遗传算法解决TSP(旅行商)问题
项目地址:gitee
用遗传算法来解决旅行商问题
旅行商问题
也叫旅行推销员问题(Traveling salesman problem:TSP):给定一系列城市和每对城市之间的距离,求访问每座城市一次并回到起点城市的最短回路.它是组合优化中的一个NP难问题 .
解法思路
途程构建法:从距离矩阵中产生一个近似最佳解的途径
途程改善法:先给定一个可行的途程,然后进行改善,一直到不能改善为止
经典解决算法
枚举法(采用深度优先策略),回溯法,分支限界法(FIFO队列思想),贪心算法
现代算法(启发式算法)
遗传算法、模拟退火法、蚁群算法、禁忌搜索算法、贪婪算法和神经网络等
NP难问题
NP:Non-deterministic Polynomial,多项式复杂程度的非确定性问题
在算法中的一个衡量程序优劣的重要指标:复杂度,通常复杂度是一个多项式的最高量级
$P(n)=anm+bn+cn{m-2}...+dn+e+fn+gn^{-2}+...$
$O(P(n))=n^m$
若存在这样确定的多项式,那么就是一个P类问题(确定多项式)
不存在的话,就是一个NP类问题.
如最经典的TSP问题,如果用枚举法,对于n个城市求最短回路就需要(n-1)!次,就不是多项式了.
遗传算法
遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm,GA)是一种根据大自然中生物演化规律设计的.该算法通过数学的方式,利用计算机仿真运算,将问题的求解过程转换成类似生物进化中染色体基因交叉,变异等过程.
在求解复杂的组合优化问题时,相对于一些常规的优化算法,通常能较快地获得较好得优化结果
基本特征
编码(基因,个体):gen
由于遗传算法不能直接处理问题空间的参数,所以需要通过编码将要求解的问题表示成遗传空间的染色体.一个基因就是解决问题的一种解,一个种群,就是一组这样的解,遗传算法就是通过多代进化,淘汰得到最优解的过程
适应度函数fitness
适应度,表示某一个体对环境的适应能力,也表示该个体的繁殖能力,遗传算法的适应度函数也叫评价函数,是用来判断群体中的个体优劣程度的指标
遗传算法在搜索进化过程中一般不需要其他外部信息,仅用评估函数来评估个体或解的优劣,并作为以后遗传操作的依据。由于遗传算法中,适应度函数要比较排序并在此基础上计算选择概率,所以适应度函数的值要取正值。由此可见,在不少场合,将目标函数映射成求最大值形式且函数值非负的适应度函数是必要的
初始群体选取pop
遗传算法中初始群体的个体选取是随机的,一般来讲,初始群体的设定可采取如下的策略:
a)根据问题固有知识,设法把握最优解所占空间在整个问题空间中的分布范围,然后,在此分布范围内设定初始群体
b)先随机生成一定数目的个体,然后从中挑出最好的个体加到初始群体中。这种过程不断迭代,直到初始群体中个体数达到了预先确定的规模
运算过程
(1)初始化
设置最大进化代数T,随机生成M个个体作为初始群体P(0),并随机打乱(shuffle)顺序产生基因
(2)个体评价
计算群体P(t)中各个个体的适应度,采用比值法(最短距离/)来定义每个基因的适应度
(3)选择运算(淘汰差的基因)
将选择算子作用于群体。选择的目的是把优化的个体直接遗传到下一代或通过配对交叉产生新的个体再遗传到下一代。选择操作是建立在群体中个体的适应度评估基础上的
本实验采用锦标赛算子算子,也就是优胜劣汰,适应度低于平均值的基因被淘汰(重组变异),特点是差的基因一定会被淘汰
适应度函数用最短距离/该基因的距离表示
(ps:也使用过轮盘赌法,但是因为其随机性太大,导致无法收敛(只能到40000),已弃用)
(4)交叉运算
将交叉算子作用于群体。遗传算法中起核心作用的就是交叉算子
本实验采用单点交叉算子,就是截取一段基因,嫁接到另一段
(5)变异运算
将变异算子作用于群体。即是对群体中的个体串的某些基因座上的基因值作变动
本实验通过反转基因片段来实现变异

(6)终止条件判断
当t=T,则以进化过程中所得到的具有最大适应度个体作为最优解输出,终止计算。
p1len=index1时,就是迭代到22时,插入temp,后续接着插入
(7)收敛
只要采样数足够大,运行时间足够长,理论上一定能找到最优解,但是现实中是难以达到的.所以本次实验认定最短距离低于20000时即收敛(实际实验中最小距离是19067:迭代10000代),即最大迭代10000次,若最短距离不能达到20000以下,则认为不能收敛
算法实现
TSP类
①导库
from random import shuffle
