智能电网的电能预估及价值分析
智能电网的电能预估及价值分析
一、实验目的与要求
1、掌握使用pandas库处理数据的基本方法。
2、掌握对时间序列类数据预处理的基本方法。
3、掌握使用matplotlib结合pandas库对数据分析可视化处理的基本方法。
二、实验内容
1、利用python中pandas等库读取数据,并完成数据的预处理。
2、利用matplotlib等库完成对数据的可视化。
3、使用Sklearn库的相关系数建立决策树模型,对模型进行训练,使用测试集测试后对模型的效果进行评价。
三、实验步骤
1.数据预处理。读取所提供的数据文件,检查文件中时间序列是否完整,有无缺失值,重复值。
(1)导入所需要使用的包
import os
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.dates as mdate
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from matplotlib.dates import DateFormatter, WeekdayLocator, DayLocator, MONDAY,YEARLY
import dateutil.relativedelta
import time
from matplotlib.pyplot import MultipleLocator
from pandas.core.common import SettingWithCopyWarning
from sklearn import tree#决策树模型
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split#划分测试集合与训练集合
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV#用于找到最优模型
from scipy.stats import pearsonr
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
#设置字体
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei']
(2)读取文件
file_path='/data/bigfiles/data3.csv'
data=pd.read_csv(file_path)
(3)查看数据的基本统计信息
data.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 87648 entries, 0 to 87647
Data columns (total 8 columns):
日期 87648 non-null object
小时 87648 non-null float64
干球温度 87648 non-null float64
露点温度 87648 non-null float64
湿球温度 87648 non-null float64
湿度 87648 non-null float64
电价 87648 non-null float64
电力负荷 87648 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(7), object(1)
memory usage: 5.3+ MB
(4)检查数据是否完整
# 查看数据长度
std_rng=pd.date_range(start='2006/1/1',end='2011/1/1',freq='D')
len(std_rng)
1827
(5)求日平均数据并添加日类型
data['湿度']=data['湿度'].map(lambda x :float(x))
#湿度转换成 浮点类型
data['日最高湿度']=data["湿度"]
data['日最低湿度']=data["湿度"]
data['日均电力负荷']=data['电力负荷']
data['日最高电力负荷']=data['电力负荷']
data['日最低电力负荷']=data['电力负荷']
# 将日期设为行索引
data=data.set_index(['日期'])
data
| 小时 | 干球温度 | 露点温度 | 湿球温度 | 湿度 | 电价 | 电力负荷 | 日最高湿度 | 日最低湿度 | 日均电力负荷 | 日最高电力负荷 | 日最低电力负荷 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 日期 | ||||||||||||
| 2006/1/1 | 0.5 | 23.90 | 21.65 | 22.40 | 87.5 | 19.67 | 8013.27833 | 87.5 | 87.5 | 8013.27833 | 8013.27833 | 8013.27833 |
| 2006/1/1 | 1.0 | 23.90 | 21.70 | 22.40 | 88.0 | 18.56 | 7726.89167 | 88.0 | 88.0 | 7726.89167 | 7726.89167 | 7726.89167 |
