深入剖析Java虚拟机内存结构
深入剖析Java虚拟机内存模型
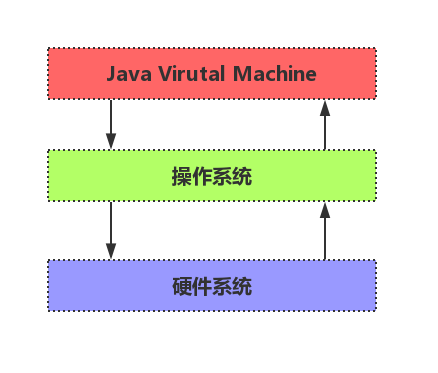
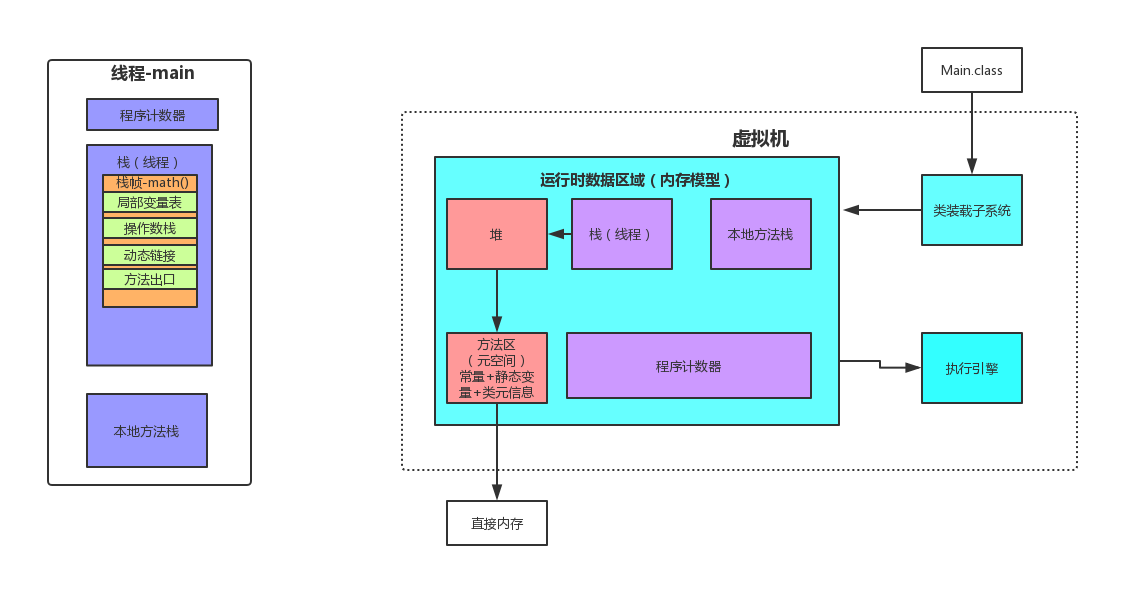
JVM整体架构
JVM整体架构如下:
通过编写代码来分析整个内存区域
public class Math {
public static final Integer CONSTANT = 666;
public int compute(){
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = (a + b) * 10;
return c;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Math math = new Math();
math.compute();
}
}
对上述代码的class文件进行javap - c Math.class > Math.txt
javap -c是对代码进行反汇编
得到Math.txt文件
对compute方法进行分析:
public int compute();
Code:
0: iconst_1 // 将int型(1)推送至栈顶
1: istore_1 // 将栈顶int型数值存入第二个本地变量
2: iconst_2 // 将int型(2)推送至栈顶
3: istore_2 // 将栈顶int型数值存入第三个本地变量
