Week1 Union-Find
前言:
Union-Find是没学过的数据结构吧,在学kruskal算法的时候看网上都是用并查集来解决是否在同一个连通分量的问题,但是没有深究。感觉这个还是挺重要的,一是可以快速解决是否在同一个连通分量的问题,而是可以看有多少个联通分支。
核心思想:
并查集解决的问题就是看两个点是否连通。
其核心思想在于用数组记录每个点,但是不是记录每个点的集合,而是记录每个点的父节点。这样像一棵树一样可以通过迭代一直找到根节点,比较两个点的根节点就知道它们是否联通了。
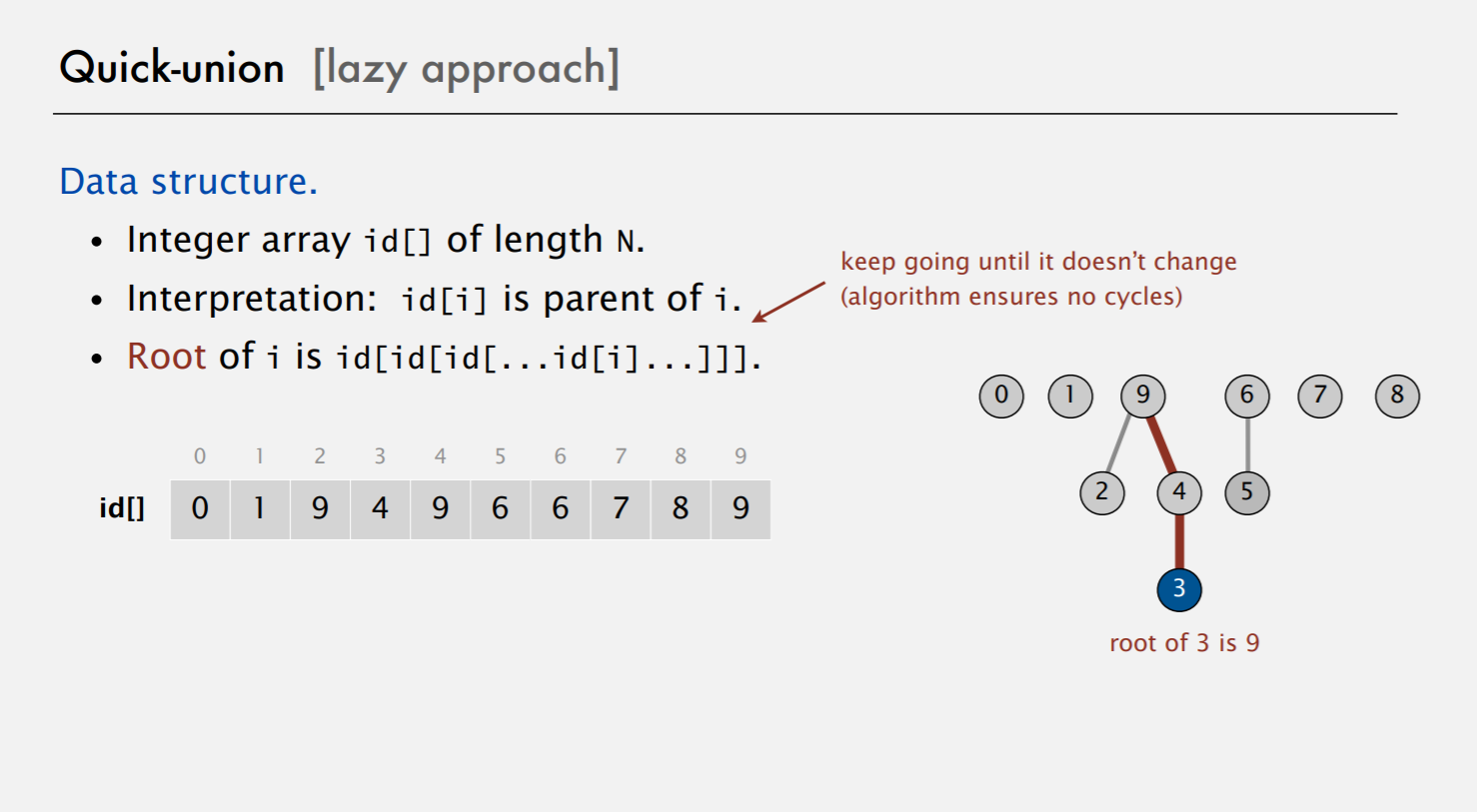
操作+代码:
并查集的操作就基于它的核心思想。
将两个连通分量并联-union:一直迭代到两个根结点,然后改变一个根节点的值,使它的父节点为另一个根节点即可。
查找是否相连-find:比较根节点即可。
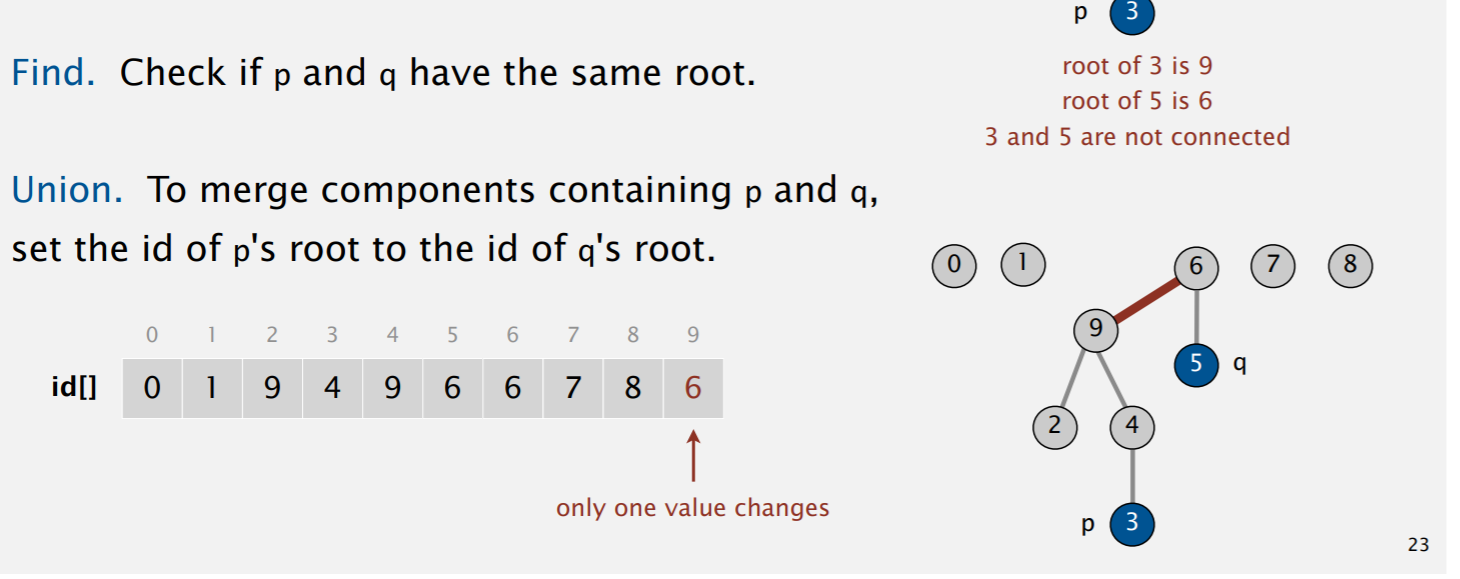
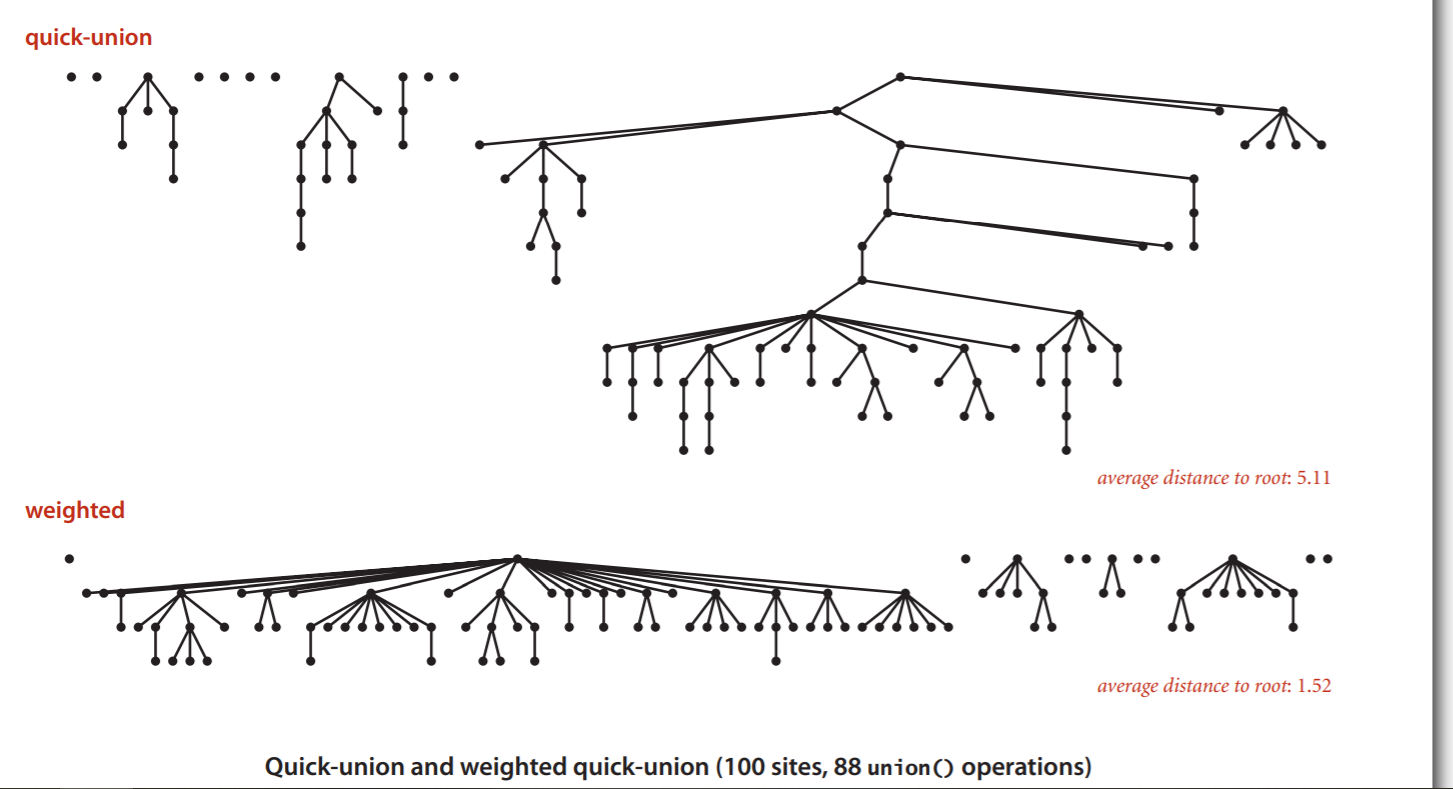
改进:因为随意地将根节点改变很有可能最后地树很高,这样查根耗时很长,因此需要使用带权并查集。
带权并查集:将每个连通分量的结点个数当作它的权值,每次让权值小的接到权值大的数的下面,这样就会使整个树平整。
路径压缩:如果在find过程中,某个结点不是根节点。那么让它的父节点连到它父节点的父节点,并且直接检查它的父节点。
代码:(直接贴包里的了)
public class UF { private int[] parent; // parent[i] = parent of i private byte[] rank; // rank[i] = rank of subtree rooted at i (never more than 31) private int count; // number of components /** * Initializes an empty union-find data structure with * {@code n} elements {@code 0} through {@code n-1}. * Initially, each elements is in its own set. * * @param n the number of elements * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code n < 0} */ public UF(int n) { if (n < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); count = n; parent = new int[n]; rank = new byte[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { parent[i] = i; rank[i] = 0; } } /** * Returns