NCHUWXW第一次大作业总结
NCHUWXW第一次大作业总结
第一个博客 ^_^
目录
1. 开始学JAVA的初始
2. 设计与分析:总结三次题目集的知识点、题量、难度等情况,重点对题目的提交源码进行分析
3. 采坑心得:对源码的提交过程中出现的问题及心得进行总结
4. 总结:对本阶段三次题目集的综合性总结,学到了什么,哪些地方需要进一步学习及研究,对教师、课程、作业、实验、课上及课下组织方式等方面的改进建议及意见。
一 . 开始学JAVA的初始
1. 这个学期才开始学习java,因为开始三小了所以也学了一点Python,也了解了一点面向对象的思想,我们那个三小项目是检测口罩,这个必须要用面向对象,如果面向过程的话,那么断开一个点的话其他的东西就完全废了,其次还要用树莓派虚拟机来搞所以面向对象是完全必要的。
2. 一开始那些类和方法完全不懂就是无脑去写,用面向过程的想法来用JAVA的语法来写,所以完全就是管中窥豹了,后面学会调用和上课的时间就明白了。其实就是方法,结构体,只不过在面向过程里面,结构体是一个总的一些对象,然后在主函数去用它,但是这个类 就不一样,将每个要干的分开来,然后在主函数里去拼成最终的机器。所以面向对象是很必要的,因为在一个团队里,每个程序员写的都是不同的功能,当你写的东西去动了主函数的话,就会非常麻烦
3.尽量别抄别人的代码,因为在java里调试和错误都是很严格的,不跟C一样错了也能运行,调试简单,分开简单。抄要抄思想和别人新的东西,变成自己的,抄也有技巧的。因为学计算机一开始就是学外国的,我们肯定能反超,但是现在我们连一伙的都没有学懂,怎么 去学别的呢。
4.像以后还有多态和继承就在下一次的博客里去写吧(也有可能放鸽子)
二. 设计与分析:总结三次题目集的知识点、题量、难度等情况,重点对题目的提交源码进行分析
1.面向对象程序设计-2021-物联网-1
总结:这个知识点没啥可说的,基本上就是算法分析和麻烦,特别是税率,基本上就是if else语句的运用和回忆了一下冒泡排序,还有在java里面用数组的特殊方法,下面重点讲解,还有一些小bug,可以说一说。
知识点 1 题量 4 难度 3 (满分5)
(1.计算两个数的和) 这个就不要讲了吧它提供的正常规范格式就是这个代码,不必多说了吧。直接上代码,输入每个语言不一样具体可以去看看书
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Liangshujia {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
Scanner s=new Scanner(System.in);
int m=s.nextInt();
int n=s.nextInt();
int num=m+n;
System.out.print(num);
}
}
(2.电话键盘字母数字转换)这个主要不能输入单个字符要输入一个字符串然后用charAT来取第一个字符然后进行if else判断。输出的话要用+来连接两个不一样的输出,否则会输出错误
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner str=new Scanner(System.in);
String shuru=str.nextLine();
char c=shuru.charAt(0);
if((c>='a'&&c<='c')||(c>='A'&&c<='C'))
System.out.println(2);
else if((c>='d'&&c<='f')||(c>='D'&&c<='F'))
System.out.println(3);
else if((c>='g'&&c<='i')||(c>='G'&&c<='I'))
System.out.println(4);
else if((c>='j'&&c<='l')||(c>='J'&&c<='L'))
System.out.println(5);
else if((c>='m'&&c<='o')||(c>='M'&&c<='O'))
System.out.println(6);
else if((c>='p'&&c<='s')||(c>='P'&&c<='S'))
System.out.println(7);
else if((c>='T'&&c<='V')||(c>='t'&&c<='v'))
System.out.println(8);
else if((c>='w'&&c<='z')||(c>='W'&&c<='Z'))
System.out.println(9);
else
System.out.println(c+" is an invalid input");
}
}
(3.成绩分级管理)这个就直接上
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
Scanner n=new Scanner(System.in);
int num=n.nextInt();
if(num<60)
System.out.println("E");
else if(num>=60&&num<70)
System.out.println("D");
else if(num>=70&&num<80)
System.out.println("C");
else if(num>=80&&num<90)
System.out.println("B");
else if(num>=90)
System.out.println("A");
}
}
(4.计算税率)这个就是无语的题,就是死算,和算法,然后就是if else
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
int a = input.nextInt();
double b = input.nextDouble();
double s;
if(a!=1&&a!=2&&a!=3&&a!=0||b<0)
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
else if(a==0)//Single
{
if(b>=0&&b<=8350)
{
s=b*0.1;
System.out.print(s);
}
else if(b>8350&&b<=33950)
{
s=8350*0.1+(b-8350)*0.15;
System.out.print(s);
}
else if(b>33950&&b<=82250)
{
s=8350*0.1+(33950-8350)*0.15+(b-33950)*0.25;
System.out.print(s);
}
else if(b>82250&&b<=171550)
{
s=8350*0.1+(33950-8350)*0.15+(82250-33950)*0.25+(b-82250)*0.28;