4: iload_1 // 将第二个int型本地变量推送至栈顶
5: iload_2 // 将第三个int型本地变量推送至栈顶
6: iadd // 将栈顶两int型数值相加并将结果压入栈顶
7: bipush 10 // 将单字节的常量值(-128~127)推送至栈顶
9: imul // 将栈顶两int型数值相乘并将结果压入栈顶
10: istore_3 // 将栈顶int型数值存入第四个本地变量
11: iload_3 // 将第四个int型本地变量推送至栈顶
12: ireturn
上面程序,在JVM中的运行时区域如下:
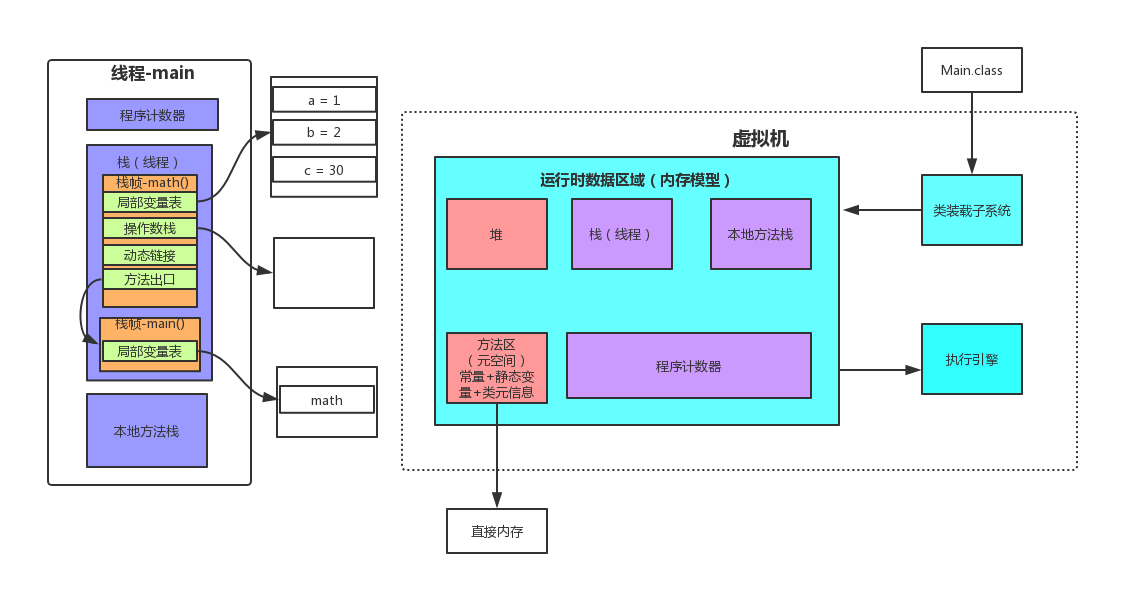
栈
操作的操作暂时的数据存放到操作数栈。
main()的局部变量表存放对象的引用地址。
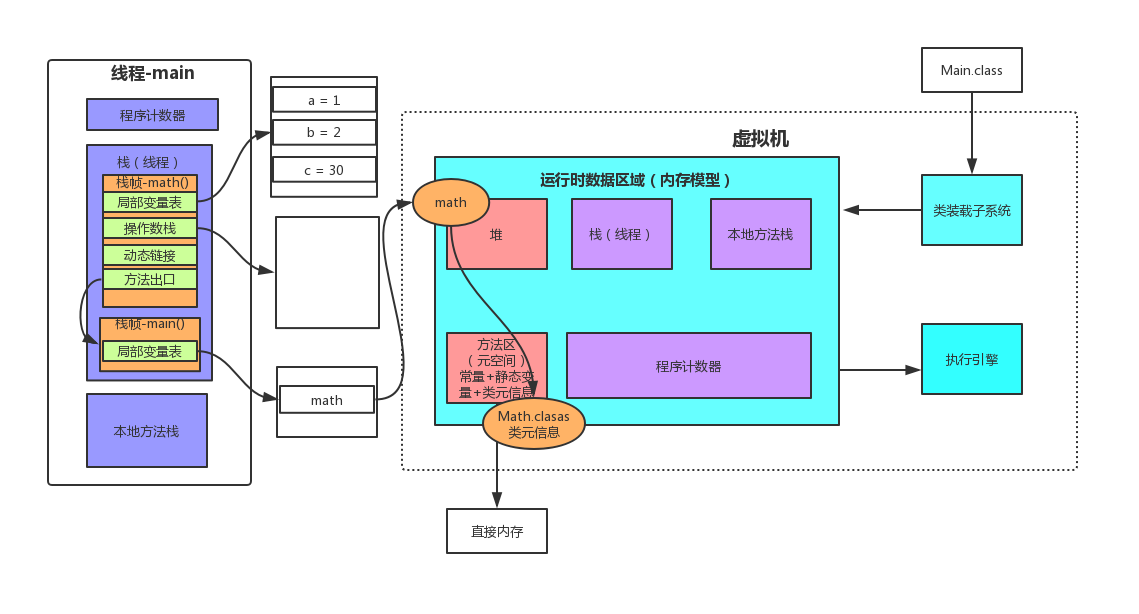
动态链接
动态链接就是当我们这个程序运行main方法时,当执行math对象额compute方法时,去compute方法执行,compute方法算是符号引用,找到符号引用所在的方法体,执行。
执行javap -v Math.class > Math.txt得到字节码文件
找到main方法所在的位置
public static void main(java.lang.String[]);
descriptor: ([Ljava/lang/String;)V
flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_STATIC
