Contest3913 - 计科23级算法设计与分析上机作业-02
题目链接
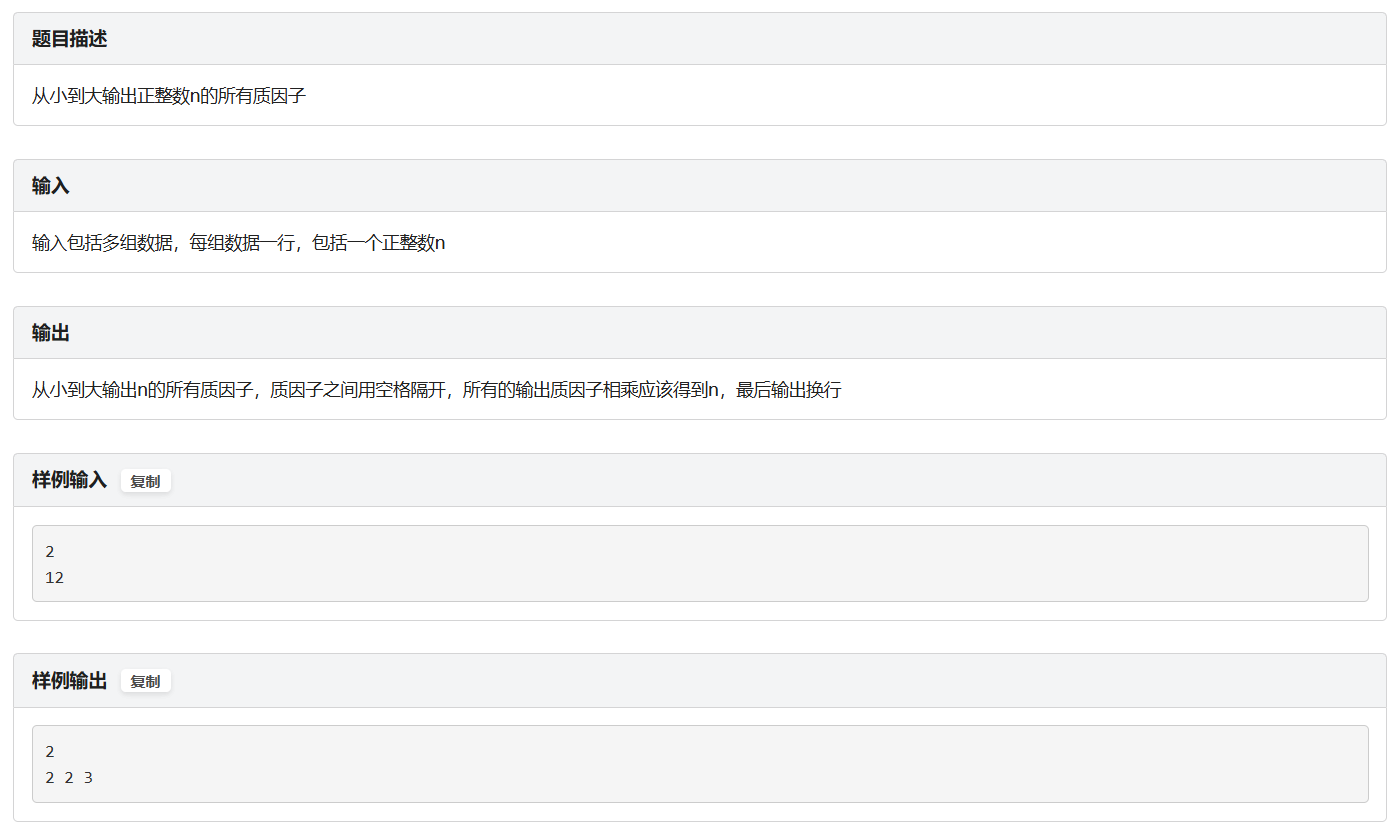
A. 因式分解
题面
思路
分解质因数模板题
示例代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
//#define int ll
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define all(x) x.begin(),x.end()
#define fer(i, m, n) for(int i = m; i < n; ++i)
#define ferd(i, m, n) for(int i = m; i >= n; --i)
#define dbg(x) cout << #x << ' ' << char(61) << ' ' << x << '\n'
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 2e5 + 2;
const int inf = 1e9;
void get(vector<int> &arr, int n){
for(int i = 2; i <= n / i; i++){
while(n % i == 0){
arr.push_back(i);
n /= i;
}
}
if(n > 1) arr.push_back(n);
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr);
int n;
while(cin >> n) {
vector<int> arr;
get(arr, n);
for(auto x : arr) cout << x << ' ';
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
B.去除重复字母
题面

思路
用哈希数组纪录\(26\)个字母的出现状态,在遍历每个字符时同步更新状态
示例代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
