(Composite Pattern)
Composite Pattern
The purpose is to represent individual objects and composite objects with the same interface, so that the client can handle individual objects and composite objects in a consistent manner。In short, it's to inherit from the same abstract class,A common example is a folder in the system, where files, folders, and files in a directory all have the same function (display, add (no file), delete, etc.).So we abstracted it into an abstract class so that every call to a single object was uniform。Two common modes
- safe mode(For example, if there is no new function in the file, then this interface cannot be exposed to the client)
- Transparency mode(The operations on files, folders, and directories are the same, and we can call them even if there is no individual without a certain function, because they inherit the same interface,This violates the principle of minimum knowledge,Therefore, it will not be elaborated in this article)
General corporateOrganizational structure, folders, etc., can be implemented with this.
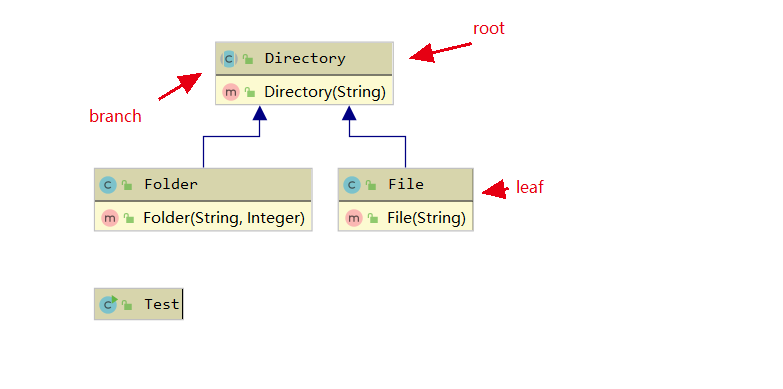
In general, the composition pattern requires an abstract component, a branch node, and a leaf node,Let's take an example of a folder。
To display
First of all we should create root that is directory
abstract class Directory { Directory(String name) { this.name = name; } String name; abstract void show(); }
Second we should create branch that is Folder(because each files are contained in Flolders)
public class Folder extends Directory {
// save all file ,you should not put File as restrictive condition,because you do not know how many file there are List<Directory> list; // we should consider its level then according this to arrange series Integer level; public Folder(String name, Integer level) { super(name); this.level = level; this.list = new ArrayList<Directory>(); } @Override void show() { System.out.println(this.name); for (Directory dir : this.list) { // code in block of if are used to show construction of Files,you can ignore the logic if (this.level != null) { for (int i = 0; i < this.level; i++) { System.out.print(" "); } for (int i = 0; i < this.level; i++) { if (i == 0) { System.out.print("+"); } System.out.print("-"); } } dir.show(); } } public boolean add(Directory directory) { return this.list.add(directory); } public void list() { for (Directory directory : list) { System.out.println(directory.name); } } }
To test
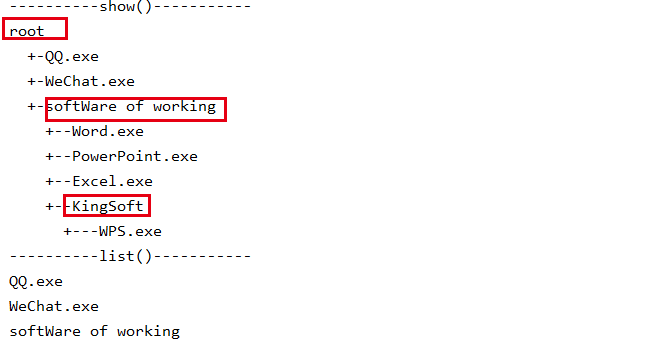
public static void main(String[] args) { Folder root = new Folder("root",1); File qq = new File("QQ.exe"); File wx = new File("WeChat.exe"); root.add(qq); root.add(wx); // working Folder Folder office = new Folder("softWare of working",2); File word = new File("Word.exe"); File ppt = new File("PowerPoint.exe"); File excel = new File("Excel.exe"); office.add(word); office.add(ppt); office.add(excel); //This is a son Folder that belong to working Folder Folder wps = new Folder("KingSoft",3); wps.add(new File("WPS.exe")); office.add(wps); root.add(office); System.out.println("----------show()-----------"); root.show(); System.out.println("----------list()-----------"); root.list(); }
as a result
We can assemble them easily with Composite Pattern.
How is composite pattern applied into sorce of code
java.util.HashMap#putAll
java.util.ArrayList#addAll(java.util.Collection<? extends E>)
apparently,Arraylist must be bound to implements Connection(like list root we have mentioned)
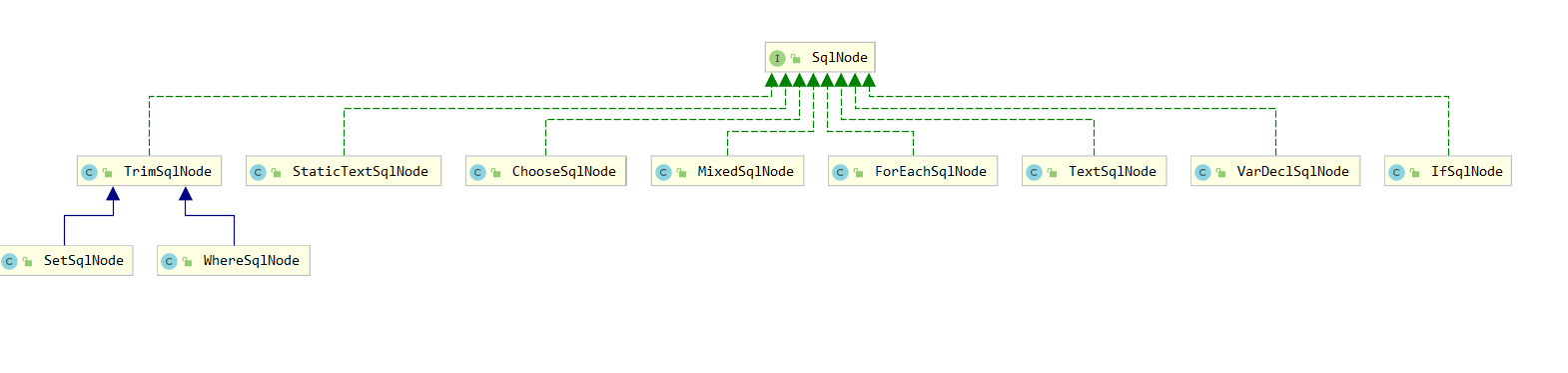
org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.SqlNode#apply
we open all of them at will, we will find them all pass on the same classes that is sqlNode
![]()
Sum up
advantage:
- it is convenient to control the whole construction with a List( List<Directory> list)
disadvantage:
- it is hard to design the top class of interface(we have to extract same point then construct our top interface/class)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号