实训笔记_基础强化01
1、Java
1.1 概述
是SUN(Standford University Network,斯坦福大学网络公司)1995年推出的一门高级编程语言;
是一种面向Internet的编程语言。java一开始富有吸引力是因为java程序可以在web浏览器中运行。这些java程序被称为java小程序(applet)。applet使用现代的图形用户界面与web用户进行交互。applet内嵌在html代码中;
随着java技术在web方面的不断成熟,已经成为web应用程序的首选开发语言(java工程师、后端开发工程师);
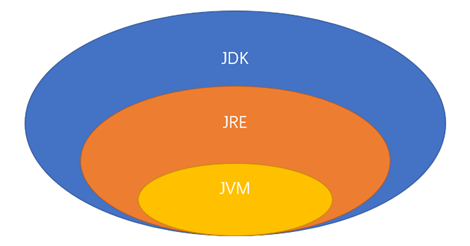
1.2 JDK,JRE介绍
JDK(Java Development Kit,java开发工具包)
① JDK是提供给Java开发人员使用的,其中包含了java的开发工具和JRE。所以安装了JDK,就不需要再单独安装JRE了
② 其中的开发工具:编译工具(javac.exe)、打包工具(jar.exe)等
JRE(Java Runtime Environment,Java运行环境)
① 包括Java虚拟机(JVM,Java Virtual Machine)和Java程序所需的核心类库等
② 如果想要运行一个开发好的Java程序,计算机中只需要安装JRE即可
简单来说,使用JDK开发工具完成的java程序,交给JRE去运行
示意图:
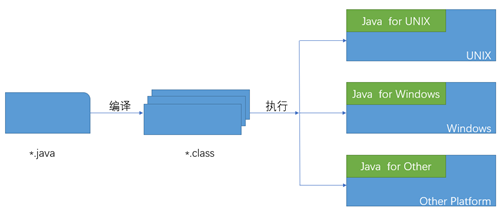
1.3 JVM介绍
Java虚拟机(Java Virtual Machine):
① JVM是一个虚拟的计算机,具有指令集并使用不同的存储区域。负责执行指令,管理数据、内存、寄存器。
② 对于不同的平台(系统),有不同的虚拟机
③ 只有某平台提供了对应的Java虚拟机,Java程序才可以在此平台运行
④ Java虚拟机机制屏蔽了底层运行平台的差别,实现了“一次编译,到处运行”
1.4 面向对象
Java是一门面向对象的语言。
面向对象涉及到几个概念:类、对象、属性、行为。
类:对一些具体事物的抽象
对象:实际存在的事物
属性:对象特有的特点
行为:对象具体的行为
1.5 集合
- 集合、数组都是对多个数据进行存储操作的结构,简称Java容器(Java集合框架)。
- 数组在存储多个数据方面的缺点:
a) 一旦初始化以后,其长度就不可修改
b) 数组中提供的方法非常有限,对于添加、删除、插入数据等操作,非常不方便,同时效率也低
c) 获取数组中实际元素的个数的需求,数组没有现成的属性或方法可用
d) 数组存储数据的特点 :有序、可重复。对于无序、不可重复的需求,不能满足
3.Java集合可分为Collection和Map两种体系
a) Collection接口:单列数据,定义了存储一组对象的方法的集合
i. List:元素有序、可重复的集合
ii. Set:元素无序、不可重复的集合
b) Map接口:双列数据,保存具有映射关系“key-value对”的集合
对于List接口,我们主要使用ArrayList实现类。
2、MySQL
2.1 概述
在实际的开发中,无论是做什么项目,最终都要涉及到数据的操作。
对于项目中的数据,我们一般是需要保存到数据库中的。
数据库分为关系型数据库和非关系型数据库。
常见的关系型数据库有:MySQL、Oracle、SQLserver等等。
2.2 创建表
创建一个student表,含有字段:id、name、sex、age、birthday、weight。
|
createtable student( id int primarykey auto_increment, name varchar(30)notnull, sex varchar(3)default'男', age int, birthday date, weight double(3,1) ); |
2.3 添加数据
|
insertinto student values(null,'张无忌','男',20,'1999-03-03',80.2); insertinto student values(null,'赵敏','女',18,'2001-04-03',50.3); insertinto student values(null,'刘备','男',50,'1980-02-03',80.9); |
2.4 修改数据
修改id=3的数据。
| update student set name='宋江', age=59where id=3; |
2.5 查询数据
查询id=2的数据、查询姓张的数据
|
select*from student where id=2; select*from student where name like'张%'; |
2.6 删除数据
删除id=3的数据
| deletefrom student where id=3; |
2.7分页查询
在实际开发中,表中的数据特别多,不可能一次性的给用户全部展示出来,最好要分页展示!