//#define int ll
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define all(x) x.begin(),x.end()
#define fer(i, m, n) for(int i = m; i < n; ++i)
#define ferd(i, m, n) for(int i = m; i >= n; --i)
#define dbg(x) cout << #x << ' ' << char(61) << ' ' << x << '\n'
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 2e5 + 2;
const int inf = 1e9;
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr);
string s;
while (cin >> s) {
vector<bool> v(26);
for(auto c : s) {
if(!v[c - 'a']) {cout << c; v[c - 'a'] = true;}
}
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
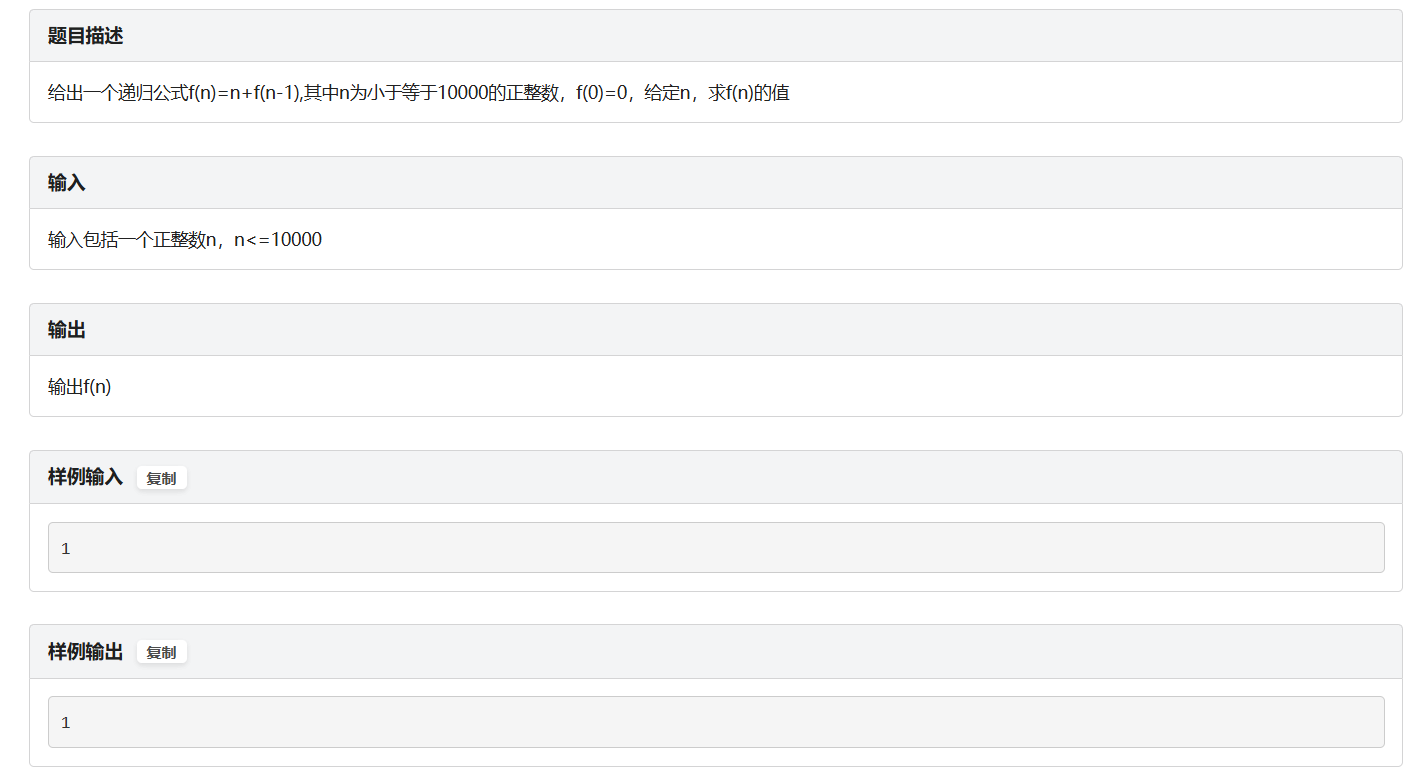
C.递归求和
题面
思路
模拟即可
示例代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
//#define int ll
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define all(x) x.begin(),x.end()
#define fer(i, m, n) for(int i = m; i < n; ++i)
#define ferd(i, m, n) for(int i = m; i >= n; --i)
#define dbg(x) cout << #x << ' ' << char(61) << ' ' << x << '\n'