| 2006/1/1 | 1.5 | 23.80 | 21.65 | 22.35 | 88.0 | 19.09 | 7372.85833 | 88.0 | 88.0 | 7372.85833 | 7372.85833 | 7372.85833 |
| 2006/1/1 | 2.0 | 23.70 | 21.60 | 22.30 | 88.0 | 17.40 | 7071.83333 | 88.0 | 88.0 | 7071.83333 | 7071.83333 | 7071.83333 |
| 2006/1/1 | 2.5 | 23.70 | 21.60 | 22.30 | 88.0 | 17.00 | 6865.44000 | 88.0 | 88.0 | 6865.44000 | 6865.44000 | 6865.44000 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 2010/12/31 | 22.0 | 22.60 | 19.10 | 20.40 | 81.0 | 23.86 | 8449.54000 | 81.0 | 81.0 | 8449.54000 | 8449.54000 | 8449.54000 |
| 2010/12/31 | 22.5 | 22.45 | 19.05 | 20.30 | 81.5 | 26.49 | 8508.16000 | 81.5 | 81.5 | 8508.16000 | 8508.16000 | 8508.16000 |
| 2010/12/31 | 23.0 | 22.30 | 19.00 | 20.20 | 82.0 | 25.18 | 8413.14000 | 82.0 | 82.0 | 8413.14000 | 8413.14000 | 8413.14000 |
| 2010/12/31 | 23.5 | 22.05 | 19.05 | 20.15 | 83.5 | 26.19 | 8173.79000 | 83.5 | 83.5 | 8173.79000 | 8173.79000 | 8173.79000 |
| 2011/1/1 | 0.0 | 21.80 | 19.10 | 20.10 | 85.0 | 24.62 | 8063.36000 | 85.0 | 85.0 | 8063.36000 | 8063.36000 | 8063.36000 |
87648 rows × 12 columns
# 将日期类型转换成datatime
data.index=data.index.map(lambda x :datetime.strptime(x,'%Y/%m/%d'))
data['日']=data.index
# 定义中文包
week_cn = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
data['日']=data['日'].map(lambda x: week_cn[pd.to_datetime(x).weekday()])
datas =data.groupby('日期').agg({"干球温度":"mean","露点温度":"mean","湿球温度":"mean","湿度":"mean","日最高湿度":"max","日最低湿度":"min","电价":"mean","日最高电力负荷":"max","日最低电力负荷":"min","日均电力负荷":"mean","日":"mean"})
# 对缺失的值进行填补
datas.head(30)
| 干球温度 | 露点温度 | 湿球温度 | 湿度 | 日最高湿度 | 日最低湿度 | 电价 | 日最高电力负荷 | 日最低电力负荷 | 日均电力负荷 | 日 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 日期 | |||||||||||
| 2006-01-01 | 32.790426 | 16.987234 | 22.910638 | 50.244681 | 90.0 | 15.0 | 43.721702 | 11112.76333 | 6388.27833 | 9188.743865 | 7 |
| 2006-01-02 | 20.855208 | 17.447917 | 18.757292 | 81.072917 | 92.0 | 73.0 | 16.273542 | 8456.72833 | 6364.80333 | 7686.274860 | 1 |
| 2006-01-03 | 23.122917 | 16.632292 | 19.172917 | 69.770833 | 92.0 | 33.0 | 43.863958 | 10674.23500 | 6035.49833 | 8664.448403 | 2 |