总共有95条数据
每页显示10条数据
分几页:10页
用户要看第7页的数据:
(页码-1)*每页的记录数,页码*每页的记录数
每页显示2条数据,查询第5页的数据
| select*from student limit8,2; |
limit a,b 表示从索引是a开始,总共取b条。表中的索引是从0开始的。
3、JDBC
3.1 概述
JDBC就是Java Database Connectivity,表示数据库连接
JDBC是一种Java连接操作数据库的一种技术(MyBatis、Hibernate、JPA等等)
JDBC是Java提供的,在java.sql包和javax.sql包中
JDBC是一种规范,一组接口(实现类由数据库厂商提供,即数据库驱动包)
我们通过使用JDBC技术就可以操作各种各样的数据库!
3.2 JDBC使用步骤
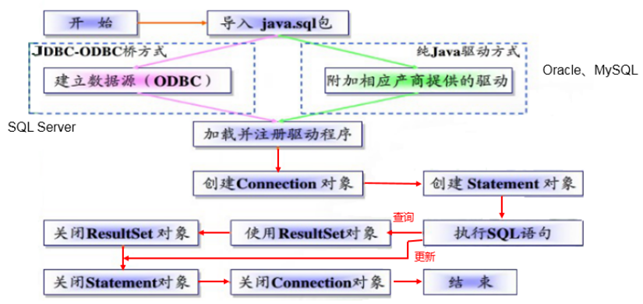
使用完数据库相关的资源后,必须要关闭,如果不关闭就会驻留内存中,造成内存泄漏!更严重的是造成内存溢出!
步骤:
1. 在工程中导入数据库驱动包
2. 加载并注册数据库驱动
3. 使用驱动管理器去创建数据库连接
4. 编写SQL语句
5. 创建一个语句对象
6. 执行SQL语句
7. 得到一个结果集
8. 使用结果
9. 关闭所有数据库相关的资源
3.3 获取数据库连接
我们要使用JDBC去存取数据到数据库,必须先要和数据库建立连接。有了连接后才能进行CRUD操作。
方式一:(记得导入数据库驱动包)
|
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//加载并注册数据库驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//获取数据库连接 Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai", "root", "root3306");
System.out.println(connection); } } |
方式二:(将各种数据库信息写到配置文件中)
jdbc.properties文件:
|
driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai user=root password=root3306 |
|
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.load(new FileInputStream(new File("jdbc.properties")));
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver"); String url = properties.getProperty("url"); String user = properties.getProperty("user"); String password = properties.getProperty("password");
//加载并注册数据库驱动 Class.forName(driver);
//获取数据库连接 Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println(connection); } } |
3.4 使用PS实现添加
数据库有student表,应该在Java中也创建一个Student的类!
类 == 表对应
类中的属性 == 表中的字段
ORM思想:Object Relation Mapping 对象关系映射 Mybatis
使用PrepareStatement实现数据的添加。
PrepareStatement是由数据库连接创建的,它可以用来执行SQL语句,而且它会对SQL语句进行预编译,可以有效的防止SQL注入,比较安全。
1. 创建一个学生表
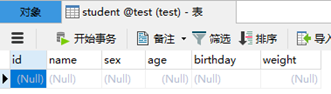
2. 编写一个Student类
3. 写添加的代码:
|
public void test2() throws Exception{ //用户要添加的数据 Student s = new Student(null, "张三", "男", 20, new Date(birthdayDate.getTime()), 89.5);
//读取配置文件信息 Properties prop = new Properties(); prop.load(new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties")); String driver = prop.getProperty("driver"); String url = prop.getProperty("url"); String user = prop.getProperty("user"); String password = prop.getProperty("password");
//加载数据库驱动 Class.forName(driver);
//获取数据库连接 Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
String sql = "insert into student values(null, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
//创建预编译语句对象 PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//设置占位符的值 ps.setObject(1, s.getName()); ps.setObject(2, s.getSex()); ps.setObject(3, s.getAge()); ps.setObject(4, s.getBirthday()); ps.setObject(5, s.getWeight());
//查询使用 executeQuery() 增删改使用 executeUpdate() int i = ps.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(i > 0 ? "添加成功" : "添加失败");
//关闭资源 ps.close(); conn.close(); } |
3.5 数据库工具类
因为对数据库的增删改查操作,都需要先连接到数据库才能进行,所以,获取数据库连接的操作我们经常用,那最好将这个操作写到一个工具类中,便于使用!