from random import random
from random import randint
from City import *
from Func import *
shuffle:洗牌,用于随机打乱序列,也就是生成初始基因
random:生成[0,1)之间的随机数,实现变异和交叉
randint:用于生成范围内的随机整数,实现变异和交叉的的基因操作
②类成员
pop=[] #种群数组
pop_size=-1 #种群大小
c_rate=-1 #交叉率
m_rate=-1 #变异率
ga_num=-1 #最大迭代次数
fitness=[] #适应度数组
best_dist=-1 #记录最短距离
best_gen=[] #记录目前最优旅行方案
city=City() #城市类
③构造方法
def __init__(self,c_rate:float=0.5,m_rate:float=0.05,pop_size:int=100):
'''best_gen:最优的基因;flag:标志初始迭代;target_dis:目标距离
c_rate:交叉率,默认0.5;m_rate:变异率:默认0.05
pop_size:种群大小,默认100;ga_num:迭代次数,默认300
'''
self.fitness=[0 for i in range(self.pop_size)]
self.c_rate=c_rate
self.m_rate=m_rate
self.pop_size=pop_size
④初始化
def init(self,filepath:str="./data/china.txt"):
self.city.loadCity(filepath)
self.pop=self.createPop(self.pop_size)#创建种群
self.fitness=self.getFitness(self.pop)#计算适应度
⑤创建种群
创建种群,就是将个体添加到种群中
返回一个二维列表,列表的每项都是从0到city_size
def createPop(self,size:int):
'''size是种群pop一维的shape,返回一个种群pop'''
pop=[]
for i in range(size):
gen=list(range(self.city.city_size))
shuffle(gen)
pop.append(gen)
return pop
⑥计算种群适应度
比值法
def getFitness(self,pop:list):
'''参数pop是种群,返回一个列表gf,装载整个种群的适应度'''
gf=[] #记录适应度
for i in range(len(pop)):
gen=pop[i] #取一个基因
dis=self.city.genDistance(gen)
fit=self.best_dist/dis #适应度用当前最优距离/该个体的距离,比值越接近1,适应度越高
gf.append(fit)
return gf
⑦交叉
def cross(self,parent1:list,parent2:list):#交叉p1,p2的部分基因
'''参数p1,p2是待交叉的两个基因'''
if random()>self.c_rate: #如果此时生成的概率大于交叉率,则不交叉
return parent1
index1=randint(0,self.city.city_size-1)
index2=randint(index1,self.city.city_size-1)#[0,1,2...index1...index2...citysize-1]
tempGene=parent2[index1:index2]#截取的基因片段,从index1到index2
newGene=[]
p1len=0
for g in parent1:
if p1len==index1:
newGene.extend(tempGene)#插入基因片段
if g not in tempGene:
newGene.append(g)
p1len+=1
return newGene
⑧变异
def mutate(self,gen:list):
if random()>self.m_rate:#如果大于变异率,则不变异
return gen
index1=randint(0,self.city.city_size-1)
index2=randint(index1,self.city.city_size-1)#还是生成随机片段