| 2006-01-04 | 20.312500 | 15.073958 | 17.218750 | 71.864583 | 80.5 | 67.0 | 16.958333 | 9115.16167 | 6232.96667 | 8060.226216 | 3 |
| 2006-01-05 | 19.586458 | 18.015625 | 18.608333 | 90.718750 | 96.0 | 76.0 | 16.535625 | 9145.73833 | 6062.90500 | 8081.884756 | 4 |
| 2006-01-06 | 22.277083 | 18.770833 | 20.056250 | 81.177083 | 98.0 | 64.0 | 16.927500 | 9673.71000 | 6100.96833 | 8292.417466 | 5 |
| 2006-01-07 | 22.555208 | 17.836458 | 19.612500 | 75.677083 | 93.0 | 59.0 | 15.888958 | 8541.36500 | 5979.96667 | 7620.753992 | 6 |
| 2006-01-08 | 23.533333 | 17.887500 | 20.000000 | 71.250000 | 85.0 | 58.0 | 16.264167 | 8504.99667 | 5841.69333 | 7552.765243 | 7 |
| 2006-01-09 | 24.022917 | 20.504167 | 21.719792 | 81.364583 | 95.0 | 64.0 | 19.757292 | 10643.02833 | 6045.60667 | 8844.571910 | 1 |
| 2006-01-10 | 25.386458 | 21.983333 | 23.097917 | 81.875000 | 93.0 | 67.0 | 32.939375 | 12174.29000 | 6493.04667 | 9754.662396 | 2 |
| 2006-01-11 | 25.367708 | 21.119792 | 22.548958 | 78.750000 | 95.0 | 47.0 | 31.764167 | 12221.79500 | 6850.93167 | 9746.585139 | 3 |
| 2006-01-12 | 23.495833 | 20.695833 | 21.661458 | 84.604167 | 95.0 | 69.0 | 25.126042 | 10858.03167 | 6574.69333 | 9164.433056 | 4 |
| 2006-01-13 | 23.608333 | 20.312500 | 21.480208 | 82.031250 | 90.0 | 72.0 | 19.868750 | 10301.34000 | 6581.40500 | 8850.319861 | 5 |
| 2006-01-14 | 24.253125 | 20.995833 | 22.080208 | 82.739583 | 94.0 | 67.0 | 21.000417 | 10652.51833 | 6256.08833 | 8635.826492 | 6 |
| 2006-01-15 | 22.350000 | 17.861458 | 19.575000 | 76.479167 | 96.0 | 61.0 | 15.725417 | 8478.99333 | 6044.62167 | 7662.240695 | 7 |
| 2006-01-16 | 22.698958 | 21.400000 | 21.826042 | 92.614583 | 98.0 | 80.0 | 17.917500 | 10843.35667 | 6218.35667 | 9027.497256 | 1 |
| 2006-01-17 | 23.360417 | 20.847917 | 21.706250 | 86.572917 | 98.0 | 63.0 | 18.510833 | 10589.74500 | 6515.38500 | 9099.179757 | 2 |
| 2006-01-18 | 20.894792 | 17.382292 | 18.737500 | 80.614583 | 93.0 | 69.0 | 16.334583 | 9977.47167 | 6450.04000 | 8585.024723 | 3 |
| 2006-01-19 | 21.169792 | 15.673958 | 17.893750 | 71.177083 | 83.0 | 58.0 | 20.896667 | 9719.08833 | 6203.51333 | 8484.019445 | 4 |
| 2006-01-20 | 23.046875 | 16.936458 | 19.292708 | 68.937500 | 82.0 | 54.0 | 22.438750 | 9970.94667 | 6319.94000 | 8672.169306 | 5 |
