个人项目-论文查重
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | 计科23级12班 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | 个人项目 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 设计并实现论文查重算法,实现原文与抄袭版论文的相似度计算,并输出重复率。使用 PSP 表格记录开发时间,进行单元测试、性能分析与优化,掌握 GitHub 项目管理与提交方法。 |
✨ github链接:https://github.com/Wangyio-2/Wangyio-2/tree/main/3223004344
一、PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 20 | 30 |
| · Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 20 | 30 |
| Development | 开发 | 630 | 650 |
| · Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 300 | 210 |
| · Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 45 | 40 |
| · Design Review | 设计复审 | 30 | 25 |
| · Coding Standard | 代码规范 (制定开发规范) | 15 | 15 |
| · Design | 具体设计 | 40 | 45 |
| · Coding | 具体编码 | 120 | 150 |
| · Code Review | 代码复审 | 35 | 35 |
| · Test | 测试 (自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 45 | 130 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 140 | 230 |
| · Test Report | 测试报告 | 90 | 120 |
| · Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 15 | 15 |
| · Postmortem | 事后总结,并提出过程改进计划 | 35 | 95 |
| Total | 合计 | 790 | 910 |
二、计算模块接口的设计与实现过程
1. 模块与函数组织
文件处理模块
read_file(file_path)
功能:读取文本内容,返回字符串;支持文件不存在时容错处理。write_result(file_path, orig_path, plag_path, similarity)
功能:输出结果文件,包含原文文件路径、抄袭版文件路径及重复率;每个抄袭版文件独立输出。
文本预处理模块
preprocess(text, use_stopwords=True)
功能:将文本小写化、分词,可按需过滤停用词和数字;输出标准化词列表,为相似度计算提供输入。
