类的底层探究_cache
在之前的类的底层探究中, 我们并未对于类结构体中的cache_t进行详细说明,那么本节我们来看一下cache
一、cache的结构总览
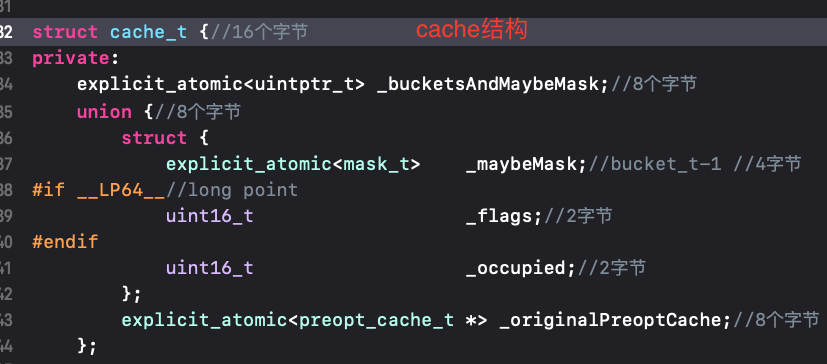
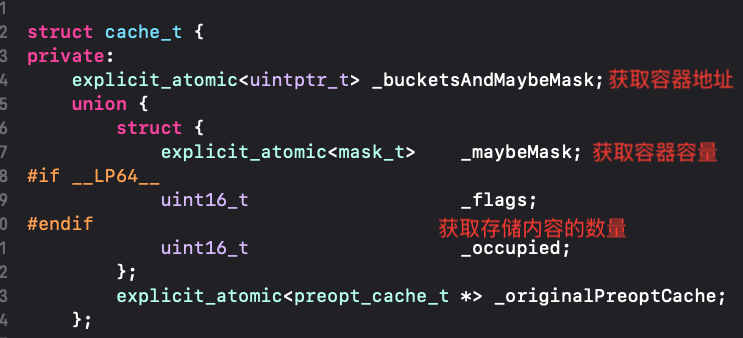
我们之前已经知道了cache占据了16个字节,那么我们来具体看一下cache,他本身存储了一个指针_bucketsAndMayBeMask是8个字节,还存储了一个联合体union,其中包含了_maybeMask(4字节)、_flags(2字节)、_occupied(2字节)、_originalPreoptcache(8字节指针)。
二、cache内部结构解析
LGPerson *p = [LGPerson alloc];
[p method1];
我们简单的通过一行代码来找到通过类对象偏移16字节的地址打印出cache:
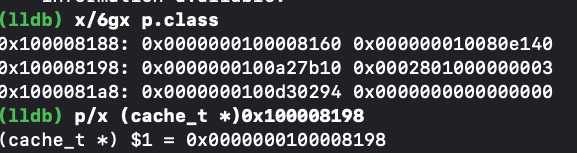
接着,我们对其中的属性逐个打印,但是无法获取我们想要的得到的存储方法的信息,因此我们从objc的源码出发探究cache的内部实现。我们从cache_t的方法中发现了一个insert方法,不难看出这个方法于插入方法有些关系。
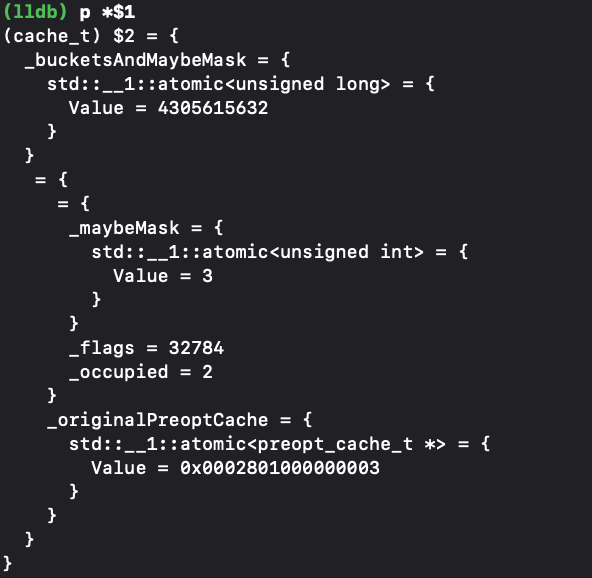
接着,我们进入这个方法:
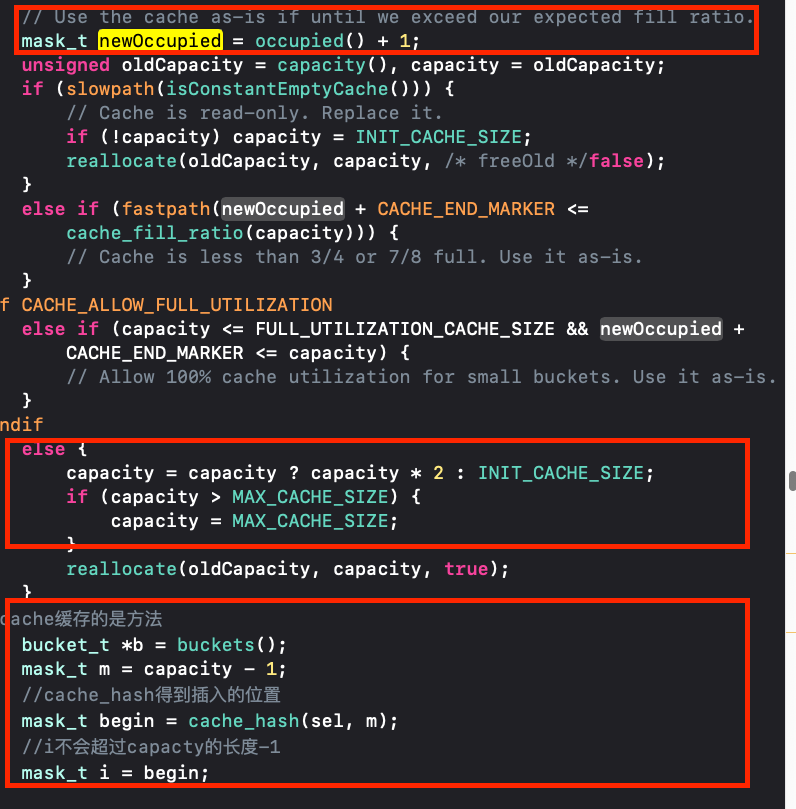
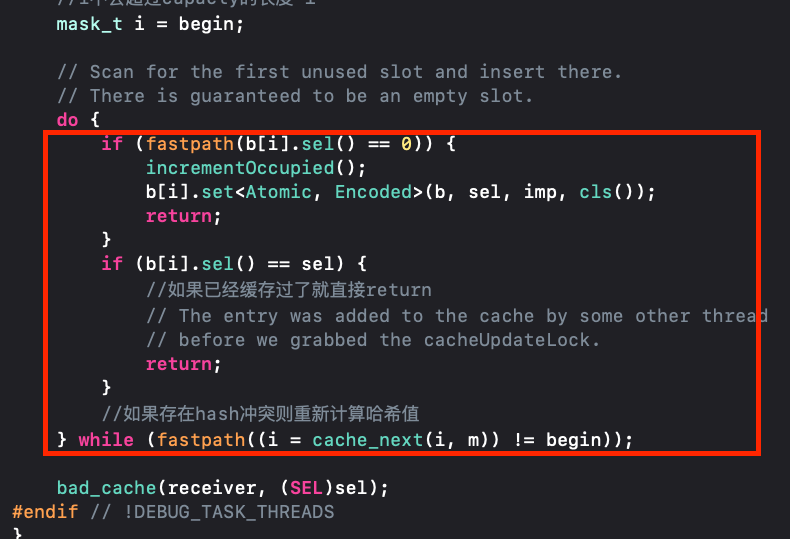
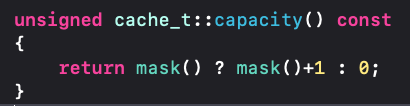
对于insert内部,我们可以看到是如何存放方法的,这里先对几个参数作简单说明:occuiped是数据占据大小,capacity是buckets的长度,buckets是存放数据的地方。
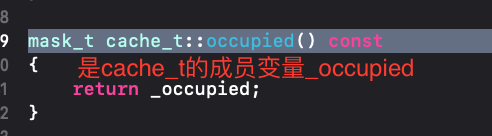
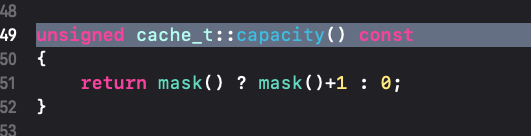
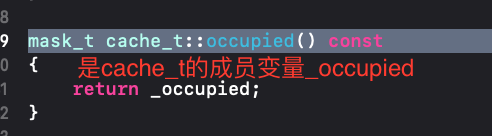
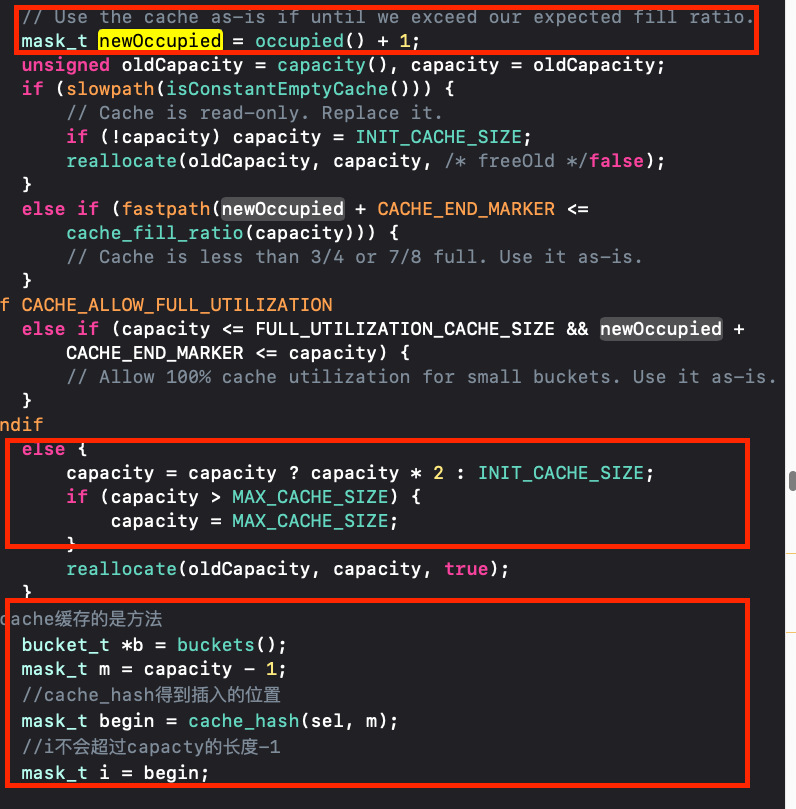
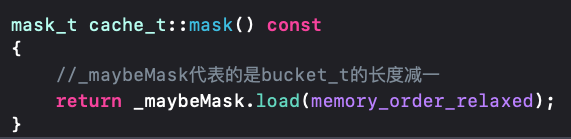
capacity是通过mask方法获取的,而mask其实是通过cache的成员变量_maybeMask获取的,capacity的长度等于_maybeMask+1,如果这里_maybeMask为空,则capacity为0。
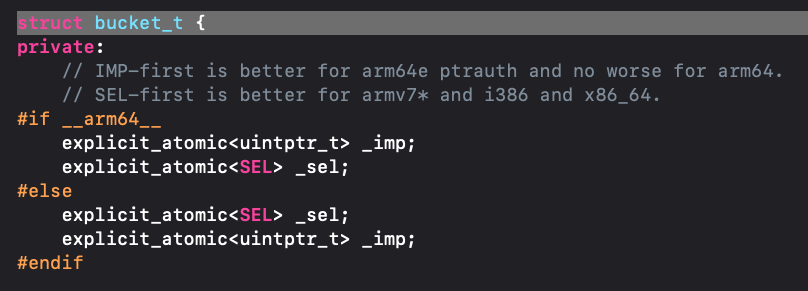
bucket_t
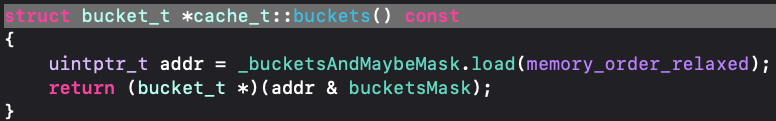
我们先来看看buckets是如何获取的?他是通过cache的成员变量_bucketsAndMaybeMask获取的
接着,我们来看一下bucket_t的具体结构:bucket_t
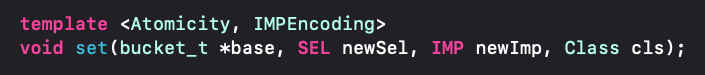
存储是imp和sel,并且提供了set模版方法来存储存储imp和sel
最后,我们来总结一下cache_t内部各个属性的用处:
三、cache存入数据分析
当我们基本明白cache_t内部的结构之后,我们来分析一下cache是如何存储的:当某个方法需要被缓存时,需要先判断容量是否需要被扩容,然后进行存储缓存。