newGene=self.reverse_gen(gen,index1,index2)#利用翻转基因来变异
return newGene
变异的方式:反转基因
def reverse_gen(self,gen:list,i:int,j:int):
if i>=j: #错误顺序
return gen
if j>self.city.city_size-1:#过界
return gen
tempGene=gen[i:j]
tempGene.reverse()
newGene=gen[0:i]+tempGene+gen[j:self.city.city_size]
return newGene
⑨选择算子
轮盘赌法:
def selectPop2(self,pop:list):#换选择算子
probility=[]
for i in range(len(self.fitness)):
probility.append(self.fitness[i] / sum(self.fitness))
index_list=choice(self.pop_size,probility)
choispop=[]
for i in index_list:
choispop.append(pop[i])
return choispop
无法收敛,弃用
锦标赛算子:
选择种群,优胜劣汰法则,好的基因保留下来,差的基因进行交叉和变异
选出fitness的最大值和平均数,低于平均数的基因,就和最好的基因交叉,然后变异
def selectPop(self,pop:list):
best_f_index=self.fitness.index(max(self.fitness))#最大值的位置
av=sum(self.fitness)/len(self.fitness)
for i in range(self.pop_size):
if i!=best_f_index and self.fitness[i]<av:
pi=self.cross(pop[best_f_index],pop[i])
pi=self.mutate(pi)
pop[i]=pi
return pop
⑩主程序,迭代进化
def evolution(self,ga_num:int=500):#尽量多个模块,多用参数和返回值,不要把功能都堆在一个函数中
'''ga_num:最大迭代次数,默认为500
返回值是最优基因列表和最优距离列表,用来绘图
'''
self.ga_num=ga_num
best_dis_list=[] #用来画折线图的y值
best_pop_list=[] #用每代的最优基因来画路线图
for i in range(self.ga_num):
best_f_index=self.fitness.index(max(self.fitness))#适应度最好的
local_best_gen=self.pop[best_f_index]#局部最优基因
local_best_dist=self.city.genDistance(local_best_gen)#局部最短距离
if i==0:
self.best_gen=local_best_gen
self.best_dist=self.city.genDistance(self.best_gen)
#比较替换
if local_best_dist<self.best_dist:#如果出现了更优化的解,则替换
self.best_gen=local_best_gen
#主遗传程序:淘汰种群-随机交叉,变异:选择种群-计算适应度-交叉-变异
self.pop=self.selectPop(self.pop)
self.fitness=self.getFitness(self.pop)
for j in range(self.pop_size):
r=randint(0,self.pop_size-1)
if j!=r:
self.pop[j]=self.cross(self.pop[j],self.pop[r])#交叉第j和r个基因
self.pop[j]=self.mutate(self.pop[j])
#每次迭代完后
self.best_dist=self.city.genDistance(self.best_gen)#记录最短距离
# print("迭代%d次,最短距离:%s" % (i,self.best_dist))
best_dis_list.append(self.best_dist) #添加折线图的y值