相似度计算模块
lcs_ratio(seq1, seq2)
功能:基于最长公共子序列(LCS)计算词序相似度。cosine_similarity(tokens1, tokens2)
功能:基于词频向量计算余弦相似度,衡量词汇覆盖率。hybrid_similarity(orig_text, plag_text)
功能:核心算法接口,融合 LCS 与余弦相似度,加权输出最终重复率百分比;结合停用词优化和完整分词实现顺序与词频兼顾。
控制与批量处理模块
process_file_pair(orig_path, plag_path, ans_path)
功能:单组文件处理流程,包括读取文件 → 相似度计算 → 写入结果 → 输出日志。main()
功能:程序入口,解析命令行参数或批量文件列表,调用process_file_pair()完成单组或批量查重任务。
2. 函数调用关系与计算流程

- 控制模块 (
main、process_file_pair)
负责调度整个查重流程,支持单组和批量处理。 - 文件模块 (
read_file、write_result)
处理数据输入输出和日志管理。 - 算法模块 (
hybrid_similarity)
内部调用 LCS 与余弦相似度,输出最终重复率。
算法关键点与独到之处
-
高精度混合相似度算法
使用 最长公共子序列(LCS) 捕捉词序信息,能够反映文本改写、增删和段落重排等变化。
使用 余弦相似度 衡量词频覆盖率,顺序无关,能够检测文字替换或词序调整的抄袭。
加权融合公式:最终相似度 = 0.6 * 余弦相似度 + 0.4 * LCS相似度兼顾词序与词频,提升查重精度。
-
停用词优化策略
LCS 相似度使用去停用词列表orig_tokens_stop与plag_tokens_stop,减少高频功能词对匹配结果的干扰。
余弦相似度使用完整分词orig_tokens_full与plag_tokens_full,保证词频统计完整。 -
模块化设计与接口规范
文本预处理:preprocess()提供统一接口,控制停用词过滤和数字处理。
相似度计算:
lcs_ratio(seq1, seq2):计算最长公共子序列比例,衡量词序相似度。
cosine_similarity(tokens1, tokens2):通过词频向量计算余弦相似度。
文件处理:
read_file(file_path):读取文本并去除首尾空白,支持文件不存在时容错。
write_result(file_path, orig_path, plag_path, similarity):输出结果文件,包含原文、抄袭版路径和重复率。
控制与批量处理:
process_file_pair(orig_path, plag_path, ans_path):单组文件处理流程,包括读取文件、计算相似度、写入结果。
main():解析命令行或批量文件列表,循环调用process_file_pair()。 -
批量处理与输出格式化
支持批量处理多组论文查重,自动循环调用查重算法。
每个抄袭文件生成独立结果文件,包含原文路径、抄袭版路径及重复率。
输出日志清晰,便于管理和统计。 -
容错与健壮性
文件不存在或为空时自动跳过,保证批量处理不中断。