|
/* * 数据库工具类 * 1. 获取连接 * 2. 关闭连接 */ publicclass JDBCUtils {
privatestatic String driver; privatestatic String url; privatestatic String user; privatestatic String password;
//静态代码块,静态代码块会随着类的加载而加载,类只会加载一次,静态代码块中的内容也只会执行一次 static{ try { //读取配置文件信息 Properties prop = new Properties(); prop.load(JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties")); driver = prop.getProperty("driver"); url = prop.getProperty("url"); user = prop.getProperty("user"); password = prop.getProperty("password"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
//工具类中的方法往往都是static修饰的,就可以直接用类名.方法名 去调用方法 publicstatic Connection getConn() throws Exception{
//加载并注册数据库驱动 Class.forName(driver);
//获取数据库连接 Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
returnconn; }
//关闭连接 publicstaticvoid closeConn(ResultSet rs, PreparedStatement ps, Connection conn){ if(rs != null){ try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
if(ps != null){ try { ps.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
if(conn != null){ try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } |
3.6 使用PS实现删除
|
/* * 使用PrepareStatement实现数据的删除 */ @Test publicvoid test3(){
//操作数据
//获取数据库连接 Connection conn = null;
//创建预编译语句对象 PreparedStatement ps = null;
try { //读取配置文件信息 Properties prop = new Properties(); prop.load(new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties")); String driver = prop.getProperty("driver"); String url = prop.getProperty("url"); String user = prop.getProperty("user"); String password = prop.getProperty("password"); //加载并注册数据库驱动 Class.forName(driver); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); String sql = "delete from student where id=?"; ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); //设置SQL语句中占位符的值 ps.setInt(1, 5); //执行SQL inti = ps.executeUpdate(); System.out.println(i > 0 ? "删除成功!" : "删除失败!"); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception } finally{ if(ps != null){ //关闭连接 try { ps.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
if(conn != null){ try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } |
3.7 使用PS实现修改
|
/* * 使用PrepareStatement进行数据的修改 */ @Test public void test3() throws Exception{
//读取配置文件信息 Properties prop = new Properties(); prop.load(Test1.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties"));
String driver = prop.getProperty("driver"); String url = prop.getProperty("url"); String user = prop.getProperty("user"); String password = prop.getProperty("password");
//加载并注册数据库驱动 Class.forName(driver);
//获取数据库连接 Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
//创建预编译语句对象 String sql = "update emp set name=?, did=?, hiredate=? where id=?"; PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//设置SQL中占位符的值 ps.setObject(1, "孙一宁"); ps.setObject(2, 4); ps.setObject(3, "2000-05-05"); ps.setObject(4, 5);
//执行SQL语句 int i = ps.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(i > 0 ? "修改成功!" : "修改失败!");
//关闭资源 ps.close(); conn.close(); } |
3.8 使用PS实现查询
|
/* * 数据库工具类 */ public class JDBCUtils {
private static String driver; private static String url; private static String user; private static String password;
static{ try { //读取配置文件信息 Properties prop = new Properties(); prop.load(JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties")); driver = prop.getProperty("driver"); url = prop.getProperty("url"); user = prop.getProperty("user"); password = prop.getProperty("password"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
/* * 获取数据库连接 */ public static Connection getConn() throws Exception{
Class.forName(driver);
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
return conn; }
/* * 关闭资源 */ public static void closeConn(ResultSet rs, PreparedStatement ps, Connection conn){ if(rs != null){ try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
if(ps != null){ try { ps.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
