Vision Transformer
ViT 实现了将 Transformer 应用到 CV 领域。
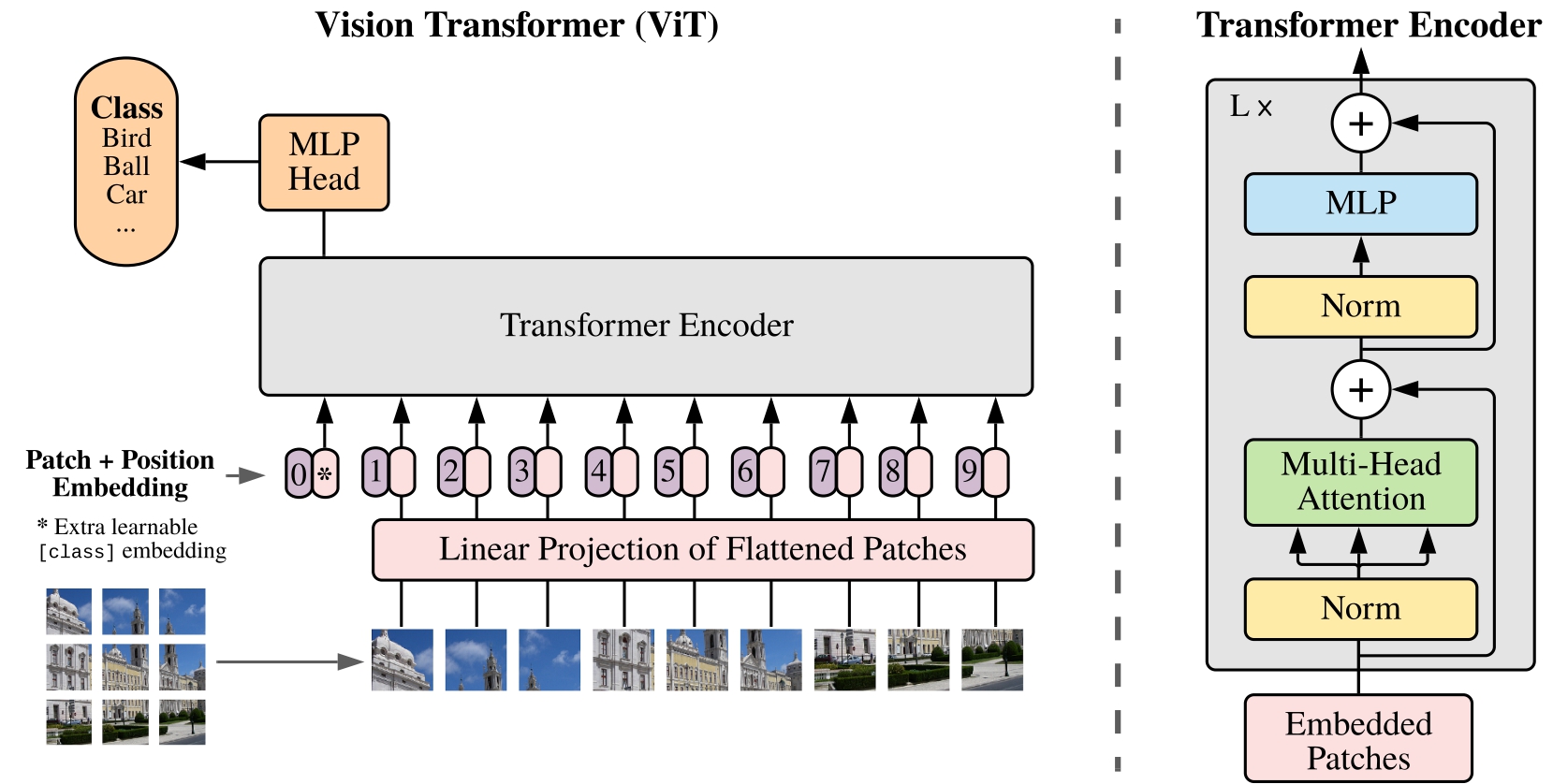
模型定义
import torch as th
import torch.nn as nn
class SimpleViT(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
image_size=28,
image_dim=1,
patch_size=7,
num_classes=10,
dim=128,
depth=4,
heads=4,
mlp_dim=256
):
super().__init__()
assert image_size % patch_size == 0, 'Image dimensions must be divisible by the patch size.'
num_patches = (image_size // patch_size) ** 2
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.dim = dim
# 切割图片并映射到嵌入维度
self.to_patch = nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=image_dim,
out_channels=dim,
kernel_size=patch_size,
stride=patch_size
)
self.cls_embedding = nn.Parameter(th.randn(1, 1, dim))
self.pos_embedding = nn.Parameter(th.randn(1, 1+num_patches, dim))
# Transformer 编码器
self.transformer = nn.TransformerEncoder(
nn.TransformerEncoderLayer(d_model=dim, nhead=heads, dim_feedforward=mlp_dim, batch_first=True),
num_layers=depth
)
# 分类头
self.mlp_head = nn.Sequential(
nn.LayerNorm(dim),
nn.Linear(dim, num_classes)
)
def forward(self, x):
B = x.shape[0]
x = self.to_patch(x).reshape(B, -1, self.dim) # [B, N, D]
cls = self.cls_embedding.expand(B, -1, -1) # [B, 1, D]
x = th.cat((cls, x), dim=1) # [B, 1+N, D]
x = x + self.pos_embedding
x = self.transformer(x)
x = x[:, 0, :] # 取出 cls
x = self.mlp_head(x) # 对 cls 分类
return x
数据准备
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor()])
train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=True, download=True, transform=transform)
test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=False, download=True, transform=transform)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=1000, shuffle=False)
训练与测试
device = th.device('cuda' if th.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model = SimpleViT().to(device)
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 训练
for epoch in range(5):
model.train()
for images, labels in train_loader:
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(images)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print(f'Epoch {epoch+1}/{5} - Loss: {loss.item():.4f}')
# 测试
model.eval()
correct = 0
total = 0
with th.no_grad():
for images, labels in test_loader:
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
outputs = model(images)
_, pred = th.max(outputs, 1)
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (pred == labels).sum().item()
print(f'Accuracy: {100 * correct / total:.2f}%')
与 CNN 的比较
| 特性 | CNN | ViT |
|---|---|---|
| 归纳偏置 | 强(局部性、平移不变性) | 弱(主要靠数据学习) |
| 对小数据集表现 | 很好,易于训练,收敛快 | 容易过拟合,需要更多数据和正则化 |
| 参数量 | 少,计算高效 | 多,计算量大 |
| 适合场景 | 小图片、结构简单、样本量少的任务 | 大图片、结构复杂、样本量大的任务 |


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号