错误和异常被及时捕获并输出提示,提高系统稳定性。
代码可直接运行也可以接受命令行传参。
三、代码分析与优化
分析工具与方法
在本项目中,为了保证代码质量和可维护性,我采用了两个 Python 代码质量分析工具:主要使用 Flake8 进行代码风格检查,并结合 pylint 验证整体质量评分。优化设计函数用时大约2h。
- Flake8
用于检查代码风格是否符合 PEP8 规范(空格、缩进、行长度、函数定义之间的空行数等)。
能发现常见的低级错误和不规范写法。
执行命令flake8 main.py test.py,没有输出错误信息,说明没有明显的风格或简单语法问题,在代码风格、基本语法等方面符合检查要求。 - pylint
提供更严格的静态分析,检查变量命名、未使用的导入、潜在逻辑错误等。
会给出综合评分,便于跟踪代码质量的改进。
输出Your code has been rated at 10.00/10,说明在代码结构、命名规范、逻辑清晰度、潜在错误等各方面都达到极高标准。
优化前后性能分析
1. 优化目标
在初版实现中,通过性能分析(cProfile 或 py-spy 等工具)发现性能瓶颈主要集中在以下几个环节:
- 分词(
jieba.lcut)
每次调用jieba.lcut都需要加载词典、构建前缀树等操作,成本较高。
在hybrid_similarity中,原文和抄袭文分别进行了两次分词(含停用词和完整分词),整个算法中jieba.lcut被重复调用 4 次。
对于长文本或批量文件,重复分词导致 CPU 时间明显增加。 - 余弦相似度(
tokens.count())
原实现中,为构造词频向量,对词汇表中的每个词都在文本列表中调用tokens.count()。
假设文本长度为 n,词汇表大小为 m,则复杂度为 O(n·m),当 n 和 m 都较大时,耗时显著。 - 最长公共子序列(LCS,
SequenceMatcher)
对长文本,SequenceMatcher计算 LCS 的时间复杂度接近 O(n·m)。
对短文本问题不明显,但在批量处理大量长文本时成为潜在性能瓶颈。
优化目标:
- 减少冗余分词调用次数,节省重复计算开销。
- 降低余弦相似度的时间复杂度,提高大文本处理效率。
- 保留对 LCS 的进一步优化空间(例如后续可使用动态规划或启发式算法替代
SequenceMatcher)。
2. 优化方法
-
分词优化
引入tokenize(text)函数:对文本只调用一次jieba.lcut,生成两套分词结果: -
停用词过滤版:用于 LCS 相似度计算。
-
完整分词版:用于余弦相似度计算。
优点:
避免了原本 4 次jieba.lcut调用的重复计算。
保证分词结果一致性,并减少函数内部复杂度。 -
余弦相似度优化
使用collections.Counter统计词频,替代原来的tokens.count()遍历。
优化前:vec1 = np.array([tokens1.count(w) for w in vocab]) vec2 = np.array([tokens2.count(w) for w in vocab])
时间复杂度 O(n²),n 为文本长度
优化后:
python counter1, counter2 = Counter(tokens1), Counter(tokens2) vec1 = np.array([counter1[w] for w in vocab]) vec2 = np.array([counter2[w] for w in vocab])
时间复杂度降为 O(n),大幅提高计算效率。
- 接口保持一致
hybrid_similarity(orig_text, plag_text)对外接口保持不变,调用方式和返回值与优化前一致。- 内部优化完全透明,无需修改现有调用代码。
- 便于单元测试和性能比较。
优化前
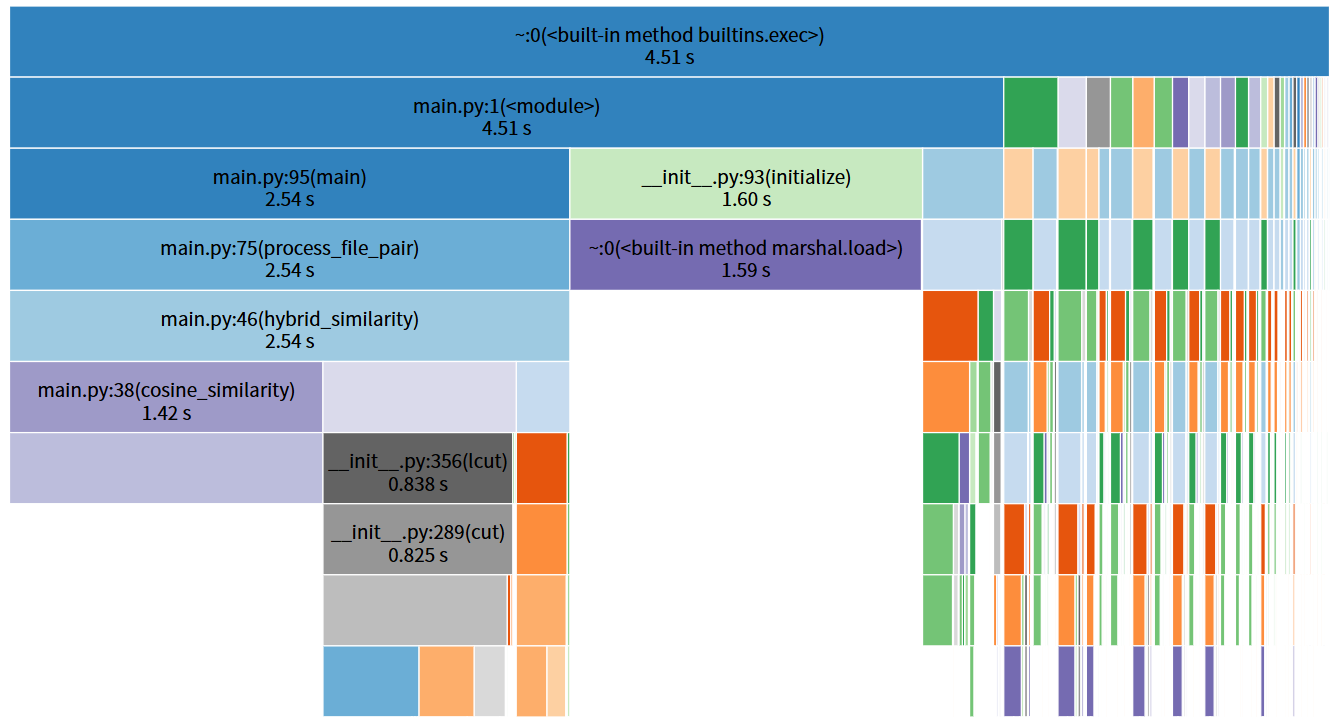
优化后
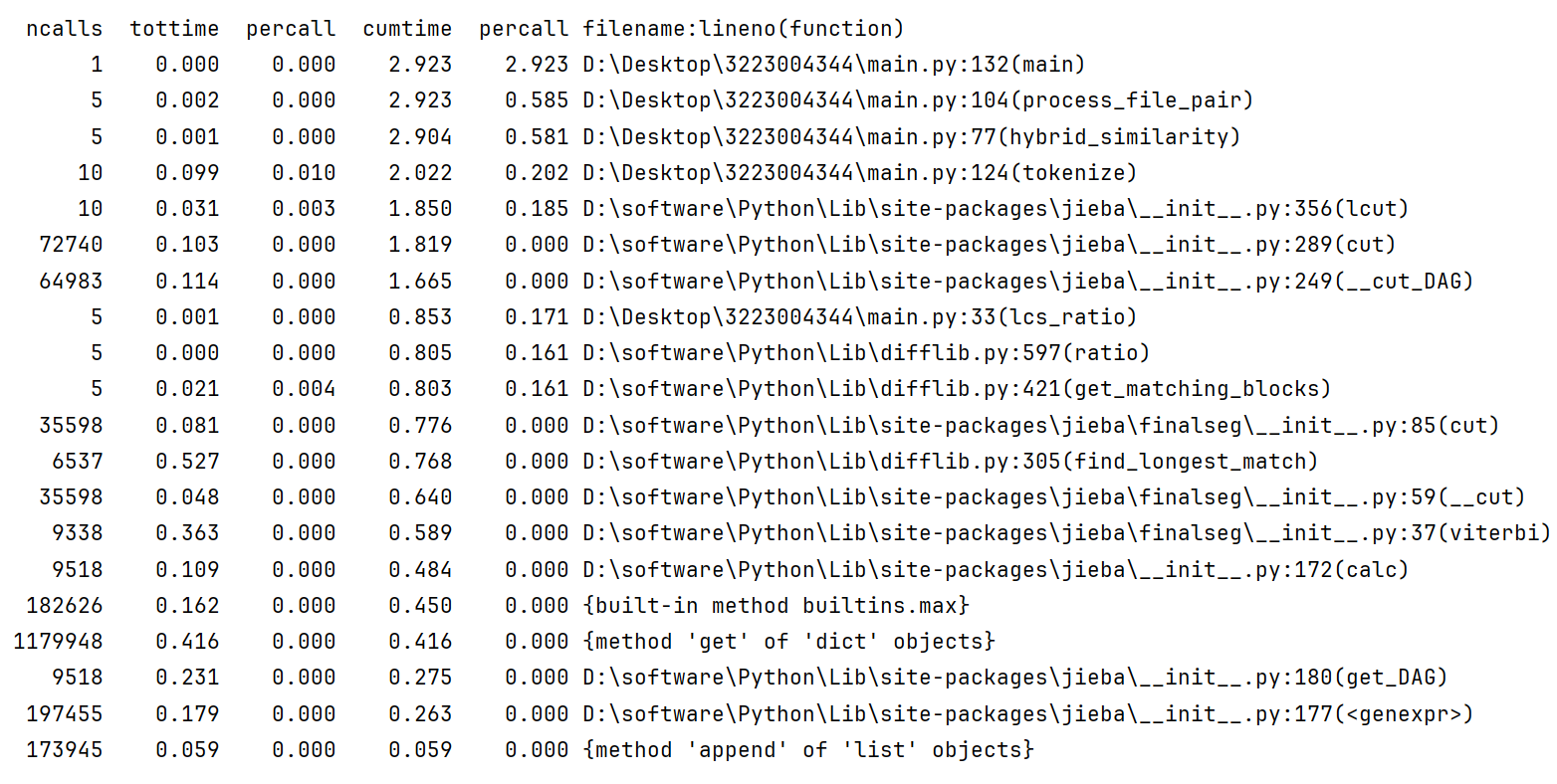
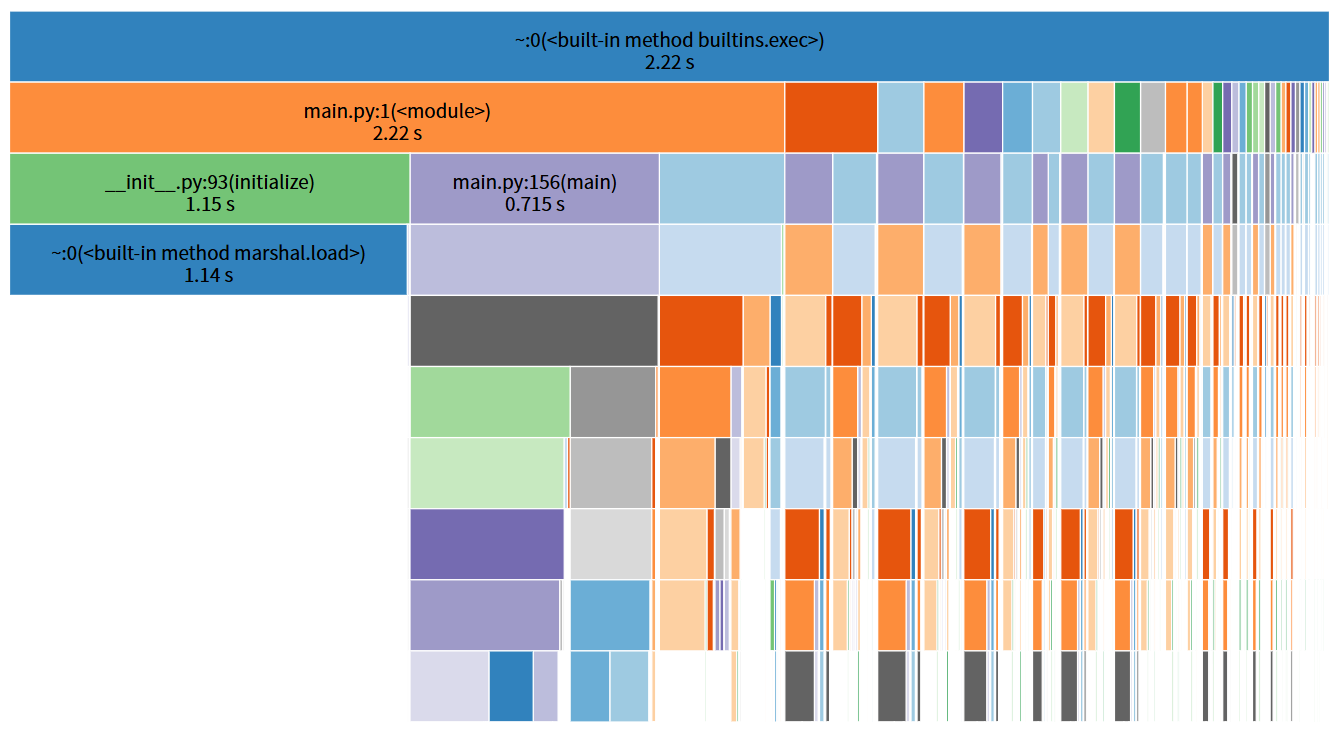
耗时函数分析
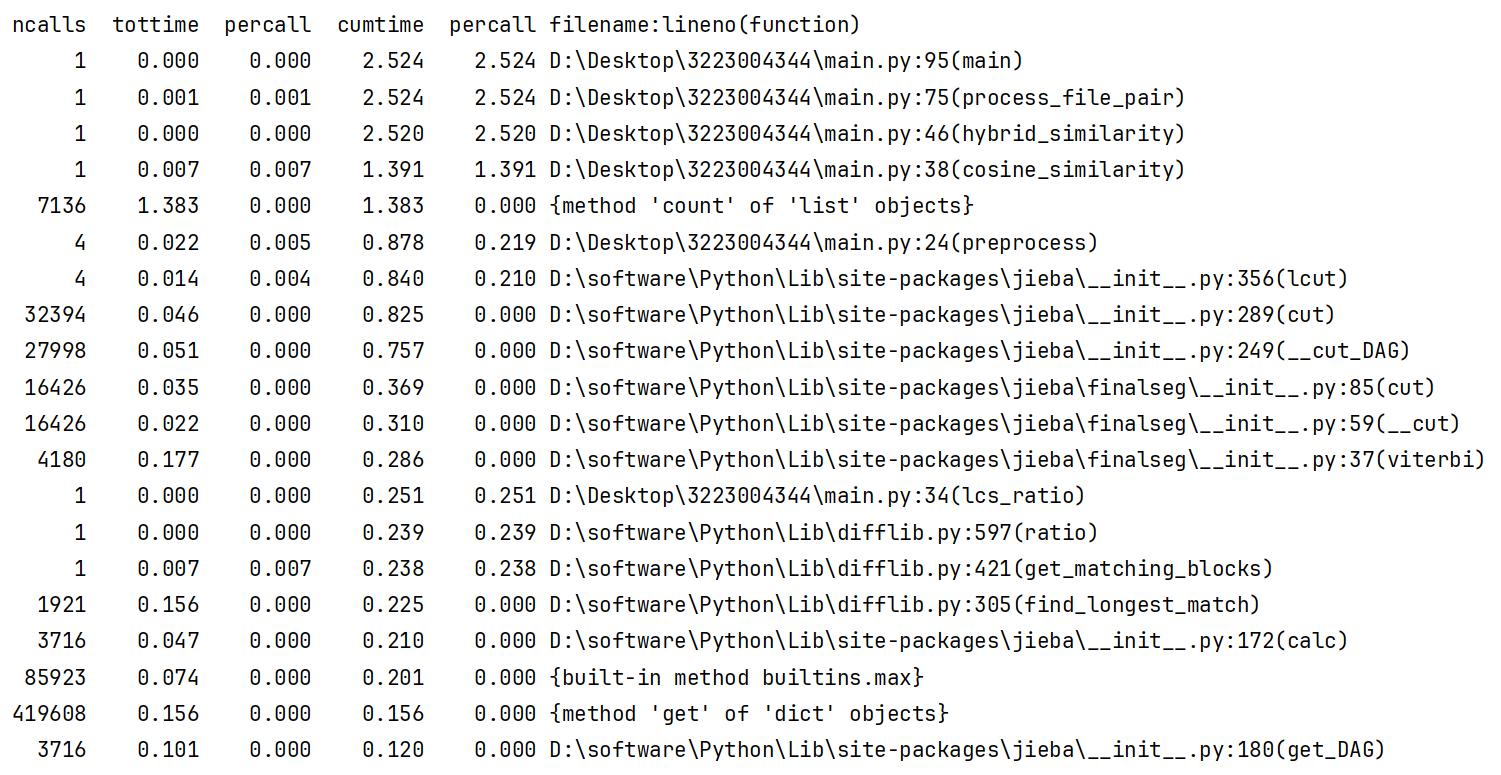
从 cProfile 输出看,程序中耗时较高的函数:
hybrid_similarity:累计耗时 2.52s,主要包含 LCS 和余弦相似度计算。cosine_similarity:累计耗时 1.39s,原始实现中使用list.count,导致上千次调用,每次都在遍历列表,复杂度高。jieba.lcut:累计耗时 0.84s,多次重复调用分词。SequenceMatcher相关函数 :lcs_ratio调用耗时 0.251s,用于最长公共子序列计算。preprocess:累计耗时 0.878s,包括停用词过滤和分词处理。
四、模块部分单元测试
单元测试覆盖率
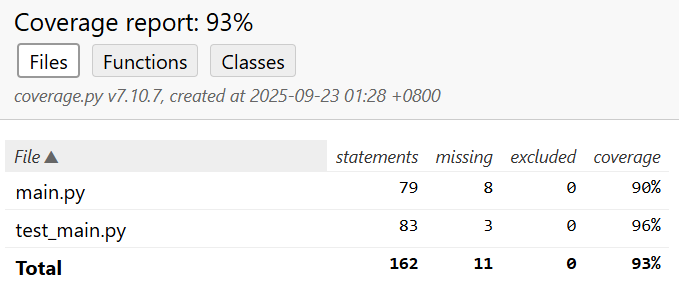
共 14 个测试用例:
TestFileExceptions: 1 ,TestTextSimilarity: 10 ,TestProcessFilePair: 2 ,TestMainFunction: 2
部分单元测试展示
TestFileExceptions
class TestFileExceptions(unittest.TestCase):
"""测试文件异常处理"""
def test_write_result_ioerror(self):
"""模拟 write_result 抛出 IOError"""
with patch("builtins.open", mock_open()) as m_open:
with patch("main.write_result", side_effect=IOError):
try:
process_file_pair("orig.txt", "plag.txt", "results")
except IOError:
self.fail("process_file_pair 不应抛出 IOError")
test_write_result_ioerror模拟write_result抛出IOError,验证process_file_pair能否在写入失败时不崩溃。- 使用
patch替换write_result,捕获异常后通过self.fail确保流程稳定,提升程序容错能力。
TestTextSimilarity
