Vofa上位机发送float数据(justfloat协议)
Vofa上位机发送float数据(justfloat协议)
0.小端浮点数
本协议是小端浮点数组形式的字节流协议,纯十六进制浮点传输,节省带宽。此协议非常适合用在通道数量多、发送频率高的时候。
0.0 问题:
-
发什么?
小端浮点数 -
什么是小端浮点数?
小端和大端差别在于:字节存储顺序(以32位float
0x12345678为例)端序类型 内存地址增长方向(低→高) 实际存储顺序 大端序 12 34 56 78高位字节在前(人类直观顺序) 小端序 78 56 34 12低位字节在前(反向存储)
bf 10 59 3f //单精度浮点数发送
//低位字节在前先发
0.1单精度浮点数float(补充,不究原理可以不看)
0.1.1 IEEE-754
IEEE-754(IEEE二进制浮点数算术标准)标准规定了
EEE 754规定了四种表示浮点数值的方式:单精确度(32位)、双精确度(64位)、延伸单精确度(43比特以上,很少使用)与延伸双精确度(79比特以上,通常以80位实现)。
0.1.2 单精度浮点数表示方式
IEEE二进制浮点数算术标准(IEEE 754)是20世纪80年代以来最广泛使用的浮点数运算标准,为许多CPU与浮点运算器所采用。
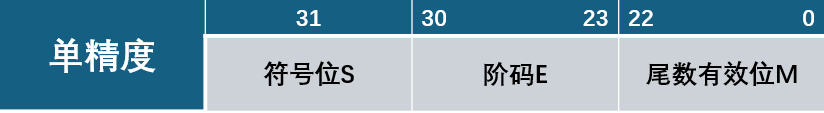
$\frac{M}{2^{23}}为小数部分$
例如:
$$(0.0625_{10} = (0.0001)_{2} = (-1)^0 \times (1 + \frac{0}{2^{23}}) \times 2^{123-127}$$即
$$S = 0 \\M = 0 \\ E = 123$$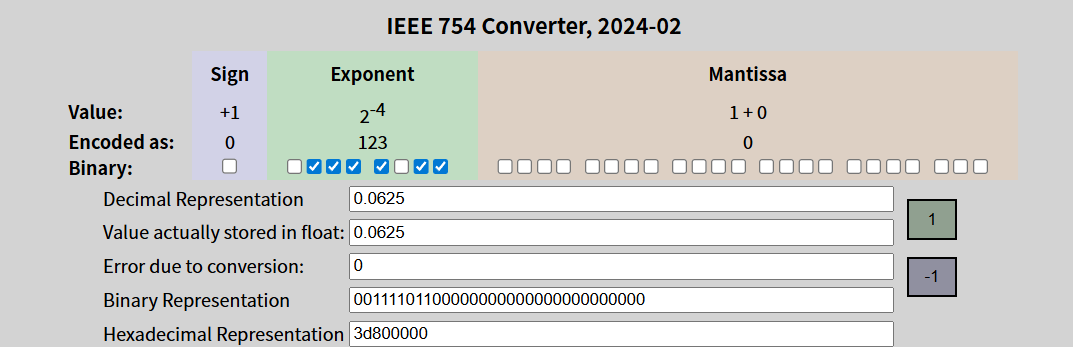
由此,我们明显可以看出,浮点数的表示除了满足2的整数倍之类的情况总是存在误差的。
1. DEMO 程序说明
核心:发送的单精度浮点数转变为4个字节Byte数据发送,每一帧数据后需接包尾 00 00 80 7f
1.1 mid_debug_uart.h
- 用户数据
//需要添加多少数据,就往enum里加
typedef enum
{
D1=0,
D2,
DATA_COUNT_MAX
}Data_Index;
- 数据包结构体
typedef struct { float fdata[DATA_COUNT_MAX]; uint8_t tail[4]; }Vofa_Packet;
extern Vofa_Packet Vofa_packet;
1.2 mid_debug_uart.c
定义发送的数据
Vofa_Packet Vofa_packet;
- 包尾初始化
/**
* @brief: 初始化包尾
* @note: Must to use Vofa
*/
void Vofa_Init(Vofa_Packet *frame)
{
frame->tail[0] = 0x00;
frame->tail[1] = 0x00;
frame->tail[2] = 0x80;
frame->tail[3] = 0x7f;
}
- 发送浮点数
/**
* @brief:Vofa_SendFloat
* @note:
*/
void Vofa_SendFloat(Vofa_Packet *packet)
{
uint8_t byte[4];
uint8_t i;
uint32_t temp;
for(i=0;i<DATA_COUNT_MAX;i++)
{
temp = *((uint32_t*)&packet->fdata[i]); // Reinterpret float as Uint32
byte[0] = (uint8_t)(temp);
byte[1] = (uint8_t)(temp >> 8);
byte[2] = (uint8_t)(temp >> 16);
byte[3] = (uint8_t)(temp >> 24);
debug_uart_send_array(byte,4);
}
debug_uart_send_array(packet->tail,4);
}
- 发送字节函数(底层)Byte
/** * @brief 输入字节(阻塞式发送) hex */ void debug_uart_send_byte(uint8_t byte) { while( DL_UART_isBusy(UART_DEBUG_INST) == true ); DL_UART_Main_transmitData(UART_DEBUG_INST, byte); }
void debug_uart_send_array(uint8_t *Array,uint8_t length)
{
for(int i=0;i<length;i++)