//cache缓存的是方法 bucket_t *b = buckets(); mask_t m = capacity - 1; //cache_hash得到插入的位置 mask_t begin = cache_hash(sel, m); //i不会超过capacty的长度-1 mask_t i = begin; // Scan for the first unused slot and insert there. // There is guaranteed to be an empty slot. do { if (fastpath(b[i].sel() == 0)) { incrementOccupied(); b[i].set<Atomic, Encoded>(b, sel, imp, cls()); return; } if (b[i].sel() == sel) { //如果已经缓存过了就直接return // The entry was added to the cache by some other thread // before we grabbed the cacheUpdateLock. return; } //如果存在hash冲突则重新计算哈希值 } while (fastpath((i = cache_next(i, m)) != begin));
3.1 缓存存储
1.通过_bucketsAndMaybeMask来获取bucket_t容器(其实就是一个散列表)
bucket_t *b = buckets();
2.通过哈希算法算出当前需要存储的位置
mask_t m = capacity - 1;
mask_t begin = cache_hash(sel, m);
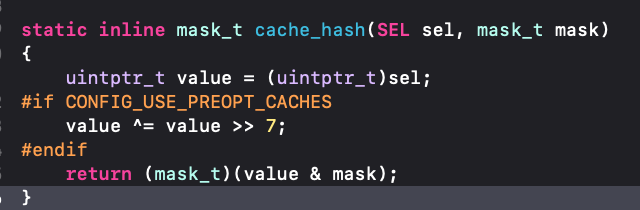
首先根据buckets的长度-1来获取一个mask_t的值,然后用这个值计算存储位置的mask,然后通过cache_hash方法计算位置,cache_hash是通过mask & sel 来得到一个在【0,capacity】的索引:
3.根据索引判断该位置是否可以存储(等于0说明该位置没有被使用,可以被存储,否则该位置存储的方法与将要存储的方法相同)。
if (fastpath(b[i].sel() == 0)) { incrementOccupied(); b[i].set<Atomic, Encoded>(b, sel, imp, cls()); return; } if (b[i].sel() == sel) { //如果已经缓存过了就直接return // The entry was added to the cache by some other thread // before we grabbed the cacheUpdateLock. return; }
4.如果出现了哈希冲突则需要解决,这里通过cache_next方法,对于cache_next方法不同的架构是不同的计算方式,在arm64架构下 如果当前位置为0 ,去判断 buckets的做后一个位置能否存储,如果不为0,则查看前面一个位置是否可以存储。
while (fastpath((i = cache_next(i, m)) != begin));
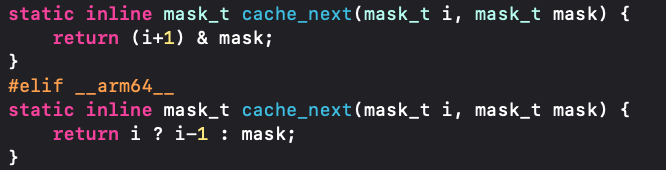
