Template Method Pattern
(Template Method Pattern)
Define a skeleton that allows subclasses to provide implementations for one or more of the steps. In short, the methods of one class are used to standardize the process, and the subclasses implement these methods in order to achieve the purpose of process unification。The public behavior of each subclass is extracted and placed in the public parent class, where a process can be handed over to the subclass to implement itself, and the child class can also choose not to implement, as the parent class can define a hook method, so as to tell the parent class whether to implement the parent class's implementation method,One of the most typical examples is JDBCTEMPLATE.I'll write a demo of a simple course release, and then write a demo that simulates a jdbctempleate。
launch a course
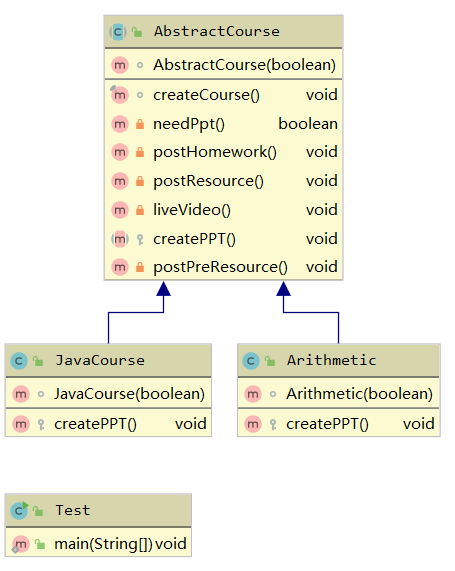
public abstract class AbstractCourse { boolean needPpt; AbstractCourse(boolean needPpt) { this.needPpt = needPpt; }
// the whole process will be controled here final void createCourse() { postPreResource(); liveVideo(); postResource(); postHomework();
// here we judge whether the method that should be exucuted or not if (needPpt()) { createPPT(); } } private boolean needPpt() { return needPpt; } private void postHomework(){ System.out.println("postHomework"); } private void postResource(){ System.out.println("postResource"); } private void liveVideo(){ System.out.println("liveVideo"); } // this is a hook method protected abstract void createPPT(); private void postPreResource(){ System.out.println("postPreResource"); } }
- first, we should have a method to control the whole process
- second,we could have a method to let subclass to implement,we call hook method
- finally,we can give subclass power whether i need implement father class or not
public class Arithmetic extends AbstractCourse { Arithmetic(boolean needPpt) { super(needPpt); } @Override protected void createPPT() { System.out.println("createPPT of Arithmetic"); } } public class JavaCourse extends AbstractCourse { JavaCourse(boolean needPpt) { super(needPpt); } @Override protected void createPPT() { System.out.println("create ppt of java"); } }
To test(we can control whether we need to create a ppt or not dynamically)
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Arithmetic arithmetic=new Arithmetic(true); arithmetic.createCourse(); System.out.println("---------JavaCourse-----------------"); JavaCourse javaCourse=new JavaCourse(false); javaCourse.createCourse(); } }
there is a scene to simulate jdbcTemplate
public abstract class JdbcTemplate { private DataSource dataSource; public JdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) { this.dataSource = dataSource; }
// formulate a process public final List<?> executeQuery(String sql, RowMapper<?> rowMapper, Object[] values) { try { //simulate get data Connection connection = this.getConnection(); PreparedStatement statement = this.createPrePareStatement(connection, sql); ResultSet resultSet = this.executeQuery(statement, values);
