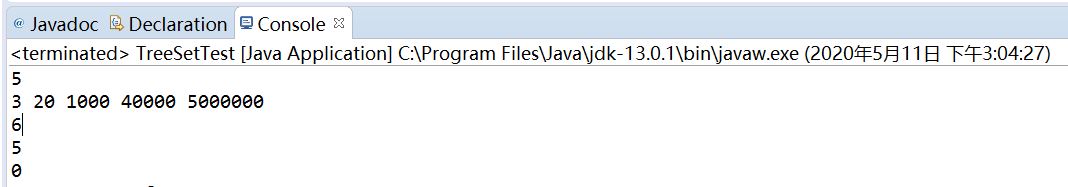
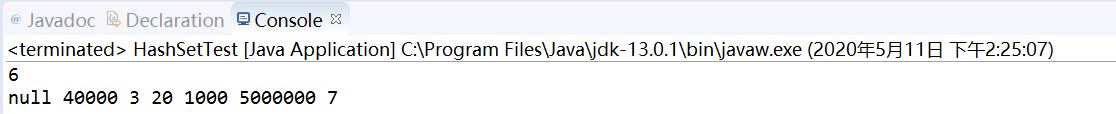
public class TreeSetTest { public static void main(String[] args) { TreeSet<Integer> ts = new TreeSet<Integer>(); // ts.add(null); 错误,不支持null ts.add(1000); ts.add(20); ts.add(3); ts.add(40000); ts.add(5000000); ts.add(3); //3 重复 System.out.println(ts.size()); //5 for(Integer i:ts) { System.out.print(i+" "); } System.out.println(); if(!ts.contains(6)) { ts.add(6); } System.out.println(ts.size()); //6 ts.remove(3); System.out.println(ts.size()); //5 ts.clear(); System.out.println(ts.size()); //0
LinkedHashSet
- 继承HashSet,基于HashMap实现,可以容纳null元素。
- 不支持同步
- 通过一个双向链表维护插入顺序(插入顺序保留)
示例代码:
public class LinkedHashSetTest { public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedHashSet<Integer> lhs = new LinkedHashSet<Integer>(); lhs.add(null); lhs.add(1000); lhs.add(20); lhs.add(3); lhs.add(40000); lhs.add(5000000); lhs.add(3); //3 重复 lhs.add(null); //null 重复 System.out.println(lhs.size()); //6 for(Integer i:lhs) { System.out.print(i+" "); } System.out.println(); if(!lhs.contains(6)) { lhs.add(6); } System.out.println(lhs.size()); //7 lhs.remove(3); System.out.println(lhs.size()); //6
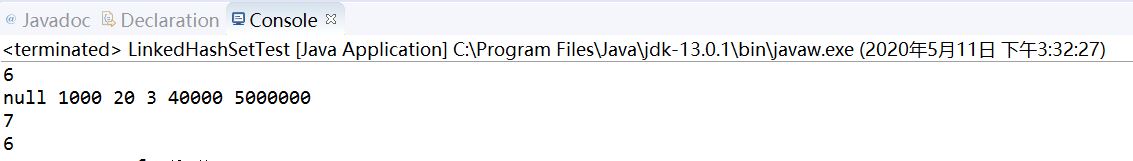
可以很清楚的看出,LinkedHashSet可以容纳null元素,而且因为保留了顺序,其遍历顺序和插入顺序一致。
HashSet和LinkedHashSet判定元素重复原则
- 判定两个元素的hashcode返回值是否相同,若不同返回false
- 两者的hashcode相同,判定equals方法,若不同返回false,否则返回true
- hashcode和equals方法所有类都有,因为Object类有
我们先写一个一个Cat类和Dog类,Cat 类没有hashcode方法,Dog类重写了hashcode方法,其返回具体的size。代码如下:
/*Cat类本身没有hashcode(),而是继承Objiect类的, * 而Object类的hashcode()会返回对象信息和内存 * 地址经过运算后的一个int值,所以他们的hashcode返回值是不一样的 */ class Cat { private int size; public Cat(int size) { this.size = size; } }
/* * Dog类本身改写了hashcode()方法,其返回值是具体 * 的size。所以两个 不同的Dog(4),他们的hashcode * 返回值是相同的 */ class Dog { private int size; public Dog(int s) { size = s; } public int getSize() { return size; } public boolean equals(Object obj2) { System.out.println("Dog equals()~~~~~~~~~~~"); if(0==size - ((Dog) obj2).getSize()) { return true; } else { return false; } } public int hashCode() { System.out.println("Dog hashCode()~~~~~~~~~~~"); return size; } public String toString() { System.out.print("Dog toString()~~~~~~~~~~~"); return size + ""; } }