System.out.print(s);
}
else if(b>171550&&b<=372950)
{
s=8350*0.1+(33950-8350)*0.15+(82250-33950)*0.25+(171550-82250)*0.28+(b-171550)*0.33;
System.out.print(s);
}
else if(b>372950)
{
s=835+(33950-8350)*0.15+(82250-33950)*0.25+(171550-82250)*0.28+(372950-171550)*0.33+(b-372950)*0.35;
System.out.print(s);
}
}
else if(a==1)//Married Filling Jointly or Qualified Widoe(er)
{
if(b>=0&&b<=16700)
{
s=b*0.1;
System.out.print(s);
}
else if(b>16700&&b<=67900)
{
s=16700*0.1+(b-16700)*0.15;
System.out.print(s);
}
else if(b>67900&&b<=137050)
{
s=16700*0.1+(67900-16700)*0.15+(b-67900)*0.25;
System.out.print(s);
}
else if(b>137050&&b<=208850)
{
s=16700*0.1+(67900-16700)*0.15+(137050-67900)*0.25+(b-137050)*0.28;
System.out.print(s);
}
else if(b>208850&&b<=372950)
{
s=16700*0.1+(67900-16700)*0.15+(137050-67900)*0.25+(208850-137050)*0.28+(b-208850)*0.33;
System.out.print(s);
}
else if(b>372950)
{
s=1670+(67900-16700)*0.15+(137050-67900)*0.25+(208850-137050)*0.28+(372950-208850)*0.33+(b-372950)*0.35;
System.out.print(s);
}
}
else if(a==2) //Married Filling Separately
{
if(b>=0&&b<=8350)
{
s=b*0.1;
System.out.print(s);
}
else if(b>8350&&b<=33950)
{
s=8350*0.1+(b-8350)*0.15;
System.out.print(s);
}
else if(b>33950&&b<=68525)
{
s=8350*0.1+(33950-8350)*0.15+(b-33950)*0.25;
System.out.print(s);
}
else if(b>=68525&&b<=104425)
{
s=8350*0.1+(33950-8350)*0.15+(68525-33950)*0.25+(b-68525)*0.28;
System.out.print(s);
}
else if(b>104425&&b<=186475)
{
s=8350*0.1+(33950-8350)*0.15+(68525-33950)*0.25+(104425-68525)*0.28+(b-104425)*0.33;
System.out.print(s);
}
else if(b>186475)
{
s=835+(33950-8350)*0.15+(68525-33950)*0.25+(104425-68525)*0.28+(186475-104425)*0.33+(b-186475)*0.35;
System.out.print(s);
}
}
else if(a==3)//Head of Household
{
if(b>=0&&b<=11950)
{
s=b*0.1;
System.out.print(s);
}
else if(b>11950&&b<=45500)
{
s=11950*0.1+(b-11950)*0.15;
System.out.print(s);
}
else if(b>45500&&b<=117450)
{
s=11950*0.1+(45500-11950)*0.15+(b-45500)*0.25;
System.out.print(s);
}
else if(b>117450&&b<=190200)
{
s=11950*0.1+(45500-11950)*0.15+(117450-45500)*0.25+(b-117450)*0.28;
System.out.print(s);
}
else if(b>190200&&b<=372950)
{
s=11950*0.1+(45500-11950)*0.15+(117450-45500)*0.25+(190200-117450)*0.28+(b-190200)*0.33;
System.out.print(s);
}
else if(b>372950)
{
s=1195+(45500-11950)*0.15+(117450-45500)*0.25+(190200-117450)*0.28+(372950-190200)*0.33+(b-372950)*0.35;
System.out.print(s);
}
}
}
}
(5.计算钱币 )这个就是原来C语言里的算法了,就是最简单的取每个数字,学一下算法
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
double sum=input.nextDouble();
double y[]=new double[10];
System.out.println((int)(sum/10)+"张十元");
y[0]=sum%10;
System.out.println((int)(y[0]/5)+"张五元");
y[1]=y[0]%5;
System.out.println((int)(y[1]/1)+"张一元");
y[2]=y[1]%1;
System.out.println((int)(y[2]/0.5)+"个五角");
y[3]=y[2]%0.5;
System.out.println((int)(y[3]/0.1)+"个一角");
y[4]=y[3]%0.1;
System.out.println((int)(y[4]/0.02)+"个贰分");
y[5]=y[4]%0.02;
System.out.println((int)(y[5]/0.01)+"个壹分");
}
}
(6.使用一维数组求平均值)循环输入数组里的值然后求平均值
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
