10.Java SDK源码分析系列笔记-TreeMap
1. 是什么
基于红黑树(平衡二叉搜索树)实现,效率为O(logN)的key-value对。
迭代时输出的顺序是
- 按照key的自然顺序来遍历的
- 也可以使用自定义的Comparator进行排序
2. 使用
public class TreeMapTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
TreeMap<String, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("1", "a");
map.put("3", "c");
map.put("2", "b");
map.put("4", "d");
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet())
{
/*
* 1=a
2=b
3=c
4=d
* */
System.out.println(entry);
}
}
}
3. 源码分析
3.1. uml
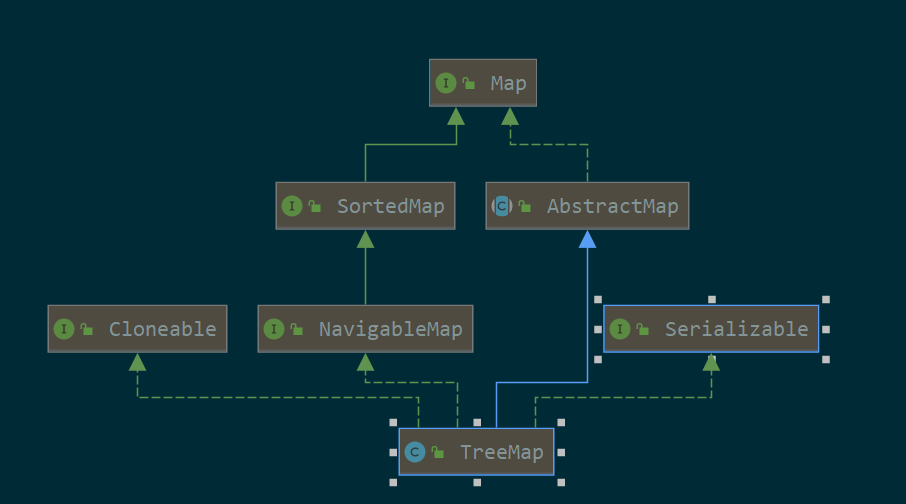
3.2. 构造方法
public class TreeMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable//NavigableMap是个有序的map接口
{
//使用compartor来排序key
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;
//红黑树的root
private transient Entry<K,V> root;
//红黑树的size
private transient int size = 0;
private transient int modCount = 0;
//无参构造,默认按key的自然顺序排序
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}
//自定义comparator进行排序
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
}
3.3. put
public V put(K key, V value) {
//root节点为空,那么先构造红黑树
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) {
//有自定义的comparator则使用自定义的comparator,否则使用key的compareTo(因此key必须实现Comparable接口)
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
//有自定义的comparator
if (cpr != null) {
//二叉搜索树的搜索操作
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
//比当前节点小走左边
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
//比当前节点大走右边
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
//找到了,替换value
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
//没有自定义的comparator
else {
//key必须不为空
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
//逻辑同上
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
//把节点实际插入到树中
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
//维持红黑树的平衡
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
3.4. get
public V get(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
//自定义compartor走这段,实际跟下面的差不多
if (comparator != null)
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
//二叉搜索树的搜索操作,从root节点出发寻找
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
return null;
}
3.5. containsKey
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
//简单的调用getEntry方法,同get
return getEntry(key) != null;
}
3.6. remove
public V remove(Object key) {
//查到节点
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
if (p == null)
return null;
V oldValue = p.value;
//删除该节点
deleteEntry(p);
return oldValue;
}
private void deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> p) {
modCount++;
size;
//删除节点有左右孩子,找到successor节点,并让p指向此节点
if (p.left != null && p.right != null) {
Entry<K,V> s = successor(p);
p.key = s.key;
p.value = s.value;
p = s;
}
// 代替删除节点的节点(有左孩子则使用左孩子,否则右孩子)
Entry<K,V> replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right);
//使用左孩子或者右孩子替换当前删除节点
if (replacement != null) {
// Link replacement to parent
replacement.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = replacement;
else if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = replacement;
else
p.parent.right = replacement;
// 清空删除节点的指针
p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;
// 红黑树平衡
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(replacement);
//树中只有一个节点(就是删除节点)
} else if (p.parent == null) {
root = null;
} else {//没有左右孩子
if (p.color == BLACK)
// 红黑树平衡
fixAfterDeletion(p);
//那么修改父节点的指针即可
if (p.parent != null) {
if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = null;
else if (p == p.parent.right)
p.parent.right = null;
p.parent = null;
}
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号