Code:
stack=2, locals=2, args_size=1
0: new #2 // class com/tugohost/jvm/Math
3: dup
4: invokespecial #3 // Method "<init>":()V
7: astore_1
8: aload_1
9: invokevirtual #4 // Method compute:()I
12: pop
13: return
LineNumberTable:
line 17: 0
line 18: 8
line 19: 13
LocalVariableTable:
Start Length Slot Name Signature
0 14 0 args [Ljava/lang/String;
8 6 1 math Lcom/tugohost/jvm/Math;
其中
9: invokevirtual #4 // Method compute:()I
这一行表示,main函数中的math对象调用compute方法,
再往上找,找到常量池
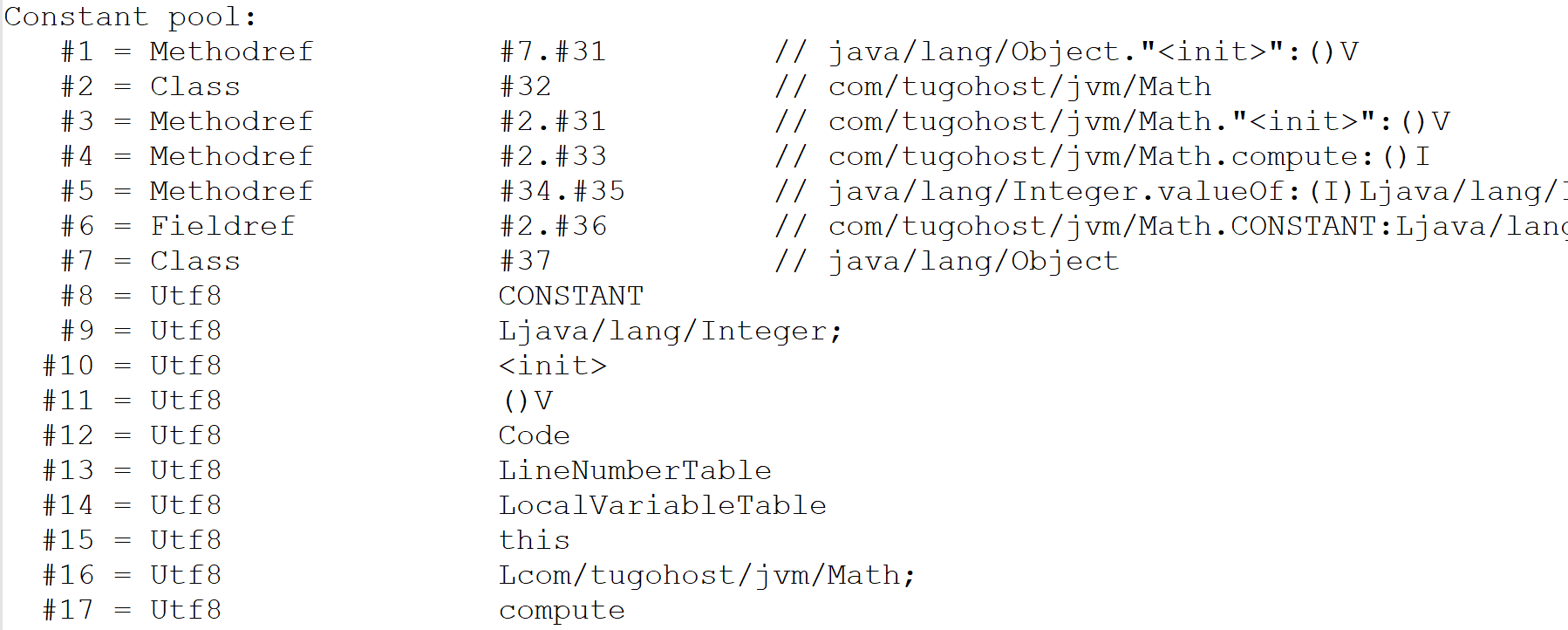
找到
#4 = Methodref #2.#33 // com/tugohost/jvm/Math.compute:()I
再找#2、#33
2 = Class #32 // com/tugohost/jvm/Math
3 = Methodref #2.#31 // com/tugohost/jvm/Math."