double sum;
int[] y=new int [5];
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
y[i]=input.nextInt();
}
sum=(y[0]+y[1]+y[2]+y[3]+y[4]);
System.out.println(sum/5);
}
}
(7.对多个整数进行排序) 输入数组继续,然后用C的冒泡排序
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=input.nextInt();
int a[]=new int [n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
a[i]=input.nextInt();
}
int t=0;
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n-i-1;j++)
{
if(a[j]>a[j+1])
{
int temp=a[j];
a[j]=a[j+1];
a[j+1]=temp;
}
}
}
System.out.print("The sorted numbers are:");
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
System.out.print(a[i]+" ");
}
}
}
(8.判断三角形类型) 这个就是if else的判定,不过要注意一个细节,就是在判断直角三角形用勾股定理的时候,不能用=因为计算机没有无理数去匹配例如1+1=2,这时候根号2就找不到了,所以并没有用,要小于0.001
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); double a,b,c,temp; a=input.nextDouble();b=input.nextDouble();c=input.nextDouble(); if(a>b) { temp=a;a=b;b=temp; } if(a>c) { temp=a;a=c;c=temp; } if(b>c) { temp=b;b=c;c=temp; }//上面就是简单排个序 double sum; sum=a*a+b*b-c*c;//计算勾股定理的值 if(a>=1&&a<=200&&b>=1&&b<=200&&c>=1&&c<=200) { if(a+b>c) { if(a==b&&b==c&&a==c) System.out.println("Equilateral triangle"); else if((sum<0.000001)&&(a==b)) System.out.println("Isosceles right-angled triangle"); else if((a==b&&a!=c)||(a==c&&b!=a)||(b==c&&a!=c)) System.out.println("Isosceles triangle"); else if(a*a+b*b-c*c<0.000001) System.out.println("Right-angled triangle"); else System.out.println("General triangle"); } else System.out.println("Not a triangle"); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } }
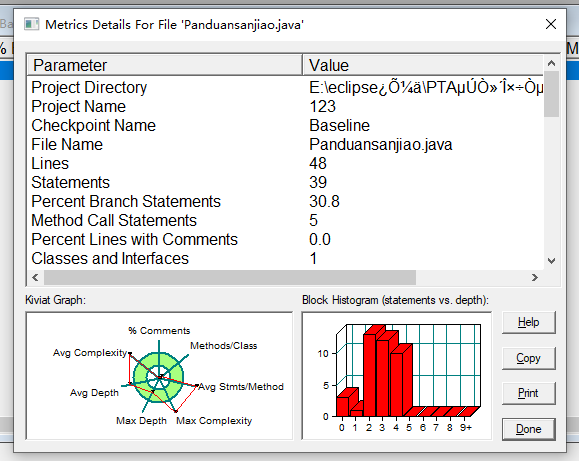
这个重点就是看复杂度,这个直接最大的复杂度调到23,就离谱,需要用class来改变了否则就是复杂度爆棚
2.面向对象程序设计-2021-物联网-2
总结: 前面三道题就不说了,其实后面就是前面的东西了没有必要的吧,。这次开始就有类的比较了,学习类和调用它的方法,来写出这个题,所以说知识点还是OK的,难度也没有太高,一只调试就可以出来了。
知识点 : 3 题量:2 难度:2
(1.求下一天)啊一开始就要学会拆分,不然还是面向过程,学了跟没学似的,把判断闰年,日期合法,下一天,都写到其他方法里面去,然后在主函数里面调用他们,下面第一个写好主函数里要干啥,然后没有的就可以直接创建出来,不需要那么麻烦了,这边默认你搞好了,直接开讲那三个方法调用
判断闰年.首先传入一个参数year,这个不跟C一样要在开头写一个,直接在java类里面直接创建就行了,不需要再在开头写一个函数名字,。好写一个bool的方法因为只是判断是不是闰年,所以返回一个bool的真假就好了,闰年判断就不讲了哈,忘了就百度,
private static boolean runnian(int year)
{
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
boolean runnian=true;
if((year%4==0&&year%100!=0)||(year%400==0))
return runnian;
else
return false;
}
日期合法.发现了吧这个只能用check去返回值否则则会报错的哦,然后这个要注意下闰年多一天,所以在创建日期数组的时候要注意稍稍改变一下,然后日期合法就出来了,
public static boolean check(int year,int month,int day)
{
boolean check=true;
int a[]=new int[]{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
if(runnian(year)==false)
a[2]=28;
if(year>=1820&&year<=2020&&month>0&&month<=12&&day<=a[month]&&day>0)
return check;
else
return false;
}
判断下一天.首先需要日期合法,合法在进行下一步操作,首先年份跨年的时候就要+1变1,其次就是正常还有月份夸的时候要注意一下,置一还有+1
public static void numOfDays(int year, int month, int day)
{
int[] a=new int[]{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int d=0,m=0;
if(runnian(year)==false)
a[2] = 28;
if(check(year,month,day))
{
if(month==12)
{
if(day==a[month])
{
year = year+1;
m = 1;
d=1;
}
else
{
m=month;
d =day +1;
}
}
else
{