best_pop_list.append(self.best_gen) #添加基因,用于画图
#把用来画图的list返回
return best_dis_list,best_pop_list
数据处理与功能函数库
City类
City类用于加载数据,并存储数据于类成员,提供计算城市距离的方法
①类成员
city_x=[]#x坐标
city_y=[]#y坐标
city_name=[]#城市标签
city_size=0
filepath=""
②加载数据
def loadCity(self,filepath:str):
'''filepath:文件路径'''
file=open(filepath).readlines()
arr=[file[i].strip('\n').split('\t') for i in range(len(file))]#split去除中间的,strip去前后的
for i in arr:
self.city_name.append(i[0])
self.city_x.append(eval(i[1]))
self.city_y.append(eval(i[2]))
self.city_size=len(arr)
③两个城市之间的距离
def cityDistance(self,c1:int,c2:int):
'''c1,c2是城市列表的序号,返回两个城市间的距离'''
d=((self.city_x[c1]-self.city_x[c2])**2+(self.city_y[c1]-self.city_y[c2])**2)**0.5
return d
④一个基因的总距离
def genDistance(self,gen:list):
'''gen是pop的一个基因,返回值为这个基因表示的路径长度'''
distance=0.0
for i in range(-1,self.city_size-1):#用-1到len-1刚好是所有的距离
i1,i2=gen[i],gen[i+1]
distance+=self.cityDistance(i1,i2)
return distance
Func函数库
①图片转化成gif
def picsTogif():
'''将保存的图片转成视频'''
system('cd ./pics/ && ffmpeg -r 5 -i %d.png -vf palettegen palette.png && ffmpeg -y -r 5 -i %d.png -i palette.png -lavfi paletteuse output.gif')
system('cd ./pics/ && del *.png palette.png')
②保存数据
def writeFile(context:list,filepath:str='./data/gen.ini',mode:str='w'):
'''写文件:保存数据'''
with open(filepath,mode) as f:
f.write(str(context))
f.write('\n')
③实现choice()
def choice(pop_size:int,probility:list):
'''实现np.random.choice()
pop_size:种群大小,也是目标size
probility:概率列表
'''
choispop=[]
while len(choispop)<pop_size:
for i in range(pop_size):
if random()<=probility[i]:
choispop.append(i)
return choispop
用于轮盘赌法的随机选择序列
可视化处理
Draw函数库
①导库
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from copy import deepcopy
from City import *
deepcopy:拷贝数据,防止对原序列做改动
②数据转换:被调用
def dataTransform(gen:list):
'''转换数据函数'''
city=City()
x=[];y=[];t=[]
for i in gen:
x.append(city.city_x[i])
y.append(city.city_y[i])
t.append(city.city_name[i])
return x,y,t
③根据基因绘制路线图:被调用
def genDraw(gen:list):
'''根据一个基因画路线图'''