// here could be a hook method List<?> result = this.parseResultSet(resultSet, rowMapper); return result; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // get connection return null; } private List<?> parseResultSet(ResultSet resultSet, RowMapper<?> rowMapper) throws Exception { List<Object> result = new ArrayList<Object>(); int rowNum = 1; while (resultSet.next()) { Object o = rowMapper.mapRow(resultSet, rowNum++); result.add(o); } return result; } private ResultSet executeQuery(PreparedStatement statement, Object[] values) throws SQLException { for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) { statement.setObject(i, values); } return statement.executeQuery(); } private PreparedStatement createPrePareStatement(Connection connection, String sql) throws SQLException { return connection.prepareStatement(sql); } private Connection getConnection() throws Exception { return this.dataSource.getConnection(); } }
each dao want to query whole data should to implement a interface called RowMapper,in class named JdbcTemplate will cope with the RowMapper you implement
public class MemberDao extends JdbcTemplate { public MemberDao(DataSource dataSource) { super(dataSource); } public List<?> selectAll() { String sql="Select * from t_member"; return super.executeQuery(sql, new () { @Override public Member mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws Exception { Member member = new Member(); member.setUsername(rs.getString("username")); member.setPassword(rs.getString("password")); member.setAge(rs.getInt("age")); member.setAddr(rs.getString("addr")); return member; } },null); } }
additional assistant class
public interface RowMapper<T> { T mapRow(ResultSet resultSet,int rowNum) throws Exception; } @Data public class Member { private String username; private String password; private String nickname; private int age; private String addr; }
To test
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { MemberDao memberDao=new MemberDao(null); memberDao.selectAll(); } }
How is Template Method used in source of code
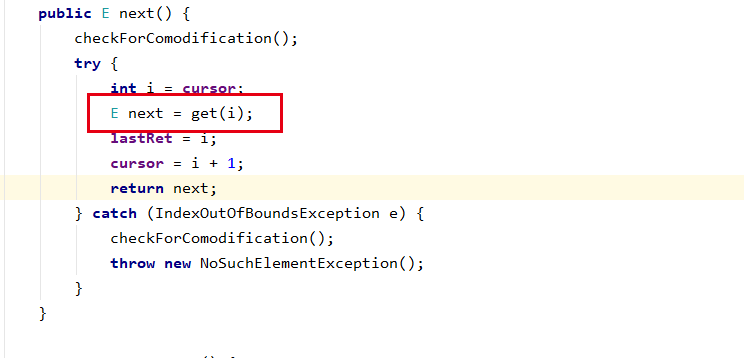
java.util.AbstractList#get
apparently,it is an abstract method(hook method),but it is called in the same class, as we mentiond other examples
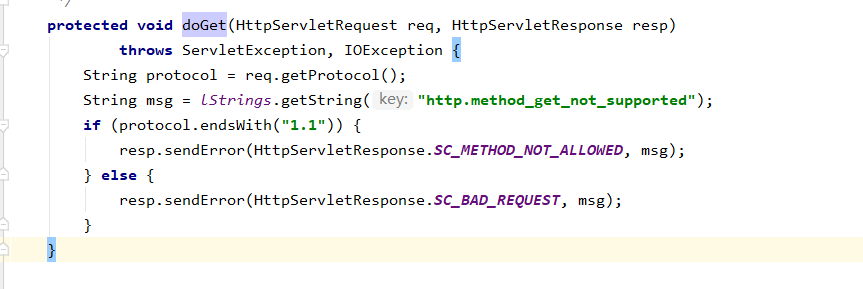
javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet#doGet(actually,in source of code, it wasn't implemented, so it like a hook method)
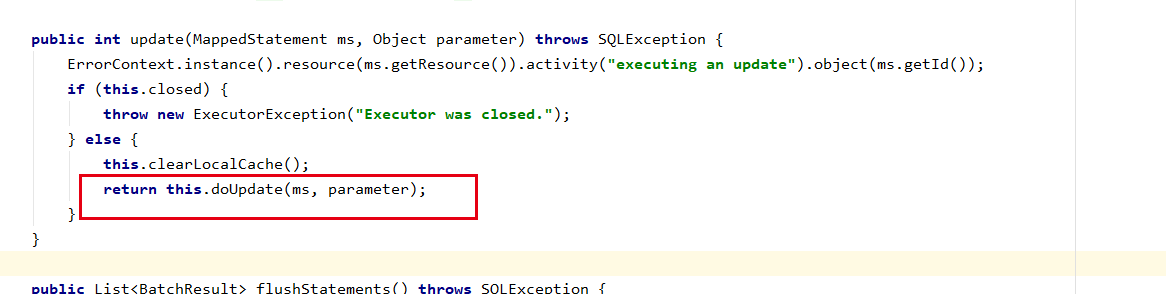
org.apache.ibatis.executor.BaseExecutor#doUpdate
Sum up
advantages:
- reusability:makeing the same logical code in the one class
- expansibility:different subclass do different code
disadvatnages:
if we need add a new method,that means we need to add a new method to every subclasses





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号