实验一
实验一:
源代码:
点击查看代码
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
template<typename T>
void output(const T &c);
void test1();
void test2();
void test3();
int main()
{
std::cout<<"测试1:\n";
test1();
std::cout<<"测试2:\n";
test2();
std::cout<<"测试3:\n";
test3();
}
template<typename T>
void output(const T &c)
{
for(auto &i:c)
{
std::cout<<i<<' ';
}
std::cout<<'\n';
}
void test1()
{
using namespace std;
string s0{"0123456789"};
cout<<"s0="<<s0<<endl;
string s1(s0);
reverse(s1.begin(),s1.end());
cout<<"s1="<<s1<<endl;
string s2(s0.size(),' ');
reverse_copy(s0.begin(),s0.end(),s2.begin());
cout<<"s2="<<s2<<endl;
}
void test2()
{
using namespace std;
vector<int> v0{2,0,4,9};
cout<<"v0:";
output(v0);
vector<int> v1{v0};
reverse(v1.begin(),v1.end());
cout<<"v1:";
output(v1);
vector<int> v2{v0};
reverse_copy(v0.begin(),v0.end(),v2.begin());
cout<<"v2:";
output(v2);
}
void test3()
{
using namespace std;
vector<int>v0{0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
cout<<"v0:";
output(v0);
vector<int> v1{v0};
rotate(v1.begin(),v1.begin()+1,v1.end());
cout<<"v1:";
output(v1);
vector<int> v2{v0};
rotate(v2.begin(),v2.begin()+2,v2.end());
cout<<"v2:";
output(v2);
vector<int> v3{v0};
rotate(v3.begin(),v3.end()-1,v3.end());
cout<<"v3:";
output(v3);
vector<int> v4{v0};
rotate(v4.begin(),v4.end()-2,v4.end());
cout<<"v4:";
output(v4);
}
结果:
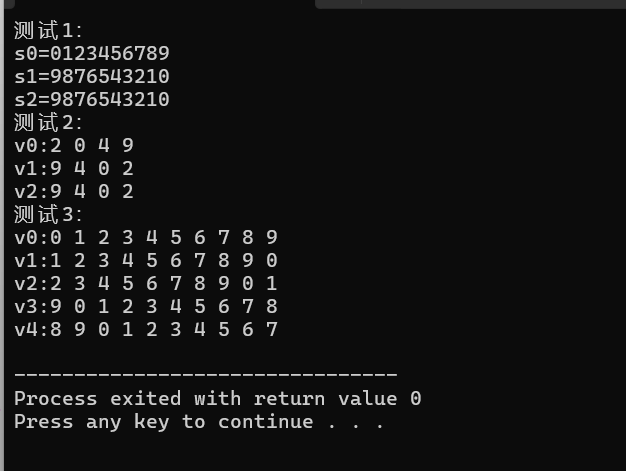
问题一:reverse是直接反转原数据,而reverse_copy是将原数据反转后复制到新的地方,不改变原数据顺序。
问题二:rotate 算法通过循环移位来改变元素顺序。第一个参数是原数据第一个数,第三个参数是原数据最后一个数,左移时,第二个参数是移动后第一个参数在原数据中的位置,右移时,第二个参数是移动后最后一个参数在原数据中的位置。
实验二:
点击查看代码
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<numeric>
#include<iomanip>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<ctime>
template<typename T>
void output(const T &c);
int generate_random_number();
void test1();
void test2();
int main()
{
std::srand(std::time(0));
std::cout<<"测试1:\n";
test1();
std::cout<<"\n测试2:\n";
test2();
}
template<typename T>
void output(const T &c)
{
for(auto &i:c)
{
std::cout<<i<<' ';
}
std::cout<<'\n';
}
int generate_random_number()
{
return std::rand()%101;
}
void test1()
{
using namespace std;
vector<int> v0(10);
generate(v0.begin(),v0.end(),generate_random_number);
cout<<"v0:";
output(v0);
vector<int> v1{v0};
sort(v1.begin(),v1.end());
cout<<"v2:";
output(v1);
