第五次实验
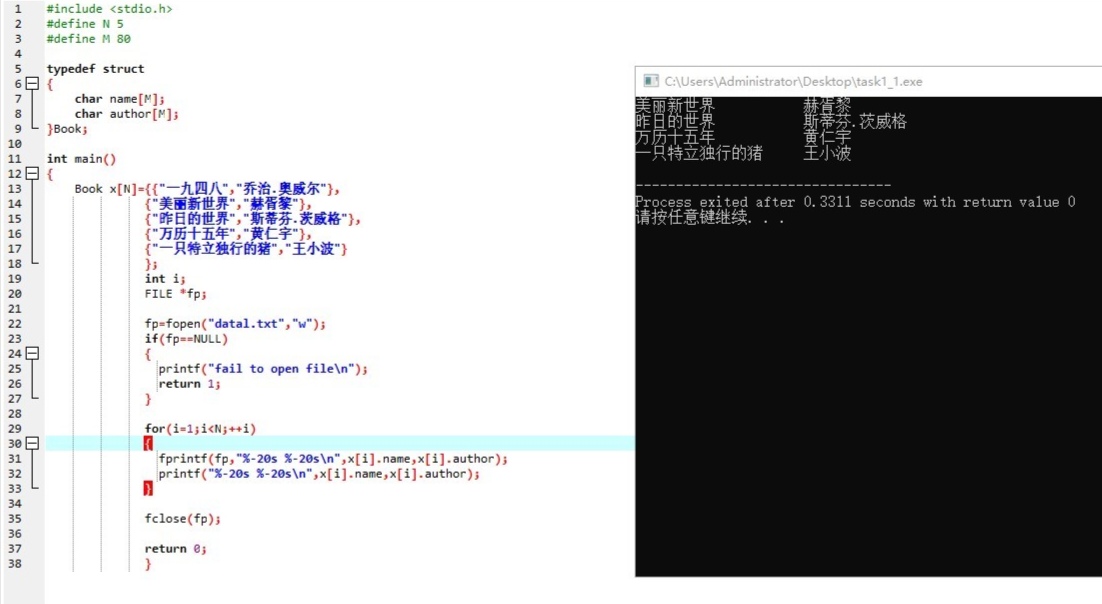
#include <stdio.h> #define N 5 #define M 80 typedef struct { char name[M]; char author[M]; }Book; int main() { Book x[N]={{"一九四八","乔治.奥威尔"}, {"美丽新世界","赫胥黎"}, {"昨日的世界","斯蒂芬.茨威格"}, {"万历十五年","黄仁宇"}, {"一只特立独行的猪","王小波"} }; int i; FILE *fp; fp=fopen("datal.txt","w"); if(fp==NULL) { printf("fail to open file\n"); return 1; } for(i=1;i<N;++i) { fprintf(fp,"%-20s %-20s\n",x[i].name,x[i].author); printf("%-20s %-20s\n",x[i].name,x[i].author); } fclose(fp); return 0; }
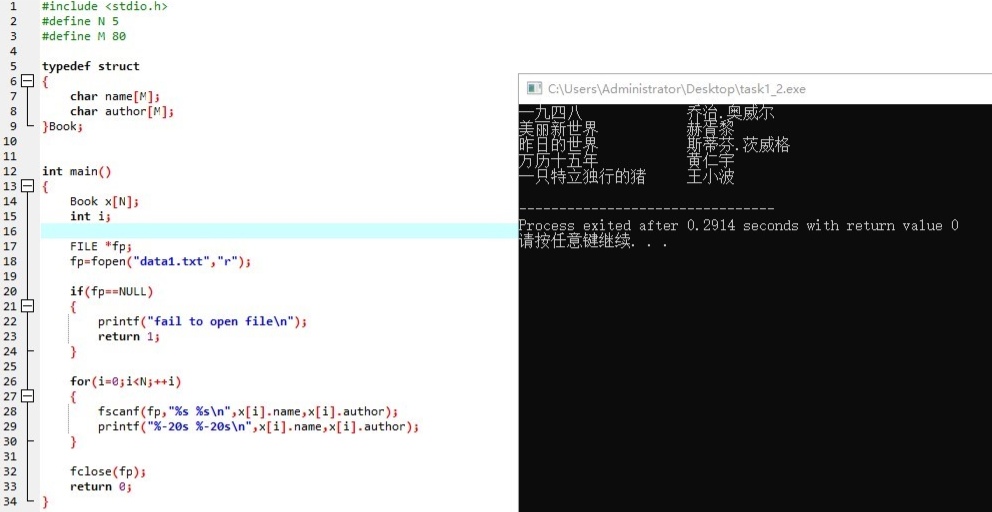