class TestTextSimilarity(unittest.TestCase):
"""测试文本处理及相似度函数"""
def setUp(self):
"""每个测试前创建临时文件"""
self.orig_file = "temp_orig.txt"
self.plag_file = "temp_plag.txt"
with open(self.orig_file, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write("今天我去了图书馆,看了一本书。")
with open(self.plag_file, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write("我今天去图书馆读书了。")
def tearDown(self):
"""每个测试后删除临时文件"""
for file in [self.orig_file, self.plag_file, "temp_result.txt"]:
if os.path.exists(file):
os.remove(file)
@patch("os.path.exists", return_value=True)
@patch("builtins.open", new_callable=mock_open, read_data="今天我去了图书馆")
def test_read_file_exists(self, mock_file, mock_exists):
"""测试文件读取:存在文件"""
content = read_file("temp.txt")
self.assertIn("图书馆", content)
@patch("os.path.exists", return_value=False)
def test_read_file_not_exists(self, mock_exists):
"""测试文件读取:不存在文件"""
content = read_file("not_exist.txt")
self.assertEqual(content, "")
def test_preprocess_with_stopwords(self):
tokens = preprocess("今天是一个好日子。", use_stopwords=True)
self.assertNotIn("今天", tokens)
def test_preprocess_without_stopwords(self):
tokens = preprocess("今天是一个好日子。", use_stopwords=False)
self.assertIn("今天", tokens)
def test_lcs_ratio_similarity(self):
ratio = lcs_ratio(["今天", "图书馆"], ["今天", "书店"])
self.assertGreaterEqual(ratio, 0.3)
def test_cosine_similarity_basic(self):
sim = cosine_similarity(["图书馆", "书"], ["图书馆", "阅读"])