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 2e5 + 2;
const int inf = 1e9;
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr);
int f[10005];
int n;
cin >> n;
f[0] = 0;
fer(i, 1, n + 1) f[i] = i + f[i - 1];
cout << f[n];
return 0;
}
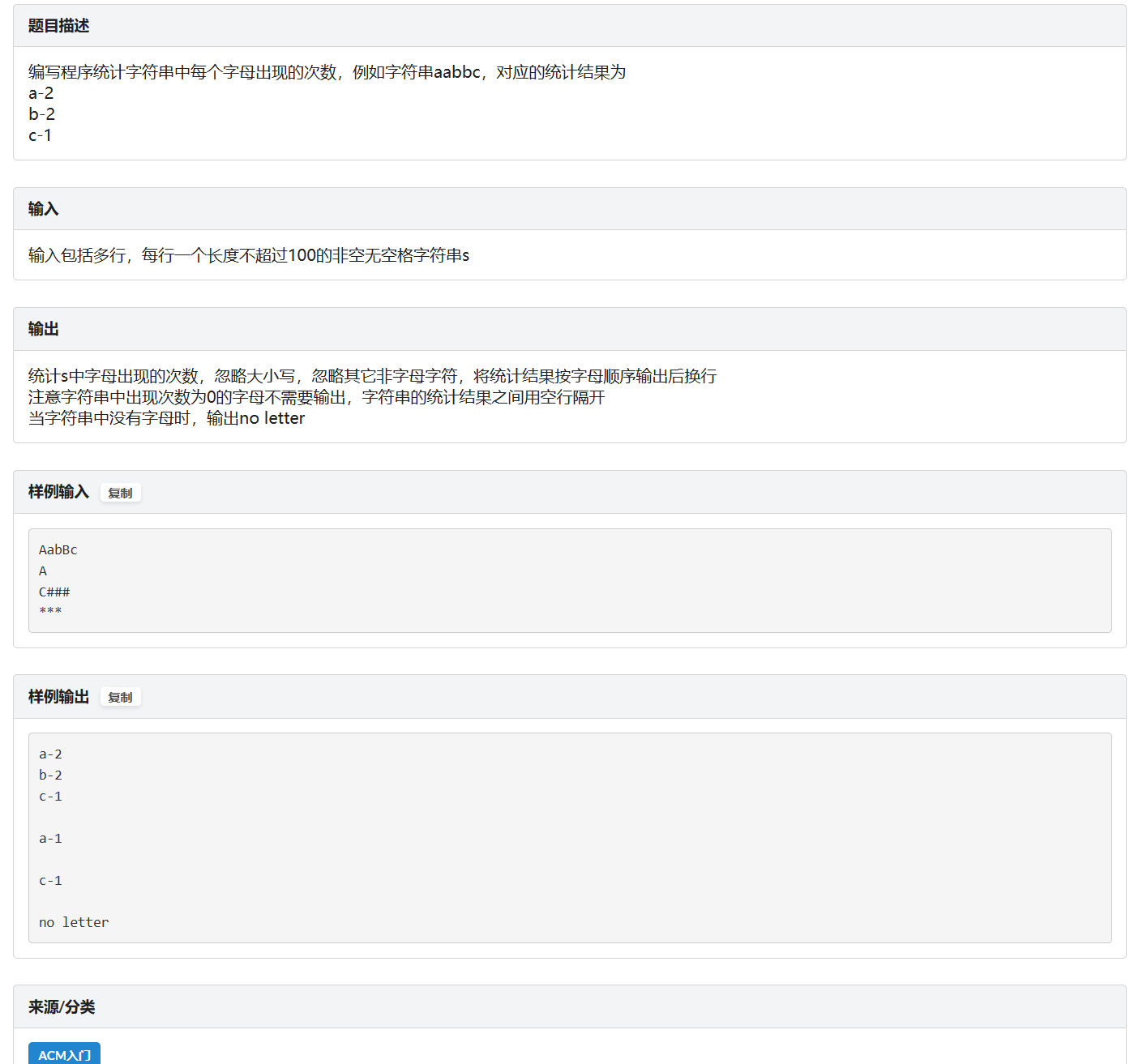
D.统计字符串中每个字母出现的次数
题面
思路
用map直接模拟即可
示例代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
//#define int ll
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define all(x) x.begin(),x.end()
#define fer(i, m, n) for(int i = m; i < n; ++i)
#define ferd(i, m, n) for(int i = m; i >= n; --i)
#define dbg(x) cout << #x << ' ' << char(61) << ' ' << x << '\n'
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 2e5 + 2;
const int inf = 1e9;
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr);
string s;
while(cin >> s){
map<int, int> mp;
for(char c : s) {
if(c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') mp[c - 'a']++;