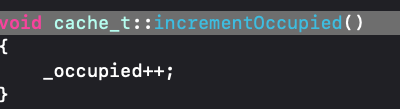
5.存储数据,如果找到可以存储的位置,则cache的_occupied+1,并通过bucket_t的set方法存储,并且重新将sel签名后存储。
if (fastpath(b[i].sel() == 0)) { incrementOccupied(); b[i].set<Atomic, Encoded>(b, sel, imp, cls()); return; }
3.2扩容
对于散列表存储数据,肯定会出现容量不够的情况,所以cache的缓存必然是需要处理容量的问题,下面就来分析一下在不同架构是如何进行扩容的,系统已经将这些差异定义为了宏定义。
#if __arm__ || __x86_64__ || __i386__ #define CACHE_END_MARKER 1 static inline mask_t cache_fill_ratio(mask_t capacity) { return capacity * 3 / 4; } #elif __arm64__ && !__LP64__ #define CACHE_END_MARKER 0 static inline mask_t cache_fill_ratio(mask_t capacity) { return capacity * 3 / 4; } #elif __arm64__ && __LP64__ #define CACHE_END_MARKER 0 static inline mask_t cache_fill_ratio(mask_t capacity) { return capacity * 7 / 8; } #define CACHE_ALLOW_FULL_UTILIZATION 1 #else #error unknown architecture #endif enum { #if CACHE_END_MARKER || (__arm64__ && !__LP64__) INIT_CACHE_SIZE_LOG2 = 2, #else support INIT_CACHE_SIZE_LOG2 = 1, #endif INIT_CACHE_SIZE = (1 << INIT_CACHE_SIZE_LOG2), MAX_CACHE_SIZE_LOG2 = 16, MAX_CACHE_SIZE = (1 << MAX_CACHE_SIZE_LOG2), FULL_UTILIZATION_CACHE_SIZE_LOG2 = 3, FULL_UTILIZATION_CACHE_SIZE = (1 << FULL_UTILIZATION_CACHE_SIZE_LOG2), };
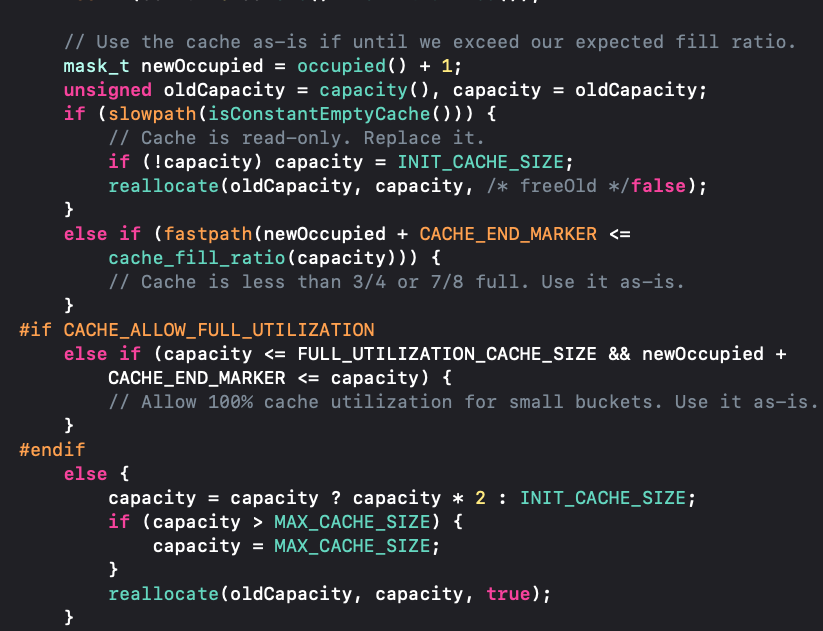
整体上的扩容分为了四种情况,接下来,我们一一的看下:
1.cache为空:当cache为空,说明是第一次来到缓存数据,所以此时需要初始化一个INIT_CACHE_SIZE的buckets(以下我们简称为桶子);对于INIT_CACHE_SIZE 可以根据宏定义的得知,在arm64或M1下为 2 ,x86下为4。
if (!capacity) capacity = INIT_CACHE_SIZE;
2.看cache中占用的长度是否达到扩容的标准:判断是否需要扩容是通过newOccupied + CACHE_END_MARKER <= cache_fill_ratio(capacity)判断的