{
debug_uart_send_byte(Array[i]);
}
}
2.测试
2.1 main.c测试
在main.c函数线初始化数据包
Vofa_Init(&Vofa_packet);while (1) { t+=tb; if(t>=2*_PI) { t-=2*_PI; } Vofa_packet.fdata[D1] = _sin(t); Vofa_packet.fdata[D2] = _cos(t); Vofa_SendFloat(&Vofa_packet); delay_ms(3); }
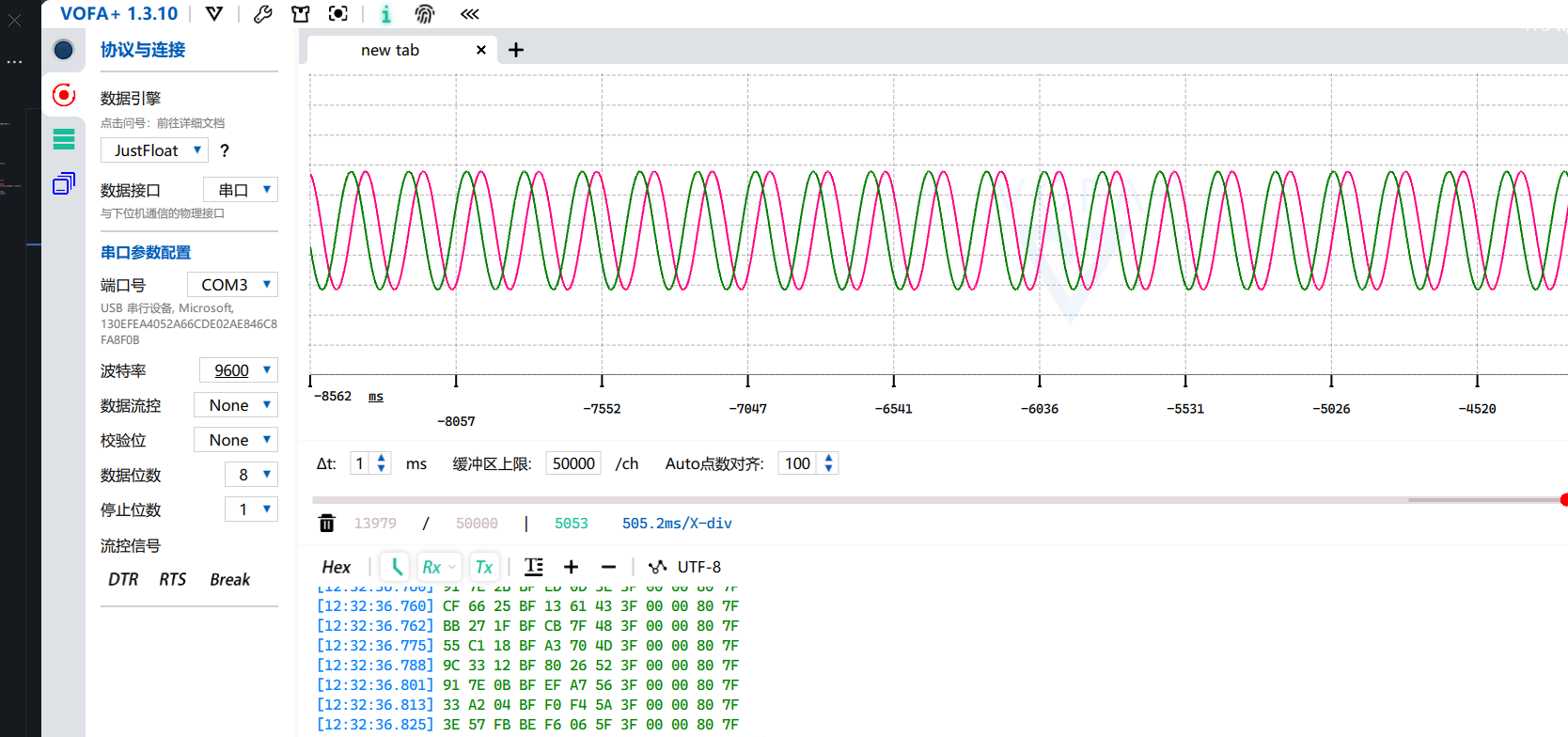
在vof上位机中查看波形:
2.2 mid_utils.c
其中_PI、_sin和_cos在我的mid_utils.c和mid_utils.h中,使用查表法来提升正弦运算速度@author:彭志辉
/** * @brief: 辅助性函数或工具方法,用于解决常见问题和任务 * @author: PengZhihui * @date: 2025-08-28 */include "mid_utils.h"
/**
- @brief: 200点正弦波数据,范围0~10000 sin*10000
- @note: int array instead of float array
2x storage save (int 2Byte float 4 Byte )200 points per cycle, 5 cycles per second when timer 1ms4x200 points per 360 deg*/
const int sine_array[200] = {0, 79, 158, 237, 316, 395, 473, 552, 631, 710, 789, 867, 946, 1024, 1103, 1181,
1260, 1338, 1416, 1494, 1572, 1650, 1728, 1806, 1883, 1961, 2038, 2115, 2192,
2269, 2346, 2423, 2499, 2575, 2652, 2728, 2804, 2879, 2955, 3030, 3105, 3180,
3255, 3329, 3404, 3478, 3552, 3625, 3699, 3772, 3845, 3918, 3990, 4063, 4135,
4206, 4278, 4349, 4420, 4491, 4561, 4631, 4701, 4770, 4840, 4909, 4977, 5046,
5113, 5181, 5249, 5316, 5382, 5449, 5515, 5580, 5646, 5711, 5775, 5839, 5903,
5967, 6030, 6093, 6155, 6217, 6279, 6340, 6401, 6461, 6521, 6581, 6640, 6699,
6758, 6815, 6873, 6930, 6987, 7043, 7099, 7154, 7209, 7264, 7318, 7371, 7424,
7477, 7529, 7581, 7632, 7683, 7733, 7783, 7832, 7881, 7930, 7977, 8025, 8072,
8118, 8164, 8209, 8254, 8298, 8342, 8385, 8428, 8470, 8512, 8553, 8594, 8634,
8673, 8712, 8751, 8789, 8826, 8863, 8899, 8935, 8970, 9005, 9039, 9072, 9105,
9138, 9169, 9201, 9231, 9261, 9291, 9320, 9348, 9376, 9403, 9429, 9455, 9481,
9506, 9530, 9554, 9577, 9599, 9621, 9642, 9663, 9683, 9702, 9721, 9739, 9757,
9774, 9790, 9806, 9821, 9836, 9850, 9863, 9876, 9888, 9899, 9910, 9920, 9930,
9939, 9947, 9955, 9962, 9969, 9975, 9980, 9985, 9989, 9992, 9995, 9997, 9999,
10000, 10000};/**
*@brief: sine calculation by using fixed size array
*@param a: angle in between 0 and 2PI
*@note: ~40us (float array)
~50us (int array)