"😦)V
所以这个过程就是动态链接的过程。
本地方法栈
本地方法栈就是存储native方法
堆
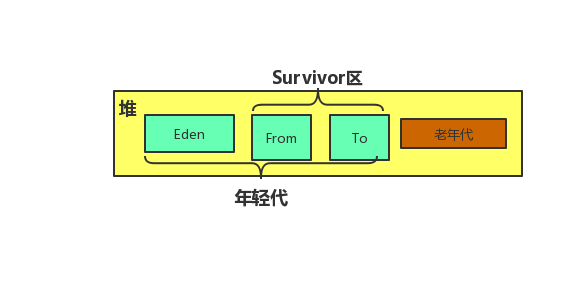
如果Eden区放满,会minor GC,如果还存活的对象,会放到From区生命值+1,同理会放到To区生命值+1,如果生命值大于某个值(可以自己设置),会放到老年代。
通过写一个死循环代码来看看堆中垃圾收集器的工作:
public class HeapTest {
byte[] a = new byte[1024 * 100]; // 100Kb
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ArrayList<HeapTest> heapTests = new ArrayList<>();
while (true){
heapTests.add(new HeapTest());
Thread.sleep(10);
}
}
}
通过命令行jvisualvm 打开Java visualVM
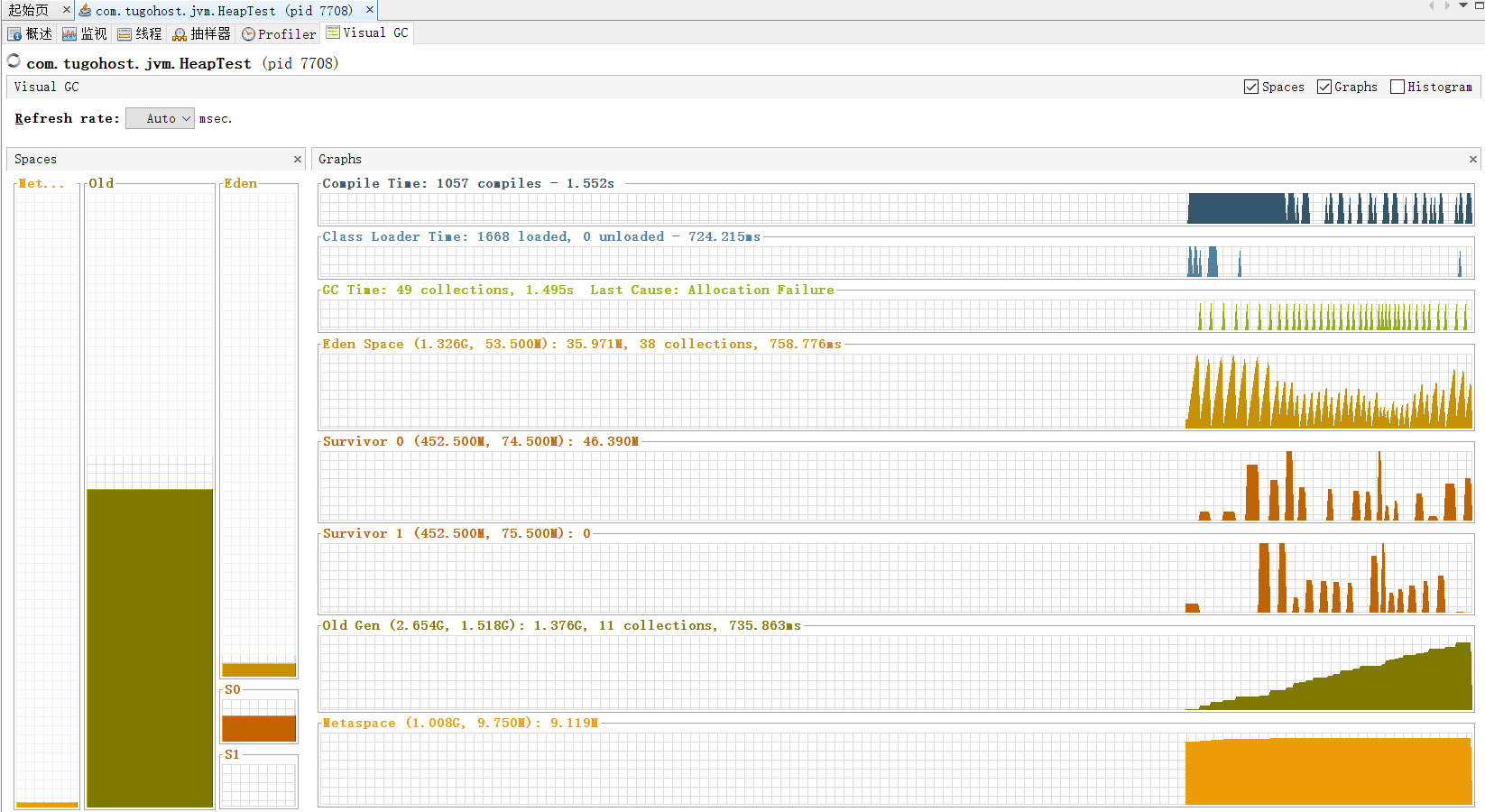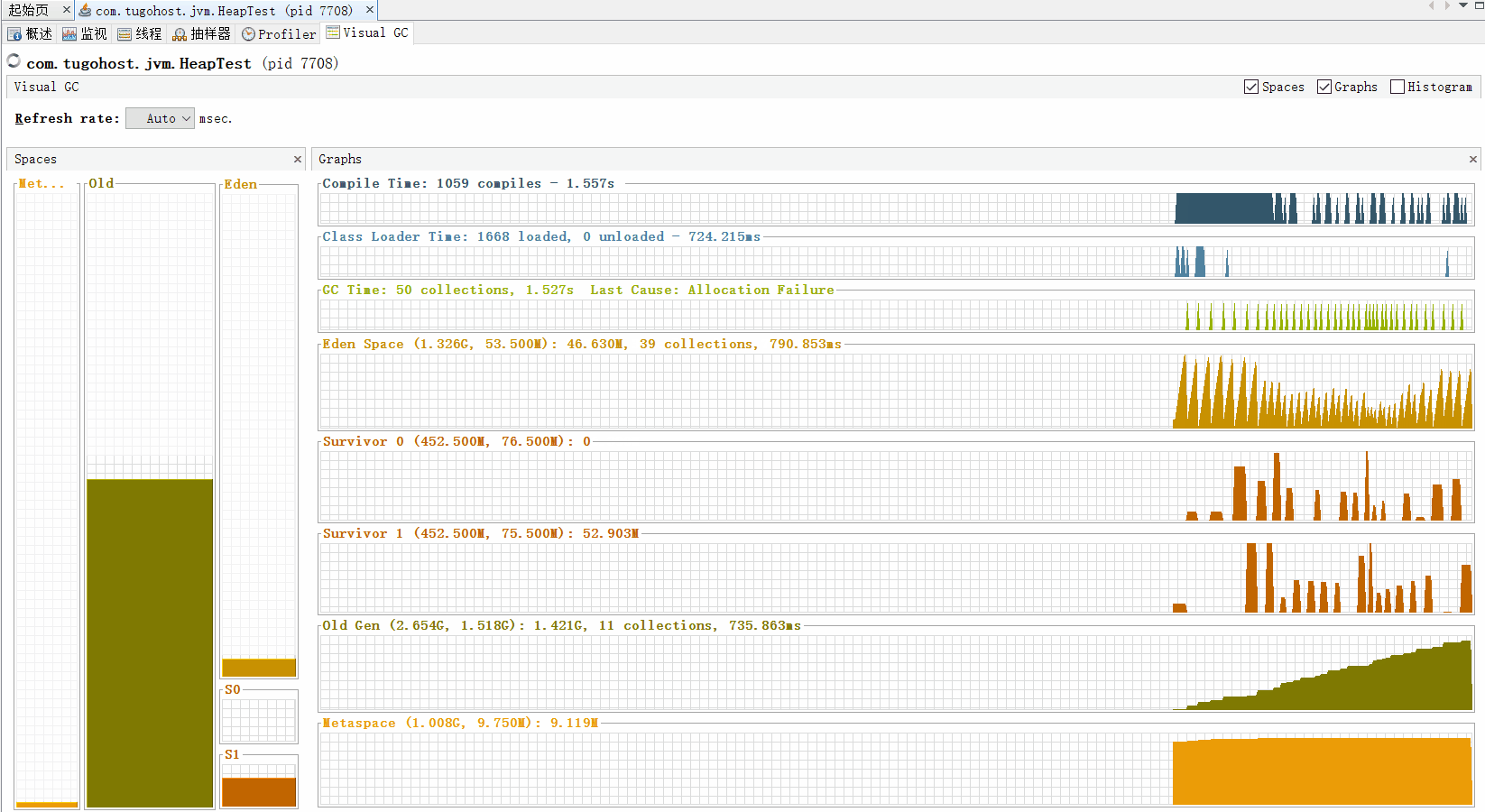