| 2006-01-21 | 24.168750 | 19.107292 | 20.911458 | 73.968750 | 84.5 | 62.0 | 46.051458 | 10521.93167 | 6199.52333 | 8693.989653 | 6 |
| 2006-01-22 | 24.412500 | 19.813542 | 21.429167 | 76.468750 | 94.0 | 59.0 | 36.657500 | 10510.95667 | 6259.67333 | 8707.004375 | 7 |
| 2006-01-23 | 24.558333 | 20.515625 | 21.896875 | 78.666667 | 90.0 | 66.0 | 106.587292 | 12674.64333 | 6590.63167 | 10124.172847 | 1 |
| 2006-01-24 | 21.555208 | 18.565625 | 19.681250 | 83.406250 | 93.0 | 69.0 | 22.543125 | 10597.25833 | 6839.21667 | 9087.451111 | 2 |
| 2006-01-25 | 20.404167 | 17.433333 | 18.590625 | 83.593750 | 97.0 | 68.0 | 22.963333 | 9902.47667 | 6404.41167 | 8647.444028 | 3 |
| 2006-01-26 | 22.982292 | 19.335417 | 20.641667 | 80.083333 | 90.0 | 70.0 | 23.195625 | 9404.52500 | 6215.56000 | 8193.167396 | 4 |
| 2006-01-27 | 24.482292 | 20.520833 | 21.882292 | 79.229167 | 94.0 | 66.0 | 39.246042 | 11952.90000 | 6412.55167 | 9484.763229 | 5 |
| 2006-01-28 | 24.717708 | 18.366667 | 20.701042 | 69.104167 | 87.0 | 50.0 | 19.693750 | 10059.30333 | 6389.71833 | 8544.133229 | 6 |
| 2006-01-29 | 24.348958 | 18.191667 | 20.469792 | 69.854167 | 90.0 | 47.0 | 21.477917 | 9810.24500 | 6177.64000 | 8231.146563 | 7 |
| 2006-01-30 | 24.290625 | 19.226042 | 21.026042 | 74.427083 | 91.0 | 58.0 | 25.206458 | 12201.74667 | 6403.69833 | 9689.812222 | 1 |
(6)存储预处理后的文件
data.to_csv('/data/bigfiles/预处理后文件.csv')
2、数据可视化。
(1)读取预处理后的文件
data=pd.read_csv('/data/bigfiles/预处理后文件.csv')
(2)绘制各气象信息的时间序列曲线
charts=datas["2006/01/01":"2010/02/01"]
charts.index=charts.index.map(lambda x:str(x)[:10])
# 创建一个画布
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15.6,7.2))
# 在画布上添加一个子视图
ax = plt.subplot(111)
# 将x轴的刻度进行格式化
x_major_locator=MultipleLocator(300) # 把x轴的刻度间隔设置为原来的2倍
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(x_major_locator) # 把x轴的主刻度设置为1的倍数
# 画折线
line1,=ax.plot(charts.index,charts['湿度'],'r-',label='湿度')
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f056d061f98>
# 创建一个画布
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15.6,7.2))
# 在画布上添加一个子视图
ax = plt.subplot(111)
# 将x轴的刻度进行格式化
x_major_locator=MultipleLocator(300) # 把x轴的刻度间隔设置为原来的2倍
