SpringCloud-Netflix( GateWay)
SpringCloud-Netflix(GateWay)
We found that after the introduction of microservices, there are a series of problems, such as the front-end passing a request and carrying the token to the back-end, and each microservice needs to analyze and authenticate the token. Sometimes we need to process the response data of the microservice and the data passed by the request, so we may write the same code in multiple microservices. Then we can do these things uniformly in the gateway (rate limiting, caching, security, routing, etc.)。
Outline of the GateWay
Request process: When a request is delivered, the request is routed and matched with an assertion, and if it is matched, it is then filtered through the filter and forwarded to the relevant service provider.Spring Cloud GatewayThe goal is to replace ZUUL, which not only provides a unified routing mode, but also provides basic gateway functions based on the filter chain, such as security, monitoring/burial, and current limiting. There are three important parts that we need to pay attention to:
- [ route]: is equivalent to the location in nginx (a route contains a predicate and filter).
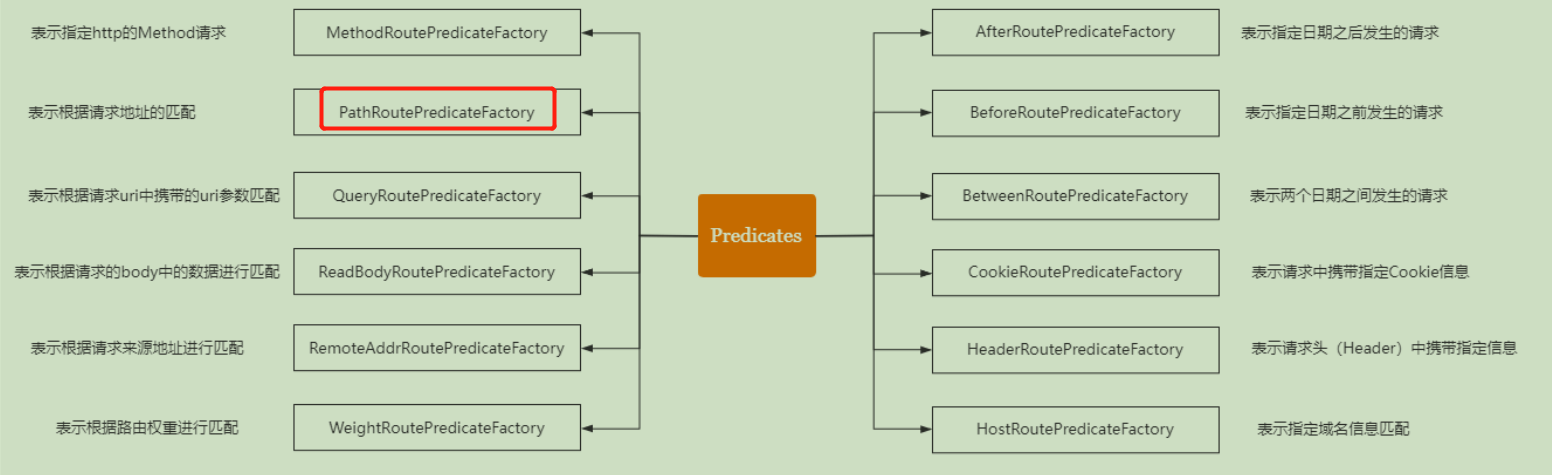
- [ assertion (Predicate)]: indicates whether to match the configured predicate of the current request. If there is a match, you will be redirected to the corresponding URI.
- Related configurations:(https://docs.spring.io/spring-cloud-gateway/docs/current/reference/html/#gateway-request-predicates-factories)
- 【Filter)】:Filters can modify requests or responses before/after they have been processed
Usage of the Gateway
【predicate】:Our requests are intercepted and routed to the path we specify.
