单链表的定义与基本操作
单链表操作实现
1.什么是单链表?
单链表是一种常见的线性数据结构,由一系列节点组成,每个节点包含两个部分:数据域 和 指针域。数据域存储实际数据,指针域指向下一个节点。在单链表中,数据元素可以非连续地存储在内存中,而节点之间通过指针相互连接。
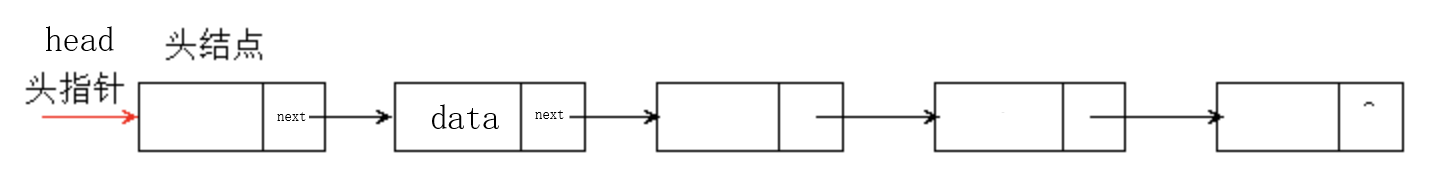
2.代码实现
链表的创建、插入、删除、查找等常用操作。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int DataType_t;
//构造链表的节点,列表中所有的数据类型应该是相同的
typedef struct LinkedList
{
DataType_t data;//节点的数据域
struct LinkedList *next;//结点的指针域
}LList_t;
//创建一个空链表,空链表应该有一个头节点,对链表进行初始化
LList_t* LList_Create(void)
{
//1.给头节点申请空间
LList_t *Head = (LList_t *)calloc(1,sizeof(LList_t));
if(NULL == Head)
{
perror("Calloc memory for the Head is failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
//头节点初始化,头节点是不存储有效内容
Head->next = NULL;
return Head;
}
//生成新的有效结点
LList_t* LList_NewNode(DataType_t data)
{
LList_t *New = (LList_t *)calloc(1,sizeof(LList_t));
if(NULL == New)
{
perror("Calloc memory for the New is failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
//新节点初始化
New->next = NULL;
New->data = data;
return New;
}
//在链表头部插入结点
bool LList_HeadInsert(LList_t *Head,DataType_t data)
{
LList_t *New = LList_NewNode(data);
if(NULL == New)
{
perror("Create NewNode is Failed !\n");
return false;
}
//若链表无有效结点
if(NULL == Head->next)
{
Head->next = New;
return true;
}
//在头结点后插入结点
New->next = Head->next;
Head->next = New;
return true;
}
//遍历链表每个结点
void LList_Print(LList_t *Head)
{
if (Head == NULL || Head->next == NULL) {
printf("链表为空!\n");
return;
}
LList_t *current = Head->next;
printf("链表内容: ");
while (current != NULL) {
printf("%d ", current->data);
current = current->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
//在链表尾部插入结点
bool LList_TailInsert(LList_t *Head,DataType_t data)
{
LList_t *New = LList_NewNode(data);
if(NULL == New)
{
perror("Create NewNode is Failed !\n");
return false;
}
//找到最后一个结点位置
while(Head->next != NULL)
{
Head = Head->next;
}
Head->next = New;
return true;
}
//根据结点数据域的值来指定在目标结点后插入新结点
bool LList_DestInsert(LList_t *Head,DataType_t dest,DataType_t data)
{
LList_t *New = LList_NewNode(data);
if(NULL == New)
{
perror("Create NewNode is Failed !\n");
return false;
}
//链表只有头结点,新结点直接放在头结点之后
if(NULL == Head->next)
{
Head->next = New;
return true;
}
LList_t *current = Head->next;
while((current != NULL) && (current->data != dest))
{