if(day==a[month])
{
m = month + 1;
d = 1;
}
else
{
m=month;
d = day+1;
}
}
System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+m+"-"+d);
}
else
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
好了直接全代码了,main里面创建三个year,day,month,然后检查和直接调用天数
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
int year=input.nextInt();
int month=input.nextInt();
int day=input.nextInt();
if(check(year,month,day)==false)
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
else
{
numOfDays(year,month,day);
}
}
public static boolean check(int year,int month,int day)
{
boolean check=true;
int a[]=new int[]{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
if(runnian(year)==false)
a[2]=28;
if(year>=1820&&year<=2020&&month>0&&month<=12&&day<=a[month]&&day>0)
return check;
else
return false;
}
private static boolean runnian(int year)
{
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
boolean runnian=true;
if((year%4==0&&year%100!=0)||(year%400==0))
return runnian;
else
return false;
}
public static void numOfDays(int year, int month, int day)
{
int[] a=new int[]{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int d=0,m=0;
if(runnian(year)==false)
a[2] = 28;
if(check(year,month,day))
{
if(month==12)
{
if(day==a[month])
{
year = year+1;
m = 1;
d=1;
}
else
{
m=month;
d =day +1;
}
}
else
{
if(day==a[month])
{
m = month + 1;
d = 1;
}
else
{
m=month;
d = day+1;
}
}
System.out.println("Next date is:"+year+"-"+m+"-"+d);
}
else
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}

发现没有,这个用了方法之后最大的圈复杂度直接就变成10了,完全就很爽了,所以圈复杂度还是有必要的,因为we are 伐木累。
(2.求前N天)
这个哈跟上面一样的一个下一天就是前N天,判断闰年和日期合法就不搞了直接看前N天
前N天首先哈要注意这个N他会有 负数输入的情况所以要讨论,那我就讲一个正的,负的你们自己去想下哈,首先跟上面一样的,month要注意那这个就是1的时候了,首先看会不会跳,跳的话,月份减一,依旧这个月天数去减N,然后在用上一个月的去减这个值,没有的话,直接就day-N就好了,那1月的话就要注意跳年了,计算情况要自己想一下了,,这个应该很简单的吧
public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day,int n)
{
int[] a=new int[]{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int d=0,m=0,b;
if(!isLeapYear(year))
a[2] = 28;
if(checkInputValidity(year,month,day,n))
{
if(n>0)
{
if(month!=1)
{
if(n<day)
{
m=month;
d=day-n;
}
else
{
b=n-day;
m=month-1;
d=a[month-1]-b;
}
}
else
{
if(n<day)
{
m=month;
d=day-n;
}
else
{
b=n-day;
year=year-1;
m=12;
d=31-b;
}
}
System.out.println(n+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+m+"-"+d);
}
else
{
n=-n;
if(month!=12)
{
if(n+day<a[month])
{
m=month;
d=day+n;
}
else
{
b=n+day;
m=month+1;
d=b-a[month];
}
}
else
{
if(n+day<a[month])
{
m=month;
d=day+n;
}
else
{
b=n+day;
year=year+1;
m=1;
d=b-a[month];
}
}
n=-n;
System.out.println(n+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+m+"-"+d);
}
}
else
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
好了,听懂扣个1,直接上代码了,这个没有输入的考虑情况,直接就好了
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
//主函数
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner x = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = x.nextInt();
int month = x.nextInt();
int day = x.nextInt();
int n=x.nextInt();
nextDate(year,month,day,n);
}