引入gateway的pom,And because we want to throttle the rate, we also introduce the Podam of Redis。
![]() View Code
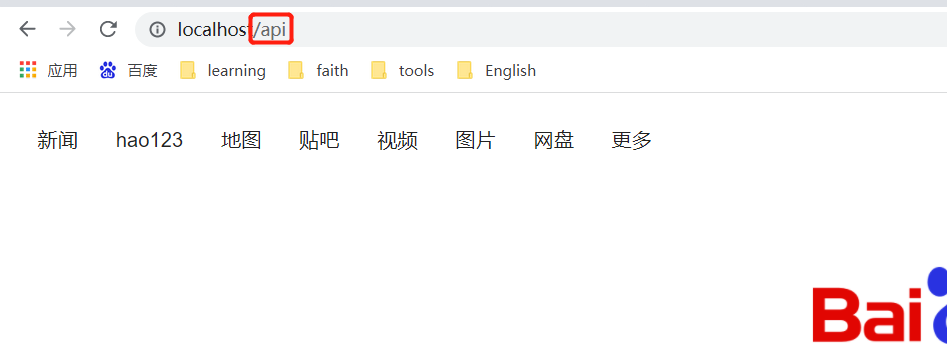
View Code<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis- reactive</artifactId> </dependency>我们首先配置一个实例,在predicates中我们配置拦截路径 ,所有请求带有api的都会走我们的程序,并且我们把他路由到baidu的首页中。其中的【StripPrefix】指的是转发请求的时候,去除我们第一个关键字,这里既是【api】
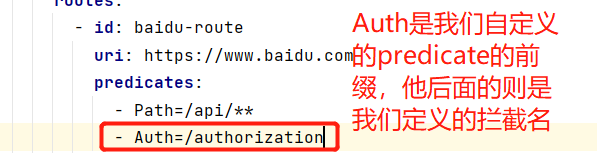
![]() View Codespring: application: name: glenmall-gateway cloud: gateway: routes: - id: baidu-route uri: https://www.baidu.com predicates: - Path=/api/** - Auth=/authorization filters: - StripPrefix=1
View Codespring: application: name: glenmall-gateway cloud: gateway: routes: - id: baidu-route uri: https://www.baidu.com predicates: - Path=/api/** - Auth=/authorization filters: - StripPrefix=1
同时我们可以自定义自己的Predicate,我们在配置文件中写的Path是他们内置的一个名为【PathRoutePredicateFactory】的predicate
创建自己的predicate,必须继承AbstractRoutePredicateFactory,并且重写他的apply#
![]() View Code@Component //请求中包含【authorization】则走这个 public class AuthRoutePredicateFactory extends AbstractRoutePredicateFactory<AuthRoutePredicateFactory.Config> { public static final String NAME_KEY="name"; public AuthRoutePredicateFactory() { super(Config.class); } @Override public Predicate<ServerWebExchange> apply(Config config) { return exchange->{ HttpHeaders headers = exchange.getRequest().getHeaders(); //如果header中有我们配置的authorization则返回true List<String> header = headers.get(config.getName()); return true; }; } //这个是设置我们在配置文件中设置的参数内容的 @Override public List<String> shortcutFieldOrder() { return Collections.singletonList(NAME_KEY); } public static class Config { public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } private String name; } }
View Code@Component //请求中包含【authorization】则走这个 public class AuthRoutePredicateFactory extends AbstractRoutePredicateFactory<AuthRoutePredicateFactory.Config> { public static final String NAME_KEY="name"; public AuthRoutePredicateFactory() { super(Config.class); } @Override public Predicate<ServerWebExchange> apply(Config config) { return exchange->{ HttpHeaders headers = exchange.getRequest().getHeaders(); //如果header中有我们配置的authorization则返回true List<String> header = headers.get(config.getName()); return true; }; } //这个是设置我们在配置文件中设置的参数内容的 @Override public List<String> shortcutFieldOrder() { return Collections.singletonList(NAME_KEY); } public static class Config { public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } private String name; } }上述配置文件中已经包含了对应自定义predicate的配置,当一个请求过来的时候,会去查看是否包含authorization的属性。而
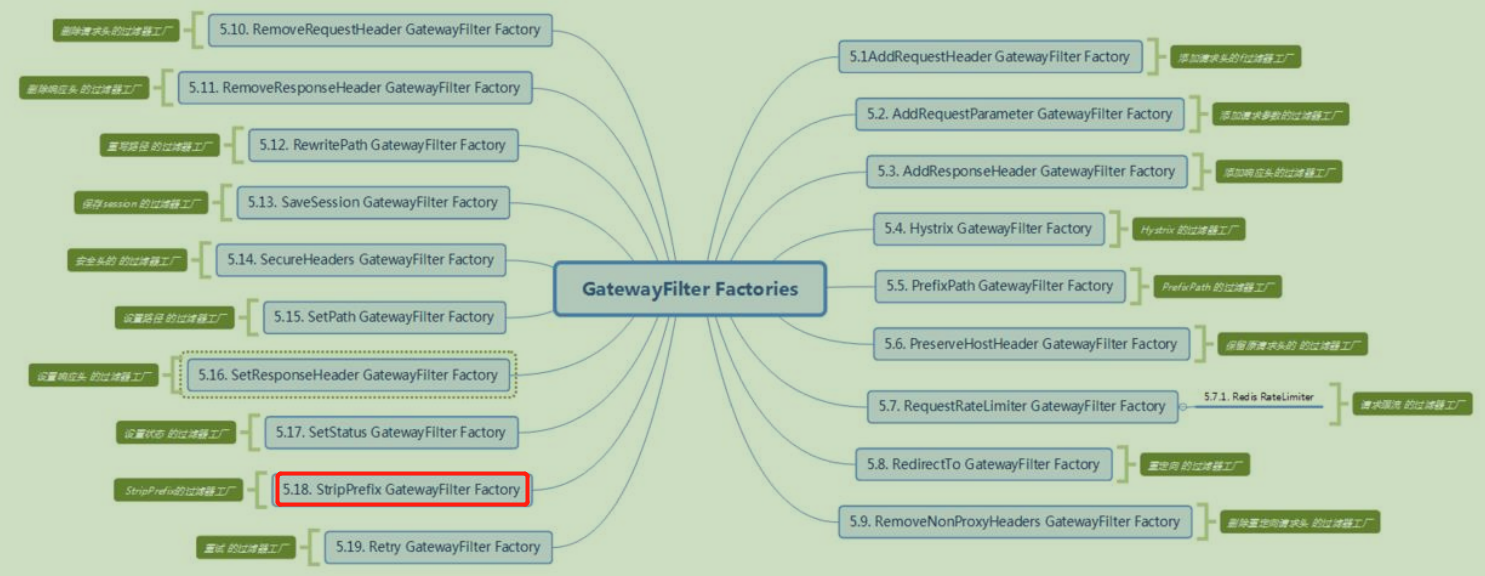
【filter】:分为【全局的】,和【路由级别】的。当一个请求过来的时候,他可以对我们的请求进行修改,当一个响应返回的时候,他同时可以对我们的响应进行修改。他里面提供了很多的filter。我们上面的配置中用到了【StripPrefix】,他的作用是指定数字,转发的时候把对应数字上的url去除。对应的配置在【https://docs.spring.io/spring-cloud-gateway/docs/current/reference/html/#gatewayfilter-factories】
【路由级别】:当一个请求匹配到哪个路由,则会被对应路由下配置的过滤器所作用。 我们这里使用
RequestRateLimiter实现一个限流,他底层使用的令牌桶的机制,并且和redis进行了结合。tips:
【name】: 我们想使用的他内部提供的filter的名称,就是我们上图中的那些。
【key-resolver】:指的是我们想要通过什么进行限流,我们这里用SpEL表达式,填写的是我们自定义的类的名称,在这个类中我们使用ip进行限流
相关配置:
![]() View Code- id: limit-route uri: https://www.baidu.com predicates: - Path=/limit/** filters: - StripPrefix=1 - name: RequestRateLimiter args: key-resolver: "#{@ipAddressKeyResolver}" #令牌桶的填充速度 redis-rate-limiter.replenishRate: 1 #令牌桶的容量 redis-rate-limiter.burstCapacity: 2 #每个请求需要获得的令牌数量 redis-rate-limiter.requestedTokens: 1 - Demo=Glen redis: port: 6379 host: 192.168.43.5
View Code- id: limit-route uri: https://www.baidu.com predicates: - Path=/limit/** filters: - StripPrefix=1 - name: RequestRateLimiter args: key-resolver: "#{@ipAddressKeyResolver}" #令牌桶的填充速度 redis-rate-limiter.replenishRate: 1 #令牌桶的容量 redis-rate-limiter.burstCapacity: 2 #每个请求需要获得的令牌数量 redis-rate-limiter.requestedTokens: 1 - Demo=Glen redis: port: 6379 host: 192.168.43.5限流的key的类:
![]() View Code@Component public class IpAddressKeyResolver implements KeyResolver { @Override public Mono<String> resolve(ServerWebExchange exchange) { return Mono.just(Objects.requireNonNull(exchange.getRequest().getRemoteAddress()).getAddress().getHostAddress()); } }
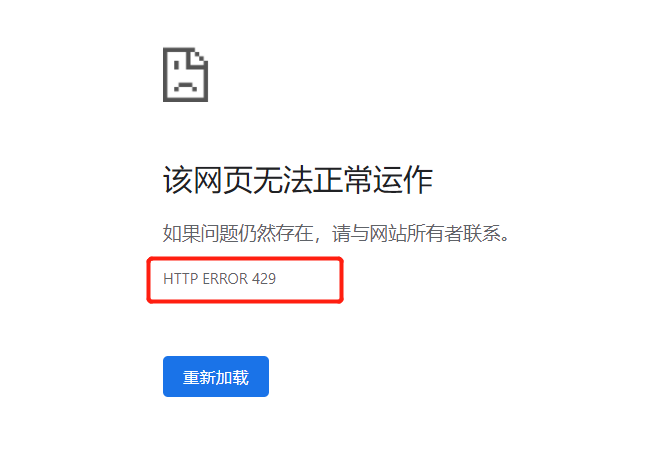
