11.Java SDK源码分析系列笔记-Hashtable
1. 是什么
线程安全的hashmap
2. 如何使用
public class HashtableTest
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
{
Hashtable<Integer, Integer> map = new Hashtable<>();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
{
map.put(i, i);
}
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 100000; i < 200000; i++)
{
map.put(i, i);
}
});
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(map.size());
for (int i = 0; i < 200000; i++)
{
if (!map.contains(i))
{
throw new RuntimeException("并发put有问题");//不会抛出异常说明并发put没问题
}
System.out.println(map.remove(i));
}
}
}
3. 原理分析
3.1. uml
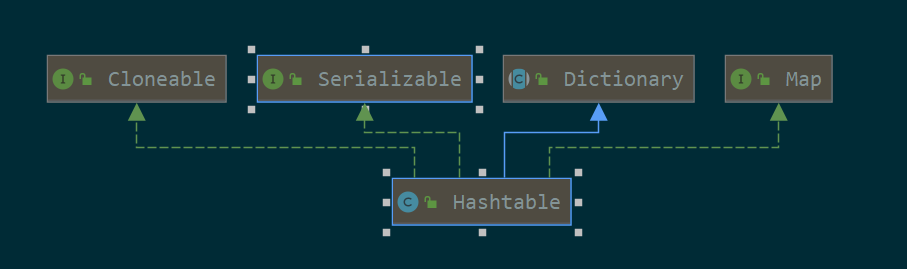
可克隆,可序列化,实现了Map接口
3.2. 构造方法
使用链地址法(单链表)解决Hash冲突
初始化容量为11,默认的加载因子为0.75
public class Hashtable<K,V>
extends Dictionary<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
//使用Entry数组实现
private transient Entry<?,?>[] table;
//map中实际元素的个数
private transient int count;
//以下两个决定了什么时候扩容
private int threshold;
private float loadFactor;
private transient int modCount = 0;
public Hashtable() {
//初始化容量为11,加载因子为0.75
this(11, 0.75f);
}
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
//检查参数合法
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Load: "+loadFactor);
if (initialCapacity==0)
initialCapacity = 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
//创建table数组
table = new Entry<?,?>[initialCapacity];
//threshold取int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE 8和initialCapacity * loadFactor中的小者
threshold = (int)Math.min(initialCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
}
}
3.3. put方法
//加了synchronized
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
//与HashMap不同,这里value不能为null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
//计算下标
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
//遍历链表直到找到相等的节点或者到末尾
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
//找到了,替换value
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
//没有找到,新建节点加入链表
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
}
3.3.1. 使用synchronized加锁
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
//...
}
3.3.2. 计算key落在entry数组中的哪个位置【或者说哪个链表】
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
//计算下标
//计算index是通过对数组长度取模而不是使用与操作
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
3.3.3. 遍历链表直到找到相等的节点或者到末尾
//遍历链表直到找到相等的节点或者到末尾
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
//找到了,替换value
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
3.3.4. 没有找到,新建节点加入链表头部
- addEntry方法
private void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int index) {
modCount++;
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
//判断是否需要扩容
if (count >= threshold) {
// Rehash the table if the threshold is exceeded
rehash();
tab = table;
hash = key.hashCode();
index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
}
// Creates the new entry.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>) tab[index];
//新建节点并且直接放入数组相应位置
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
count++;
}
3.3.4.1. 扩容
- rehash方法
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected void rehash() {
int oldCapacity = table.length;
Entry<?,?>[] oldMap = table;
// overflowconscious code
//新capacity=旧capacity*2+1
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1;
//如果容量超过了MAX_ARRAY_SIZE(int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE 8),那么以MAX_ARRAY_SIZE为准
if (newCapacity MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {
if (oldCapacity == MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)
// Keep running with MAX_ARRAY_SIZE buckets
return;
newCapacity = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
//以新capacity创建新数组
Entry<?,?>[] newMap = new Entry<?,?>[newCapacity];
modCount++;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
table = newMap;
//由后往前遍历entry数组
for (int i = oldCapacity ; i > 0 ;) {
//从头到尾遍历链表
for (Entry<K,V> old = (Entry<K,V>)oldMap[i] ; old != null ; ) {
//e表示此次要迁移的节点,old表示下一个要迁移的节点
Entry<K,V> e = old;
old = old.next;
//计算e在新entry数组中的位置
int index = (e.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % newCapacity;
//把e的next指向新entry数组中的位置(链表的头节点)
e.next = (Entry<K,V>)newMap[index];
//再把新entry数组中的位置赋值为e
//等于就是头插法
newMap[index] = e;
}
}
}
3.4. get方法
//加了synchronized
public synchronized V get(Object key) {
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
//计算在那个链表中
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
//遍历链表找到相等的节点
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return (V)e.value;
}
}
return null;
}
3.4.1. 使用synchronized加锁
public synchronized V get(Object key) {
}
3.4.2. 计算key落在entry数组中的哪个位置【或者说哪个链表】
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
//计算在那个链表中
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
3.4.3. 遍历链表直到找到相等的节点或者到末尾
//遍历链表找到相等的节点
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return (V)e.value;
}
}
3.5. remove方法
使用synchronized修饰
同get方法找到节点,删除的操作就是链表节点的删除操作
public synchronized V remove(Object key) {
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(Entry<K,V> prev = null ; e != null ; prev = e, e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
modCount++;
if (prev != null) {
//不是头节点
prev.next = e.next;
} else {
//头节点
tab[index] = e.next;
}
count;
//help GC
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = null;
return oldValue;
}
}
return null;
}
3.5.1. 使用synchronized加锁
public synchronized V remove(Object key) {
}
3.5.2. 计算key落在entry数组中的哪个位置【或者说哪个链表】
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
3.5.3. 遍历链表直到找到相等的节点或者到末尾,把value置为null
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(Entry<K,V> prev = null ; e != null ; prev = e, e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
modCount++;
if (prev != null) {
//不是头节点
prev.next = e.next;
} else {
//头节点
tab[index] = e.next;
}
count;
//help GC
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = null;
return oldValue;
}
}
3.6. containsKey方法
//加了synchronized
public synchronized boolean containsKey(Object key) {
//以下逻辑同get方法
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
3.6.1. 使用synchronized加锁
public synchronized boolean containsKey(Object key) {
}
3.6.2. 计算key落在entry数组中的哪个位置【或者说哪个链表】
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
3.6.3. 遍历链表直到找到相等的节点或者到末尾
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号