vector<int>v2{v0};
sort(v2.begin()+1,v2.end()-1);
cout<<"v2:";
output(v2);
}
void test2()
{
using namespace std;
vector<int>v0(10);
generate(v0.begin(),v0.end(),generate_random_number);
cout<<"v0:";
output(v0);
auto min_iter=min_element(v0.begin(),v0.end());
auto max_iter=max_element(v0.begin(),v0.end());
cout<<"最小值:"<<*min_iter<<endl;
cout<<"最大值:"<<*max_iter<<endl;
auto ans=minmax_element(v0.begin(),v0.end());
cout<<"最小值:"<<*(ans.first)<<endl;
cout<<"最大值:"<<*(ans.second)<<endl;
double avg1=accumulate(v0.begin(),v0.end(),0.0)/v0.size();
cout<<"均值:"<<fixed<<setprecision(2)<<avg1<<endl;
sort(v0.begin(),v0.end());
double avg2=accumulate(v0.begin()+1,v0.end()-1,0.0)/(v0.size()-2);
cout<<"去掉最大值、最小值之后,均值:"<<avg2<<endl;
}
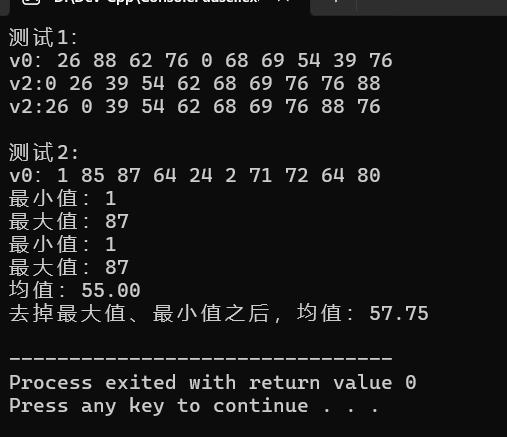
①generate作用:在一个指定的目标区间内,连续地填入或“生成”特定的值。
②可以一次性找到最大值和最小值,简化代码,减少工作量。
实验三:
点击查看代码
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cctype>
unsigned char func(unsigned char c);
void test1();
void test2();
int main()
{
std::cout<<"测试1:字符串大小写转换\n";
test1();
std::cout<<"\n测试2:字符变换\n";
test2();
}
unsigned char func(unsigned char c)
{
if(c=='z')
{
return 'a';
}
if(c=='Z')
{
return 'A';
}
if(std::isalpha(c))
{
return static_cast<unsigned char>(c+1);
}
return c;
}
void test1()
{
std::string s1{"Hello World 2049!"};
std::cout<<"s1="<<s1<<'\n';
std::string s2;
for(auto c:s1)
{
s2+=std::tolower(c);
}
std::cout<<"s2="<<s2<<'\n';
std::string s3;
for(auto c:s1)
{
s3+=std::toupper(c);
}
std::cout<<"s3="<<s3<<'\n';
}
void test2()
{
std::string s1{"I love cosmos!"};
std::cout<<"s1="<<s1<<'\n';
std::string s2(s1.size(),' ');
std::transform(s1.begin(),s1.end(),s2.begin(),func);
std::cout<<"s2="<<s2<<'\n';
}
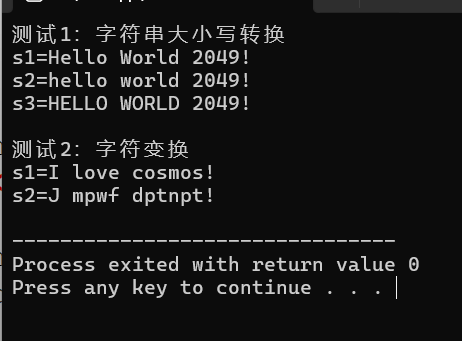
①输出字符串中每个字符的后一位字母。
②tolower是将字母转换成小写字母,toupper是将字母转换成大写字母。
③第一个参数是输入的起始位置,第二个参数是输入的结束位置,第三个参数是输出的起始位置,第四个参数是操作函数。输出相同,但与s2.begin()不同的是,s1.begin()是将原数据覆盖后输出,而s2.begin()是另建一个存储空间后输出,更安全。
实验四:
点击查看代码
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
bool is_palindrome(const std::string &s);
bool is_palindrome_ignore_case(const std::string &s);
int main()
{
using namespace std;
string s;
while(cin>>s)
{
cout<<boolalpha
<<"区分大小写:"<<is_palindrome(s)<<"\n"
<<"不区分大小写:"<<is_palindrome_ignore_case(s)<<"\n\n";
}
}
bool is_palindrome(const std::string &s)
{
std::string s1{s};
std::reverse(s1.begin(),s1.end());