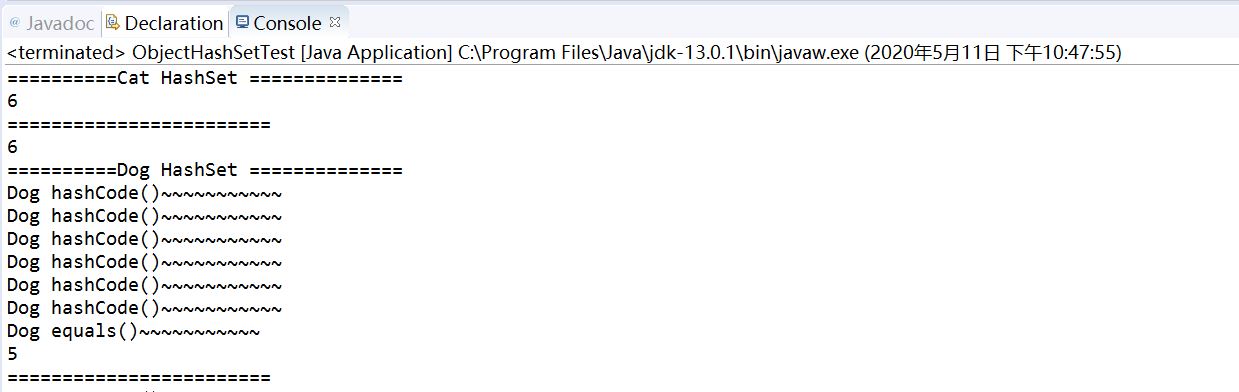
public class ObjectHashSetTest { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("==========Cat HashSet =============="); HashSet<Cat> hs = new HashSet<Cat>(); hs.add(new Cat(2)); hs.add(new Cat(1)); hs.add(new Cat(3)); hs.add(new Cat(5)); hs.add(new Cat(4)); hs.add(new Cat(4)); System.out.println(hs.size()); //6 System.out.println("========================"); LinkedHashSet<Cat> lhs= new LinkedHashSet<Cat>(); lhs.add(new Cat(2)); lhs.add(new Cat(1)); lhs.add(new Cat(3)); lhs.add(new Cat(5)); lhs.add(new Cat(4)); lhs.add(new Cat(4)); System.out.println(lhs.size()); //6 System.out.println("==========Dog HashSet =============="); HashSet<Dog> hs2 = new HashSet<Dog>(); hs2.add(new Dog(2)); hs2.add(new Dog(1)); hs2.add(new Dog(3)); hs2.add(new Dog(5)); hs2.add(new Dog(4)); hs2.add(new Dog(4)); System.out.println(hs2.size()); //5 System.out.println("========================"); LinkedHashSet<Dog> lhs2= new LinkedHashSet<Dog>(); lhs2.add(new Dog(2)); lhs2.add(new Dog(1)); lhs2.add(new Dog(3)); lhs2.add(new Dog(5)); lhs2.add(new Dog(4)); lhs2.add(new Dog(4)); System.out.println(lhs2.size()); //5
可以最后得出Dog类通过hashcode方法识别出来Dog(4)判定是相同的,所以第二个Dog(4)不会被放入容器中。
Map(映射)
- 两个集合之间元素对应关系
- 键值对应(K-V对),{key,value}。
主要的三种类:
- HashMap
- TreeMap
- LinkedHashMap
HashMap
- K-V对,K和V都允许为null
- 不同步,多线程不安全
- 无序的
- 主要的方法:clear、containValue、containKey、get、put、remove、size
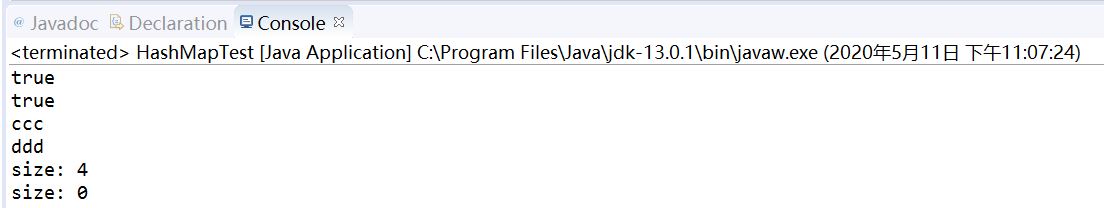
public static void main(String[] args) { HashMap<Integer,String> hm =new HashMap<Integer,String>(); hm.put(1, null); hm.put(null, "abc"); hm.put(1000, "aaa"); hm.put(2, "bbb"); hm.put(30000, "ccc"); System.out.println(hm.containsValue("aaa")); System.out.println(hm.containsKey(30000)); System.out.println(hm.get(30000)); hm.put(30000, "ddd"); //更新覆盖ccc System.out.println(hm.get(30000)); hm.remove(2); System.out.println("size: " + hm.size()); hm.clear(); System.out.println("size: " + hm.size());
LinkedHashMap
- 基于双向链表维持插入顺序的HashMap。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号