View Code@Component public class IpAddressKeyResolver implements KeyResolver { @Override public Mono<String> resolve(ServerWebExchange exchange) { return Mono.just(Objects.requireNonNull(exchange.getRequest().getRemoteAddress()).getAddress().getHostAddress()); } }测试后,发现它会被路由到baidu的首页,但是当我们联系请求超过2次后,他就会进入spring的429的界面,因为我们在配置文件中设置的就是2个令牌的容量
官网上说当连续的请求超过令牌桶中的数量,就会造成请求丢弃,并且出现429的现象。
实现自己的过滤器,继承AbstractGatewayFilterFactory,并且重写他的apply方法,在这个方法中我们处理请求的获取和返回。他的命名规则是【***GatewayFilterFactory】,所以我们这里的名称按照他的命名规则为DemoGatewayFilterFactory
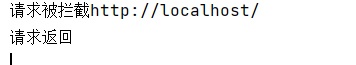
![]() View Code@Component public class DemoGatewayFilterFactory extends AbstractGatewayFilterFactory<DemoGatewayFilterFactory.DemoConfig> { public static final String NAME_KEY="name"; public DemoGatewayFilterFactory() { super(DemoConfig.class); } // 重新apply,他会把咱们的config传递进来 @Override public GatewayFilter apply(DemoConfig config) { return (exchange, chain) -> { System.out.println("请求被拦截"+config.getName()); return chain.filter(exchange).then(Mono.fromRunnable( ()->{ System.out.println("请求返回"); })); }; } //表示配置填写的顺序,这里只有一个name,比如第一个我们填写Glen那会把内容赋值到Glen中 @Override public List<String> shortcutFieldOrder() { return Collections.singletonList(NAME_KEY); } public static class DemoConfig{ public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } private String name; } }
View Code@Component public class DemoGatewayFilterFactory extends AbstractGatewayFilterFactory<DemoGatewayFilterFactory.DemoConfig> { public static final String NAME_KEY="name"; public DemoGatewayFilterFactory() { super(DemoConfig.class); } // 重新apply,他会把咱们的config传递进来 @Override public GatewayFilter apply(DemoConfig config) { return (exchange, chain) -> { System.out.println("请求被拦截"+config.getName()); return chain.filter(exchange).then(Mono.fromRunnable( ()->{ System.out.println("请求返回"); })); }; } //表示配置填写的顺序,这里只有一个name,比如第一个我们填写Glen那会把内容赋值到Glen中 @Override public List<String> shortcutFieldOrder() { return Collections.singletonList(NAME_KEY); } public static class DemoConfig{ public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } private String name; } }相关配置(demo指的是我们的自定义的filter名称,Glen指的是我们自定义类中的name)
![]() View Code- Demo=Glen
View Code- Demo=Glen
【全局】: 类似于一个通用的配置,对所有的请求都起作用。