self.assertGreater(sim, 0.0)
def test_hybrid_similarity_normal(self):
sim = hybrid_similarity("我去图书馆学习", "今天我去图书馆看书")
self.assertGreater(sim, 30.0)
def test_hybrid_similarity_empty(self):
sim = hybrid_similarity("", "")
self.assertEqual(sim, 0.0)
def test_hybrid_similarity_identical(self):
sim = hybrid_similarity("测试文本", "测试文本")
self.assertEqual(sim, 100.0)
test_read_file_exists使用mock_open和patch模拟文件存在的情况,验证read_file正确读取文件内容,并包含关键字“图书馆”。test_read_file_not_exists模拟文件不存在的分支,确保返回空字符串,覆盖文件不存在逻辑。test_preprocess_with_stopwords与test_preprocess_without_stopwords验证preprocess的停用词处理能力,测试停用词过滤与保留两种模式,保证文本处理结果正确,为相似度计算提供正确输入。test_lcs_ratio_similarity验证最长公共子序列(LCS)相似度计算,test_cosine_similarity_basic验证余弦相似度计算,两者提供相似度算法的基础功能测试。test_hybrid_similarity_normal测试正常文本的混合相似度,确保混合算法的合理性。test_hybrid_similarity_empty和test_hybrid_similarity_identical分别测试空文本和完全相同文本的边界情况,保证混合相似度函数在特殊场景下的稳定性。
TestProcessFilePair
class TestProcessFilePair(unittest.TestCase):
"""测试 process_file_pair 函数"""
@patch("main.write_result")
@patch("main.read_file", return_value="测试内容")
def test_process_file_pair_basic(self, mock_read, mock_write):
process_file_pair("orig.txt", "plag.txt", "results")
mock_read.assert_any_call("orig.txt")
mock_read.assert_any_call("plag.txt")
mock_write.assert_called_once()
@patch("main.read_file", return_value="")
@patch("main.write_result")
def test_process_file_pair_empty_file(self, mock_write, mock_read):
