[ Springboot Security 01] Basic Security
SpringBoot Security
1. Software Security
access control/ defence attacks
SQL injection
2. Authentication & Authorization
Authentication(who you are): password, token. 401
Authorization(what a u allowed to do): roles/ authority 403
RBAC model: Role-based access control
give authority to roles, and assign user to roles;
in spring security: authorization is like:
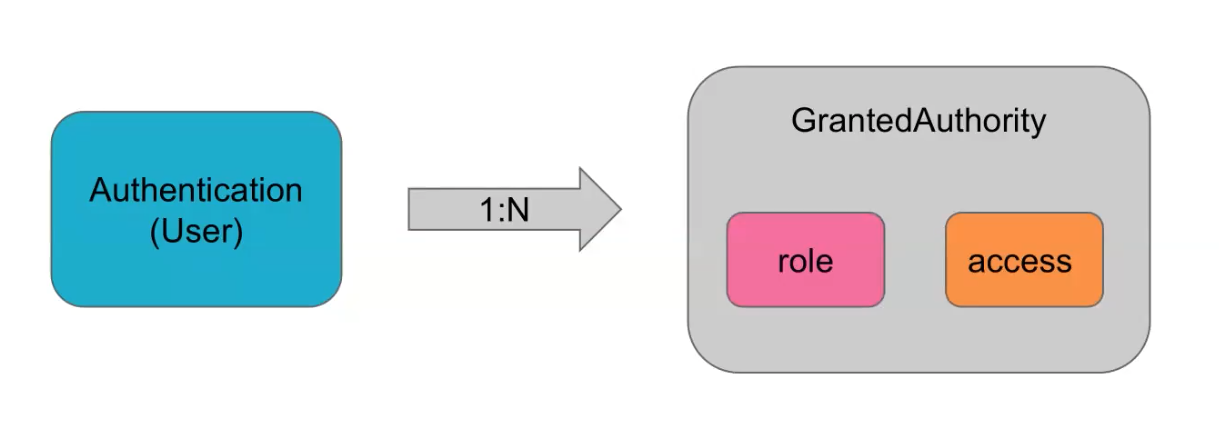
3. Spring Security:
1. add dependency to build.gradle : starter-security