#include <stdio.h> #define N 5 #define M 80 typedef struct { char name[M]; char author[M]; }Book; int main() { Book x[N]; int i; FILE *fp; fp=fopen("data1.txt","r"); if(fp==NULL) { printf("fail to open file\n"); return 1; } for(i=0;i<N;++i) { fscanf(fp,"%s %s\n",x[i].name,x[i].author); printf("%-20s %-20s\n",x[i].name,x[i].author); } fclose(fp); return 0; }
答:scanf 函数的参数需要指针型,x.num,x.score[]这些都是普通变量,前面需要加指针符&转化成对应的指针.而x.name为字符数组,name就是该数组第一个数组的指针位置,所以不需要加&.
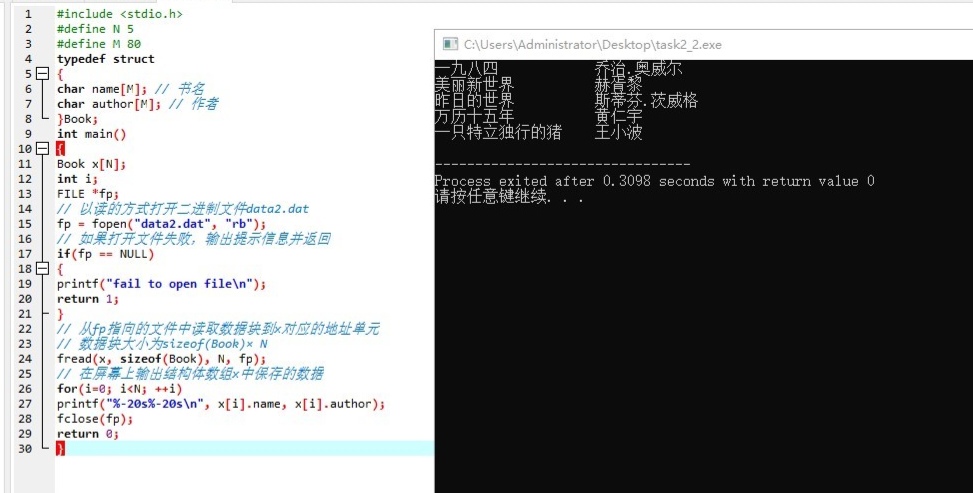
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 5
#define M 80
typedef struct
{
char name[M]; // 书名
char author[M]; // 作者
}Book;
int main()
{