precision +-0.005
*@note: 126.6873 = 199 / (π/2)
a:(0,π/2) -> (0,199)
*/
float _sin(float a)
{
if (a < _PI_2)
{
return 0.0001f * sine_array[_round(126.6873f * a)]; // int array optimized
}
else if (a < _PI)
{
return 0.0001f * sine_array[398 - _round(126.6873f * a)]; // int array optimized
}
else if (a < _3PI_2)
{
return -0.0001f * sine_array[-398 + _round(126.6873f * a)]; // int array optimized
}
else
{
return -0.0001f * sine_array[796 - _round(126.6873f * a)]; // int array optimized
}
}float _cos(float a)
{
float a_sin = a + _PI_2;
a_sin = a_sin > _2PI ? a_sin - _2PI : a_sin;
return _sin(a_sin);
}/**
@brief:square root approximation function using
@note:计算平方根的近似值
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fast_inverse_square_root
*/
float _sqrtApprox(float number)
{//low in fat
long i;
float y;
// float x;
// const float f = 1.5F; // better precision// x = number * 0.5F;
y = number;
i = (long) &y;
i = 0x5f375a86 - (i >> 1);
y = (float) &i;
// y = y * ( f - ( x * y * y ) ); // better precision
return number * y;
}/**
- @brief: 计算快速平方根倒数(fast inverse square root)
- @note:
*/
float FastInvSqrt(float x)
{
float halfx = 0.5f * x;
float y = x;
long i = *(long *)&y;
i = 0x5f3759df - (i >> 1);
y = *(float *)&i;
y = y * (1.5f - (halfx * y * y));
return y;
}
2.3 mid_utlis.h
#ifndef __MID_UTILS_H__ #define __MID_UTILS_H__// sign function
define _sign(a) ( ( (a) < 0 ) ? -1 : ( (a) > 0 ) )
define _round(x) ((x)>=0?(long)((x)+0.5f):(long)((x)-0.5f))
define _constrain(amt, low, high) ((amt)<(low)?(low)😦(amt)>(high)?(high):(amt)))
// utility defines
define _2_SQRT3 1.15470053838f
define _SQRT3 1.73205080757f
define _1_SQRT3 0.57735026919f
define _SQRT3_2 0.86602540378f
define _SQRT2 1.41421356237f
define _120_D2R 2.09439510239f
define _PI 3.14159265359f
define _PI_2 1.57079632679f
define _PI_3 1.0471975512f
define _2PI 6.28318530718f
define _3PI_2 4.71238898038f
define _PI_6 0.52359877559f
float _sin(float a);
float _cos(float a);endif
3.总结和不足
若是纠结发送的数据,可以开启串口DMA降低对系统主频的占用





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号