pta作业集4~6总结
PTA题目集4~6总结
(1)前言:(总结三次作业知识点,题量,难度等情况)
第四次作业:
知识点:
1.正则表达式的灵活运用
2.对聚合的运用
3.继承相关知识点(覆写,构造方法,私有属性的获取与修改等)运用
题量:
三道
难度系数:五颗星(自认为挺难的)
第五次作业:
知识点:
1.对字符串中分隔其中的各个词组的方法运用及对各组词组大小的比较方法
2.对数组的运用及数组合并的方法运用
3.对三种基本排序-选择,冒泡,插入算法的运用
4.对Java关键字的认识
5.对正则表达式的灵活运用
6.对聚合的运用
题量:
5道
难度系数:五颗星(自认为挺难的)
第六次作业:
知识点:
1.正则表达式的运用
2.对字符串转换成一个个字符知识点运用及排序算法
3.继承与多态的灵活运用
4.对接口与多态的灵活运用
题量:
6道
难度系数:四颗星(总体看来还算简单,第五题稍复杂些)
(2)设计与分析:
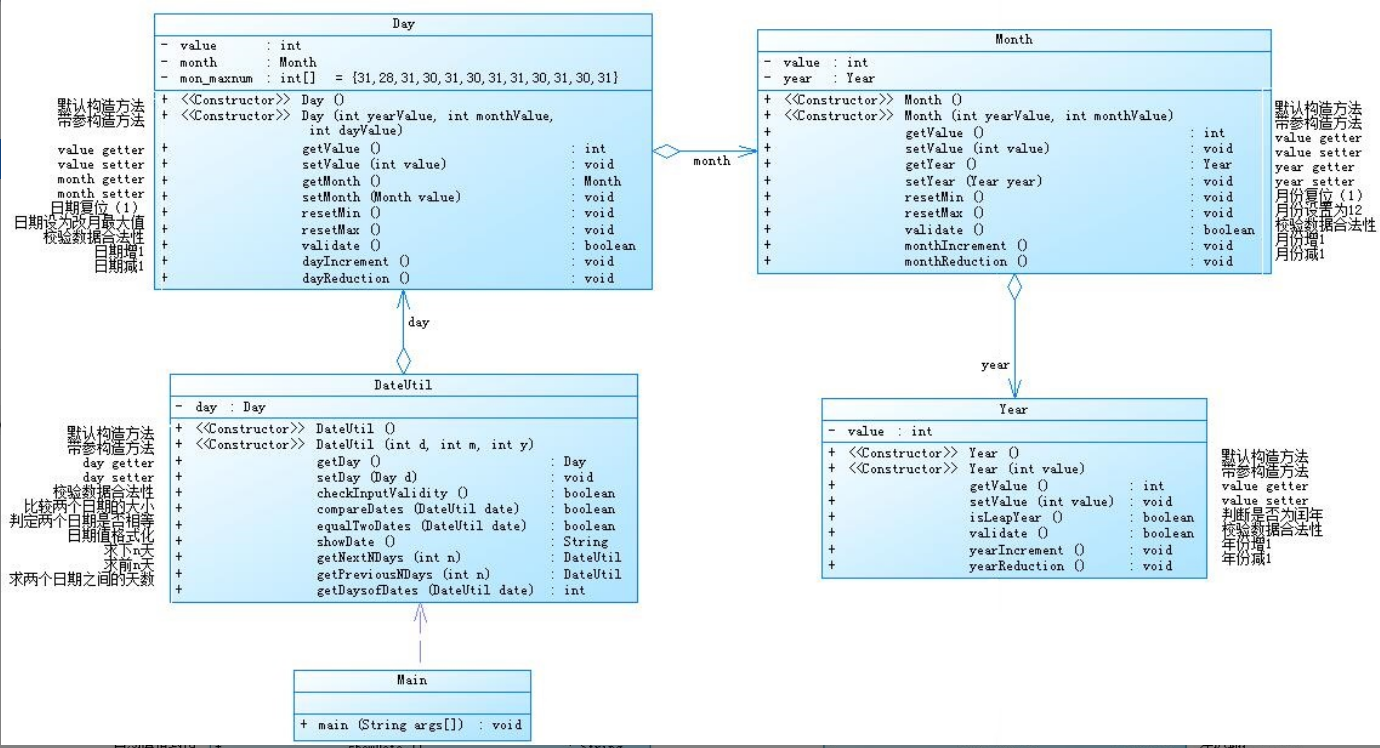
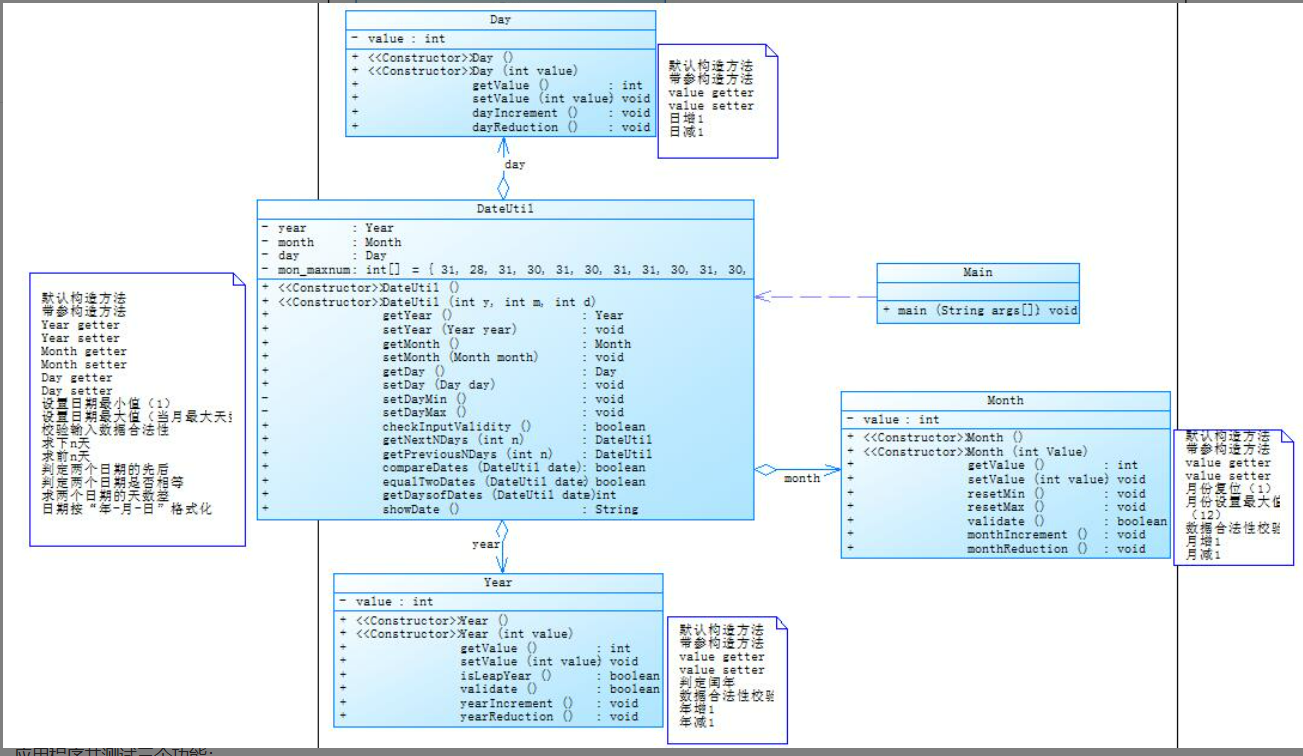
1.作业集4(7-2),题目集5(7-5)两种日期类聚合设计的优略比较
7-2类图:
7-5类图:
首先阐述这两者运用聚合的设计实现:
将已有对象采用接口纳入到新的对象中成为新对象的一部分并实现复用
比较:
在前者聚合使用中,每一个新的类将焦点集中于一个新的类中,一个类一个类层层相依,彼此之间关系比较紧密,但是容易随着部分的销毁而使整个程序被破坏,例如将Year这个类删除后,整个程序将会开始出现问题。总言之,前者的内聚较高,类之间没用体现明显的少调用别的类,从项目的角度而言,模块之间依赖性强。
在后者聚合使用中,一个整体,多个部分,相对于前者而言,后者的依赖性不是很强,复用性较高,且在破坏其中一个部分的情况下不会对主体和其他部分产生影响。总言之,后者的低内聚明显,在类的角度上也有少调用别的类,在项目角度上,模块之间的依赖性并不算强。
2.作业集4(7-3),题目集6(7-5 7-6)三中渐进式图形继承设计的思路与技术运用(继承,封装,多态,接口)
题目集4(7-3)类图:
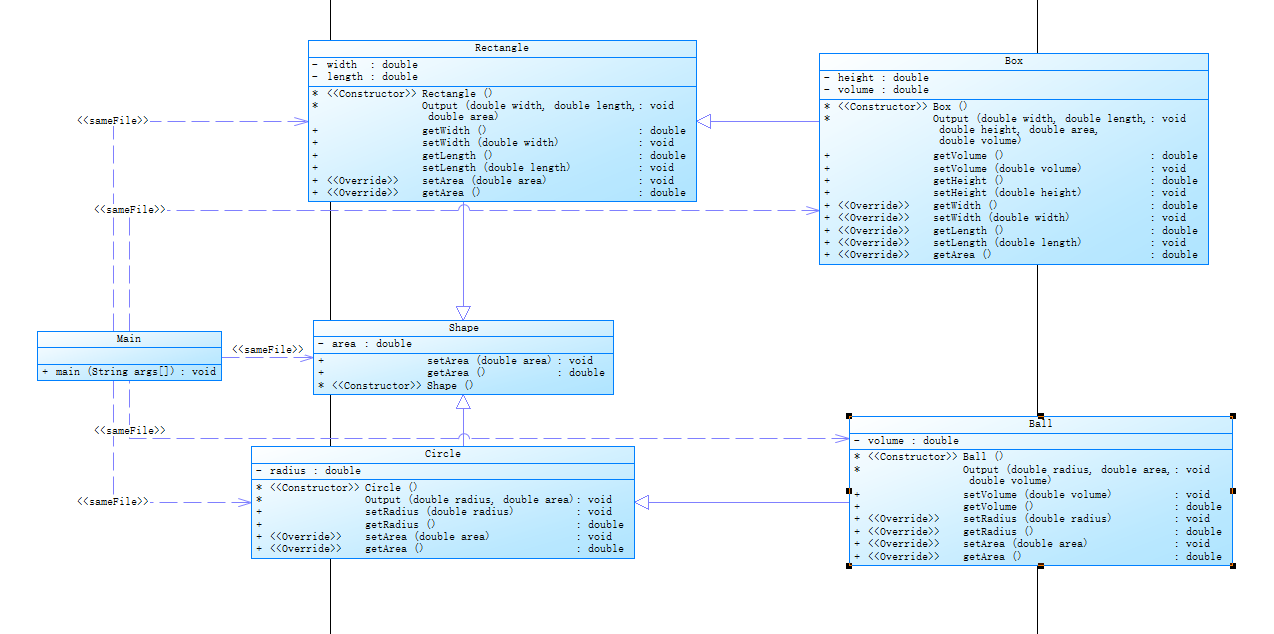
以Shape类为其中的第一代父类,cicle类和Rectangle类作为子一类继承第一代父类,再将cicle类和Rectangle类作为第二代父类继承给子二类实现代码的复用,同时在子类中实现功能的扩展。代码之间依赖性比较强。
题目集6(7-5)类图:
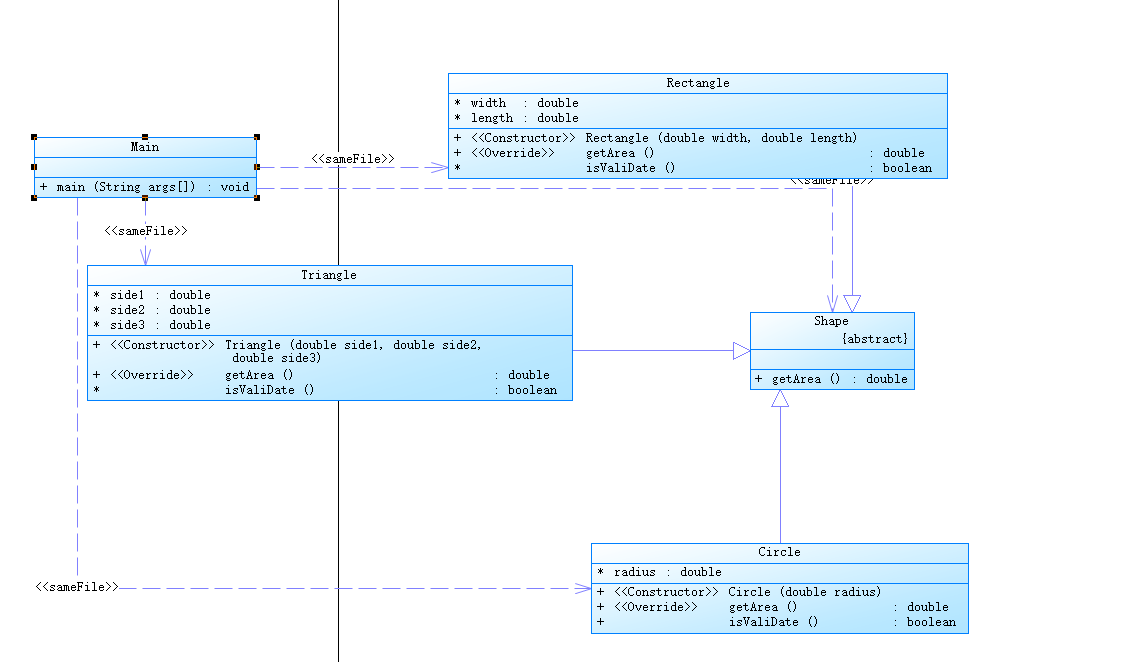
将Shape类封装提供一个有效的途径来保护Shape数据不被意外的破坏。使用属性时不仅可以控制存取数据的合法性,操作方法也比较灵活。
题目集6(7-6)类图:
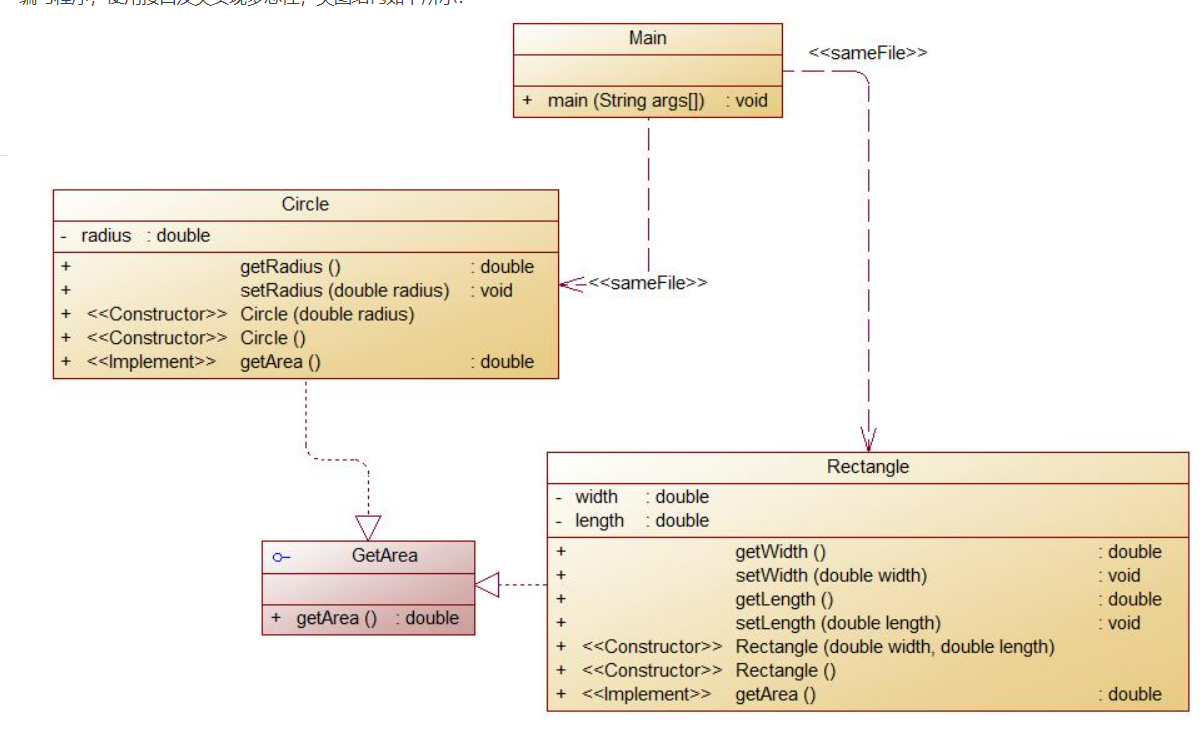
创建接口GetArea,利用接口可以多实现的特点,在Circle类和Rectangle类中实现接口中方法getArea();同时采用接口有利于程序的安全与严密,利于后期的维护。
3.对三次题目集中用到的正则表达式技术的分析总结
题目集4正则表达式运用:
一:日期及输入数据匹配
在题目一中利用正则表达式对水文数据处理,以下为一个时间一个水文数据上利用正则处理
String regex1="(?:((?:([1-9]([0-9]{0,3}))/((?:(([1-9]|(1[0-2]))/(?:([1-9]|([1-2][0-8])|19))))|(?:(([13578])|([1][02])(/31)))|(?:(([13-9]|1[02])/(29|30)))))(?:(?:( [02468]| 1[02468]| 2[02]|):00))))";
String water ="(?:(?:(([1-9]([0-9]{0,2})))(?:((.[0-9]{1,3})?))))";
1.regex1 表示一个闰年数据校验
2.water表示目标水位、实际水位、流量:均为实型数,取值范围为[1,1000), 小数点后保留1-3位小数或无小数(也无小数点)
题目集5正则表达式运用:
一:空格匹配
在题目一中对单行输入以空格分开的单词进行最长筛选,Pattern p = Pattern. compile("[\\s]");
1.\\s表示空格
