java_File
学习一个类,我们先看静态成员变量,通过类名可以直接访问静态成员变量。其次看构造方法,通过构造方法我们可以创建对象,创建完对象后通过对象名可以访问成员方法。
概述
java.io.File是文件和目录路径名的抽象表示。主要是文件和目录的创建、查找和删除等操作。File与操作系统无关,在任何操作系统中都可以使用。
构造方法
public File(String pathname)
参数:路径名:可以是文件结尾,也可以是文件夹结尾。路径可以是相对路径,也可以是绝对路径。路径可以是存在的,也可以是不存在的。创建File对象,只是把字符串路径封装为File对象,不考虑路径的真假情况。
import java.io.File; public class Demo02File { public static void main(String[] args){ show01(); } public static void show01(){ File f1 = new File("D:\\code_study\\Activity_Demo2\\Activity_Demo2.iml"); System.out.println(f1); //new的是对象,打印确是路径,说明重写了Object类的toString方法。 } }
public File(String parent, String child)
参数:将路径分为了两部分,父路径和子路径使用起来较灵活。
File f2 = new File("D:\\","a.txt");
public File(File parent, String child)
参数:路径可能随时变化,可以使用File的方法对路径进行一些操作,在使用路径创建对象。
File parent = new File("c:\\"); File f3 = new File(parent,"a.txt");
静态成员变量
static String pathSeparator 与系统有关的路径分隔符,为了方便,它被表示为一个字符串。
static char pathSepartorChar 与系统有关的路径分隔符。
static String separator 与系统有关的默认分隔符,为了方便,它被表示为一个字符串。
static char separatorChar 与系统有关的默认分隔符。
静态成员变量通过类名能直接访问。
pathSeparator 路径分隔符号 window中为(;) 在linux系统中为(:)
separator 文件名称分隔符 windows中为(\),在linux系统中为(/)
关于文件、文件夹的常见操作
获取文件的路径、文件或文件夹名称、获取文件的大小。
public String getAbsolutePath() 返回此File的绝对路径名称字符串,其路径来源于构造方法传递。
public String getPath() 将此File转换为路径名字符串。
public String getName() 返回此File表示的文件或目录的名称。
public long length() 返回由此File表示的文件的大小,以字节为单位,不能获取文件夹大小。如果构造方法中的路径不存在,返回0。
public static void show01(){ File f1 = new File("D:\\code_study\\Activity_Demo2\\Activity_Demo2.iml"); String absolute1 = f1.getAbsolutePath(); System.out.println(absolute1); File f2 = new File("a.txt"); String absolute2 = f2.getAbsolutePath(); System.out.println(absolute2); }
![]()
public static void show2(){ File f1 = new File("D:\\code_study\\Activity_Demo2\\Activity_Demo2.iml"); String path = f1.getPath(); System.out.println(path); File f2 = new File("a.txt"); String path2 = f2.getPath(); System.out.println(path2); }
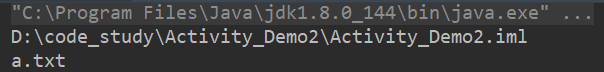
public static void show3(){ File f1 = new File("D:\\code_study\\Activity_Demo2\\Activity_Demo2.iml"); //文件存不存在没有关系。 String name = f1.getName(); System.out.println(name); File f2 = new File("Activity_Demo2.iml"); //文件存不存在没有关系。 String name2 = f2.getName(); System.out.println(name2); }
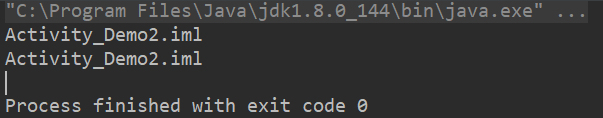
public static void show4(){ File f1 = new File("D:\\code_study\\Activity_Demo2\\Activity_Demo2.iml"); long len = f1.length(); System.out.println(len); File f2 = new File("D:\\code_study\\Activity_Demo2"); long len2 = f2.length(); System.out.println(len2); File f3 = new File("D:\\code_study\\Activity_Demo2\\Activity_Demo2.txt"); long len3 = f3.length(); System.out.println(len3); }
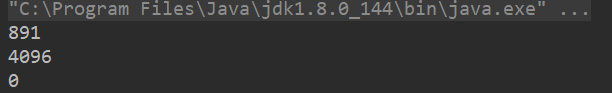
创建一个文件、文件夹。
删除文件、文件夹。
判断文件、文件夹是否存在。
对文件夹进行遍历。
关于文件、文件夹、路径的单词 path、file、directory。
posted on 2020-12-23 23:45 XiaoXiaoli 阅读(90) 评论(0) 收藏 举报


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号