if(conn != null){ try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } |
|
/* * 测试查询 * 查询姓名是 张 * 性别是男的数据 * 并按照age由小到大显示。 */ @Test public void test5() throws Exception{
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConn();
String sql = "select id,name,sex,hiredate,did from emp where name like ? and sex=?"; PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setObject(1, "张%"); ps.setObject(2, "男");
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
List<Emp> list = new ArrayList<>(); //ResultSet ===> list while(rs.next()){ int id = rs.getInt("id"); String name = rs.getString("name"); String sex = rs.getString("sex"); Date hiredate = rs.getDate("hiredate"); int did = rs.getInt("did");
Emp emp = new Emp(id, name, sex, hiredate, did);
list.add(emp); }
//遍历集合 for (Emp emp : list) { System.out.println(emp); }
// JDBCUtils.closeConn(rs, ps, conn); } |
3.9 资源的释放
释放ResultSet, Statement,Connection。
数据库连接(Connection)是非常稀有的资源,用完后必须马上释放,如果Connection不能及时正确的关闭将导致系统宕机。Connection的使用原则是尽量晚创建,尽量早的释放。
可以在finally中关闭,保证及时其他代码出现异常,资源也一定能被关闭。
4、 分层思想
4.1 概述
在实际开发中,我们的代码量是很大的,编写的类或者接口特别多
我们不可能将所有的接口、类都放在一个包中,这样不便于扩展与维护
应该根据不同的功能放在不同的包中
这其实就是分层思想
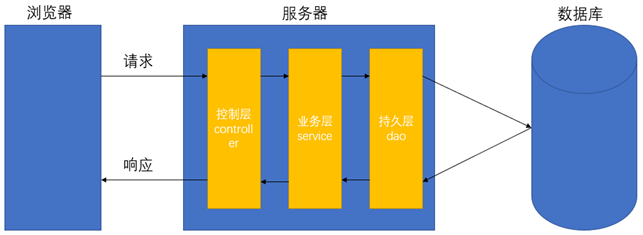
在软件开发中,我们一般使用MVC的分层思想:
M:Model,模型层,包括数据模型,业务模型
V:View,视图层,用来展示数据,指的就是页面
C:Controller,控制层,用来接收用户的请求,调用业务层处理请求,然后响应用户
4.2 具体实现
MVC分层思想具体落地的话,我们Java后端应该有以下包(package):
pojo/entity/bean/domain:存放实体类
dao/mapper:存放与数据库打交道的增删改查代码 data access object,持久层
service:存放业务相关的代码
controller/action:存放控制层相关的代码,用于接收用户的请求,响应请求。
为了便于扩展与开发,我们在service与dao层要写接口!!!
各个层的调用关系:
4.3 案例
使用分层实现一个转账功能!
张三给李四转账2000元!
数据库应该有一张账户表 账号、用户名、余额
张三钱少2000,减钱
李四钱加上2000,加钱
4.3.1 创建表
|
-- 创建账户表 createtable account( id int primarykey auto_increment, name varchar(30)notnull, money double(7,2) );
-- 插入数据 insertinto account values(null,'张三',10000); insertinto account values(null,'李四',10000);
-- 查询 select*from account; |
4.3.2 创建工程
4.3.3 导入相关jar包
mysql-connector-java-8.0.16.jar
4.3.4 编写配置文件
编写数据库的配置文件:
|
driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url=jdbc:mysql:///dbstudy?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai user=root password=root3306 |
4.3.4 编写工具类
|
/* * 数据库工具类 */ publicclass JDBCUtils {
privatestatic String driver; privatestatic String url; privatestatic String user; privatestatic String password;
static{ try { Properties prop = new Properties(); prop.load(JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties"));
driver = prop.getProperty("driver"); url = prop.getProperty("url"); user = prop.getProperty("user"); password = prop.getProperty("password"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
// 目前带的班级,学习JDBC。 publicstatic Connection getConn() throws Exception{ //加载并注册数据库驱动 Class.forName(driver); Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); returnconn; }
//关闭 publicstaticvoid closeConn(ResultSet rs, Statement st, Connection conn){ if(rs != null){ try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
if(st != null){ try { st.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
if(conn != null){ try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } |
4.3.6 编写pojo层
|
/* * 实体类,实体类和数据库表对应 */ publicclass Account {
private Integer id; private String name; private Double money; public Account() { super(); } public Account(Integer id, String name, Double money) { super(); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.money = money; } public Integer getId() { returnid; } publicvoid setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { returnname; } publicvoid setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Double getMoney() { returnmoney; } publicvoid setMoney(Double money) { this.money = money; } @Override public String toString() { return"Account [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", money=" + money + "]"; } } |
4.3.7 编写dao层
1. dao层要先写接口,在写实现类
2. 注意命名规范
3. dao层中的一个方法一件事情(或者说是只对数据库做一个操作)!