2.用p.split(str)索引str中的空格
二:匹配字符串并对其进行分组处理
在题目五统计关键字出现次数并输出问题中,如下一个所写例子所示:
Pattern p=Pattern.compile("\"(.*?)\"");
Matcher m=p.matcher(str1);
while(m.find()){
str1=str1.replace(m.group()," ");
p=Pattern.compile("\"(.*?)\"");
m=p.matcher(str1);
}
1.捕获组运用,构造Pattern对象获得一个Matcher对象
题目集6正则表达式运用:
一:匹配数字格式
在题目一中对QQ号进行校验,String regex = "[1-9][\\d]{4,14}";
1.[1-9]表示第一位数字不为0
2.[\\d]{4,14}表示接下来输入4到14个数字
在题目四中对学号进行校验
String regex1 = "[2][0][2][0](([1][1-7])|[61])((([1-3][\\d])|[40])|[0][1-9])";
String regex2 = "[2][0][2][0][7][1-3]((([1-3][\\d])|[40])|[0][1-9])";
String regex3 = "[2][0][2][0][8][12]((([1-3][\\d])|[40])|[0][1-9])";
1.[2][0][2][0]表示前四位数字为2020
2.(([1][1-7])|[61])表示11到17或61
3.[7][1-3]表示71到73
4.[8][12]表示81到82
5.((([1-3][\\d])|[40])|[0][1-9])表示01到40
二:匹配数字和字母格式
在题目三中对验证码进行校验, String regex = "[\\da-zA-Z]{4}";
1.[\\da-zA-Z]表示输入应满足数字或大小写字母
2.{4}表示对前一项匹配规则数量的限定为4
总结:
三次题目集中涉及的正则表达式主要为对字符处理,字符串分组。应用正则表达式主要体现在校验字符是否符合要求方面,对正则能否灵活在校验数据方面具有重要意义。
4,题目集5(7-4)中Java集合框架应用的总结分析
集合框架概述:集合框架是一个用来代表和操纵集合的统一架构。可以有效解决数组的劣势(不灵活和容量需要事先定义,不能随着需求的变化而扩容)。
题目描述:编写程序统计一个输入的Java源码中关键字(区分大小写)出现的次数
我的代码:
import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Set; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Scanner rd=new Scanner(System.in); String ad; StringBuilder str=new StringBuilder(); Map<String, Integer> map=new HashMap<String, Integer>(); String []key= { "abstract","assert","boolean","break","byte","case","catch", "char","class","const","continue","default","do","double","else", "enum","extends","false","final","finally","float", "for","goto","if","implements","import","instanceof", "int","interface","long","native","new","null","package", "private","protected","public","return","short","static", "strictfp","super","switch","synchronized","this","throw", "throws","transient","true","try","void","volatile","while" }; int j=0; for(int i=0;;i++) { ad=rd.nextLine(); if(ad.equals("exit")) break; if(ad.matches("(.