Ceres-Solver学习记录(一):HelloWorld
1. Introduction
利用Ceres-Solver求解带有边界约束的非线性最小二乘问题
如下形式:
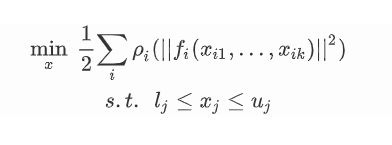
应用场景从数理统计中的曲线拟合到计算摄影学中的三维重建,都会涉及到类似上式的优化。
本教程将会学习如何利用ceres-solver来求解上式优化问题。
上式中:
- \(ρ_i(||f_i(x_{i1},...,x_{ik})||^2)\) 为一个残差块(Residual Block),\(ρ_i(·)\) 为代价函数,其输入通常为small group of scalars(一小组数)
- \(ρ_i(·)\) 为损失函数
LossFunction, 用于减弱外点(即outliers)对Problem整体cost的影响;也可以是带有scaled的函数
2. HelloWorld
https://ceres-solver.googlesource.com/ceres-solver/+/master/examples/helloworld.cc
3. Call Ceres Optimization
ceres::Problem problem;
ceres::Solver::Options options;
options.max_num_iterations = 5;
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::DENSE_SCHUR;
// options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true;
ceres::Solver::Summary summary;
ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary);
// std::cout << summary.FullReport() << std::endl;
// std::cout << summary.BriefReport() << std::endl;
- problem和option (定义问题+设定优化选项), summary为优化过程的verbose
- 需要注意:优化返回的
final_cost为上式Σ累加得到的误差值,并不代表每个样本的误差值。
参考链接
-
《How to create a C++ project using Ceres Solver》
以HelloWorld工程为例,结合CMake来构建工程
https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-create-a-c-project-using-ceres-solver-f3d67c8044f3
(暂且先用1.14.0的老版本,然后就是2.0.0版本了) -
[官网教程] non-linear least square problem
http://ceres-solver.org/nnls_tutorial.html -
how to regularized nonlinear least squares?
https://groups.google.com/g/ceres-solver/c/vkv7nixkIYU?pli=1




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号