Book x[N] = { {"一九八四", "乔治.奥威尔"},
{"美丽新世界", "赫胥黎"},
{"昨日的世界", "斯蒂芬.茨威格"},
{"万历十五年", "黄仁宇"},
{"一只特立独行的猪", "王小波"}
};
int i;
FILE *fp;
// 以写的方式打开二进制文件data2.dat
fp = fopen("data2.dat", "wb");
// 如果打开文件失败,输出提示信息并返回
if(fp == NULL)
{
printf("fail to open file\n");
return 1;
}
// 将结构体数组x中的图书信息写以数据块方式写入文件
// 把从地址x处开始sizeof(Book)×N个字节大小的数据块写入fp指向的文件
fwrite(x, sizeof(Book), N, fp);
fclose(fp);
}
答:是;是
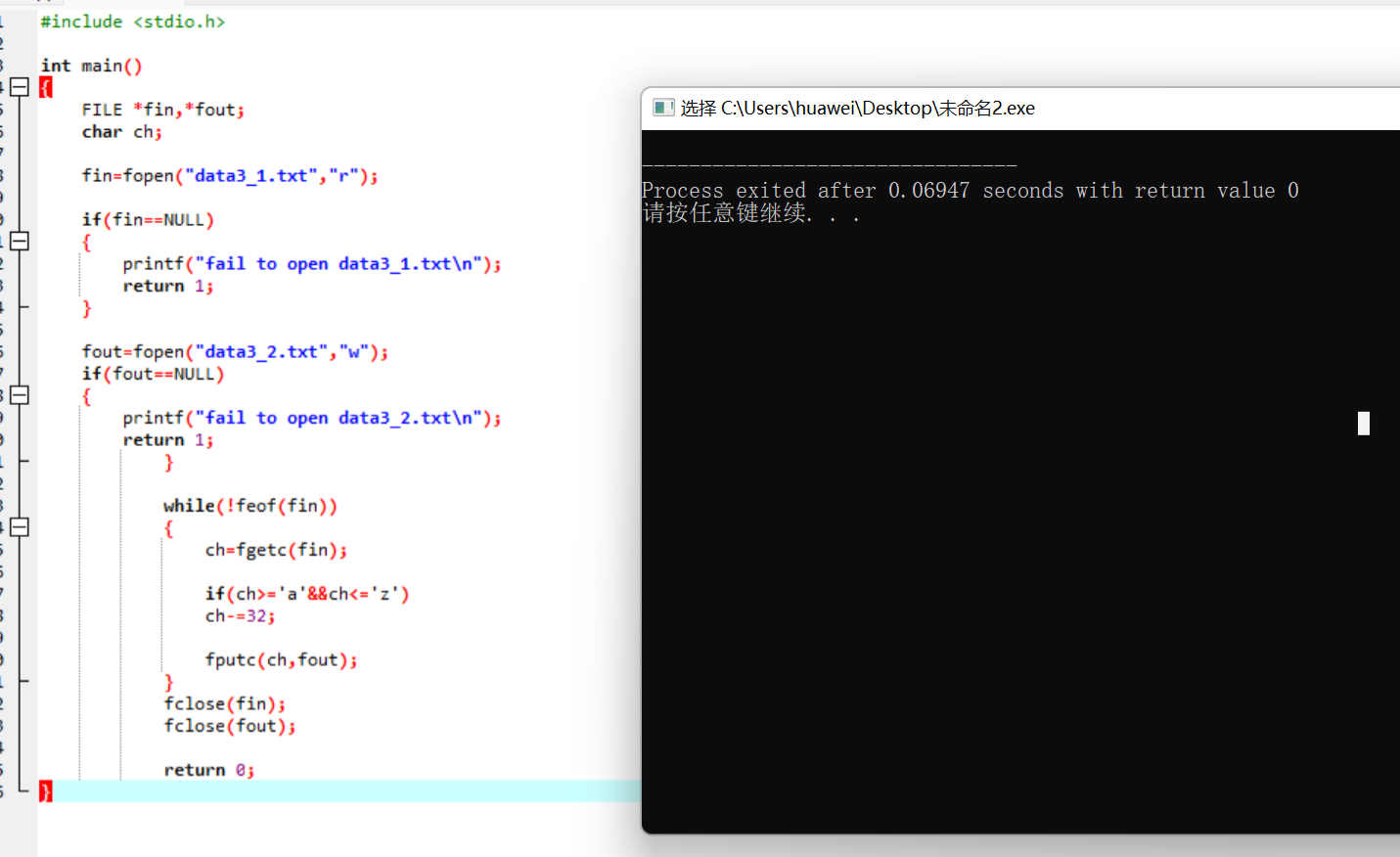
#include <stdio.h> int main() { FILE *fin,*fout; char ch; fin=fopen("data3_1.txt","r"); if(fin==NULL) { printf("fail to open data3_1.txt\n"); return 