java多线程 -2025/1/10
Java 提供了三种创建线程的方法:
通过实现 Runnable 接口;
通过继承 Thread 类本身;
通过 Callable 和 Future 创建线程。
通过实现 Runnable 接口;
package Java多线程;
class RunnableDemo implements Runnable {
private Thread t;
private String threadName;
RunnableDemo( String name) {
threadName = name;
System.out.println("Creating " + threadName );
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("Running " + threadName );
try {
for(int i = 4; i > 0; i--) {
System.out.println("Thread: " + threadName + ", " + i);
// 让线程睡眠一会
Thread.sleep(50);
}
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Thread " + threadName + " interrupted.");
}
System.out.println("Thread " + threadName + " exiting.");
}
public void start () {
System.out.println("Starting " + threadName );
if (t == null) {
t = new Thread (this, threadName);
t.start ();
}
}
}
public class TestThread {
public static void main(String args[]) {
RunnableDemo R1 = new RunnableDemo( "Thread-1");
R1.start();
RunnableDemo R2 = new RunnableDemo( "Thread-2");
R2.start();
}
}
通过继承 Thread 类本身;
package Java多线程;
class ThreadDemo extends Thread {
private Thread t;
private String threadName;
ThreadDemo( String name) {
threadName = name;
System.out.println("Creating " + threadName );
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("Running " + threadName );
try {
for(int i = 4; i > 0; i--) {
if(threadName == "Thread-1" && i == 2){
this.t.interrupt();