the canonical element of the set containing element {@code p}. * * @param p an element * @return the canonical element of the set containing {@code p} * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= p < n} */ public int find(int p) { validate(p); while (p != parent[p]) { parent[p] = parent[parent[p]]; // path compression by halving p = parent[p]; } return p; } /** * Returns the number of sets. * * @return the number of sets (between {@code 1} and {@code n}) */ public int count() { return count; } /** * Returns true if the two elements are in the same set. * * @param p one element * @param q the other element * @return {@code true} if {@code p} and {@code q} are in the same set; * {@code false} otherwise * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless * both {@code 0 <= p < n} and {@code 0 <= q < n} * @deprecated Replace with two calls to {@link #find(int)}. */ @Deprecated public boolean connected(int p, int q) { return find(p) == find(q); } /** * Merges the set containing element {@code p} with the * the set containing element {@code q}. * * @param p one element * @param q the other element * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless * both {@code 0 <= p < n} and {@code 0 <= q < n} */ public void union(int p, int q) { int rootP = find(p); int rootQ = find(q); if (rootP == rootQ) return; // make root of smaller rank point to root of larger rank if (rank[rootP] < rank[rootQ]) parent[rootP] = rootQ; else if (rank[rootP] > rank[rootQ]) parent[rootQ] = rootP; else { parent[rootQ] = rootP; rank[rootP]++; } count--; } // validate that p is a valid index private void validate(int p) { int n = parent.length; if (p < 0 || p >= n) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("index " + p + " is not between 0 and " + (n-1)); } } /** * Reads an integer {@code n} and a sequence of pairs of integers * (between {@code 0} and {@code n-1}) from standard input, where each integer * in the pair represents some element; * if the elements are in different sets, merge the two sets * and print the pair to standard output. * * @param args the command-line arguments */ public static void main(String[] args) { int n = StdIn.readInt(); UF uf = new UF(n); while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) { int p = StdIn.readInt(); int q = StdIn.readInt(); if (uf.find(p) == uf.find(q)) continue; uf.union(p, q); StdOut.println(p + " " + q); } StdOut.println(uf.count() + " components"); } }
编程作业:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/544646c410ee
这人家讲的很清楚,主要是防止backwash问题
刷题感想:
未完待续,还没刷呢。leetcode上的至少是中等的题我吐了。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号