return s==s1;
}
bool is_palindrome_ignore_case(const std::string &s)
{
std::string s2;
for(auto &i:s)
{
s2+=std::tolower(i);
}
std::string s3{s2};
std::reverse(s3.begin(),s3.end());
return s2==s3;
}
结果:
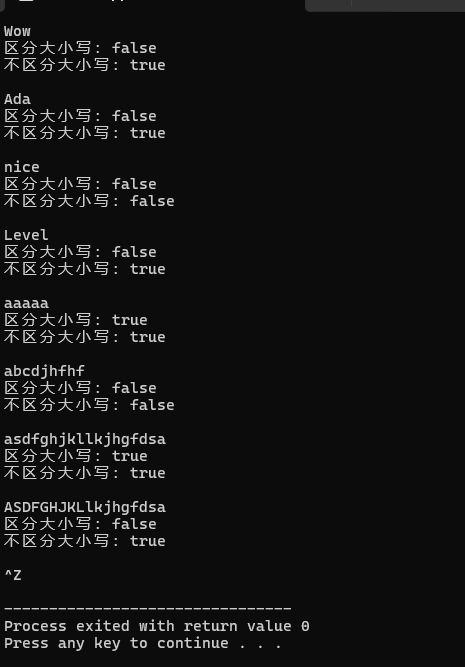
实验五:
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
std::string dec2n(int x, int n = 2);
int main()
{
int x;
while(std::cin>>x)
{
std::cout<<"十进制:"<<x<<'\n'
<<"二进制:"<<dec2n(x)<<'\n'
<<"八进制:"<<dec2n(x,8)<<'\n'
<<"十二进制:"<<dec2n(x,12)<<'\n'
<<"十六进制:"<<dec2n(x,16)<<'\n'
<<"三十二进制:"<<dec2n(x,32)<<"\n\n";
}
}
std::string dec2n(int x,int n)
{
std::string s;
int a;
if(x==0)
{
return "0";
}
while(x!=0)
{
a=x%n;
if(a<10)
{
s+='0'+a;
}
else
{
s+='A'+(a-10);
}
x/=n;
}
std::reverse(s.begin(),s.end());
return s;
}
结果:
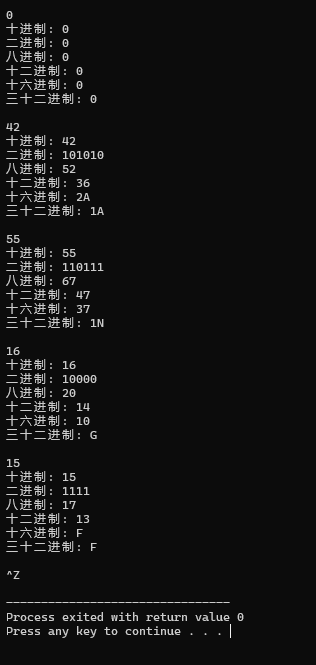
实验六:
点击查看代码
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
void test();
int main()
{
test();
}
void test()
{
using namespace std;
string s{"abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"};
string s1;
for(auto &i:s)
{
s1+=toupper(i);
}
cout<<' '<<' '<<' ';
for(auto &k:s)
{
cout<<k<<' ';
}
cout<<'\n';
int j;
for(j=1;j<=9;j++)
{
cout<<' '<<j<<' ';
rotate(s1.begin(),s1.begin()+1,s1.end());
for(auto &m:s1)
{
cout<<m<<' ';
}
cout<<'\n';
}
for(j;j<=26;j++)
{
cout<<j<<' ';
rotate(s1.begin(),s1.begin()+1,s1.end());
for(auto &n:s1)
{
cout<<n<<' ';
}
cout<<'\n';
}
}
结果:

实验七:
点击查看代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<ctime>
#include<iomanip>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
srand(time(0));
int a = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int x = rand() % 10 + 1;
int y = rand() % 10 + 1;
int o = rand() % 4;
char f;
int b;
switch (o) {
case 0:
f = '+';
b = x + y;
break;
case 1:
f = '-';
if (x < y) { swap(x, y); }
b = x - y;
break;
case 2:
f = '*';
b = x * y;
break;
case 3:
if (x < y) {
swap(x, y);
}
if (x % y != 0) {
do {
x = rand() % 10 + 1;
y = rand() % 10 + 1;
} while (x % y != 0 || y == 0);
}
f = '/';
b = x / y;
break;
}
cout << x << " " << f << " " << y << "=";
int c;
cin >> c;
if (c == b) {
a++;
}
}
double s =(double)(a) / 10 * 100;
cout << "\n正确率:" << fixed << setprecision(2) << s << "%" << endl;
return 0;
}
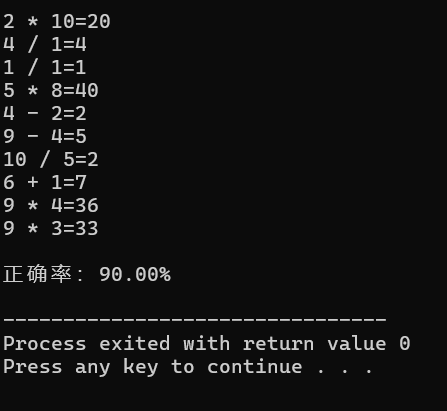
结果:





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号