vue学习笔记
MVVM

<!--导入vue-->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<body>
<!--改变方式对比-->
hello vue!<br>
<div id="app">
<!-- {{}}等价v-bindm,只显示为文本。使用v-once一次性绑定值 -->
{{message}}
<!-- v-html显示为html语句 -->
<span v-html="realHtml"></span>
</div>
<script>
let message="hello vue!";
let realHTML="<h1>hello vue!</h1>";
let vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
message: message,
realHTML: realHTML
}
});
</script>
</body>
vue
学习文档:官方文档
核心时DOM监听和数据绑定
判断-循环(v-if)
<!-- 判断v-if -->
<body>
<div id="app">
<h3 v-if="message==='true'">Yes</h3>
<h3 v-else="message==='false'">No</h3>
<h3 v-else>null</h3>
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
message: "true"
}
});
</script>
</body>
<!-- 循环v-for -->
<div id="app">
<li v-for="item in items" :key="item.message">
{{ item.message }}
</li>
</div>
<script>
let message = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
items: [
{message: 'Foo'},
{message: 'Bar'}
]
}
})
</script>
</body>
事件(v-on)
<body>
<!-- 事件v-on -->
<div id="app">
<!-- `greet` 是在下面定义的方法名 -->
<button v-on:click="greet">Greet</button>
</div>
<script>
let message = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
name: 'Vue.js'
},
// 在 `methods` 对象中定义方法
methods: {
greet: function (event) {
// `this` 在方法里指向当前 Vue 实例
alert('Hello ' + this.name + '!')
// `event` 是原生 DOM 事件
if (event) {
alert(event.target.tagName)
}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
双向数据绑定(v-model)
<body>
<!-- 双向数据绑定v-model -->
<div id="app">
输入文本:<input type="text" v-model="message">{{message}}
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: ''
}
});
</script>
</body>
v-model 会根据控件类型自动选取正确的方法来更新元素,在内部为不同的输入元素使用不同的 property 并抛出不同的事件:
- text 和 textarea 元素使用 value property 和 input 事件;
- checkbox 和 radio 使用 checked property 和 change 事件;
- select 字段将 value 作为 prop 并将 change 作为事件。
<body>
<!-- 双向数据绑定v-model -->
<div id="app">
<select v-model="message">
<option value="" selected disabled>--请选择--</option>
<option>A</option>
<option>B</option>
<option>C</option>
</select>
{{message}}
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: ''
}
});
</script>
</body>
组件
<body>
<div id="app">
<blog-post v-for="post in posts" v-bind:key="post.id" v-bind:title="post.title"/>
</div>
<script>
// 定义一个新组件
Vue.component('blog-post', {
// 通过 Prop 向子组件传递数据
props: ['title'],
template: '<h3>{{ title }}</h3>'
})
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
posts: [
{id: 1, title: 'My journey with Vue'},
{id: 2, title: 'Blogging with Vue'},
{id: 3, title: 'Why Vue is so fun'}
]
}
})
</script>
</body>
axios
Axios 是一个基于 promise 的 HTTP 库
<body>
<div id="axios">
<div>{{info.name}}</div>
<div>{{info.address.street}}</div>
<a v-bind:href="info.url">click me</a>
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el: "#axios",
data() {
return {
info: {
name: null,
url: null,
address: {
"street": null,
"city": null,
"cuntry": null
}
}
}
},
mounted() {
axios.get('../data.json').then(response => (this.info = response.data));
}
});
</script>
</body>
计算属性
计算属性即一个方法,但是这个方法的结果会缓存以后当成一个属性来用。计算属性的主要目的就是为了将不常变化的结果缓存起来,节约系统开销。只在相关响应式依赖发生改变时它们才会重新求值.