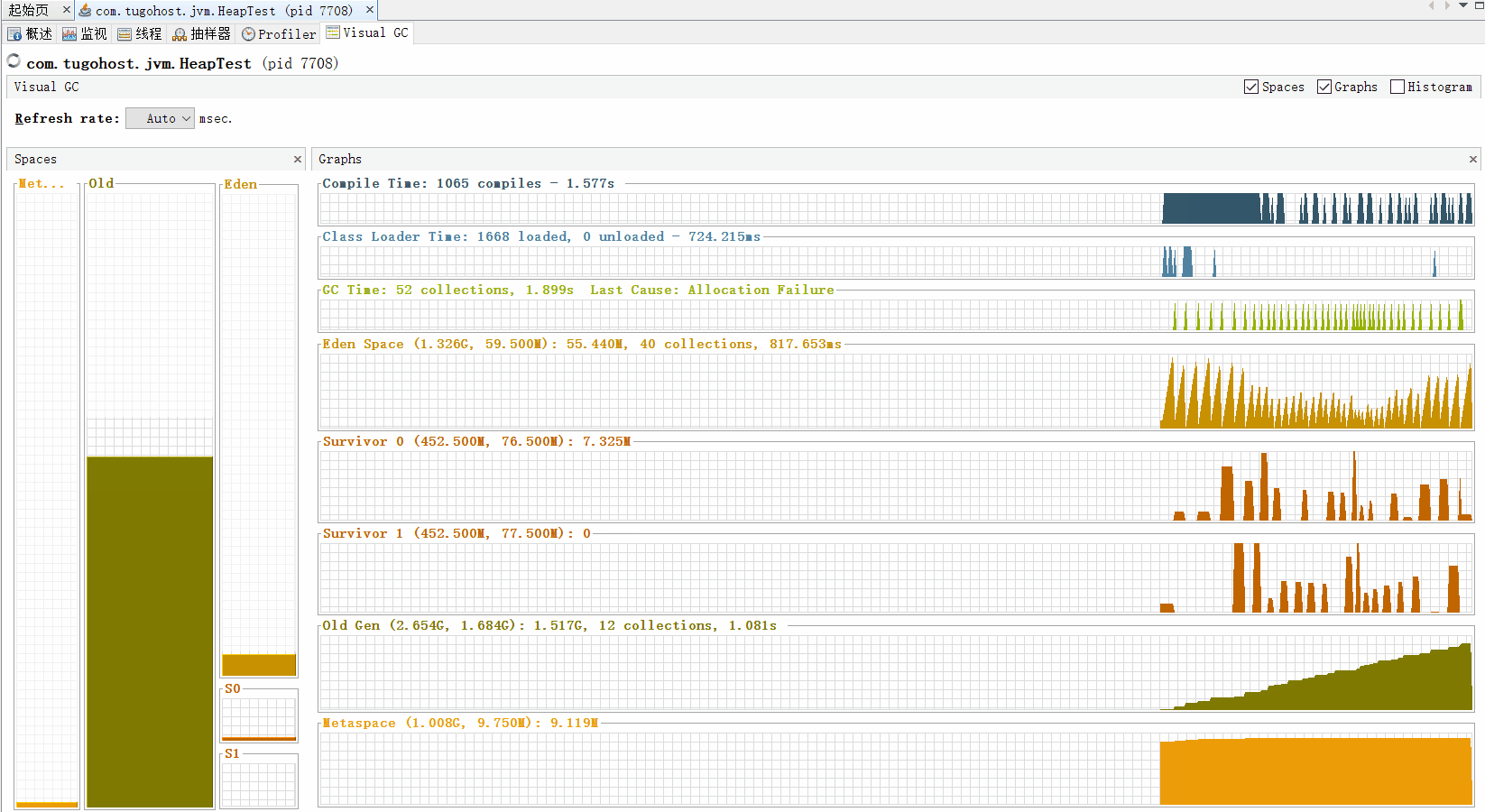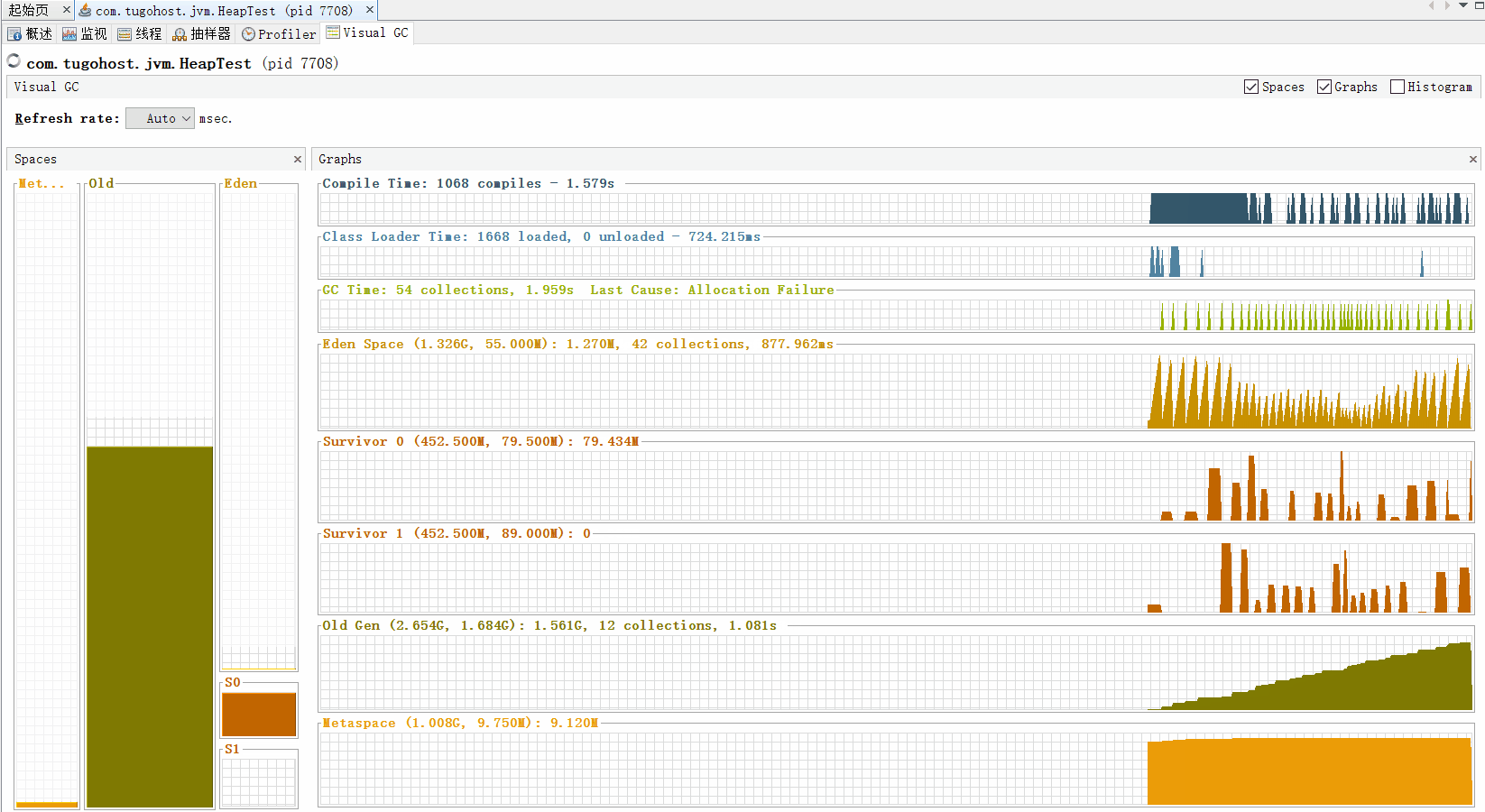
如果老年代满了触发Full GC。如果Full GC对老年代没有用,即老年代中没有无用的对象时,出现OOM效果。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号