C++工程(一):学习使用gcc编译C++工程
示例一:HelloWorld
1.1 代码
/*hello_world.cpp*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "Hello, world!" << endl;
return 0;
}
1.2 编译
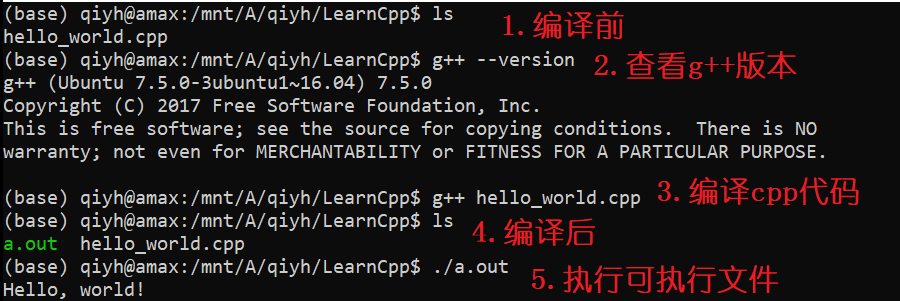
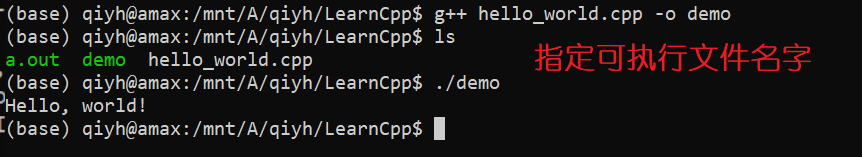
1.3 总结
g++ xxx.cpp默认生成名为a.out的可执行文件g++ xxx.cpp -o exe_filename生成名为exe_filename的可执行文件- Windows的可执行文件一般为
.exe文件,Linux下可执行文件并没有文件拓展名 - 可用
ldd命令查看可执行文件的依赖库
示例二:进阶
2.1 vector_example
/*vector_example.cpp*/
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<string> msg = {"Hello", "C++", "World", "from", "VSCode", "and the C++ extension!"};
for (const string& word : msg) {
cout << word << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
g++ main.cpp -std=c++11 支持C++11,否则会报错
2.2 thread_example
/*thread_example.cpp*/
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
int main() {
std::thread t([](){
std::cout << "hello world." << std::endl;
});
t.join();
return 0;
}
g++ main.cpp -std=c++11 -lpthread 支持C++11,include pthread(Linux系统)头文件。(包含头文件:-I, 包含lib:-L)
三、其他
3.1 Windows系统的C++编译器
- MSVC (集成在Visual Studio)
- MinGW-w64: A complete runtime environment for GCC & LLVM for 32 and 64 bit Windows (适用于32/64位Windows系统的完整 GCC & LLVM 运行环境)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号