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(x_major_locator) # 把x轴的主刻度设置为1的倍数
# 画折线
line2,=ax.plot(charts.index,charts['日最高湿度'],'b--',label='日最高湿度')
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f06514f3908>
# 创建一个画布
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15.6,7.2))
# 在画布上添加一个子视图
ax = plt.subplot(111)
# 将x轴的刻度进行格式化
x_major_locator=MultipleLocator(300) # 把x轴的刻度间隔设置为原来的2倍
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(x_major_locator) # 把x轴的主刻度设置为1的倍数
# 画折线
line3,=ax.plot(charts.index,charts['日最低湿度'],'g-',label='日最低湿度')
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f056cf01a58>
# 创建一个画布
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15.6,7.2))
# 在画布上添加一个子视图
ax = plt.subplot(111)
# 将x轴的刻度进行格式化
x_major_locator=MultipleLocator(300) # 把x轴的刻度间隔设置为原来的2倍
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(x_major_locator) # 把x轴的主刻度设置为1的倍数
# 画折线
line4,=ax.plot(charts.index,charts['露点温度'],'c--',label='露点温度')
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f056ce78c88>
# 创建一个画布
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15.6,7.2))
# 在画布上添加一个子视图
ax = plt.subplot(111)
# 将x轴的刻度进行格式化
x_major_locator=MultipleLocator(300) # 把x轴的刻度间隔设置为原来的2倍
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(x_major_locator) # 把x轴的主刻度设置为1的倍数
# 画折线
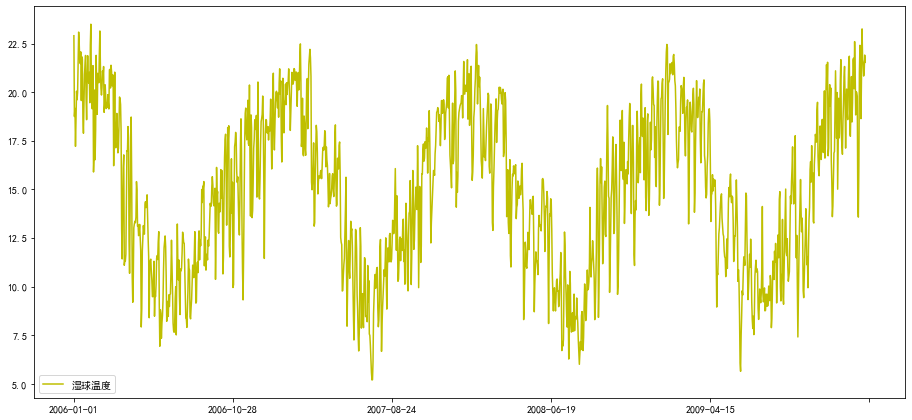
line5,=ax.plot(charts.index,charts['湿球温度'],'y-',label='湿球温度')
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f056cdfb518>
(3)绘制电价和电力负荷的时间序列曲线
chart=datas["2006/01/01":"2010/02/01"]
chart.index=chart.index.map(lambda x:str(x)[:10])
# 创建一个画布
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15.6,7.2))
# 在画布上添加一个子视图
ax = plt.subplot(111)
#将x轴的刻度进行格式化
# ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdate.DateFormatter('%Y/%m/%d'))
x_major_locator=MultipleLocator(300) # 把x轴的刻度间隔设置为原来的2倍
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(x_major_locator) # 把x轴的主刻度设置为1的倍数
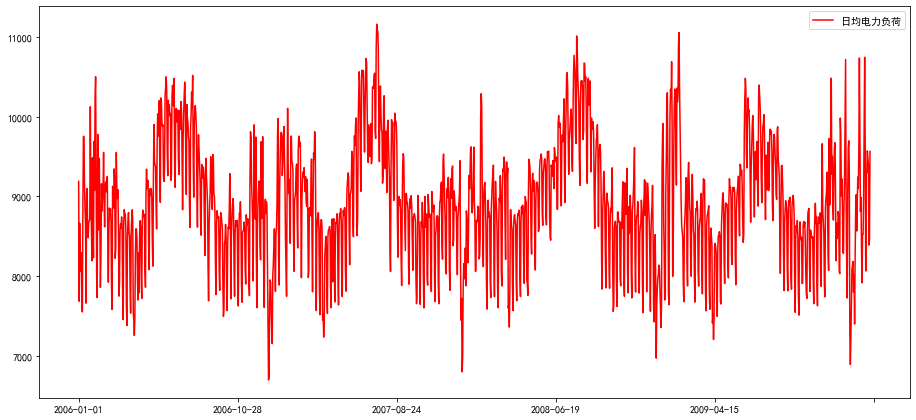
# 画折线
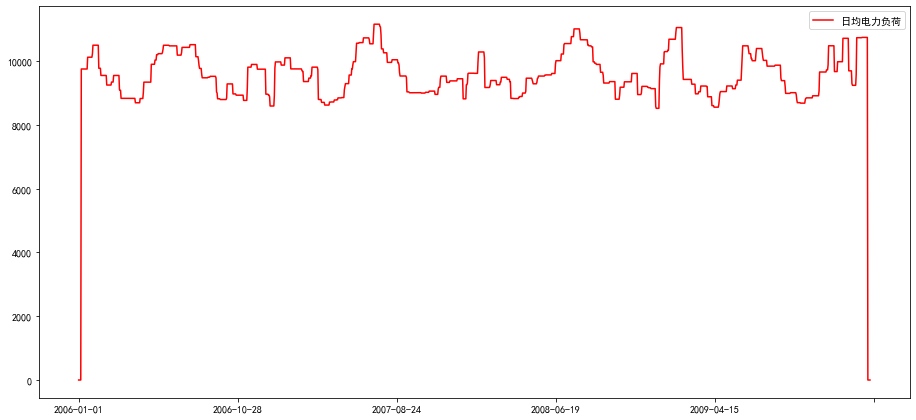
line1,=ax.plot(chart.index,chart['日均电力负荷'],'r-',label='日均电力负荷')
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f056cd7e160>
# 创建一个画布
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15.6,7.2))