process_file_pair("orig.txt", "plag.txt", "results")
mock_write.assert_not_called() # 空文件不会写入结果
test_process_file_pair_basic模拟read_file返回有效文本,并通过patch检查read_file和write_result的调用情况,验证流程逻辑正确。test_process_file_pair_empty_file模拟空文件,确保在读取为空时不会调用write_result,覆盖空文件分支。
TestMainFunction
class TestMainFunction(unittest.TestCase):
"""测试 main() 两条分支"""
@patch("main.process_file_pair")
def test_main_single_file_branch(self, mock_process):
test_args = ["main.py", "orig.txt", "plag.txt", "results"]
with patch.object(sys, "argv", test_args):
main()
mock_process.assert_called_once()
@patch("main.process_file_pair")
def test_main_batch_branch(self, mock_process):
test_args = ["main.py"]
with patch.object(sys, "argv", test_args):
main()
# 批量处理列表长度为 6
self.assertEqual(mock_process.call_count, 6)
test_main_single_file_branch使用patch.object(sys, "argv")模拟命令行参数测试单文件处理分支,确保process_file_pair被调用一次。test_main_batch_branch测试批量处理分支,模拟未提供命令行参数,验证批量处理列表的长度和调用次数(6 次),覆盖main的两条主要执行路径。
| 功能模块 | 覆盖点/测试情况 |
|---|---|
| read_file | 文件存在、文件不存在、mock 读取 |
| preprocess | 停用词过滤、保留停用词 |
| lcs_ratio | 基本相似度计算 |
| cosine_similarity | 基本余弦相似度计算 |
| hybrid_similarity | 正常文本、空文本、相同文本 |
| write_result | 文件写入成功 |
| process_file_pair | 正常文本、空文件 |
| main | 单文件模式、批量模式 |
| 异常处理 | write_result 抛 IOError 时不崩溃 |
共计 14 个测试用例,涵盖正常流程、边界条件以及异常场景。测试使用 mock 避免依赖真实文件系统,结合 setUp/tearDown 确保数据隔离,保证测试可重复、快速、无副作用。每个函数的主要逻辑分支和 main 的不同执行分支均被触发,从而达到较高的代码覆盖率。
五、计算模块部分异常处理说明