*)//(.*)")) {String b[]=ad.split("//"); str.append(b[0]+" "); } else {str.append(ad+" "); } } int count=0; String str1=str.toString(); Pattern p=Pattern.compile("\"(.*?)\""); Matcher m=p.matcher(str1); while(m.find()){ str1=str1.replace(m.group()," "); p=Pattern.compile("\"(.*?)\""); m=p.matcher(str1); } p=Pattern.compile("/\\**(.*?)/"); m=p.matcher(str1); while(m.find()){ str1=str1.replace(m.group()," "); m=p.matcher(str1); } if(str1.isEmpty()) {System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } str1=str1.replace("["," "); str1=str1.replace("]"," "); str1=str1.replace("-","a"); str1=str1.replace("*","a"); str1=str1.replace("/","a"); str1=str1.replace("+","a"); str1=str1.replace(">","a"); str1=str1.replace("=","a"); str1=str1.replace("!","a"); str1=str1.replace(":","a"); str1=str1.replace("\\","a"); str1= str1.replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z]", " "); String []s1=str1.split("[ ' ']"); for(int i=0;i<s1.length;i++) { for( j=0;j<key.length;j++) if(s1[i].equals(key[j])) { map.put(key[j], 0); } } for( int i = 0;i<s1.length;i++) { for( j=0;j<key.length;j++) if(s1[i].equals(key[j])) { count=map.get(key[j]); map.put(key[j], count+1); } } Set set=map.keySet(); Object[] arr=set.toArray(); Arrays.sort(arr); for(Object k:arr){ System.out.println(map.get(k)+"\t"+k); } } }
所含有的集合思想:利用集合将关键字数组key[]与关键字数量进行实例化存储到Map中,统计关键字的数量,随检测到关键字的数量的增加而增加。与此同时利用set 不允许重复对象 将map中的数据存储到set中,再接着利用数组对数据进行排序输出。
(3)踩坑心得:
1.由于对继承的用法不了解,所写代码在题目集四第三题图形的继承中,系统未能对所写图形测试做出有效判断:
如下图所示:
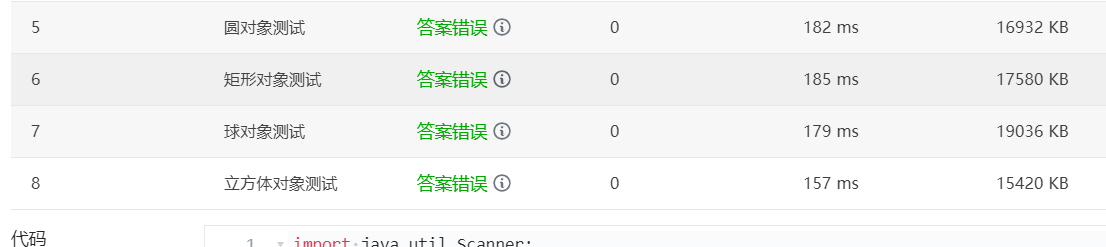
我的代码:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int choice; Scanner rd = new Scanner(System.in); choice = rd.nextInt(); if(choice==1){ //圆半径 double r = rd.nextDouble(); double s = 0; if(r>0&&r<=4){ new Circle().Output(r,s); }else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } }else if(choice==2){ double w = rd.nextDouble(); double l = rd.nextDouble(); double s = 0; if(w>0&&w<=4&&l>0&&l<=4){ new Rectangle().Output(w,l,s); }else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } }else if(choice==3){ double r1 = rd.nextDouble(); double s = 0; double v = 0; if(r1>0&&r1<=4){ new Ball().Output(r1,s,v); }else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } }else if(choice == 4){ double w1 = rd.nextDouble(); double l1 = rd.nextDouble(); double h1 = rd.nextDouble(); double s = 0; double v = 0; if(w1>0&&w1<=4&&l1>0&&l1<=4&&h1>0&&h1<=4){ new Box().Output(w1,l1,h1,s,v); }else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } }else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } } class Shape{ private double area; public void setArea(double area) { this.area = area; } public double getArea() { return 0.0; } Shape(){ System.out.println("Constructing Shape"); } } class Circle extends Shape{ private double radius; Circle(){ super(); System.out.println("Constructing Circle"); } void Output(double radius,double area){ setRadius(radius); getRadius(); setArea(area); System.out.printf("Circle's area:%.2f",super.getArea()); } public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } public double getRadius() { return radius; } @Override public void setArea(double area) { area =Math.PI*radius*radius; super.setArea(area); } @Override public double getArea() { return super.getArea(); } } class Rectangle extends Shape{ private double width,length; Rectangle(){ super(); System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle"); } void Output(double width,double length,double area){ setWidth( width); setLength(length); setArea(area); System.out.printf("Rectangle's area:%.2f",super.getArea()); } public double getWidth() { return width; } public void setWidth(double width) { this.width = width; } public double getLength() { return length; } public