x,y,t=dataTransform(gen)
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.figure(figsize=(20,10),dpi=65)
plt.axis("off")
#画点
plt.plot(x,y,'bo',markersize=4)
#标记
for i in range(len(x)):
plt.text(x[i],y[i],t[i],fontsize=15)
#画线
x=deepcopy(x);y=deepcopy(y)
x.append(x[0])
y.append(y[0])
plt.plot(x,y,color='r',linewidth=1)
return plt
④根据种群画图
def popDraw(best_pop_list:list,best_dis_list:list,picnum:int):
'''根据种群画图 \n
参数picnum是绘制gif所用的图片数量\n
picnum必须不大于迭代次数
'''
#加个判断
if picnum>len(best_dis_list):
print("Error:picnum必须不大于迭代次数ga_num")
else:
for i in range(picnum):
plt=genDraw(best_pop_list[i])
plt.title("最短距离:{}".format(best_dis_list[i]),fontsize=30,color='pink')
plt.savefig('./pics/%d.png' %((i+1)))
plt.close() #要关闭,不然会占内存
⑤绘制最终的结果
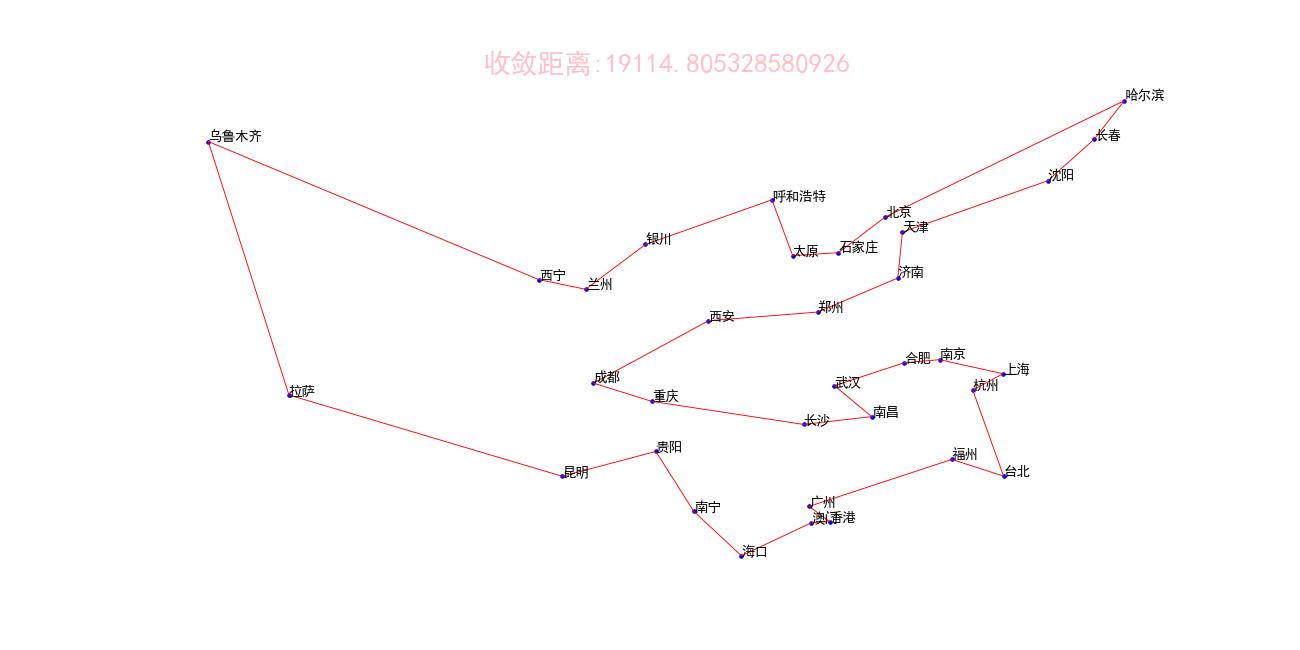
def lastDraw(last_gen:list,last_dis:float):
'''保存最后的结果图片:收敛距离'''
plt=genDraw(last_gen)
plt.title("收敛距离:{}".format(last_dis),fontsize=30,color='pink')
plt.savefig('./pics/last.jpg')
plt.close()
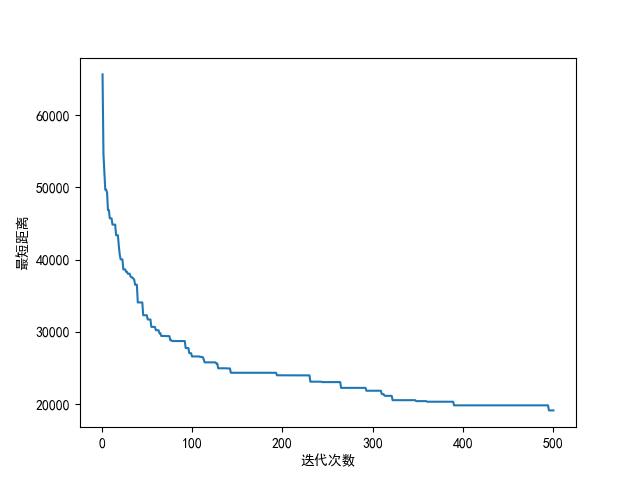
⑥绘制折线图
def drawLine(best_dis_list:list):
'''画折线图,参数list是y值'''
y=best_dis_list
x=[i+1 for i in range(len(y))]
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.ylabel('最短距离')
plt.xlabel('迭代次数')
plt.savefig("./pics/Line.jpg")
plt.close()
图片处理和转化
def picsTogif():
'''将保存的图片转成视频'''
system('cd ./pics/ && ffmpeg -r 5 -i %d.png -vf palettegen palette.png && ffmpeg -y -r 5 -i %d.png -i palette.png -lavfi paletteuse output.gif')
system('cd ./pics/ && del *.png palette.png')
调用ffmpeg,将输出的300张png图片转成每秒5帧的gif动画,实现迭代过程可视化,并删除这些图片和调色板
参数分析
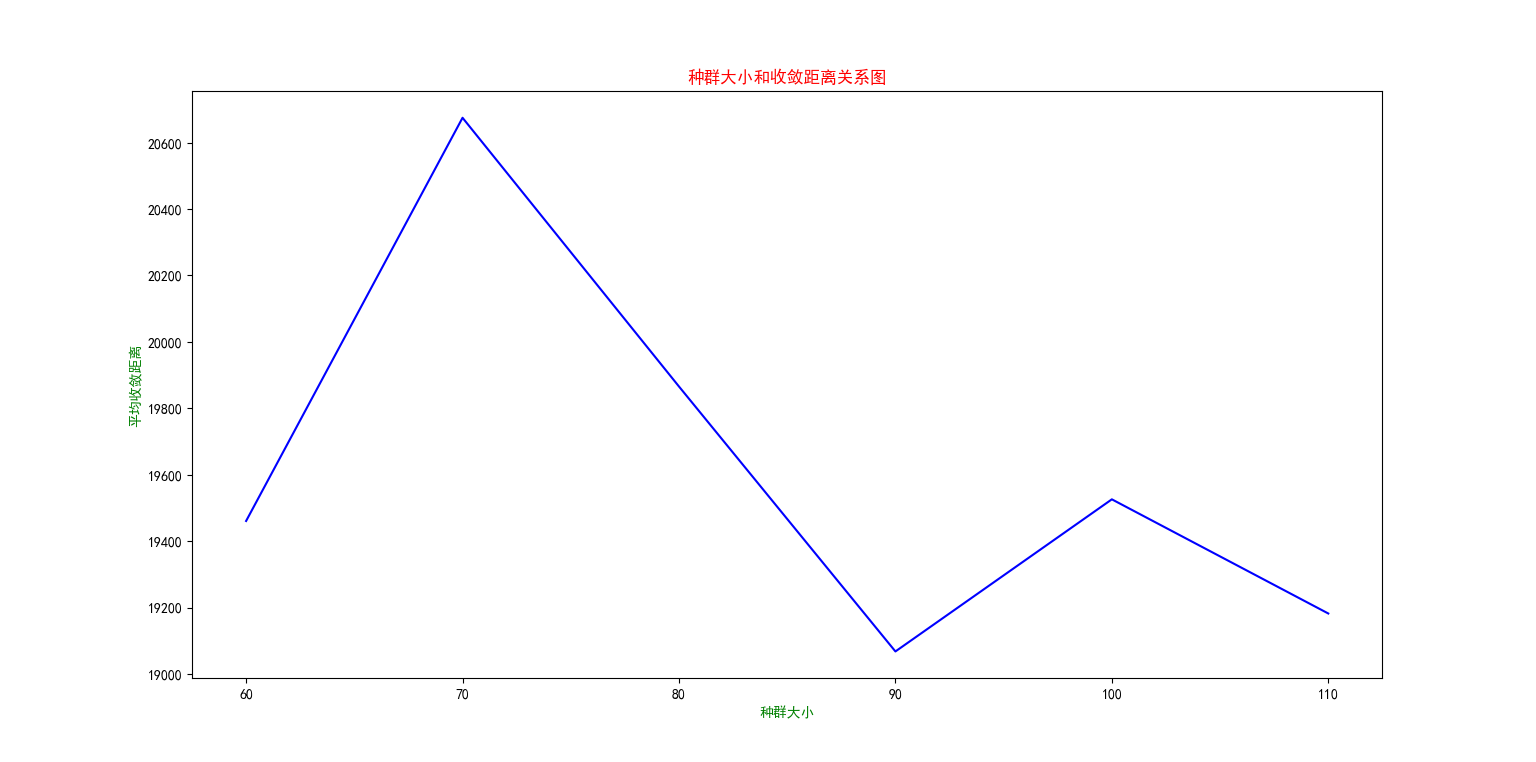
种群大小
通常,种群太小则不能提供足够的采样点,以致算法性能很差,种群太大,尽管可以增加优化信息阻止早熟收敛的发生,但无疑会增加计算量,造成收敛时间太长,表现为收敛速度缓慢.
def analysisPop():
pop=[n for n in range(60,120,10)]#20~110
constringency=[]
for i in pop:
tsp=TSP(pop_size=i)
tsp.init()
temp=[]
for j in range(5):
dis=tsp.evolution(500)[0][-1]#最后一次的最短距离
temp.append(dis)
constringency.append(sum(temp)/len(temp))#五次求平均值
#用种群大小和平均收敛距离画图
