使用条件变量构建线程安全队列
当等待线程重新获取互斥量并检查条件时,如果它并非直接响应另一个线程的通知,这就是所谓的伪唤醒(spurious wakeup),也叫虚假唤醒。
使用条件变量的线程安全队列(完整版)
点击查看代码
template<typename T>
class threadSafeQueue
{
public:
threadSafeQueue(){}
threadSafeQueue(const threadSafeQueue& other)
{
lock_guard<mutex>lock(other.m_mutex);
m_queue = other.m_queue;
}
void push(T value)
{
lock_guard<mutex>lock(m_mutex);
m_queue.push(value);
m_conditionVar.notify_one();//发送通知
cout << "push notify...\n";
}
void waitAndPop(T& value)
{
unique_lock<mutex>lock(m_mutex);
//检测条件,如果为假就释放互斥量,并阻塞该线程,直到接收到通知使条件为真
m_conditionVar.wait(lock, [this]
{
cout << "waiting...\n";
return !m_queue.empty();
}
);
cout << "end waiting...\n";
value = m_queue.front();
m_queue.pop();
}
shared_ptr<T> waitAndPop()
{
unique_lock<mutex>lock(m_mutex);
m_conditionVar.wait(lock, [this]
{
return !m_queue.empty();
}
);
shared_ptr<T>ret(make_shared<T>(m_queue.front()));
m_queue.pop();
return ret;
}
bool tryPop(T& value)
{
lock_guard<mutex>lock(m_mutex);
if (m_queue.empty())
{
return false;
}
value = m_queue.front();
m_queue.pop();
return true;
}
shared_ptr<T> tryPop()
{
lock_guard<mutex>lock(m_mutex);
if (m_queue.empty())
{
return shared_ptr<T>();
}
shared_ptr<T>ret(make_shared<T>(m_queue.front()));
m_queue.pop();
return ret;
}
bool empty()const
{
lock_guard<mutex>lock(m_mutex);
return m_queue.empty();
}
private:
mutable mutex m_mutex;
queue<T>m_queue;
condition_variable m_conditionVar;
};示例用法:
点击查看代码
threadSafeQueue<int>q;
thread t([&q]
{
int value = 0;
q.waitAndPop(value);
cout << value << endl;
}
);
thread t2([&q]
{
q.push(999);
}
);
t.join();
t2.join();运行结果:
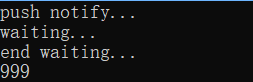
或者是这样
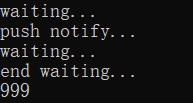
因为线程执行顺序不确定



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号