void setLength(double length) { this.length = length; } @Override public void setArea(double area) { area = width*length; super.setArea(area); } @Override public double getArea() { return super.getArea(); } } class Ball extends Circle{ private double volume; Ball(){ super(); System.out.println("Constructing Ball"); } void Output(double radius,double area,double volume){ setRadius(radius); setArea(area); setVolume(volume); System.out.printf("Ball's surface area:%.2f\n",super.getArea()); System.out.printf("Ball's volume:%.2f\n",getVolume()); } public void setVolume(double volume) { volume = (4.0/3.0)*Math.PI*Math.pow(super.getRadius(),3); this.volume = volume; } public double getVolume() { return volume; } @Override public void setRadius(double radius) { super.setRadius(radius); } @Override public double getRadius() { return super.getRadius(); } @Override public void setArea(double area) { area = 4 * Math.PI*super.getRadius()*super.getRadius(); super.setArea(area); } @Override public double getArea() { return super.getArea(); } } class Box extends Rectangle{ private double height; private double volume; Box(){ super(); System.out.println("Constructing Box"); } void Output(double width, double length, double height,double area,double volume){ setHeight(height); setLength(length); setWidth(width); //setArea(area); setVolume(volume); System.out.printf("Box's surface area:%.2f\n",getArea()); System.out.printf("Box's volume:%.2f\n",getVolume()); } public double getVolume() { return volume; } public void setVolume(double volume) { volume = height*super.getLength()*super.getWidth(); this.volume = volume; } public double getHeight() { return height; } public void setHeight(double height) { this.height = height; } @Override public double getWidth() { return super.getWidth(); } @Override public void setWidth(double width) { super.setWidth(width); } @Override public double