相关配置:和普通的配置不同的是,我们的uri中需要带有【lb】的字样。我们这里的配置是转发到我们自己的微服务节点上的。
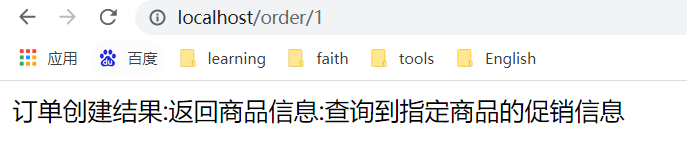
![]() View Code- id: loadbalance-route uri: lb://glenmall-portal predicates: - Path=/order/** filters: - name: RequestRateLimiter args: key-resolver: "#{@ipAddressKeyResolver}" #令牌桶的填充速度 redis-rate-limiter.replenishRate: 1 #令牌桶的容量 redis-rate-limiter.burstCapacity: 2 #每个请求需要获得的令牌数量 redis-rate-limiter.requestedTokens: 1 discovery: locator: lower-case-service-id: true enabled: true redis: port: 6379 host: 192.168.43.5 server: port: 80 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka
View Code- id: loadbalance-route uri: lb://glenmall-portal predicates: - Path=/order/** filters: - name: RequestRateLimiter args: key-resolver: "#{@ipAddressKeyResolver}" #令牌桶的填充速度 redis-rate-limiter.replenishRate: 1 #令牌桶的容量 redis-rate-limiter.burstCapacity: 2 #每个请求需要获得的令牌数量 redis-rate-limiter.requestedTokens: 1 discovery: locator: lower-case-service-id: true enabled: true redis: port: 6379 host: 192.168.43.5 server: port: 80 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka因为我们自己的微服务节点可能是集群,那么我们就需要从eureka上获取微服务节点。所以需要加上eureka的pom
![]() View Code
View Code<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId> </dependency>我们看到,我们请求的是网关,然后他自动从eureka上找到我们统一的api服务,并且转发了过去。
【动态路由】:
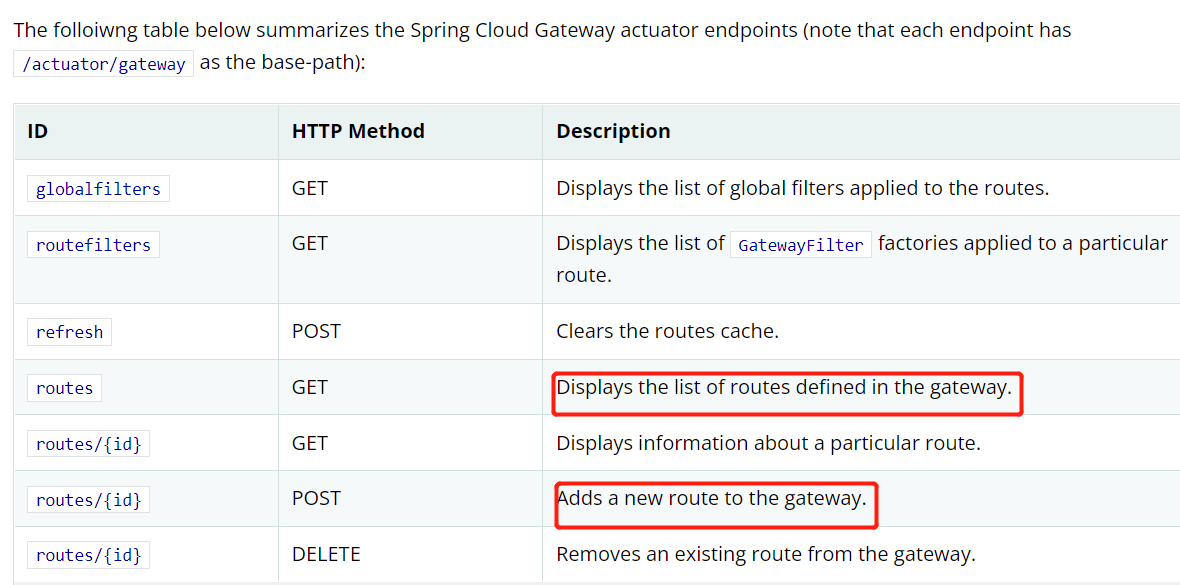
思路:我们发现可以通过actuator浏览所有的路由,并且通过他内部提供这样的接口,即可对所有路由进行获取和新增。我们发现他的查询路由的方法获取的路由数据只从RouteLocator中获取的而添加的方法调用org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.InMemoryRouteDefinitionRepository#save存储在另外一对象中(RouteDefinitionWriter),底层是一个map中的的,也就是说静态路由和我们通过url新增的路由是分开的。那也就是说,我们只用把新的数据想办法存储在RouteDefinitionWriter就可以了!那我们就可以按照InMemoryRouteDefinitionRepository的处理方式,实现RouteDefinitionRepository,只不过我们把数据维护到redis/数据库中即可。之后我们维护redis/数据库中的数据就可以了。
tips: 默认情况下使用【InMemoryRouteDefinitionRepository】,如果我们定义了自己的动态路由的时候,他则会使用我们自己的。
代码:
![]() View Code@Component public class InRedisRouteDefinitionRepository implements RouteDefinitionRepository { private final static String GATEWAY_ROUTE_KEY="gateway_dynamic_route"; @Autowired RedisTemplate<String,String> redisTemplate; //返回路由列表 @Override public Flux<RouteDefinition> getRouteDefinitions() { List<RouteDefinition> routeDefinitions=new ArrayList<>(); redisTemplate.opsForHash().values(GATEWAY_ROUTE_KEY).forEach(x-> routeDefinitions.add(JSON.parseObject(x.toString(), RouteDefinition.class))); return Flux.fromIterable(routeDefinitions); } //保存 @Override public Mono<Void> save(Mono<RouteDefinition> route) { return route.flatMap(routeDefinition -> { redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(GATEWAY_ROUTE_KEY ,routeDefinition.getId(), JSON.toJSONString(routeDefinition)); return Mono.empty(); }); } //删除 @Override public Mono<Void> delete(Mono<String> routeId) { return routeId.flatMap(id->{ if (redisTemplate.opsForHash().hasKey(GATEWAY_ROUTE_KEY,id)){ redisTemplate.opsForHash().delete(GATEWAY_ROUTE_KEY,id); return Mono.empty(); } return Mono.defer(()->Mono.error(new RuntimeException( "haven't found RouteDefinition"+id))); }); } }
View Code@Component public class InRedisRouteDefinitionRepository implements RouteDefinitionRepository { private final static String GATEWAY_ROUTE_KEY="gateway_dynamic_route"; @Autowired RedisTemplate<String,String> redisTemplate; //返回路由列表 @Override public Flux<RouteDefinition> getRouteDefinitions() { List<RouteDefinition> routeDefinitions=new ArrayList<>(); redisTemplate.opsForHash().values(GATEWAY_ROUTE_KEY).forEach(x-> routeDefinitions.add(JSON.parseObject(x.toString(), RouteDefinition.class))); return Flux.fromIterable(routeDefinitions); } //保存 @Override public Mono<Void> save(Mono<RouteDefinition> route) { return route.flatMap(routeDefinition -> { redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(GATEWAY_ROUTE_KEY ,routeDefinition.getId(), JSON.toJSONString(routeDefinition)); return Mono.empty(); }); } //删除 @Override public Mono<Void> delete(Mono<String> routeId) { return routeId.flatMap(id->{ if (redisTemplate.opsForHash().hasKey(GATEWAY_ROUTE_KEY,id)){ redisTemplate.opsForHash().delete(GATEWAY_ROUTE_KEY,id); return Mono.empty(); } return Mono.defer(()->Mono.error(new RuntimeException( "haven't found RouteDefinition"+id))); }); } }







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号