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) {
boolean isLeapYear;
isLeapYear = (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 !=0 )||year % 400 == 0;
return isLeapYear;
}
public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day,int n) {
boolean checkInputValidity;
int[] a=new int[]{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
if(!isLeapYear(year))
a[2] = 28;
checkInputValidity = (year>=1820&&year<=2020&&month>0&&month<=12&&day<=a[month]&&day>0&&n<=10&&n>=-10);
return checkInputValidity;
}
public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day,int n)
{
int[] a=new int[]{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int d=0,m=0,b;
if(!isLeapYear(year))
a[2] = 28;
if(checkInputValidity(year,month,day,n))
{
if(n>0)
{
if(month!=1)
{
if(n<day)
{
m=month;
d=day-n;
}
else
{
b=n-day;
m=month-1;
d=a[month-1]-b;
}
}
else
{
if(n<day)
{
m=month;
d=day-n;
}
else
{
b=n-day;
year=year-1;
m=12;
d=31-b;
}
}
System.out.println(n+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+m+"-"+d);
}
else
{
n=-n;
if(month!=12)
{
if(n+day<a[month])
{
m=month;
d=day+n;
}
else
{
b=n+day;
m=month+1;
d=b-a[month];
}
}
else
{
if(n+day<a[month])
{
m=month;
d=day+n;
}
else
{
b=n+day;
year=year+1;
m=1;
d=b-a[month];
}
}
n=-n;
System.out.println(n+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+m+"-"+d);
}
}
else
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
这个圈复杂就不看了,应该可以自己想吧,这个比上面情况多一点,自然复杂度就高了。
3.面向对象程序设计-2021-物联网-3
总结:前面两题很简单最后的难一点,依旧是关于类思想的写法,但是出了一个正则表达式,我觉得大家可以去由浅入深的学习一下,这个东西很方便,以后绝对用的到,而不是用数据结构栈的思想来写这个那是在太简单了把,就是代码Ctrl c ctrl v了,那实在贻笑大方了,不是说不行,但是很慢了,复杂度不知道会有多少。
知识点:4 题量:2 难度“4
(1.定义日期类)这个就不说了哈更上面一样你们就自己写下吧哈,不上主代码了,加一点输出就好了,就是前面复制粘贴,算了还是上吧。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
int year=input.nextInt();
int month=input.nextInt();
int day=input.nextInt();
if(check(year,month,day)==false)
System.out.println("Date Format is Wrong");
else
{
numOfDays(year,month,day);
}
}
public static boolean check(int year,int month,int day)
{
boolean check=true;
int a[]=new int[]{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
if(runnian(year)==false)
a[2]=28;
if(year>=1900&&year<=2000&&month>0&&month<=12&&day<=a[month]&&day>0)
return check;
else
return false;
}
private static boolean runnian(int year)
{
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
boolean runnian=true;
if((year%4==0&&year%100!=0)||(year%400==0))
return runnian;
else
return false;
}
public static void numOfDays(int year, int month, int day)
{
int[] a=new int[]{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int d=0,m=0;
if(runnian(year)==false)
a[2] = 28;
if(check(year,month,day))
{
if(month==12) {
if(day==a[month]) {
year = year+1;
m = 1;
d=1;
}
else{
m=month;
d =day +1;
}
}
else {
if(day==a[month]) {
m = month + 1;
d = 1;
}
else{
m=month;
d = day+1;
}
}
System.out.println("Next day is:"+year+"-"+m+"-"+d);
}
else
System.out.println("Date Format is Wrong");
}
}
复杂度还是一样的哈,具体为啥想一想就知道了,就改了print会有啥改变呢。 各位同学是还是不是?
(2.一元多项式求导)首先是正则表达式了,因为这个是重点!!!