|
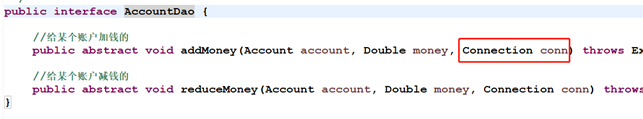
/* * 编写dao层代码,要写接口,然后在写实现类 * 注意命名规范 */ publicinterface AccountDao {
//给某个账户加钱的 publicabstractvoid addMoney(Account account, Double money);
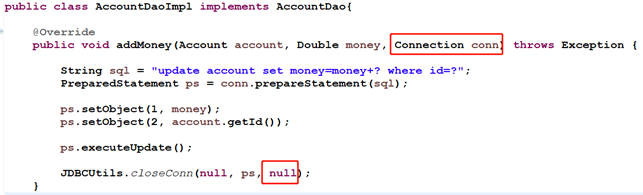
//给某个账户减钱的 publicabstractvoid reduceMoney(Account account, Double money); }/* * impl包里面放的就是实现类,implements */ publicclass AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao{
@Override publicvoid addMoney(Account account, Double money) throws Exception { Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConn();
String sql = "update account set money=money+? where id=?"; PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setObject(1, money); ps.setObject(2, account.getId());
ps.executeUpdate();
JDBCUtils.closeConn(null, ps, conn); }
@Override publicvoid reduceMoney(Account account, Double money) throws Exception { Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConn();
String sql = "update account set money=money-? where id=?"; PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setObject(1, money); ps.setObject(2, account.getId());
ps.executeUpdate();
JDBCUtils.closeConn(null, ps, conn); } } |
4.3.8 编写service层
1. service层就是与业务有关的代码,先写接口,在写实现类
2. service层中一个方法就是为了完成某个业务的
|
publicinterface AccountService {
//转账 publicabstractvoid transfer(Account a1, Account a2, Double money); }publicclass AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService{
@Override publicvoid transfer(Account a1, Account a2, Double money) { try { AccountDao accountDao = new AccountDaoImpl(); //1.减钱 accountDao.reduceMoney(a1, money);
//2.加钱 accountDao.addMoney(a2, money); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } |
4.3.9 编写测试类
|
publicclass AccountServiceTest {
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) {
AccountService accountService = new AccountServiceImpl();
Account a1 = new Account(); a1.setId(1);
Account a2 = new Account(); a2.setId(2);
Double money = 2000.0;
accountService.transfer(a1, a2, money); } } |
5、 事务
5.1 概述
事务是指一组逻辑操作,这组操作要么全部成功,要么全部失败!
事务有四个特性(ACID):
原子性:指的是事务是最小的单位,不可再分割,要么全成功,要么全失败!
一致性(consistency):事务操作前后,数据要保持一致。
隔离性(isolation):多个事务并发操作数据库数据的时候,多个事务要进行隔离,不能互相干扰!
持久性:事务一旦提交,数据库就永久将数据保存下来!
我们目前写的代码,并没有自己去控制事务!
所以我们代码很有问题!!!
应该要加上事务操作!
5.2 JDBC事务处理
1. 之前我们使用JDBC并没有去操作事务,其实它也是有事务,JDBC默认是执行完一条SQL语句之后,就会提交事务
2. 数据一旦提交,数据库就会永久保存下来了,不能反悔了
3. 一个业务层方法,往往是要调用多个dao层方法进行数据上的操作,所以,一个业务层方法里面的多个操作应该要么全部成功,要么全部失败,也就是说,一个业务层的方法应该由一个事务去控制!
4. JDBC中,提交事务commit(),回滚事务rollback()
5. 提交事务,就告诉数据库我这次的改动确定下来了!
6. 回滚事务,就告诉数据库我这次的改动反悔了,你给我把数据回到最初的状态(改动之前的状态)
7. 在JDBC中,事务处理使用connection,一个事务应该使用一个connection!
5.3 具体处理
将上面的dao层的接口及实现类做了改动
将上面的service层实现类做了改动
|
publicclass AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService{
@Override publicvoid transfer(Account a1, Account a2, Double money) { Connection conn = null; try { AccountDao accountDao = new AccountDaoImpl();
conn = JDBCUtils.getConn();
//取消自动提交事务,改为了手动提交 conn.setAutoCommit(false);
//1.减钱 accountDao.reduceMoney(a1, money, conn);
//银行网络断了!银行停电了!系统卡了! // int i = 1 / 0;
//2.加钱 accountDao.addMoney(a2, money, conn);
System.out.println("转账成功!");
//提交事务 conn.commit(); } catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("转账失败!"); e.printStackTrace(); //回滚事务 try { conn.rollback(); } catch (SQLException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } } finally{ JDBCUtils.closeConn(null, null, conn); } } |
1.1.1 创建表







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号