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.plot(pop,constringency,color='blue')
plt.axis("auto")
plt.xlabel("种群大小",color='green')
plt.ylabel("平均收敛距离",color='green')
plt.title("种群大小和收敛距离关系图",color="red")
plt.show()
分析pop_size和收敛dist的关系
固定其他参数,ga_num=500
求不同种群大小下的收敛距离,每个求5次,取平均值画图
结果图:
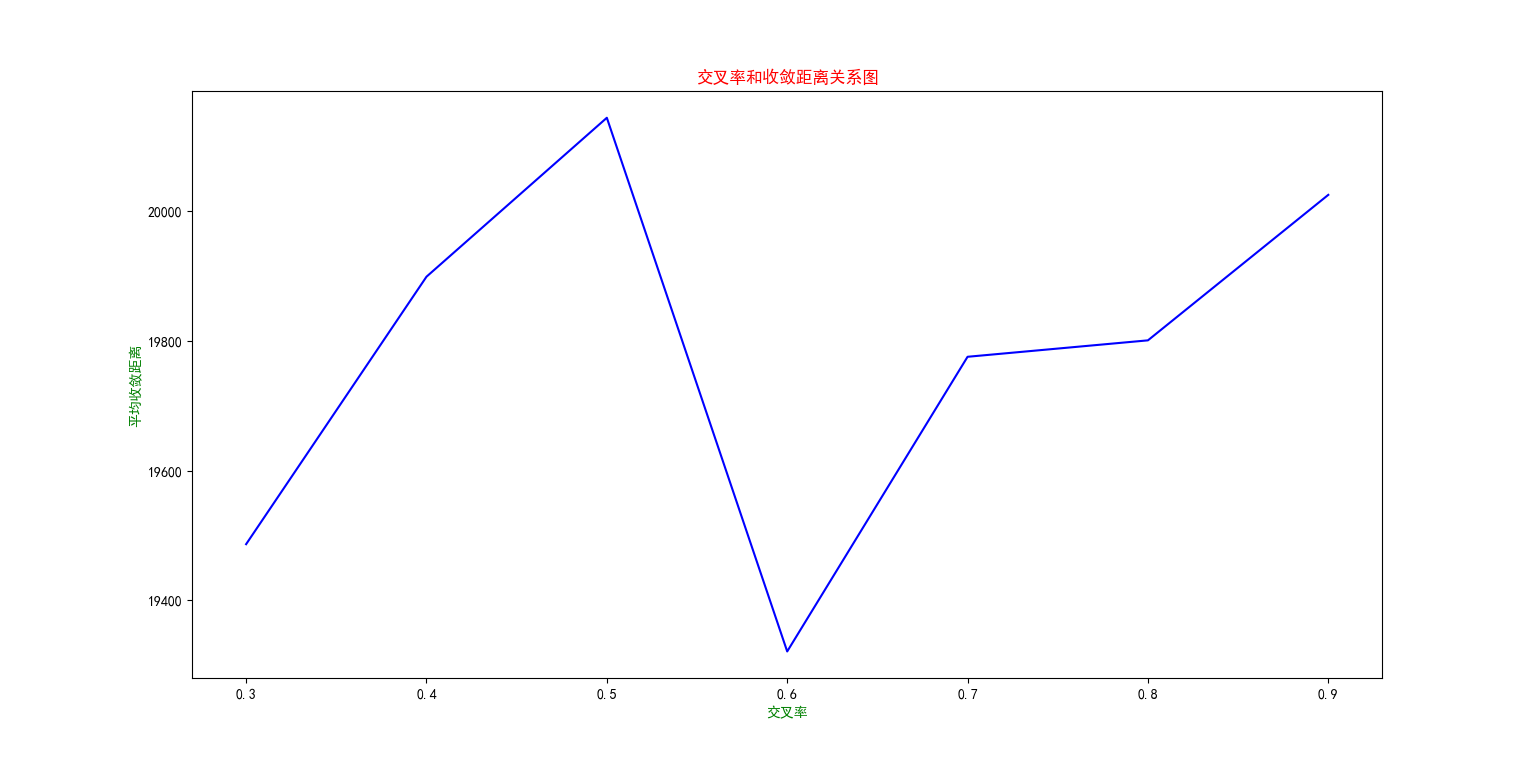
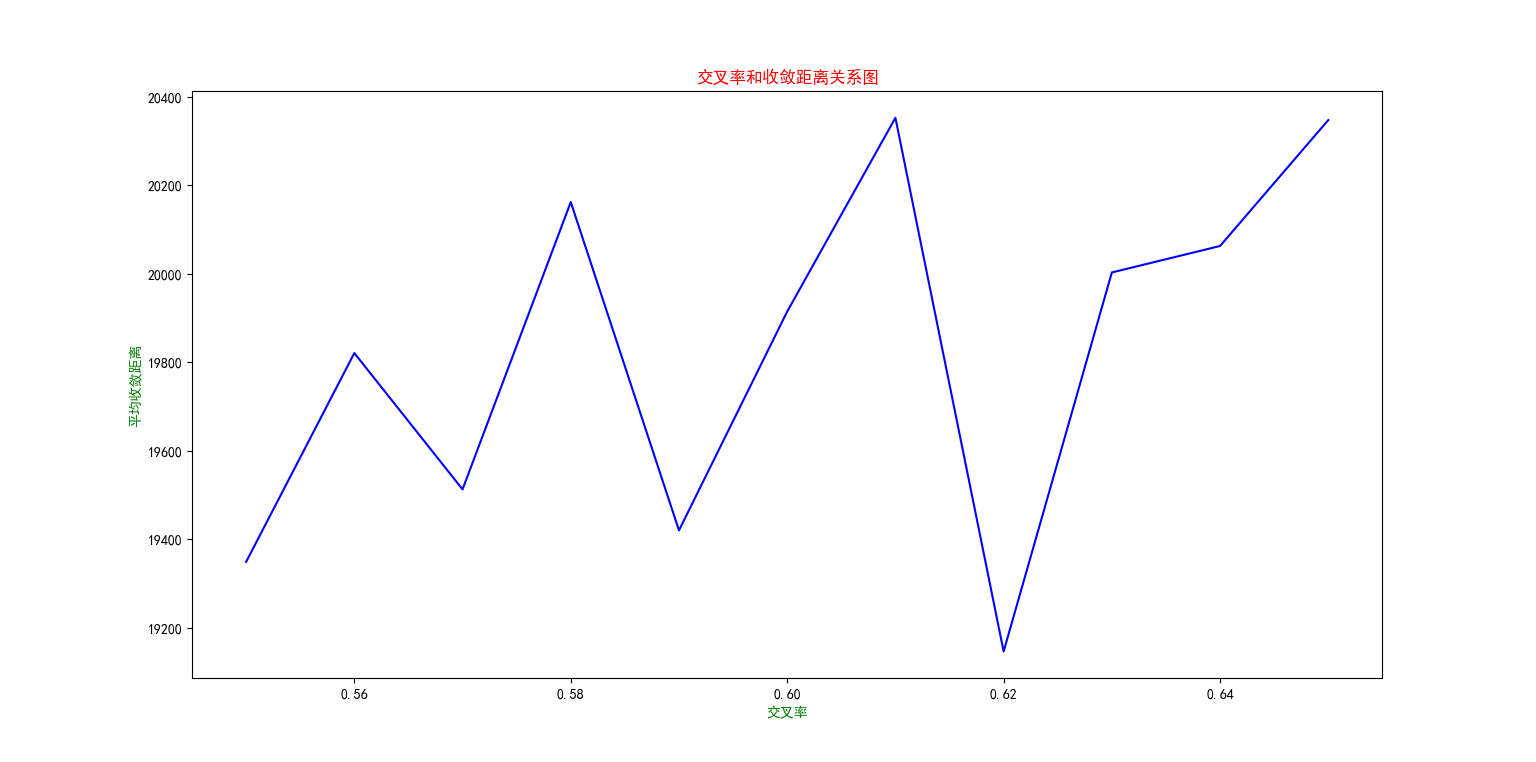
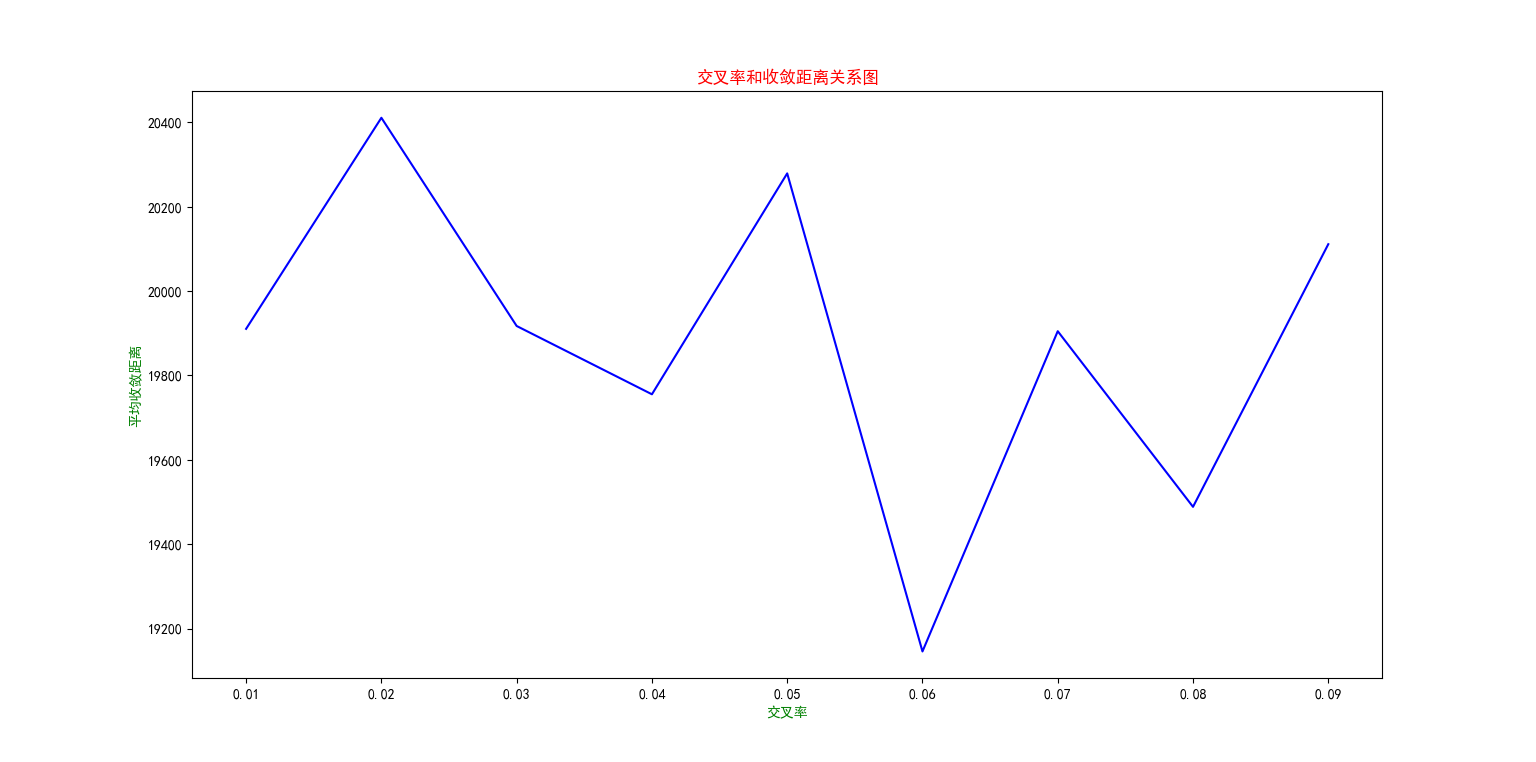
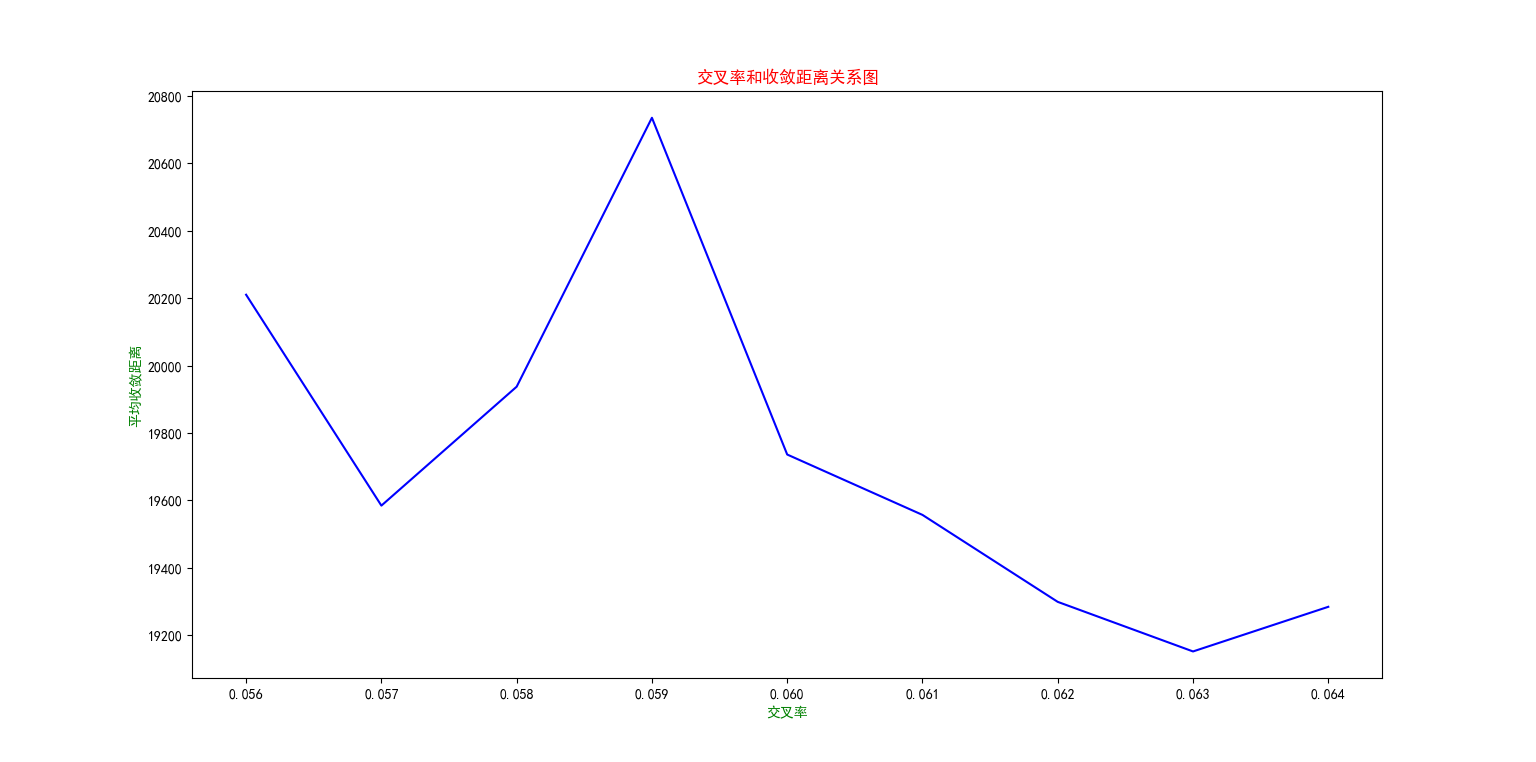
交叉率
交叉操作用于个体对,产生新的个体,实质上是在解空间中进行有效搜索。交叉概率太大时,种群中个体更新很快,会造成高适应度值的个体很快被破坏掉,概率太小时,交叉操作很少进行,从而会使搜索停滞不前,造成算法的不收敛。
def analysisCrate():
# crate=[n/10 for n in range(3,10,1)] #0.3-0.9
crate=[n/100 for n in range(55,66,1)] #得到最佳交叉率:0.62
csgc=[]
for i in crate:
tsp=TSP(c_rate=i,pop_size=90)
tsp.init()
temp=[]
for j in range(5):
dis=tsp.evolution(500)[0][-1]
temp.append(dis)
csgc.append(sum(temp)/len(temp))
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.plot(crate,csgc,color='blue')
plt.xlabel("交叉率",color='green')
plt.ylabel("平均收敛距离",color='green')
plt.title("交叉率和收敛距离关系图",color="red")
plt.show()
确定pop_size
分析Crate和收敛dist的关系
结果图:
变异率
变异操作是对种群模式的扰动有利于增加种群的多样性。但是,变异概率太小则很难产生新模式,变异概率太大则会使遗传算法成为随机搜索算法。
def analysisMrate():
# mrate=[n/100 for n in range(1,10,1)] #0.01-0.09
mrate=[n/1000 for n in range(56,65,1)]#得到最佳变异率:0.063
csgc=[]
for i in mrate:
tsp=TSP(c_rate=0.62,m_rate=i,pop_size=90)
tsp.init()
temp=[]
for j in range(5):
dis=tsp.evolution(500)[0][-1]
temp.append(dis)
csgc.append(sum(temp)/len(temp))
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.plot(mrate,csgc,color='blue')
plt.xlabel("交叉率",color='green')
plt.ylabel("平均收敛距离",color='green')
plt.title("交叉率和收敛距离关系图",color="red")
plt.show()
确定pop_size和c_rate的条件下,找最佳的变异率
分析M_rate和收敛距离的关系
结果图:
主程序
from time import time
from TSP import *
from Draw import *
#装饰器
def runtime(f):
def inner():
start=time()
f()
end=time()
print("程序执行时间为:%ds" %(end-start))
return inner
#主程序
@runtime
def main():
print("程序开始,迭代进化..")