正则表达式
1.replace检测空格换成空的在java里就是//s为空格,替换成“”
2."([+-]?[1-9][0-9]*)?" + "(\\*?[+-]?x(\\^([+-]?[1-9][0-9]*))?)?"这个就是匹配单个的表达式,是不是直接懵B,我先来直接讲解一下吧,第一个是判断+-号应该通俗吧,后面有?是什么意思呢就是后面这一个数有没有都无所谓,有就是两位数没有就是一位数,[1-9][0-9]就是两位数字十位上【1-9】个位上【0-9】对没错,这个只能搞两位数,后面这个*相当于一个无所谓的,没有他就是错的,?前面说了是后面有没有都无所谓所以这里相当于一个结束符,java里的+就是连接大家都知道吧,后面的话大家应该知道了吧可以自己去翻译一下,那下面再来讲一下正则表达式先来这个代码讲解
好了后面就是匹配了,把express跟匹配wholeexpress,然后在返回,错了就直接输出错误,对了就进行计算,
那么计算函数里
Pattern p=Pattern.compile(termExpress);
Matcher m=p.matcher(express);
这两句是先把匹配规则制定下来,然后用m把他们一个个匹配好的存储到内存池里然后由下面去调用
下面那些M.GROUP(1)和M.GROUP(4)然后进行单个的求导运算否则直接一股脑那太……,用BigInteger变成一个数字,不为空,然后来看-1还是1,后面就是指数来直接运算了来一个例子输出讲解,(rat.equals(new BigInteger("-1"))?"-x":(rat+"*x")三项运算符来看如果是-1的话就输出-x,不是就输出rat+x,那后面就懂了吧。
好了直接上了
import java.beans.Expression;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
String inputexpress=input.nextLine();
String express=inputexpress.replaceAll("\\s", "");
Solve majorexpress=new Solve();
majorexpress.Express(express);
if(majorexpress.check())
{
majorexpress.calculator();
}
else
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
int a[]=new int[100];
int b[]=new int[100];
int c[]=new int[100];
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
c[i]=a[i];
}
for(int j=0;j<10;j++)
{
c[1]=b[j];
}
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<9-i-1;j++)
{
if(c[j]>c[j+1])
{
int temp=c[j];
c[j]=c[j+1];
c[j+1]=temp;
}
}
}
}
}
class Solve
{
private String express;
private String index;
private String ratio;
private BigInteger ind;
private BigInteger rat;
public void Express(String express)
{
this.express=express;
}
String termExpress = "([+-]?[1-9][0-9]*)?" + "(\\*?[+-]?x(\\^([+-]?[1-9][0-9]*))?)?";
String wholeExpress = "(([+-]?[1-9][0-9]*)?" + "(\\*?[+-]?x(\\^([+-]?[1-9][0-9]*))?)?)+";
String constNum = "[+-]?[0-9]+";
public boolean check()
{
return Pattern.matches(wholeExpress, express);
}
public void calculator()
{
if(Pattern.matches(constNum,express))
{
System.out.println("0");
System.exit(0);
}
Pattern p=Pattern.compile(termExpress);
Matcher m=p.matcher(express);//这两句是先把匹配规则制定下来,然后用m把他们一个个匹配好的存储到内存池里然后由下面去调用
int flag=0;
while(m.find())
{
ratio=m.group(1);
index=m.group(4);
if(ratio!=null)
{
rat=new BigInteger(ratio);
if (m.group(2)!=null&&m.group(2).startsWith("-"))
{
rat=BigInteger.valueOf(-1);
}
else if (m.group(2)!=null&&m.group(2).startsWith("+"))
{
rat=BigInteger.valueOf(1);
}
}
else
{
rat=BigInteger.valueOf(1);
if (m.group()!=null&&m.group().startsWith("-"))
{
rat=BigInteger.valueOf(-1);
}