# 在画布上添加一个子视图
ax = plt.subplot(111)
#将x轴的刻度进行格式化
# ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdate.DateFormatter('%Y/%m/%d'))
x_major_locator=MultipleLocator(300) # 把x轴的刻度间隔设置为原来的2倍
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(x_major_locator) # 把x轴的主刻度设置为1的倍数
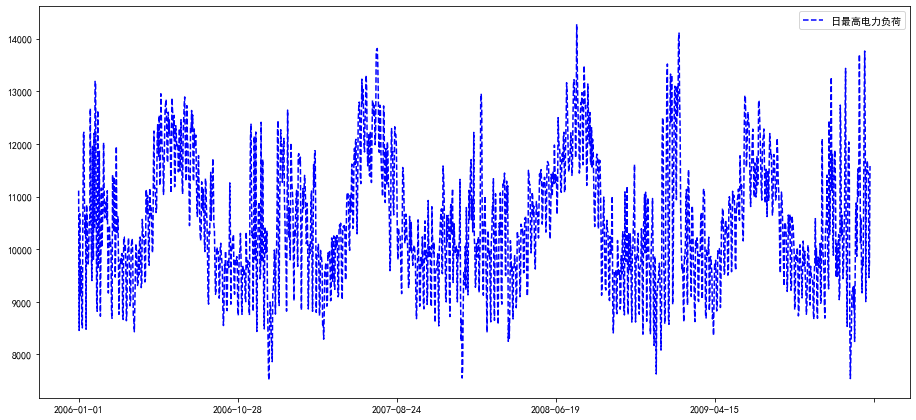
# 画折线
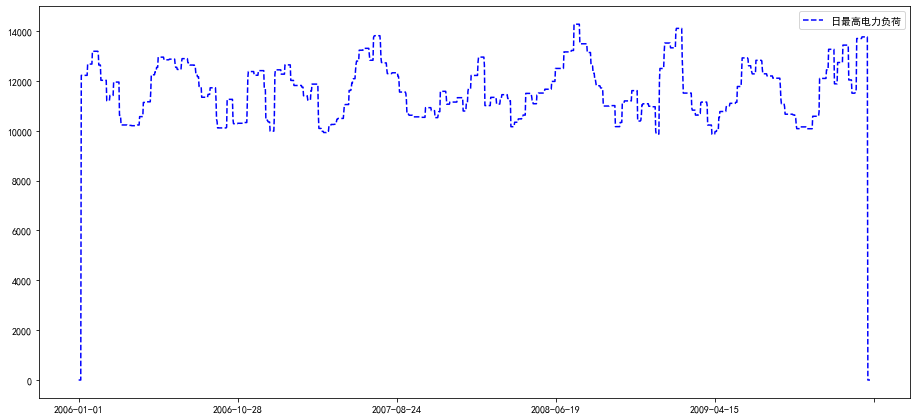
line2,=ax.plot(chart.index,chart['日最高电力负荷'],'b--',label='日最高电力负荷')
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f056cc59a58>
# 创建一个画布
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15.6,7.2))
# 在画布上添加一个子视图
ax = plt.subplot(111)
#将x轴的刻度进行格式化
# ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdate.DateFormatter('%Y/%m/%d'))
x_major_locator=MultipleLocator(300) # 把x轴的刻度间隔设置为原来的2倍
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(x_major_locator) # 把x轴的主刻度设置为1的倍数
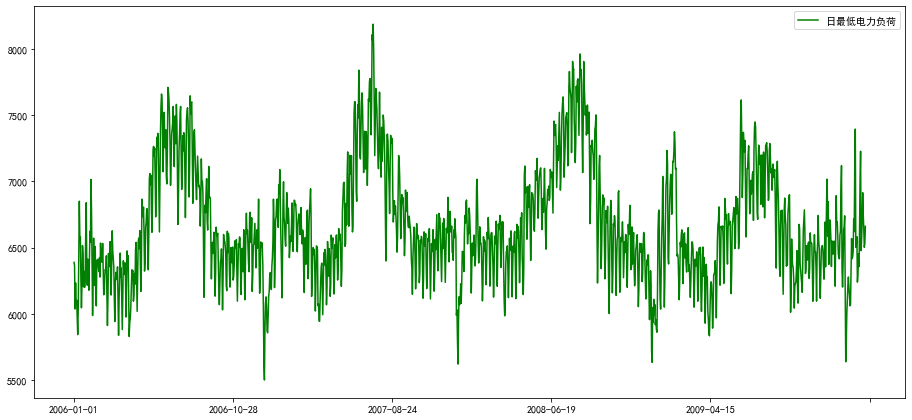
# 画折线
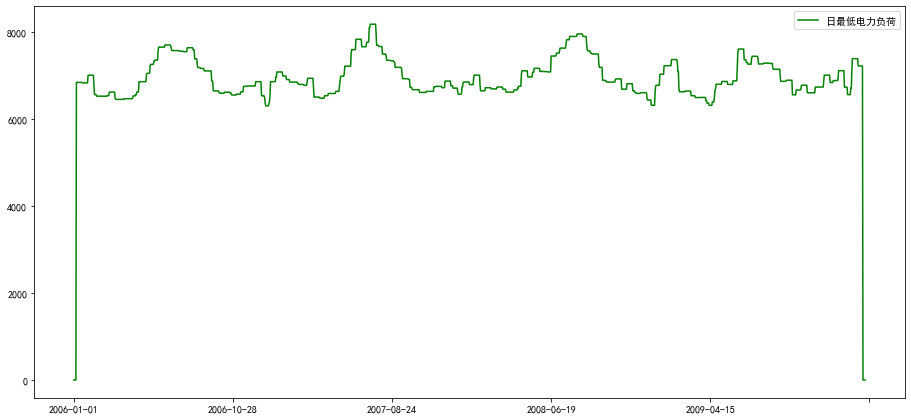
line3,=ax.plot(chart.index,chart['日最低电力负荷'],'g-',label='日最低电力负荷')
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f056436af60>
chart=datas["2006/01/01":"2010/02/01"]
chart.index=chart.index.map(lambda x:str(x)[:10])
# 创建一个画布
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15.6,7.2))
# 在画布上添加一个子视图
ax = plt.subplot(111)
# 将x轴的刻度进行格式化
# ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdate.DateFormatter('%Y/%m/%d'))
x_major_locator=MultipleLocator(300) # 把x轴的刻度间隔设置为原来的2倍
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(x_major_locator) # 把x轴的主刻度设置为1的倍数
# 画折线
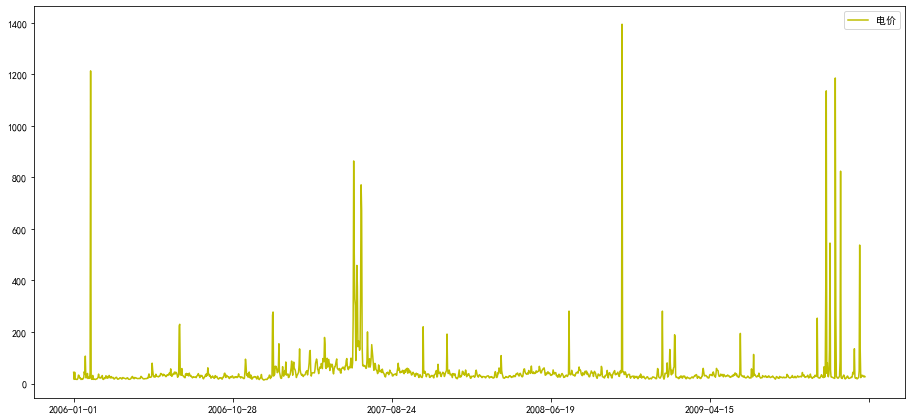
line=ax.plot(chart.index,chart['电价'],'y-',label='电价')
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f05642b8d68>
(4)编写中值滤波函数消除明显的噪音
def median_filter(data,sizes):
filter_data=np.zeros_like(data)
halfwindow=sizes
for i in range (halfwindow,len(data)-halfwindow):
window=data[i - halfwindow:i + halfwindow + 1]
filter_data[i]=np.median(window)
return filter_data
pd.options.mode.chained_assignment = None # 默认模式
chart['干球温度']=median_filter(chart['干球温度'],5)
chart['日均电力负荷']=median_filter(chart['日均电力负荷'],5)
chart['日最高电力负荷']=median_filter(chart['日最高电力负荷'],5)
chart['日最低电力负荷']=median_filter(chart['日最低电力负荷'],5)
chart['露点温度']=median_filter(chart['露点温度'],5)