tsp=TSP(0.62,0.063,90)#最三个最佳的参数
tsp.init()
dis_list,pop_list=tsp.evolution()
print("迭代完毕,正在处理图片..")
drawLine(dis_list)
lastDraw(pop_list[-1],dis_list[-1])
popDraw(pop_list,dis_list,300)
picsTogif()
print("图片处理完毕")
writeFile(dis_list,r'./data/list.ini')
writeFile(pop_list,r'./data/pop.ini')
print("保存数据完毕")
if __name__=="__main__":
main()
运行结果:
收敛距离
过程曲线图
动态化
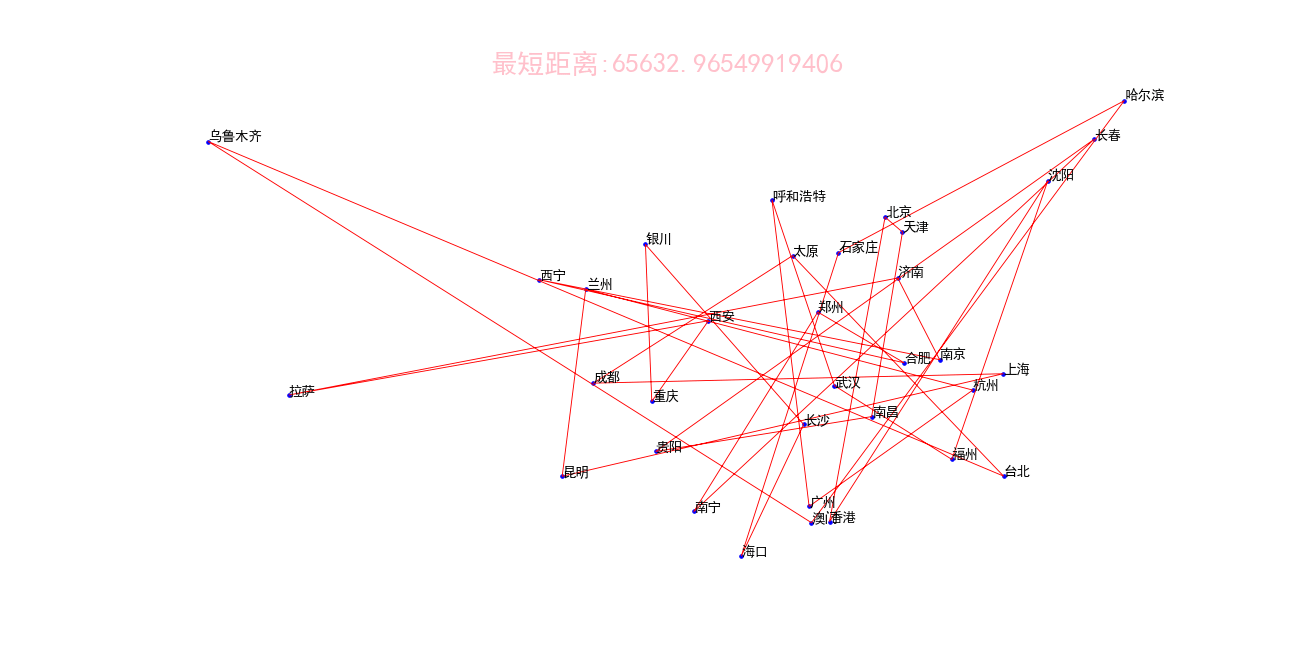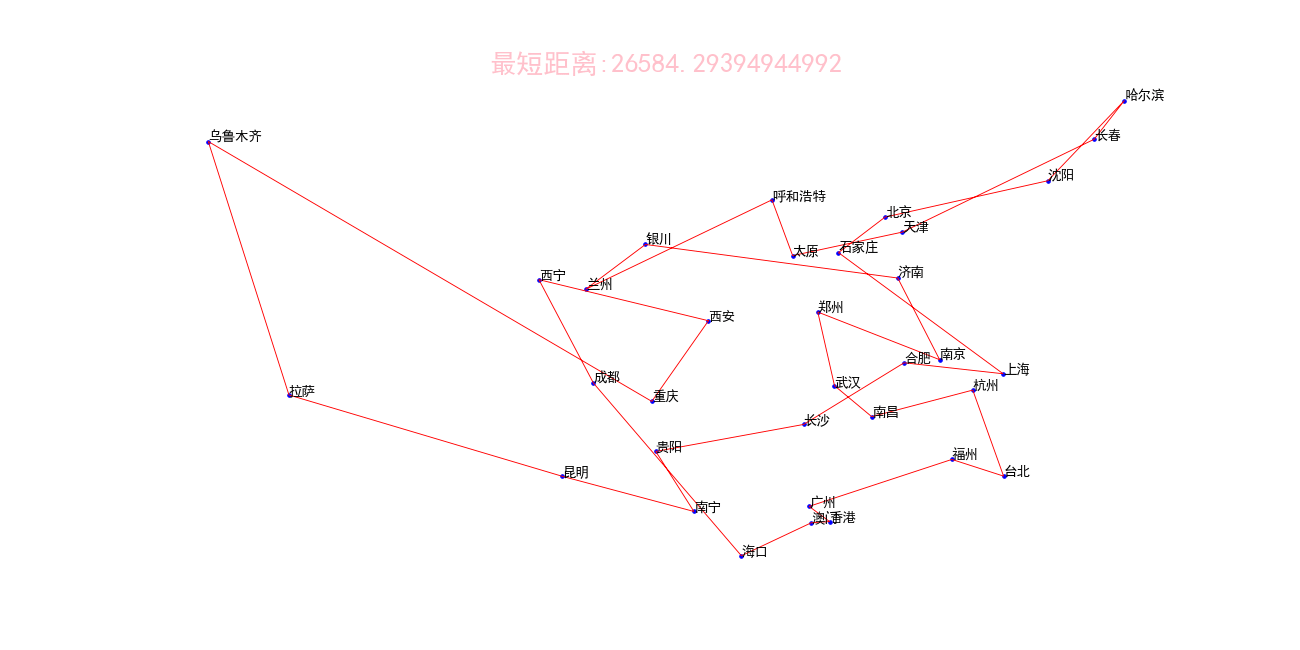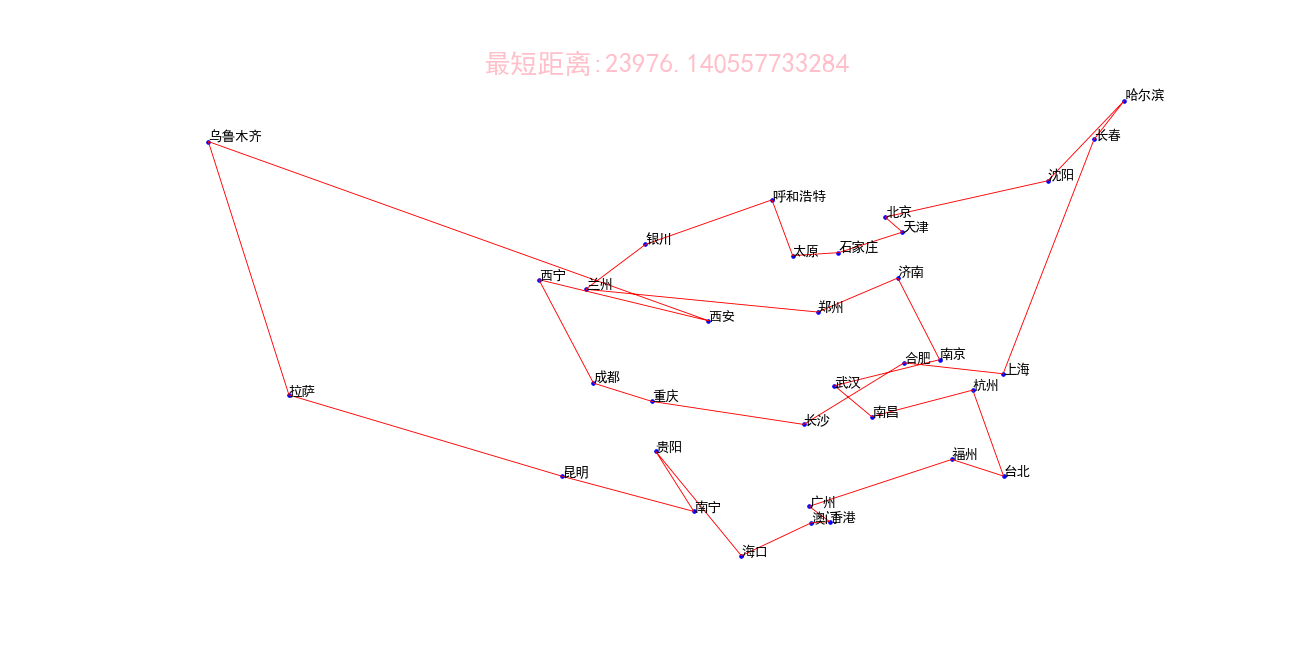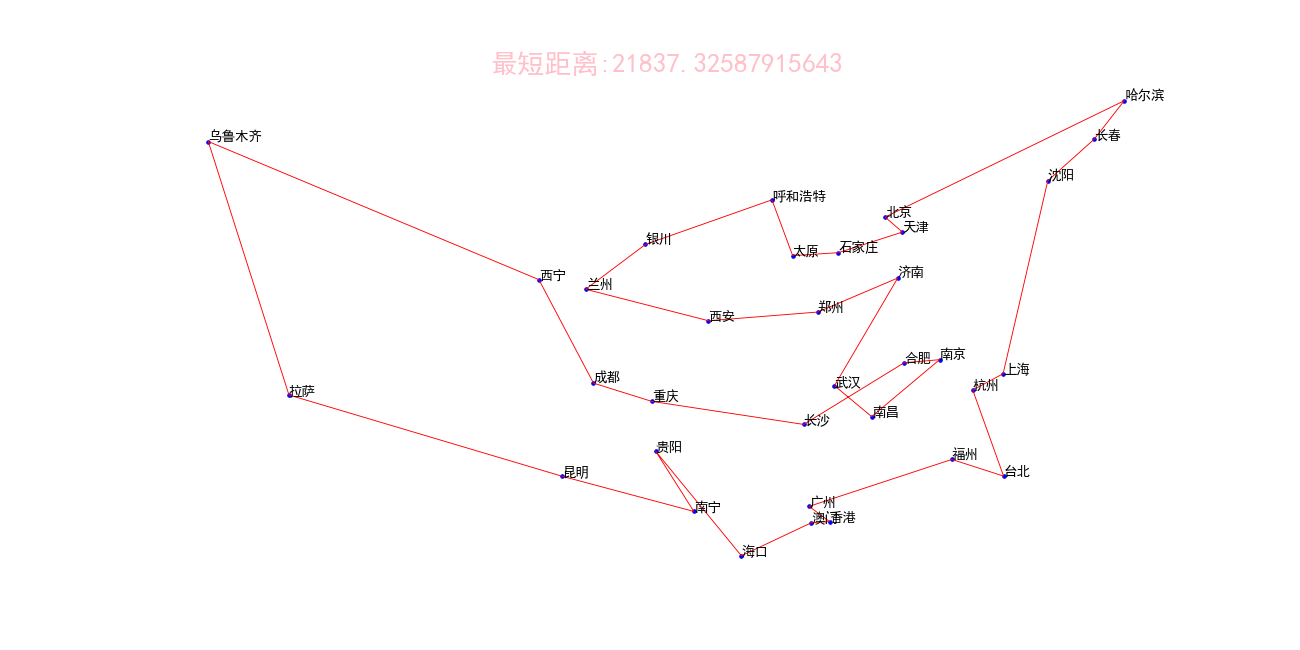
本文来自博客园,作者:Tenerome,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Tenerome/articles/GATSP.html




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号