三元LCG
题目:
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from secret import FLAG
p = getPrime(128)
step = len(FLAG) // 3
xs = [bytes_to_long(FLAG[:step]), bytes_to_long(FLAG[step:2*step]), bytes_to_long(FLAG[2*step:])]
a = getPrime(64)
b = getPrime(64)
c = getPrime(64)
a = 18038175596386287827
b = 15503291946093443851
c = 17270168560153510007
p = 307956849617421078439840909609638388517
for _ in range(10):
new_state = (a*xs[0] + b*xs[1] + c*xs[2]) % p
xs = xs[1:] + [new_state]
#print(xs)
print(xs)
print(a, b, c, p)
[255290883651191064919890629542861653873,221128501895959214555166046983862519384,108104020183858879999084358722168548984]
解题思路:
- 通过
<font style="color:rgb(6, 6, 7);">ani = MMI(a, n)</font>计算<font style="color:rgb(6, 6, 7);">a</font>在模<font style="color:rgb(6, 6, 7);">n</font>下的逆元<font style="color:rgb(6, 6, 7);">a</font><sup><font style="color:rgb(6, 6, 7);">-1</font></sup> - 然后逆元
<font style="color:rgb(6, 6, 7);">a</font><sup><font style="color:rgb(6, 6, 7);">−1</font></sup>用于解线性同余方程 - 通过线性方程
<font style="color:rgb(6, 6, 7);">seed=a</font><sup><font style="color:rgb(6, 6, 7);">−1</font></sup><font style="color:rgb(6, 6, 7);">⋅(seed−b) (mod n)</font>更新<font style="color:rgb(6, 6, 7);">seed</font>的值 - 每次更新后,将新的
<font style="color:rgb(6, 6, 7);">seed</font>放入<font style="color:rgb(6, 6, 7);">xs</font>的第一个位置,同时保留前两个值(每次将新生成的xn替换到xs的第三位上,前两位分别是上一次的二三位;依次从x8,9,10还原7回退到7,8,9 以此类推推出初始xs)
解答:
from libnum import *
a = 18038175596386287827
b = 15503291946093443851
cc = 17270168560153510007
n = 307956849617421078439840909609638388517
xs = [255290883651191064919890629542861653873,221128501895959214555166046983862519384,108104020183858879999084358722168548984]
for i in range(10):
#真实密文
c = xs[2]
#print(c)
MMI = lambda A, n,s=1,t=0,N=0: (n<2 and t%N or MMI(n,A%n,t,s-A//n*t,N or n),-1)[n<1] #逆元计算
ani = MMI(a,n)
seed = c
#计算出真实b
b = 15503291946093443851
b = b * xs[0] + cc * xs[1]
seed = (ani * (seed - b)) % n
print(seed)
xs = [seed] + xs[0:2]
print(xs)
print(n2s(int(xs[0])))
print(n2s(int(xs[1])))
print(n2s(int(xs[2])))
print("")
'''
b'flag{try_some'
b'_linear_algeb'
b'ra_technique}'
'''
ai一把梭
AI思路:
已知条件
- 最后三个状态值:
xs(代码输出的最后三个值) - 参数:
a、b、c和p - 生成公式:
new_state = (a*xs[0] + b*xs[1] + c*xs[2]) % p
解密思路
- 逆向计算:从已知的最后三个状态值出发,利用生成公式逆向推导出前面的状态值
- 恢复初始状态:通过逆向计算,逐步恢复出初始状态
xs,即最初的三个值 - 恢复
**FLAG**:将恢复的初始状态值转换回字节序列,拼接起来得到原始的FLAG
具体步骤
1. 逆向计算公式
已知: new_state=(a⋅xs[0]+b⋅xs[1]+c⋅xs[2]) mod p
逆向计算公式: 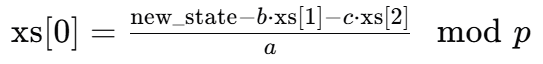
由于是在模 p 的情况下,需要计算模逆元: xs[0]=(new_state−b⋅xs[1]−c⋅xs[2])⋅a−1 mod p
其中 a−1 是 a 在模 p 下的逆元,可以通过扩展欧几里得算法计算
2. 逆向计算状态值
从已知的最后三个状态值xs开始,逐步逆向计算前面的状态值
3. 恢复初始状态
逆向计算 10 次,恢复出最初的三个状态值
4. 转换为字节序列
将恢复的三个状态值转换为字节序列,拼接起来得到原始的FLAG
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
# 已知参数
a = 18038175596386287827
b = 15503291946093443851
c = 17270168560153510007
p = 307956849617421078439840909609638388517
# 已知的最后三个状态值
xs = [255290883651191064919890629542861653873,221128501895959214555166046983862519384,108104020183858879999084358722168548984]
# 计算模逆元
def mod_inverse(x, p):
return pow(x, -1, p)
# 逆向计算
a_inv = mod_inverse(a, p)
for _ in range(10):
new_state = xs[-1]
xs = xs[:-1]
xs.insert(0, (new_state - b * xs[0] - c * xs[1]) * a_inv % p)
# 恢复初始状态
initial_states = xs
# 转换为字节序列
step = len(initial_states) // 3
flag_parts = [long_to_bytes(state) for state in initial_states]
flag = b''.join(flag_parts)
print("Recovered FLAG:", flag)
#flag{try_some_linear_algebra_technique}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号