else if(c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z') mp[c - 'A']++;
}
if(mp.empty()) cout << "no letter\n";
else {
for(auto c : mp) cout << char(c.first + 'a') << '-' << c.second << '\n';
}
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
E.十进制转换成八进制
题面

思路
直接模拟即可,或者使用oct流操作符(十六进制是'hex'流操作符),或者使用sprintf格式化输出
示例代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
//#define int ll
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define all(x) x.begin(),x.end()
#define fer(i, m, n) for(int i = m; i < n; ++i)
#define ferd(i, m, n) for(int i = m; i >= n; --i)
#define dbg(x) cout << #x << ' ' << char(61) << ' ' << x << '\n'
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 2e5 + 2;
const int inf = 1e9;
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin >> n;
string s;
while(n) {
int c = n % 8;
s += c + '0';
n /= 8;
}
reverse(all(s));
if(s[0] == '0') cout << s.substr(1) << '\n';
else cout << s << '\n';
//cout << oct << n << '\n';
// char s[100005];
// sprintf(s, "%o", n);
// cout << s << '\n';
return 0;
}
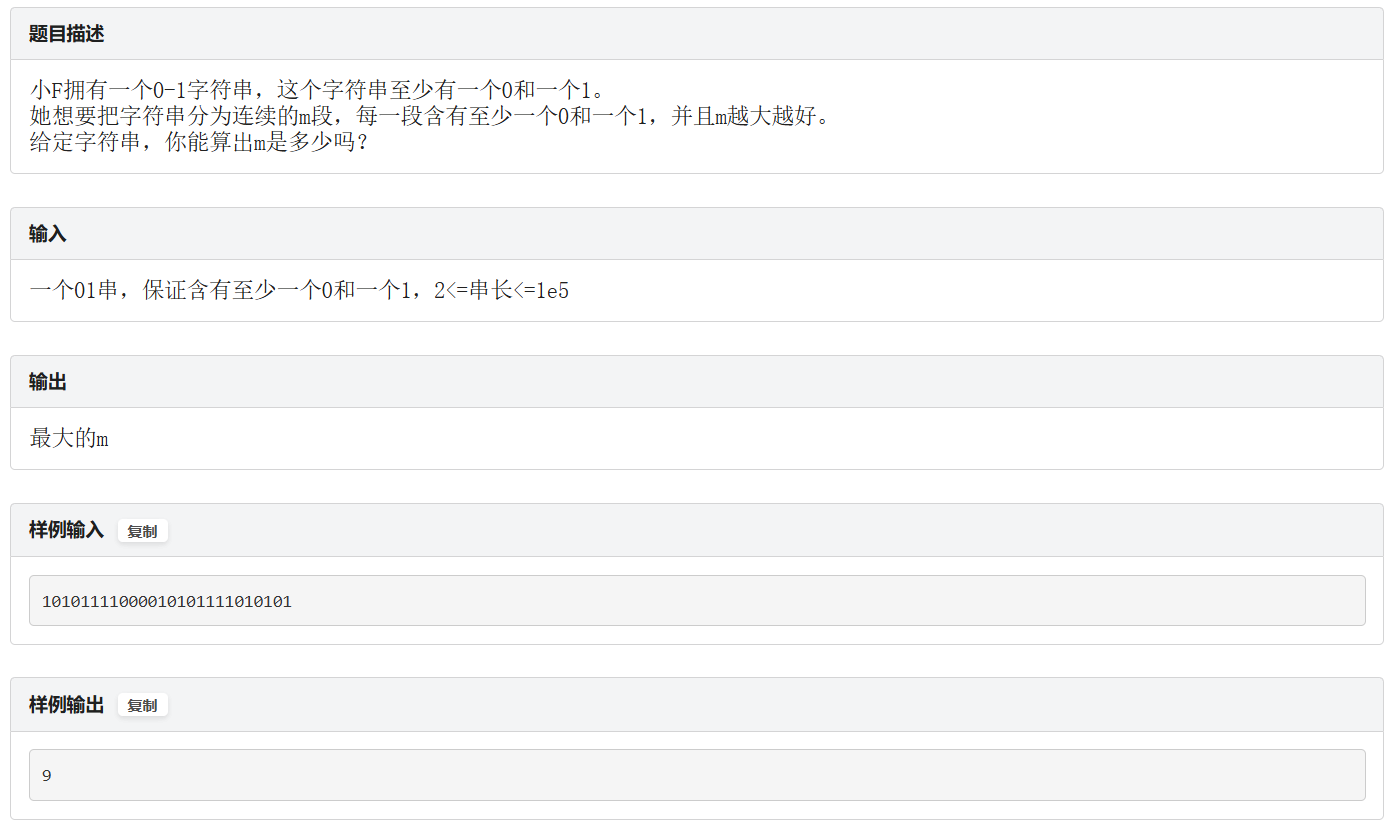
F.字串加工
题面
思路
滑动窗口,定义前后指针,当两指针范围内同时出现了\(0\)和\(1\)时(也即出现了不同的字符),更新左指针位置为右指针的后一个位置。每次操作是右指针后移。最后一部分如果没有同时包含\(0, 1\)时可以将其合并到前一部分中,所以不需要管这一部分。
示例代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
//#define int ll
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define all(x) x.begin(),x.end()
#define fer(i, m, n) for(int i = m; i < n; ++i)
#define ferd(i, m, n) for(int i = m; i >= n; --i)
#define dbg(x) cout << #x << ' ' << char(61) << ' ' << x << '\n'
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 2e5 + 2;
const int inf = 1e9;
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr);
string s;
cin >> s;
int ans = 0;
int ind1 = 0, ind2 = 0;
while(ind2 < s.size()){
if(s[ind1] != s[ind2]){
ans++;
ind1 = ind2 + 1;
}
ind2++;
}
//if(ind1 < s.size()) ans--;
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号