if (fastpath(newOccupied + CACHE_END_MARKER <= cache_fill_ratio(capacity)))
- newOccupied = occupied + 1 即存储当前sel后占用的长度
- cache_end_marker 在arm64或M1下的情况是0,在_x86_64下是1
- cache_fill_ratio(capacity)他用来获取当前架构下存储数量扩容的标准,arm64/M1是capacity * 7/8 ;_x86_64架构下是capacity * 3/4
3.判断 CACHE_ALLOW_FULL_UTILIZATION 是否存满了数据:这个判断是在CACHE_ALLOW_FULL_UTILIZATION为真的条件下才会生效,在arm64下CACHE_ALLOW_FULL_UTILIZATION为1,x86_64下为0
if (capacity <= FULL_UTILIZATION_CACHE_SIZE && newOccupied + CACHE_END_MARKER <= capacity)
CACHE_ALLOW_FULL_UTILIZATION系统中定义如下,也就是说这个值是 8;这里就是判断当容量小于 8的时候,查看存入当前 sel后是 是否超过 当前容量,如果超过就扩容
FULL_UTILIZATION_CACHE_SIZE_LOG2 = 3, FULL_UTILIZATION_CACHE_SIZE = (1 << FULL_UTILIZATION_CACHE_SIZE_LOG2),
4.如果CACHE_ALLOW_FULL_UTILIZATION为假,先计算扩容后的容量
- 当存入当前的
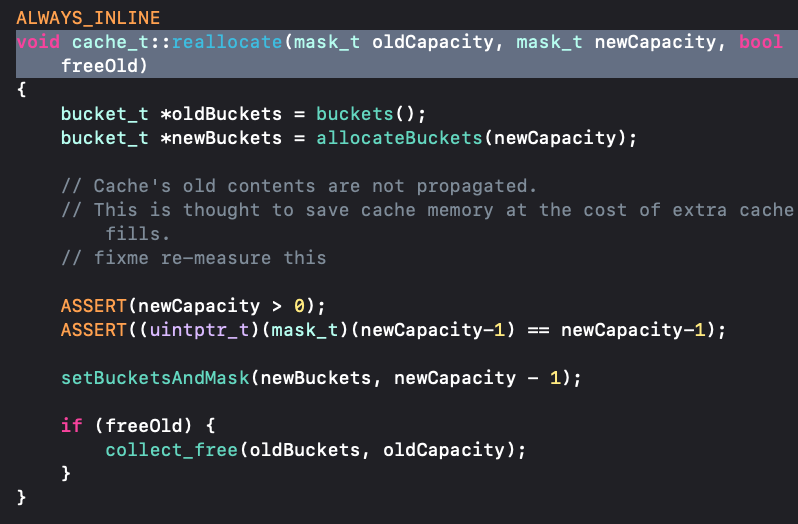
sel需要扩容时 ,此时就是把当前容量 * 2,如果计算后容量为0 ,则初始化为INIT_CACHE_SIZE,并且保证buckets的容量不会超过最大值MAX_CACHE_SIZE = 1<<16 - 重新创建
buckets,更新cache的_bucketsAndMaybeMask和_maybeMask,并释放旧的buckets
else { capacity = capacity ? capacity * 2 : INIT_CACHE_SIZE; if (capacity > MAX_CACHE_SIZE) { capacity = MAX_CACHE_SIZE; } reallocate(oldCapacity, capacity, true); }
四、真机模拟cache流程
1.模拟数据结构:根据源码来仿写类的底层结构 和 cache的底层结构,通过类型强转将类对象转换为 仿写的类对象,然后读取cache的数据查看真机中缓存的数据,注意的是底层对于真机的架构下的宏定义。
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h> #import "AppDelegate.h" #import <objc/message.h> #import "LGPerson.h" #if defined(__arm64__) && TARGET_OS_IOS && !TARGET_OS_SIMULATOR && !TARGET_OS_MACCATALYST #define CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES 1 #else #define CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES 0 #endif #define CACHE_END_MARKER 0 #define INIT_CACHE_SIZE 2 #define MAX_CACHE_SIZE_LOG2 16 #define MAX_CACHE_SIZE (1 << MAX_CACHE_SIZE_LOG2) //bucket_t源码模仿 struct hw_bucket_t { IMP _imp; SEL _sel; }; enum hw__legacy_memory_order { __mo_relaxed, __mo_consume, __mo_acquire, __mo_release, __mo_acq_rel, __mo_seq_cst }; typedef enum hw_memory_order { memory_order_relaxed = __mo_relaxed, memory_order_consume = __mo_consume, memory_order_acquire = __mo_acquire, memory_order_release = __mo_release, memory_order_acq_rel = __mo_acq_rel, memory_order_seq_cst = __mo_seq_cst, } memory_order; //cache_t源码模仿 struct hw_cache_t { uintptr_t _bucketsAndMaybeMask; // 8 uint32_t _maybeMask ; uint16_t _flags ; uint16_t _occupied ; // _bucketsAndMaybeMask is a buckets_t pointer in the low 48 bits // _maybeMask is unused, the mask is stored in the top 16 bits. // How much the mask is shifted by. static constexpr uintptr_t maskShift = 48; // Additional bits after the mask which must be zero. msgSend // takes advantage of these additional bits to construct the value // `mask << 4` from `_maskAndBuckets` in a single instruction. static constexpr uintptr_t maskZeroBits = 4; // The largest mask value we can store. static constexpr uintptr_t maxMask = ((uintptr_t)1 << (64 - maskShift)) - 1; // The mask applied to `_maskAndBuckets` to retrieve the buckets pointer. static constexpr uintptr_t bucketsMask = ((uintptr_t)1 << (maskShift - maskZeroBits)) - 1; hw_bucket_t *buckets() { return ( hw_bucket_t *)(_bucketsAndMaybeMask & bucketsMask); } uint32_t mask() const{ uintptr_t maskAndBuckets = _bucketsAndMaybeMask; return maskAndBuckets >> maskShift; } }; //class_data_bits_t源码模仿 struct hw_class_data_bits_t { uintptr_t objc_class; }; //类源码模仿 struct hw_objc_class { Class isa; Class superclass; struct hw_cache_t cache; struct hw_class_data_bits_t bits; };
2.模拟缓存方法的容量判断:根据源码中的条件判断,仿写判断,打印出当前cache的存储情况
void test(Class cls) { struct hw_objc_class *pClass = (__bridge struct hw_objc_class *)(cls); struct hw_cache_t cache = pClass->cache; uintptr_t mask = cache.mask(); uint32_t newOccupied = cache._occupied + 1; uintptr_t oldCapacity = mask ? (mask + 1) : 0, capacity = oldCapacity; // 第一次进入,还没有缓存方法 if (cache._occupied == 0 ){ capacity = INIT_CACHE_SIZE; NSLog(@"isConstantEmptyCache: oldOccupied == %d,nweOccupied ==%d ,oldCapacity == %lu, capacity == %lu" ,cache._occupied,newOccupied ,oldCapacity,capacity); // 判断是在 7 / 8 的范围内 }else if (newOccupied + CACHE_END_MARKER <= (capacity * 7 / 8)){ NSLog(@"cache_fill_ratio: oldOccupied == %d,nweOccupied ==%d ,oldCapacity == %lu, capacity == %lu" ,cache._occupied,newOccupied ,oldCapacity,capacity); //判读是容量是不是在 8以内且没存满 } else if (capacity <= 8 && newOccupied + CACHE_END_MARKER <= capacity) { NSLog(@"CACHE_ALLOW_FULL_UTILIZATION: oldOccupied == %d,nweOccupied ==%d ,oldCapacity == %lu, capacity == %lu" ,cache._occupied,newOccupied ,oldCapacity,capacity); }else { // 需要扩容 capacity = capacity ? capacity * 2 : INIT_CACHE_SIZE; if (capacity > MAX_CACHE_SIZE) { capacity = MAX_CACHE_SIZE; } //因为扩容了,所以下一个cache的Occupied 只有一个将要存进去的方法,所以此时 的 nweOccupied == 1 NSLog(@"doublecapacity: oldOccupied == %d,nweOccupied ==%d ,oldCapacity == %lu, capacity == %lu" ,cache._occupied,1 ,oldCapacity,capacity); } // struct hw_bucket_t * buckets = cache.buckets(); // // for (int i = 0; i < mask + 1; i++ ) { // SEL sel = buckets[i]._sel; // IMP imp = buckets[i]._imp; // NSLog(@"%@-%p",NSStringFromSelector(sel),imp); // } }
3.代码验证结果是否正确:由于系统中方法的调用是在 cache之后,所以在 调用方法前打印一次cache,模拟第一次缓存方法,bukets还不存在时的状况,即是 isConstantEmptyCache的情况,所以在打印的时候比较 nweOccupied 和 oldCapacity 查看是否需要扩容
Person *p = [Person alloc]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod1]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod2]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod3]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod4]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod5]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod6]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod7]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod8]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod9]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod10]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod11]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod12]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod13]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod14]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod15]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod16]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod17]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod18]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod19]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod20]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod21]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod22]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod23]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod24]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod25]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod26]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod27]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod28]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod29]; test(Person.class); [p instanceMetheod30]; test(Person.class);
具体结果见:https://gitee.com/cike111/personal-notes/blob/master/iOS%20底层探究/%2005_%20iOS%20类的底层探究%20cache.md#获取bucket_t-容器--和-存储位置
五、思考与总结
5.1 为什么要释放掉旧的buckets
- 由于哈希表的特性(地址映射),当每次总表扩容的时候,所有的元素映射都会失效,因为总容量变了,下标哈希结果也会改变
- 如果需要之前所有的缓存的方法都重新存储,消耗和花费过大
- 扩容是按照指数级增加的,如果及时清除,可以缓存更多的方法,减少扩容次数,从而提高效率
5.2 总结
- cache_t内部使用了bucket_t这个容器中存储的sel 和imp
- 当插入数据大于总容量的3/4(x86_64 / arm64 32位系统) || 7/8(真机 / arm64 64位系统)时,会对容器进行扩容处理
- 真机在容量8以内会存满在扩容
- 扩容是根据当前容量*2,按照指数级增加,需要将旧的缓存给释放掉,提高效率,减少消耗
- bucket_t是一个散列表,通过sel&capacity-1哈希算法定位存储位置
- 哈希冲突通过开放地址方式解决冲突


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号