(5)绘制滤波后的时序曲线
# 创建一个画布
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15.6,7.2))
# 在画布上添加一个子视图
ax = plt.subplot(111)
# 这里很重要 需要 将 x轴的刻度 进行格式化
# ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdate.DateFormatter('%Y/%m/%d'))
x_major_locator=MultipleLocator(300) # 把x轴的刻度间隔设置为原来的2倍
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(x_major_locator) # 把x轴的主刻度设置为1的倍数
# 画折线
line1,=ax.plot(chart.index,chart['日均电力负荷'],'r-',label='日均电力负荷')
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f056402a7f0>
# 创建一个画布
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15.6,7.2))
# 在画布上添加一个子视图
ax = plt.subplot(111)
# 这里很重要 需要 将 x轴的刻度 进行格式化
# ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdate.DateFormatter('%Y/%m/%d'))
x_major_locator=MultipleLocator(300) # 把x轴的刻度间隔设置为原来的2倍
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(x_major_locator) # 把x轴的主刻度设置为1的倍数
# 画折线
line2,=ax.plot(chart.index,chart['日最高电力负荷'],'b--',label='日最高电力负荷')
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f056cdd9550>
# 创建一个画布
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15.6,7.2))
# 在画布上添加一个子视图
ax = plt.subplot(111)
# 这里很重要 需要 将 x轴的刻度 进行格式化
# ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdate.DateFormatter('%Y/%m/%d'))
x_major_locator=MultipleLocator(300) # 把x轴的刻度间隔设置为原来的2倍
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(x_major_locator) # 把x轴的主刻度设置为1的倍数
# 画折线
line3,=ax.plot(chart.index,chart['日最低电力负荷'],'g-',label='日最低电力负荷')
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f056cde05c0>
3.相关系数。求出各量与电力负荷之间的皮尔逊相关系数,选择相关系数绝对值前3高的属性作为特征属性,用于下一步进行模型训练。
#通常情况下通过以下取值范围判断变量的相关强度: 相关系数 0.8-1.0 极强相关
#0.6-0.8 强相关 0.4-0.6 中等程度相关 0.2-0.4 弱相关 0.0-0.2 极弱相关或无相关
x=np.array([1,3,5])
y=np.array([1,3,4])
pc = pearsonr(x,y)
print("相关系数:",pc[0])
print("显著性水平:",pc[1])
相关系数: 0.9819805060619655
显著性水平: 0.1210377183236774
pccs = pearsonr(chart['湿度'],chart['日均电力负荷'])
print('湿度')
print("相关系数:",pccs[0])
print("显著性水平:",pccs[1])
湿度
相关系数: 0.008366098656828478
显著性水平: 0.7466985868452606
pccs = pearsonr(chart['干球温度'],chart['日均电力负荷'])
print('干球温度')
print("相关系数:",pccs[0])
print("显著性水平:",pccs[1])
干球温度
相关系数: 0.13553654698519382
显著性水平: 1.464772478253176e-07