current = current->next;
}
//current指到了最后一个结点的next
if (current == NULL)
{
printf("Destination node not found!\n");
free(New); // 插入失败,释放已申请的内存
return false;
}
//找到了数据域data值等于dest的结点
New ->next = current->next;
current->next = New;
return true;
}
//删除链表尾部结点
bool LList_TailDel(LList_t *Head)
{
if(NULL == Head->next)
{
printf("链表空!\n");
return false;
}
LList_t *current = Head->next;
LList_t *ex_current = Head; // 初始化为Head,用于删除操作
// 遍历链表,找到尾节点和它的前一个节点
while(current->next != NULL)
{
ex_current = current;
current = current->next;
}
// 删除尾节点
ex_current->next = NULL; // 断开与尾节点的连接
free(current); // 释放尾节点的内存
return true;
}
//删除链表头(头结点之后)的结点
bool LList_HeadDel(LList_t *Head)
{
if(NULL == Head->next)
{
printf("链表空!\n");
return false;
}
LList_t *current = Head->next;
Head->next = Head->next->next;
free(current);
current = NULL;
return true;
}
//根据结点数据域的值来删除指定目标结点
bool LList_DestDel(LList_t *Head, DataType_t dest)
{
if (NULL == Head->next)
{
printf("链表空!\n");
return false;
}
LList_t *current = Head->next;
LList_t *ex_current = Head;
// 遍历链表,直到找到目标节点或链表结束
while (current != NULL && current->data != dest)
{
ex_current = current;
current = current->next;
}
// 检查是否找到目标节点
if (current == NULL)
{
printf("没有在链表找到要删除的指定结点!\n");
return false;
}
// 删除目标节点
ex_current->next = current->next;
free(current);
current = NULL;
return true;
}
其他辅助函数
1.删除最小值结点
bool LList_MinDel(LList_t *Head)
{
// 判断链表是否为空:如果头节点的 next 为 NULL,说明链表没有有效节点
if (NULL == Head->next)
{
printf("链表空!\n");
return false;
}
// 定义当前遍历节点 current,从第一个有效节点开始
LList_t *current = Head->next;
LList_t *pre_current = Head;
// 定义最小值节点 MinNode,初始为第一个有效节点
LList_t *MinNode = current;
LList_t *pre_MinNode = Head;
// 遍历链表,寻找最小值节点
while (current != NULL)
{
// 如果当前节点的 data 小于最小值节点的 data
if(current->data < MinNode->data)
{
// 更新最小值节点及其前驱节点
MinNode = current;
pre_MinNode = pre_current;
}
// 继续向后遍历
pre_current = current;
current = current->next;
}
// 找到最小值节点后,将其从链表中删除
pre_MinNode->next = MinNode->next;
free(MinNode);
return true;
}
2.查找倒数第 k 个节点(快慢指针法)
int findKthFromEnd(LList_t *Head, int k)
{
if (Head == NULL || k <= 0) {
printf("无效输入:k必须为正整数且链表不能为空\n");
return 0;
}
LList_t *fast = Head;
LList_t *slow = Head;
int steps = 0;
// fast 先走 k 步
while (steps < k) {
if (fast == NULL) {