1; } fout=fopen("data3_2.txt","w"); if(fout==NULL) { printf("fail to open data3_2.txt\n"); return 1; } while(!feof(fin)) { ch=fgetc(fin); if(ch>='a'&&ch<='z') ch-=32; fputc(ch,fout); } fclose(fin); fclose(fout); return 0; }
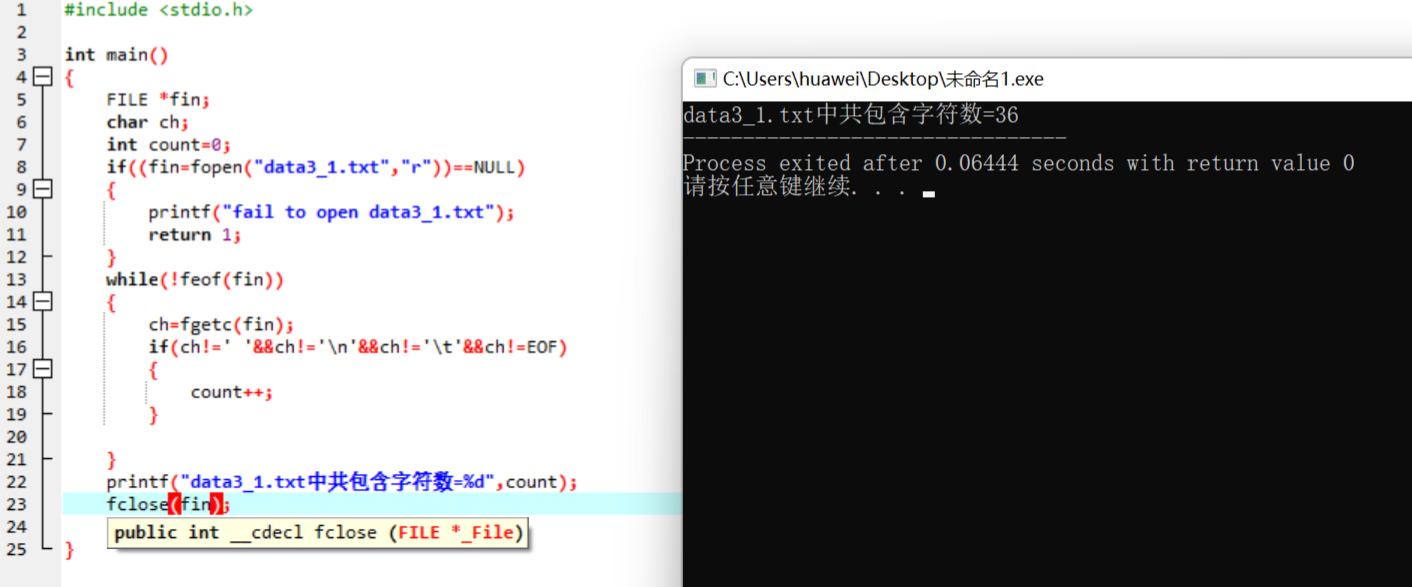
#include <stdio.h> int main() { FILE *fin; char ch; int count=0; if((fin=fopen("data3_1.txt","r"))==NULL) { printf("fail to open data3_1.txt"); return 1; } while(!feof(fin)) { ch=fgetc(fin); if(ch!=' '&&ch!='\n'&&ch!='\t'&&ch!=EOF) { count++; } } printf("data3_1.txt中共包含字符数=%d",count); fclose(fin); return 0; }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号