5.Java SDK源码分析系列笔记-Vector
目录
1. 是什么
线程安全的list
2. 如何使用
public class VectorTest
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
{
Vector<Integer> vector = new Vector<>();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
vector.add(i);
}
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 10000; i < 20000; i++)
{
vector.add(i);
}
});
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
assert vector.size() == 20000;
for (int i = 0; i < 20000; i++)
{
assert vector.contains(i);
}
vector.remove(2);
System.out.println(vector.contains(1));//true
System.out.println(vector.contains(2));//false
}
}
3. 源码分析
3.1. uml
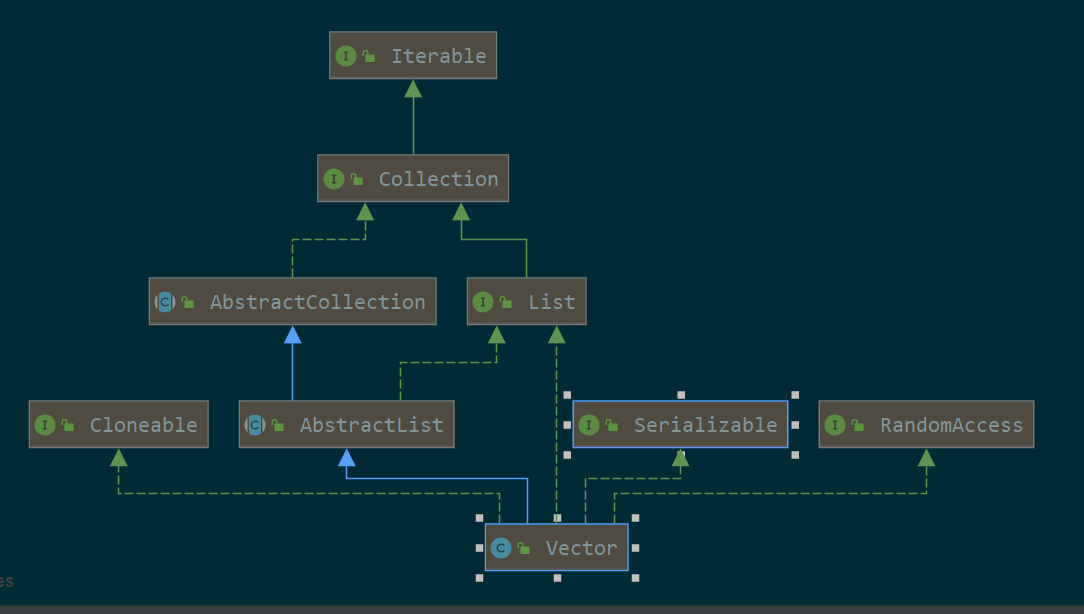
可以看出是个List,可以克隆,可以序列化,可以使用下标访问
3.2. 构造方法
默认初始化长度为10,扩容时候的增量为两倍
public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
//底层使用object数组实现
protected Object[] elementData;
//数组中实际的元素个数
protected int elementCount;
//数组扩容的增量。如果为0那么扩容为原来的两倍
protected int capacityIncrement;
public Vector() {
//初始容量为10
this(10);
}
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
//0表示扩容的时候扩为原来的两倍
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
}
3.3. add方法
不扩容的时候O(1),扩容O(N)
//加了synchronized
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
//确保容量足够容纳新加的元素
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
//直接赋值
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}
3.3.1. 加了synchronized保证线程安全
可以看出这个方法使用sychronized修饰
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
//。。。
}
3.3.2. 根据情况进行扩容并迁移旧的数组
- ensureCapacityHelper
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
// 数组容量不够,需要扩容
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
//扩容
grow(minCapacity);
}
- grow
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflowconscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
//没有指定的话扩容为两倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
//避免太小后续又需要频繁扩容
if (newCapacity minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
//避免太大OOM
if (newCapacity MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
//复制原有数组的元素到新的数组
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
3.3.3. 插入到数组末尾
//直接赋值
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
3.4. remove方法【根据下标删除】
- O(N)
public synchronized E remove(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
//获取index位置的元素,删除后返回这个元素
E oldValue = elementData(index);//就是(E) elementData[index];
//计算要移动的元素的个数
int numMoved = elementCount - index - 1;
//把index后面的所有元素复制到index开始的后续元素中--相当于删除了index位置的元素
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
//置为null,让gc回收
elementData[elementCount] = null; // Let gc do its work
return oldValue;
}
3.4.1. 加了synchronized保证线程安全
public synchronized E remove(int index) {
//...
}
3.4.2. 把要删除的元素后面的元素往前挪
//计算要移动的元素的个数
int numMoved = elementCount - index - 1;
//把index后面的所有元素复制到index开始的后续元素中--相当于删除了index位置的元素
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
3.5. contains方法
- O(N)
public boolean contains(Object o) {
//indexOf方法加了锁,如果能找到返回大于0的数
return indexOf(o, 0) >= 0;
}
- indexOf
public synchronized int indexOf(Object o, int index) {
//要找的数为null
if (o == null) {
//遍历数组找
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
//要找的数不是null
} else {
//遍历数组找
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return 1;
}
3.5.1. synchronized保证线程安全
public synchronized int indexOf(Object o, int index) {
//...
}
3.5.2. 遍历数组找到相等的元素
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
{
//...
}
4. 线程安全问题
单独的使用方法是可以保证线程安全的。但是复合操作是不能保证的,举个例子:
public Object deleteLast(Vector v){
int lastIndex = v.size()1;
v.remove(lastIndex);
}
这个自定义的deleteLast方法由size和remove组合成的复合方法,可能抛出ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号