printf("链表长度不足 %d 个节点,无法查找倒数第 %d 个节点\n", k, k);
return 0;
}
fast = fast->next;
steps++;
}
// 如果 fast 已经为 NULL,说明链表正好有 k 个节点
if (fast == NULL) {
printf("倒数第 %d 个结点的 data 值为: %d\n", k, slow->data);
return 1;
}
// 同时移动 fast 和 slow
while (fast != NULL) {
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
// 此时 slow 指向倒数第 k 个节点
printf("倒数第 %d 个结点的 data 值为: %d\n", k, slow->data);
return 1;
}
快慢指针经典算法。
fast先走 k 步,然后slow和fast一起走,当fast到达末尾时,slow正好在倒数第 k 个位置。
3.主函数测试
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
// 创建链表
printf("=== 创建空链表 ===\n");
LList_t *head = LList_Create();
if (head != NULL) {
printf("链表创建成功!\n");
}
LList_Print(head);
// 测试头插法
printf("\n=== 测试头插法 ===\n");
LList_HeadInsert(head, 10);
LList_HeadInsert(head, 20);
LList_HeadInsert(head, 30);
LList_Print(head); // 预期结果: 30 20 10
// 测试尾插法
printf("\n=== 测试尾插法 ===\n");
LList_TailInsert(head, 40);
LList_TailInsert(head, 50);
LList_Print(head); // 预期结果: 30 20 10 40 50
// 测试指定位置插入
printf("\n=== 测试指定位置插入 ===\n");
LList_DestInsert(head, 20, 25); // 在20后插入25
LList_Print(head); // 预期结果: 30 20 25 10 40 50
LList_DestInsert(head, 100, 99); // 尝试插入到不存在的节点后
// 测试查找倒数第k个节点
printf("\n=== 测试查找倒数第k个节点 ===\n");
findKthFromEnd(head, 1); // 预期结果: 50
findKthFromEnd(head, 3); // 预期结果: 10
findKthFromEnd(head, 10); // 预期结果: 链表长度不足
// 测试删除头节点
printf("\n=== 测试删除头节点 ===\n");
LList_HeadDel(head);
LList_Print(head); // 预期结果: 20 25 10 40 50
// 测试删除尾节点
printf("\n=== 测试删除尾节点 ===\n");
LList_TailDel(head);
LList_Print(head); // 预期结果: 20 25 10 40
// 测试删除指定节点
printf("\n=== 测试删除指定节点 ===\n");
LList_DestDel(head, 25);
LList_Print(head); // 预期结果: 20 10 40
LList_DestDel(head, 100); // 尝试删除不存在的节点
// 添加几个节点用于测试删除最小值
printf("\n=== 测试删除最小值节点 ===\n");
LList_TailInsert(head, 5);
LList_HeadInsert(head, 35);
LList_TailInsert(head, 15);
LList_Print(head); // 预期结果: 35 20 10 40 5 15
LList_MinDel(head); // 删除最小值5
LList_Print(head); // 预期结果: 35 20 10 40 15
LList_MinDel(head); // 删除最小值10
LList_Print(head); // 预期结果: 35 20 40 15
// 释放链表内存
printf("\n=== 释放链表内存 ===\n");
while (head->next != NULL) {
LList_HeadDel(head);
}
free(head);
head = NULL;
printf("链表已释放\n");
return 0;
}
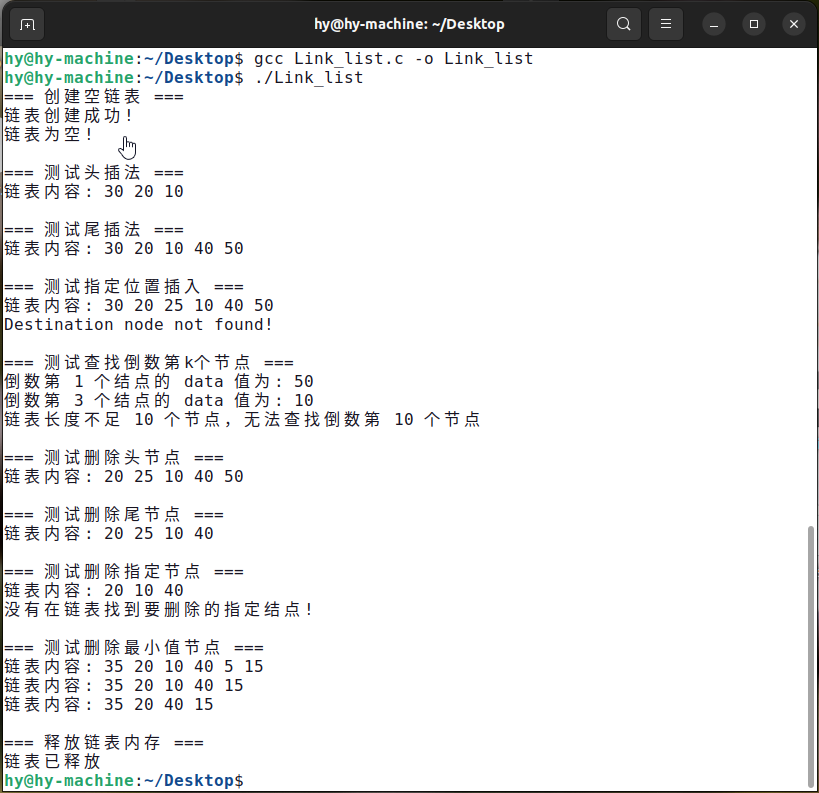
测试结果:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号