pccs = pearsonr(chart['湿球温度'],chart['日均电力负荷'])
print('湿球温度')
print("相关系数:",pccs[0])
print("显著性水平:",pccs[1])
湿球温度
相关系数: -0.2234887241034933
显著性水平: 2.3520368633274703e-18
pccs = pearsonr(chart['露点温度'],chart['日均电力负荷'])
print('露点温度')
print("相关系数:",pccs[0])
print("显著性水平:",pccs[1])
露点温度
相关系数: 0.11306119537985258
显著性水平: 1.192249332196542e-05
pccs = pearsonr(chart['电价'],chart['日均电力负荷'])
print('电价')
print("相关系数:",pccs[0])
print("显著性水平:",pccs[1])
电价
相关系数: 0.12163330223784043
显著性水平: 2.436096002707336e-06
pccs = pearsonr(chart['日最高电力负荷'],chart['日均电力负荷'])
print('日最高电力负荷')
print("相关系数:",pccs[0])
print("显著性水平:",pccs[1])
日最高电力负荷
相关系数: 0.9766023264436509
显著性水平: 0.0
pccs = pearsonr(chart['日最低电力负荷'],chart['日均电力负荷'])
print('日最低电力负荷')
print("相关系数:",pccs[0])
print("显著性水平:",pccs[1])
日最低电力负荷
相关系数: 0.9390036936914716
显著性水平: 0.0
4.数据分析。使用上一步选择的3个特征属性作为输入属性,电力负荷作为输出属性,合理划分训练集与测试集比例,选择适合的参数,使用Sklearn建立决策树模型,并对模型进行测试。
(1)建立决策树模型
X=pd.concat([chart['湿球温度'],chart['干球温度'],chart['电价']],axis=1)
Y=chart['日均电力负荷']
# 划分测试与训练集
Xtrain,Xtest,Ytrain,Ytest=train_test_split(X,Y,test_size=0.1,random_state=420)
# 选择最优参数
tree_param={'criterion':['mse','friedman_mse','mae'],'max_depth':list(range(10))}
# GridSearchCV网格搜索,搜索的是参数,即在指定的参数范围内,按步长依次调整参数,利用调整的参数训练学习器,从所有的参数中找到在验证集上精度最高的参数,这其实是一个训练和比较的过程。k折交叉验证将所有数据集分成k份,不重复地每次取其中一份做测试集,
# 用其余k-1份做训练集训练模型,之后计算该模型在测试集上的得分,将k次的得分取平均得到最后的得分。
#实例化对象
grid=GridSearchCV(tree.DecisionTreeRegressor(),param_grid=tree_param,cv=3)
regressor = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=5, min_samples_split=10)
grid = GridSearchCV(regressor, param_grid={'max_depth': [3, 5, 7], 'min_samples_split': [2, 5, 10]})
grid.fit(Xtrain, Ytrain)
#最优参数,最优分数
grid.best_params_,grid.best_score_
#建立回归树
dtr=tree.DecisionTreeRegressor(criterion='mae',max_depth =5)
#训练决策树
#预测训练结果
dtr.fit(Xtrain,Ytrain)
pred=dtr.predict(Xtest)
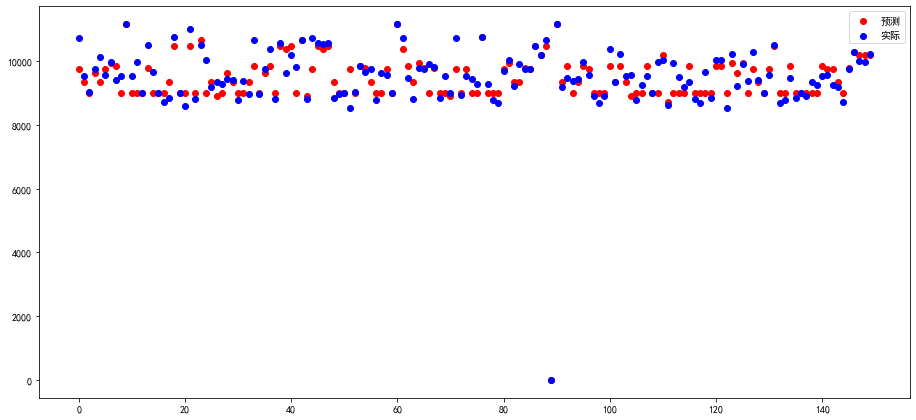
(2)绘制预测结果
fig=plt.figure(figsize=(15.6,7.2))
ax=fig.add_subplot(111)
s1=ax.scatter(range(len(pred)),pred,facecolors="red",label='预测')
s2=ax.scatter(range(len(Ytest)),Ytest,facecolors="blue",label='实际')
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f055ef94080>
实验总结:
自己总结一哈!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号