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 使用控制台可以发现vm.currentTime1()一直在变化,而vm.currentTime2不变 -->
<p>调用方法:{{currentTime1()}}</p>
<p>调用属性:{{currentTime2}}</p>
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
methods: {
currentTime1: function () {
return Date.now();
}
},
//计算属性
computed: {
currentTime2: function () {
return Date.now();
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
插槽(v-slot)
<todo>
<h1>hello vue!</h1>
</todo>
Vue.component("todo",{
template: '<div>' +
'<slot></slot>' +
'</div>'
});
自定义事件($emit)
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<mparent></mparent>
</div>
</template>
<style>
</style>
<script>
//引入页面并导出
import mparent from "./views/Parent";
export default {
components: {
mparent
}
};
</script>
第一个组件Parent.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>parent</h1>
<!-- 显示组件间传的值 -->
<h3>{{msg}}</h3>
<!-- 组件间传值 -->
<mchild v-bind:msg="'from parent msg'" @showmsg="showthemsg"></mchild>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import mchild from "./Child";
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: ""
};
},
components: {
mchild
},
methods: {
// 参数自动配置,不用再上面手写
showthemsg(val) {
this.msg = val;
}
}
};
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>>
</style>
第二个组件Child.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>child</h3>
<!-- 显示组件间传的值 -->
<h3>{{msg}}</h3>
<button @click="passmsg">emit事件传值</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// 通过<v-bind>、props组件间传值
props: {
msg: {
type: String,
default: ""
}
},
// 通过自定义事件组件间传值
methods: {
passmsg() {
this.$emit("showmsg", "emit事件传值");
}
}
};
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>>
</style>
也可用一个中间件,使用$emit触发事件,$on函数监听事件
vue-router
定义一个路由
写一个vue页面,之后在index.js中定义路由
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [{
path: '/home',
component: () => import('../views/Home.vue')
}]
})
在想使用路由组件的地方添加
<router-view/>
或跳转到组件
<!-- 使用<route-link>跳转 -->
<router-link to="/home">home</router-link>
<!-- 编程式导航 -->
<button @click="tohome">homeb</button>
使用编程式导航编写函数实现跳转功能
methods: {
tohome() {
this.$router.push({ path: "/home" });
}
}
动态路由
// 动态路由,需传送一个叫id的参数
path: '/home/:id',
使用时需传递参数,如
http://localhost:8080/#/home/234
动态路由传参
// 编写方法时使用query属性传参
this.$router.push({ path: "/home",query:{id:3}});
// 编写方法时使用params属性传参,params一般和路由名字一起用
this.$router.push({ name: "home",params:{id:3}});
嵌套路由(children)
routes: [{
// 动态路由,需传送一个叫id的参数
path: '/home/:id',
component: () => import('../views/Home.vue'),
children: [{
path: '/child',
component: () => import('../views/Child.vue')
}]
}]
之后再home页中想使用的地方添加<router-view></router-view>就行了
钩子(mounted)
可用于检查登陆状态,cookie等等浏览器事件,例子
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
console.log(to.path);
next()
});
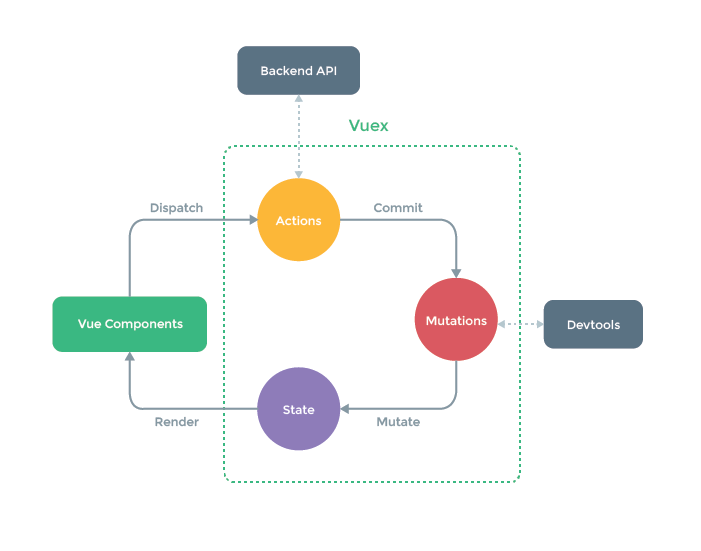
vuex



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号