else if (m.group()!=null&&m.group().startsWith("+"))
{
rat=BigInteger.valueOf(1);
}
}
if(index!=null)
{
ind=new BigInteger(index);
rat=rat.multiply(ind);
ind=ind.subtract(new BigInteger("1"));
if(rat.compareTo(new BigInteger("0"))>0&&flag==1)
{
System.out.print("+"+(rat.equals(new BigInteger("-1"))?"-x":(rat+"*x"))+(ind.equals(new BigInteger("1"))?"":("^"+ind)));
}
else
{
flag = 1;
System.out.print((rat.equals(new BigInteger("-1"))?"-x":(rat+"*x"))+(ind.equals(new BigInteger("1"))?"":("^"+ind)));
}
}
else if(m.group(2)!=null)
{
if(flag==1&&rat.compareTo(new BigInteger("0"))>0)
System.out.print(rat);
else
{
flag=1;
System.out.print(rat);
}
}
}
}
}
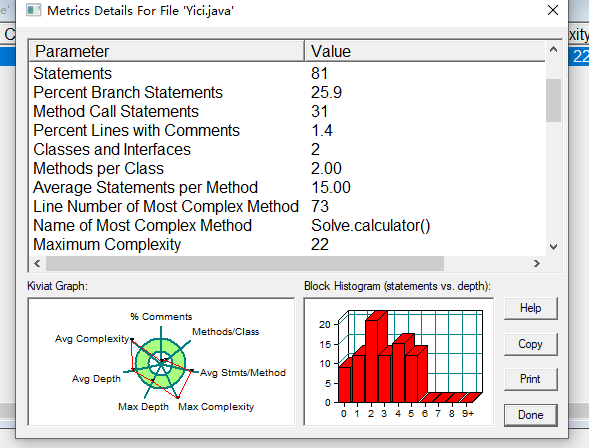
看这个就比较大了最大的也就22,其实还好了,if和else还是太多了,需要在强化一下。
正则表达式
正则表达式 – 教程 | 菜鸟教程 (runoob.com)
大家可以去看下这个网站讲解,我就来搞几个例子吧
EG.First
/*我我...我我...我我我我...要要要要...要要要要...
学学学学学...学学编编...编编编编..编..编...程程
...程程程——>我要学编程*/
public class RegexTest
{
public static void main(String[] args){
test();
}
/*
* 1. 治疗口吃:我我...我我...我我我我...要要要要...要要要要...学学学学学...学学编编...编编编编..编..编...程程...程程程
*/
/*
* 1. 治口吃
*/
public static void test(){
String str = "我我...我我...我我我我...要要要要...要要要要...学学学学学...学学编编...编编编编..编..编...程程...程程程";
//1. 将字符串中.去掉,用替换。
str = str.replaceAll("\\.+","");
//2. 替换叠词
str = str.replaceAll("(.)\\1+","$1");
System.out.println(str);
}
}
EG.Second
import java.util.TreeSet;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class RegexTest
{
public static void main(String[] args){
test();
}
/*
* ip地址排序。
* 192.168.10.34 127.0.0.1 3.3.3.3 105.70.11.55
*/
public static void test(){
String ip_str = "192.168.10.34 127.0.0.1 3.3.3.3 105.70.11.55";
//1. 为了让ip可以按照字符串顺序比较,只要让ip的每一段的位数相同。
//所以,补零,按照每一位所需最多0进行补充,每一段都加两个0。
ip_str = ip_str.replaceAll("(\\d+)","00$1");
System.out.println(ip_str);
//然后每一段保留数字3位。
ip_str = ip_str.replaceAll("0*(\\d{3})","$1");
System.out.println(ip_str);
//1. 将ip地址切出。
String[] ips = ip_str.split(" +");
TreeSet<String> ts = new TreeSet<String>();
for(String ip : ips){
ts.add(ip);
}
for(String ip : ts){
System.out.println(ip.replaceAll("0*(\\d+)","$1"));
}
}
}
这个正则有很多东西的,可以去买本书看看。
三. 采坑心得:对源码的提交过程中出现的问题及心得进行总结
那这个首先第一个就是三角的问题,会没有根号2这个值出现,其次我想讲下第三个求星期几,有一个公式大家可以去学一下,一下就出来了,但要注意的哈,就是1月2月的时候算去年的13月14月,后面几个就没有问题哈,基本上就是类好了就好了,因为这几个题都是第三题延伸的,那就最后一个表达式了,它最后一个输入是有问题的,当输出系数的时候他会没有前面的+,所以大家可以特殊的搞一下,心得就是类太好了,以后大作业那是必须要搞类了,否则那可太难了,牵一发而动全身的感觉太不好了。
四. 总结:对本阶段三次题目集的综合性总结,学到了什么,哪些地方需要进一步学习及研究,对教师、课程、作业、实验、课上及课下组织方式等方面的改进建议及意见。
学到了类,题目和知识点,要深究以后面试的话一问三不知那就太尴尬了,课上作业少一点时间吧,多讲解一下,作业很好,课程这样上很好,非常舒服。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号