在 main.py 的计算模块中,异常处理主要集中在以下几个环节,以保证程序在遇到文件或 I/O 错误时仍能稳定运行,不会中断批量处理流程。
1. 文件读取异常
函数 read_file(file_path) 负责读取文本内容,处理逻辑如下:
- 首先使用
os.path.exists(file_path)检查文件是否存在。 - 如果文件不存在,函数会打印提示信息
文件不存在: {file_path}, 已跳过并返回空字符串""。 - 调用方在接收到空字符串后会跳过该文件,不会继续执行相似度计算。
覆盖场景: - 文件存在:正常读取文本。
- 文件不存在:打印提示,返回空字符串,不抛出异常。
这种处理方式确保了批量处理时,缺失单个文件不会影响整个计算流程。
2. 文件写入异常
函数 write_result(file_path, orig_path, plag_path, similarity) 用于将相似度结果写入文件:
- 在
process_file_pair内部调用write_result时使用try-except块捕获IOError:try: write_result(ans_file, orig_path, plag_path, similarity) print(f"原文: {orig_path} | 抄袭版: {plag_path} | 重复率: {similarity}% | 输出: {ans_file}") except IOError as e: print(f"写入文件失败")
当写入失败时,仅打印 写入文件失败,不会让程序中断,也不会抛出异常到外层。
覆盖场景:
- 写入成功:结果文件生成,打印输出信息。
- 写入失败(例如权限不足、目录不存在等):捕获异常并打印提示,程序继续执行下一组文件。
3. 空文件或空文本处理
在 process_file_pair 中,读取原文或抄袭文本为空时:
if not orig_text or not plag_text:
print(f"跳过文件组: {orig_path} | {plag_path}")
return
空文本不会进入相似度计算,也不会尝试写入结果。这种设计防止了在空文件或空字符串输入下出现除零错误或其他异常。
覆盖场景:
空原文或空抄袭文本:打印提示并跳过。
非空文本:正常计算相似度并写入文件。
4.分词优化与异常安全
tokenize(text) 对文本进行一次性分词,返回去停用词分词和完整分词列表:
分词过程中,任何空字符串或仅含停用词的文本会返回空列表。
在 hybrid_similarity 中,如果去停用词的分词结果为空,则直接返回 0.0,避免 LCS 或余弦相似度计算抛出异常。
if not orig_tokens_stop or not plag_tokens_stop:
return 0.0
保证在极端文本(空文本或仅停用词)情况下,混合相似度函数不会崩溃。
六、查重结果
单组查重
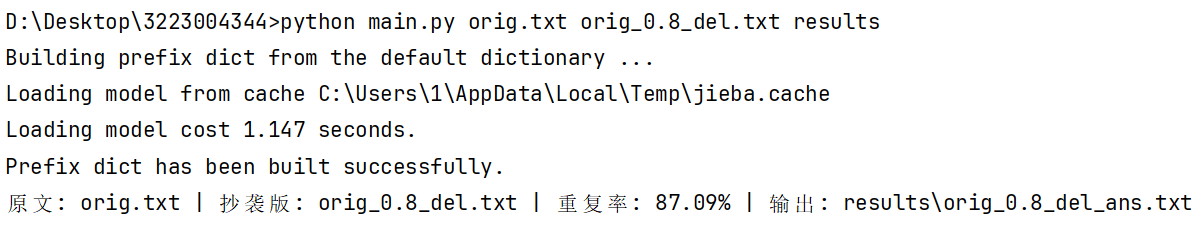
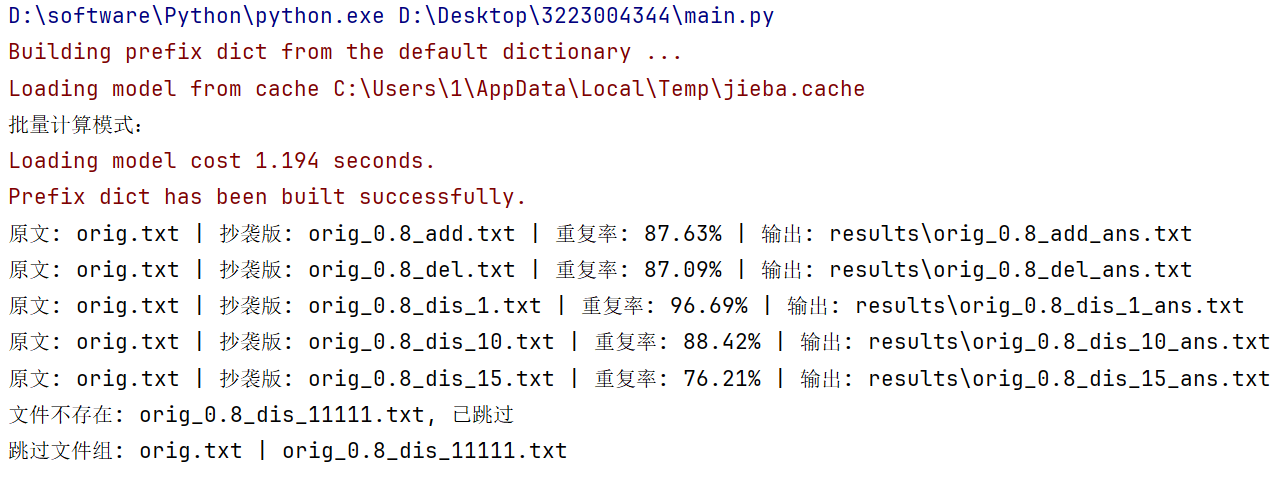
多组查重



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号