getLength() { return super.getLength(); } @Override public void setLength(double length) { super.setLength(length); } @Override public double getArea() { return 2*(getHeight()*super.getLength()+getHeight()*super.getWidth()+super.getLength()*super.getWidth()); } // @Override // public void setArea(double area) { // area = 2*(getHeight()*super.getLength()+getHeight()*super.getWidth()+super.getLength()*super.getWidth()); // super.setArearea(area); // } }
在IDK中运行样例:
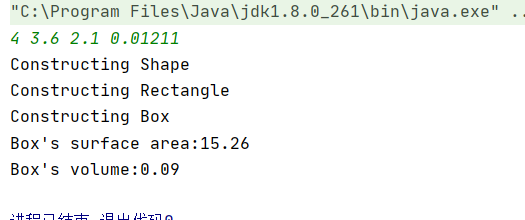
对多个图形的测试均没有问题,但是在pta上运行始终过不了,不太明白为什么。
2.由于对得出String和String数组的长度运用方法的不熟悉,在题目集五第一题找出最长的单词中对于输出最长的单词,系统显示错误
错误示例:s.length()
纠正后代码:
import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Main{ public static void main( String[] args){ Pattern p = Pattern. compile("[\\s]"); Scanner rd = new Scanner(System.in); String str = rd.nextLine(); String[] s = p.split(str); int max = 0; for(int i = 1; i<s.length; i++){ if( s[i].length()>=s[max].length()){ max=i; } } System. out.println(s[max]); } }
代码经过纠正后,对于得出String中的长度方法有了进一步的了解。
3.由于对排序算法的不了解,在题目集五第三题三种排序的算法中出现越界错误
错误代码:
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
min = i;
for (int j = i+1; j < list.length; j++) {
程序运行时,j的范围超出了list的范围程序出现报错。将划线部分一减一,代码运行正常。
4.在题目集5第三题 日期问题面向对象设计中,最后一个测试点天数差:最大值与最小值间的天数答案错误,同时对于jdk中代码的调试不太清楚,不明白哪个环节出了问题。以下是代码中最小与最大值之间的天数差,能够运行但是测试出问题。

5.在题目集6第五题中,无矩形测试始终没有通过

我的代码:
import java.lang.reflect.Array; import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<Shape> shapes= new ArrayList<Shape>(); Collection c1 = new ArrayList(); Scanner rd = new Scanner(System.in); int choice1 =rd.nextInt(); int choice2 = rd.nextInt(); int choice3 = rd.nextInt(); if(choice1>=0&&choice2>=0&&choice3>=0){ double[] area = new double[choice1+choice2+choice3]; int index = 0; double sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < choice1; i++) { double radius = rd.nextDouble(); Circle circle = new Circle(radius); Circle[] circles = new Circle[choice1]; if(circle.isValiDate()){ c1.add(new Circle(radius).getArea()); circles[i] = new Circle(radius); area[index] = circles[i].getArea(); index++; }else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } for (int j = 0; j < choice2; j++) { double width = rd.nextDouble(); double length = rd.nextDouble(); Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(width,length); Rectangle[] rectangles= new Rectangle[choice2]; if(rectangle.isValiDate()){ c1.add(new Rectangle(width,length).getArea()); rectangles[j] = new Rectangle(width,length); area[index] = rectangles[j].getArea(); index++; }else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } for (int m = 0; m < choice3; m++) { double side1 = rd.nextDouble(); double side2 = rd.nextDouble(); double side3 = rd.nextDouble(); Triangle triangle = new Triangle(side1,side2,side3); Triangle[] triangles = new Triangle[choice3]; if(triangle.isValiDate()){ c1.add(new Triangle(side1,side2,side3).getArea()); triangles[m] = new Triangle(side1,side2,side3); area[index]=triangles[m].getArea(); index++; }else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } // System.out.println(c1); ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList(c1); System.out.println("Original area:"); for (int i = 0; i < c1.size(); i++) { System.out.printf("%.2f",arrayList.get(i)); System.out.print(" "); sum = (double) arrayList.get(i)+sum; } System.out.printf("\nSum of area:%.2f",sum); System.out.printf("\nSorted area:"); System.out.println(); Arrays.sort(area); for(int i=0;i<choice1+choice2+choice3;i++){ System.out.printf("%.2f ",area[i]); } System.out.println();//加上空格; System.out.printf("Sum of area:%.2f",sum); } else if(choice1<0||choice2<0||choice3<0){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } } abstract class Shape { public abstract double getArea(); } class Circle