}
System.out.println("Thread: " + threadName + ", " + i);
// 让线程睡眠一会
Thread.sleep(50);
}
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Thread " + threadName + " interrupted.");
}
System.out.println("Thread " + threadName + " exiting.");
}
public void start () {
System.out.println("Starting " + threadName );
if (t == null) {
t = new Thread (this, threadName);
t.start ();
}
}
}
public class TestThread2 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
ThreadDemo T1 = new ThreadDemo( "Thread-1");
T1.start();
ThreadDemo T2 = new ThreadDemo( "Thread-2");
T2.start();
}
}
通过 Callable 和 Future 创建线程。
package Java多线程;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
public class CallableThreadTest implements Callable<Integer> {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
CallableThreadTest ctt = new CallableThreadTest();
FutureTask<Integer> ft = new FutureTask<>(ctt);
for(int i = 0;i < 100;i++)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 的循环变量i的值"+i);
if(i==20)
{
new Thread(ft,"有返回值的线程").start();
}
}
try
{
System.out.println("子线程的返回值:"+ft.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception
{
int i = 0;
for(;i<100;i++)
{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+i);
}
return i;
}
}
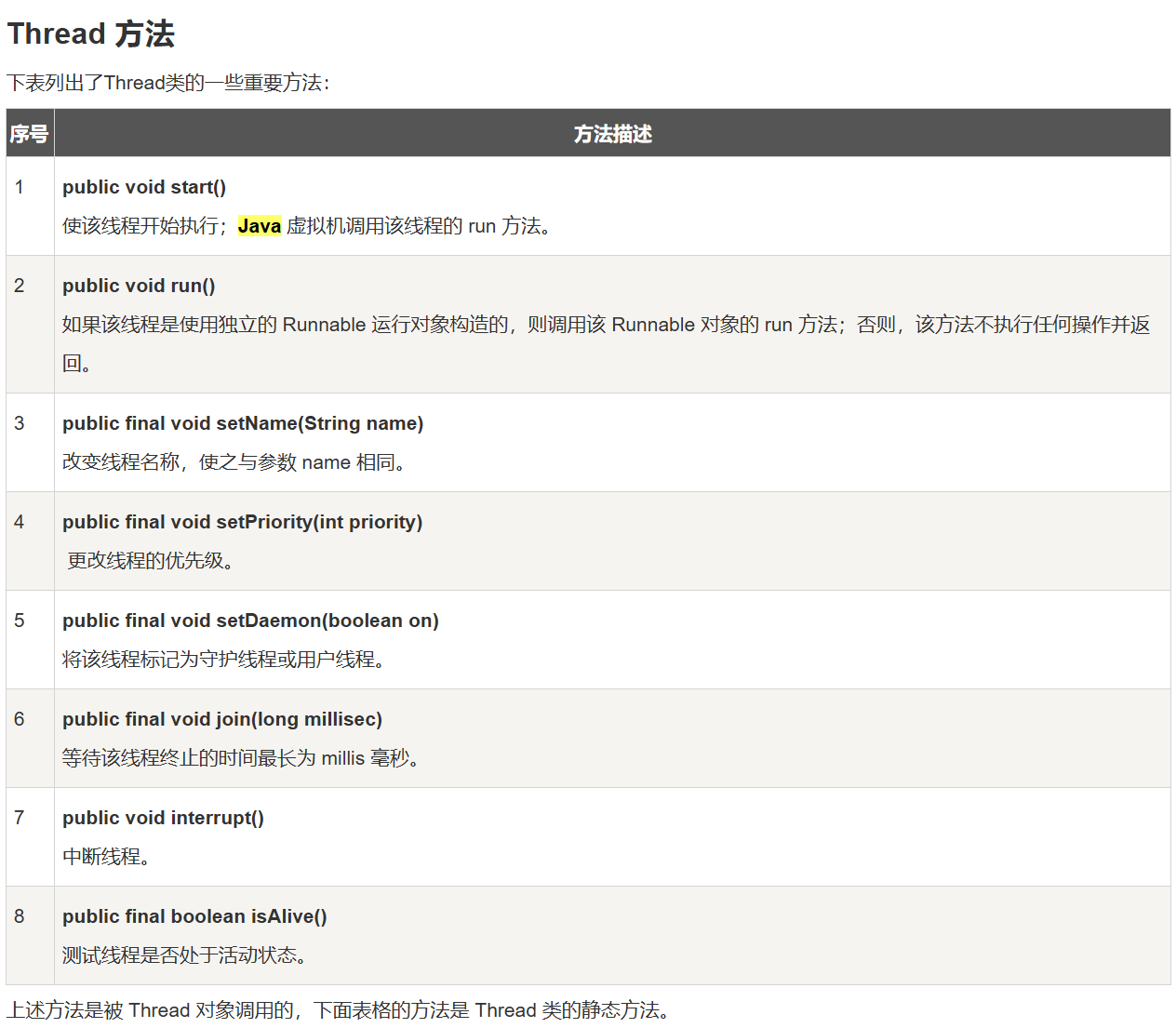
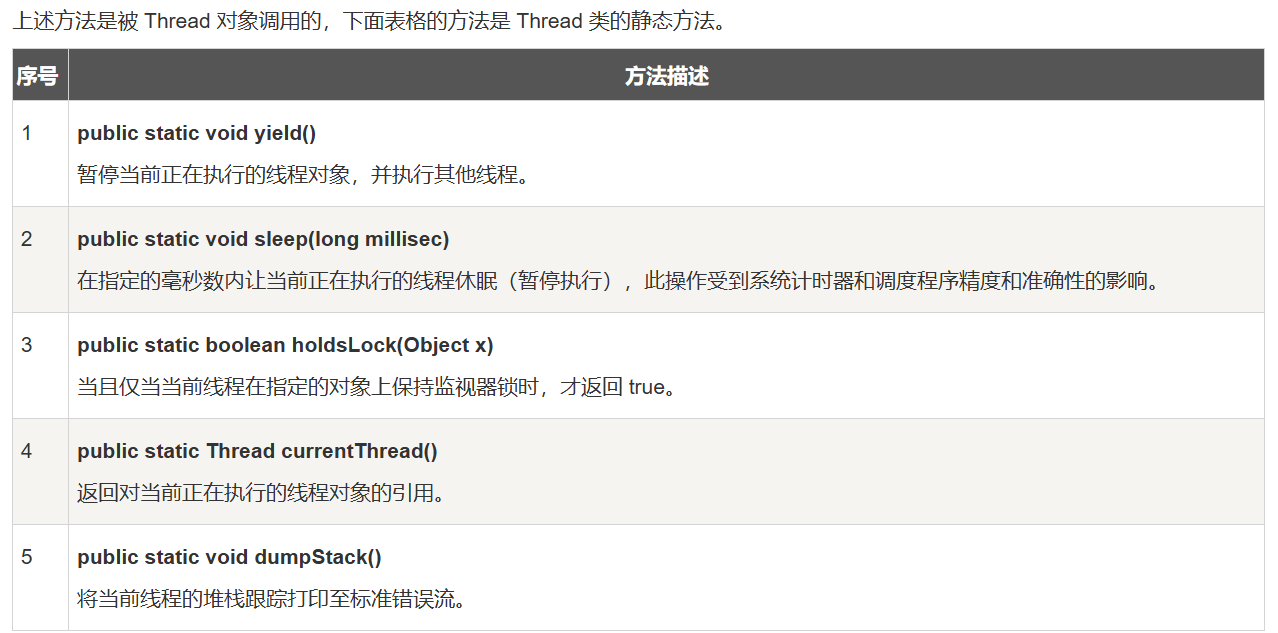
静态方法:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号