实现二叉排序树的前中后序遍历
二叉排序树定义
二叉排序树(Binary Sort Tree),也称为二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree, BST)或有序二叉树,是一种特殊的二叉树数据结构。以下是二叉排序树的一些核心概念:
一个二叉排序树或者是一棵空树,或者是具有以下性质的二叉树:
- 右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值
- 左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值
- 左右子树也分别为二叉排序树
- 不存在键值相等的节点
代码实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int DataType_t;
typedef struct BSTreeNode
{
DataType_t Keyval;
struct BSTreeNode *lchild;
struct BSTreeNode *rchild;
}BSTNode_t;
BSTNode_t* BSTree_Create(DataType_t KeyVal)
{
BSTNode_t *root = (BSTNode_t *)calloc(1,sizeof(BSTNode_t));
if(root == NULL){
perror("Calloc memory for the root is failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
root->lchild = NULL;
root->rchild = NULL;
root->Keyval = KeyVal;
return root;
}
BSTNode_t* BSTree_NewNode(DataType_t KeyVal)
{
BSTNode_t *New = (BSTNode_t *)calloc(1,sizeof(BSTNode_t));
if(New == NULL){
perror("Calloc memory for the New is failed!\n");
return NULL;
}
New->lchild = NULL;
New->rchild = NULL;
New->Keyval = KeyVal;
return New;
}
bool BSTree_InsertNode(BSTNode_t* root, DataType_t KeyVal)
{
if (root == NULL) {
printf("Error: root is NULL, cannot insert %d\n", KeyVal);
return false;
}
BSTNode_t *New = BSTree_NewNode(KeyVal);
if (New == NULL) {
printf("Create NewNode Error\n");
return false;
}
BSTNode_t *Proot = root;
while (Proot != NULL) {
if (KeyVal == Proot->Keyval) {
printf("Can not Insert, duplicate value: %d\n", KeyVal);
free(New); // 避免内存泄漏
return false;
}
else if (KeyVal < Proot->Keyval) {
if (Proot->lchild == NULL) {
Proot->lchild = New;
return true;
}
Proot = Proot->lchild;
}
else {
if (Proot->rchild == NULL) {
Proot->rchild = New;
return true;
}
Proot = Proot->rchild; //
}
}
return true; //
}
//前序遍历
bool BSTree_PreOrder(BSTNode_t* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return false;
}
printf("KeyVal = %d\n",root->Keyval);
BSTree_PreOrder(root->lchild);
BSTree_PreOrder(root->rchild);
return true;
}
//中序遍历
bool BSTree_InOrder(BSTNode_t* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return false;
}
BSTree_InOrder(root->lchild);
printf("KeyVal = %d\n",root->Keyval);
BSTree_InOrder(root->rchild);
return true;
}
//后序遍历
bool BSTree_PostOrder(BSTNode_t* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return false;
}
BSTree_PostOrder(root->lchild);
BSTree_PostOrder(root->rchild);
printf("KeyVal = %d\n",root->Keyval);
return true;
}
int main()
{
// --- 1. 测试:创建根节点 ---
printf("1. 创建根节点...\n");
BSTNode_t* root = BSTree_Create(50);
if (root) {
printf("成功创建根节点,值为: %d\n", root->Keyval);
}
// --- 2. 测试:插入多个节点 ---
printf("\n2. 插入其他节点...\n");
int values[] = {30, 70, 20, 40, 60, 80, 35, 45};
int n = sizeof(values) / sizeof(values[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (BSTree_InsertNode(root, values[i])) {
printf("成功插入: %d\n", values[i]);
}
}
// --- 3. 测试:重复插入(应失败)---
printf("\n3. 测试重复插入...\n");
BSTree_InsertNode(root, 40); // 已存在
BSTree_InsertNode(root, 50); // 根节点已存在
// --- 4. 测试:遍历操作 ---
printf("\n4. 遍历测试...\n");
printf("\n=== 前序遍历 (Pre-order) ===\n");
BSTree_PreOrder(root);
printf("\n=== 中序遍历 (In-order) - 应升序输出 ===\n");
BSTree_InOrder(root);
printf("\n=== 后序遍历 (Post-order) ===\n");
BSTree_PostOrder(root);
printf("\n7. 测试插入到 NULL 树(应失败)...\n");
BSTNode_t* emptyTree = NULL;
bool result = BSTree_InsertNode(emptyTree, 100);
if (!result) {
printf("正确:无法向 NULL 树插入节点。\n");
}
printf("\n所有测试完成\n");
return 0;
}
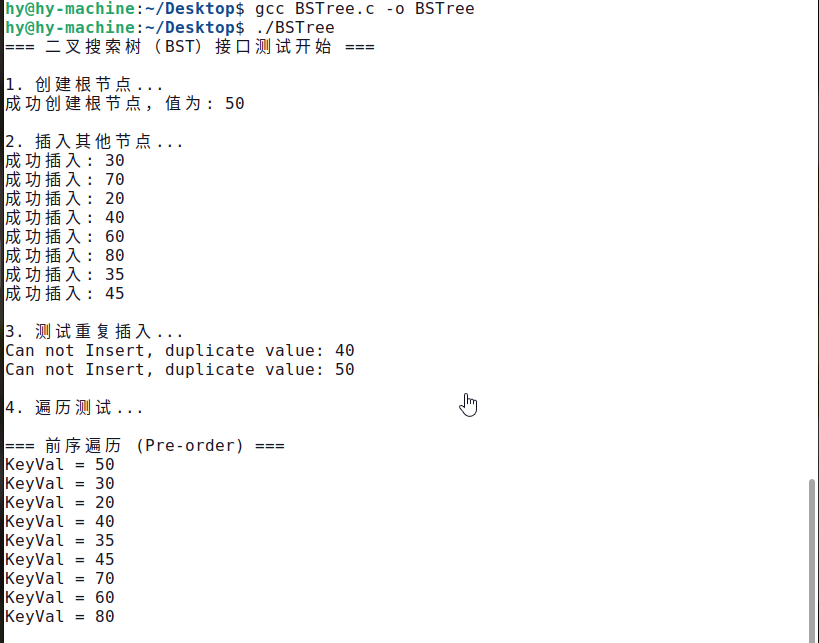
根节点的值是50,主函数中依次插入节点:30, 70, 20, 40, 60, 80, 35, 45,所以这棵树的图像长这个样子
运行结果





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号