extends Shape { double radius; public Circle(double radius) { super(); this.radius = radius; } @Override public double getArea() { double area = Math.round(Math.PI * radius * radius*100.00)*0.01d; return area; } public boolean isValiDate(){ if(radius>0){ return true; }else { return false; } } } class Rectangle extends Shape { double width; double length; public Rectangle(double width, double length) { super(); this.width = width; this.length = length; } @Override public double getArea() { double area = Math.round(width*length*100.00)*0.01d; return area; } boolean isValiDate(){ if(width>0&&length>0){ return true; }else{ return false; } } } class Triangle extends Shape { double side1; double side2; double side3; public Triangle(double side1, double side2, double side3) { super(); this.side1 = side1; this.side2 = side2; this.side3 = side3; } @Override public double getArea() { double s = (side1 + side2 + side3) / 2; double area=Math.round(Math.sqrt(s * (s - side1) * (s - side2) * (s - side3))*100.00)*0.01d; return area; } boolean isValiDate(){ if(side1+side2>side3&&side1+side3>side2&&side2+side3>side1){ return true; }else { return false; } } }
对其尝试进行无矩形测试:
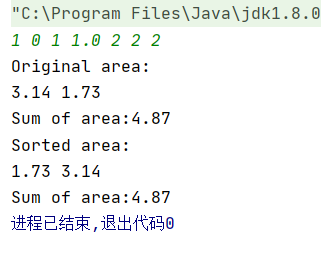
代码也是运行正常,但是测试点上显示错误,表示不太明白。
(4)改进建议:
1、多加练习——学会对正则表达式、聚合、继承与多态相关知识点、字符串比较方法、数组排序及接口等相关知识的灵活运用,对于问题的出现,要及时发现并纠正。
2、紧跟进度——明显感觉到跟不上作业知识点的步伐,要善于利用时间学习,对于知识点的学习与运用做到心中有度。
3、深入理解知识点的应用——对用相关知识点的用法尽量做到熟悉,注意方法的使用。
4、温故知新——对于学过的知识及时巩固,对于再次运用时,尽量做到得心应手,而不是又如同新的知识一般,仿佛没学过一样。
5、学习如何用jdk调试程序——对于出现的问题,不太明白哪里出现问题。
(5)总结:
在本次作业集的训练中,我对正则表达式、聚合、继承与多态相关知识点、字符串比较方法、数组排序及接口等相关知识有了进一步的了解,但还是不太熟悉它们的用法,在一些细节方面时有出错,对于知识的训练还是有待加强。
对老师的建议:
希望老师能够对pta中相关题目的错误情况(像错的知识点方面及应该注意的相关事项等方面)能够进行一个总结和讲解。同时希望老师能够说明一下为什么程序运行正确时,整个测试点还是过不了。
对课程的建议:
我们的课程采取的是线上和线下相互进行的教学模式,线上课程的更新超前线下老师的授课,感觉老师容易在线上课程进度的影响下,对线下课程进度加快速度,希望老师的进度稍稍慢一点。
然后就是,对于线上课程发布的作业及互评作业,容易被忽略。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号