2. when run bootRun and access api, will be a login page supported by spring security
3. default username : user, password will be found in log
4. add configuration in application.yml
spring.security.user.name: user
spring.security.user.password: 123
if choose basic authentication: username and password will be put in http request header, encoded by Base64;
4. Spring Security configuration
use form to login:
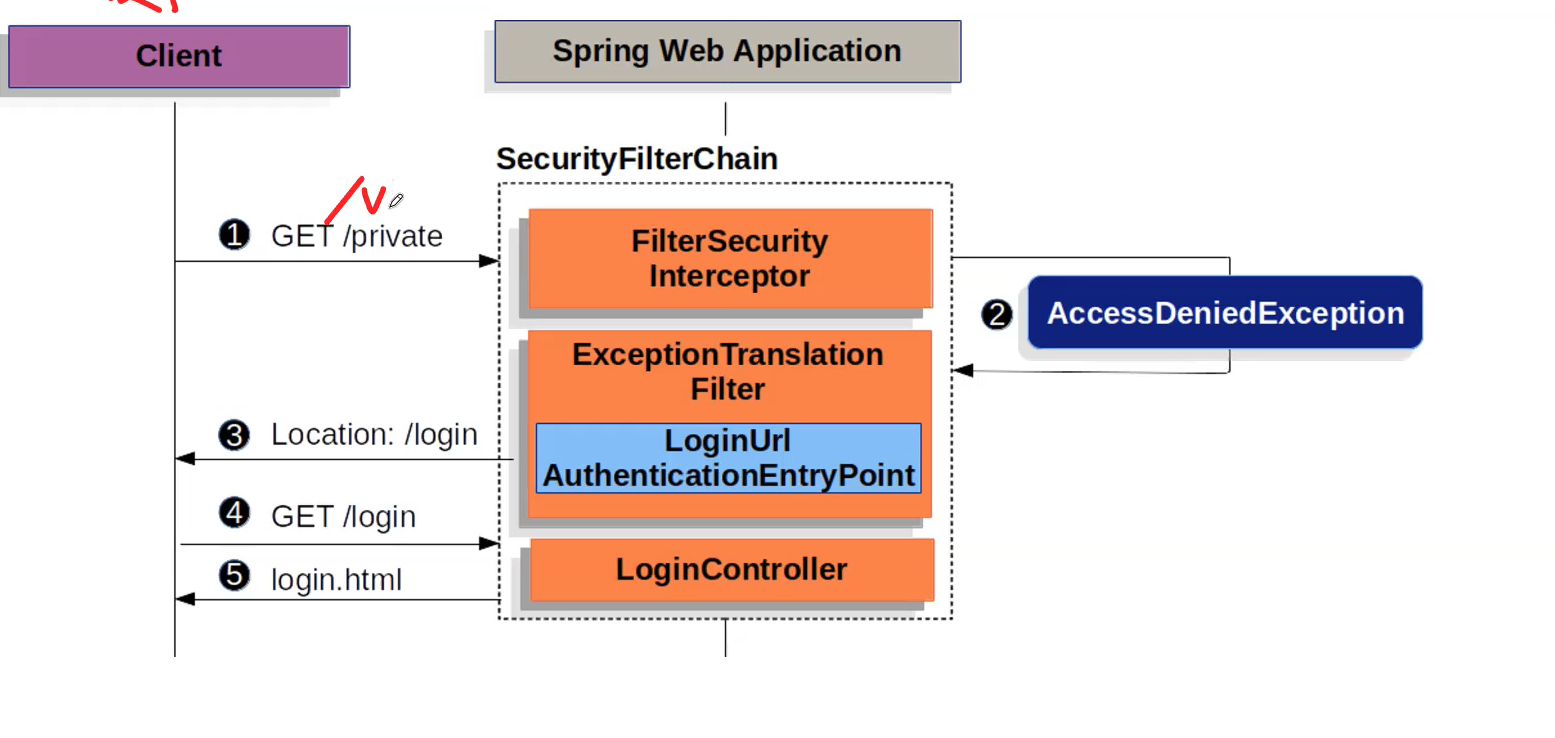
Basic Authentication by postman:
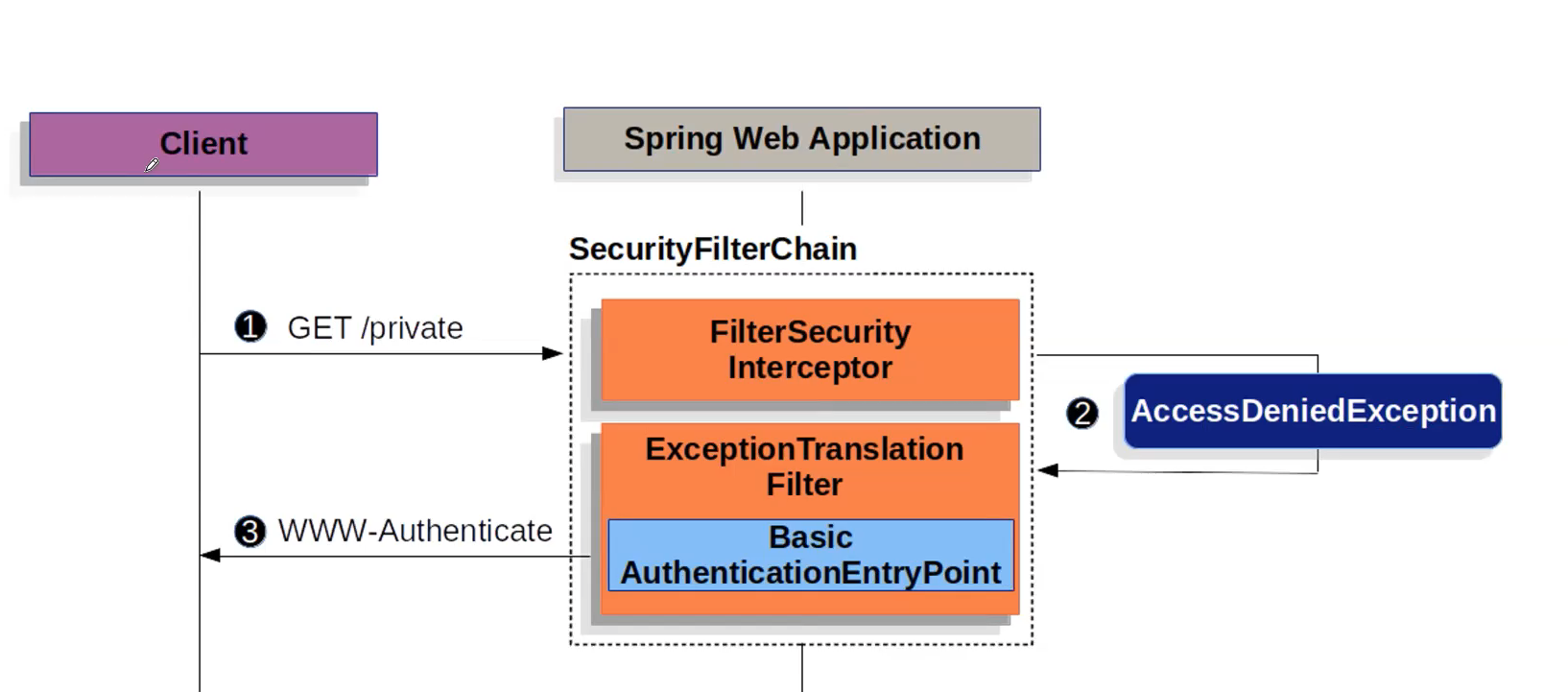
spring security principle:
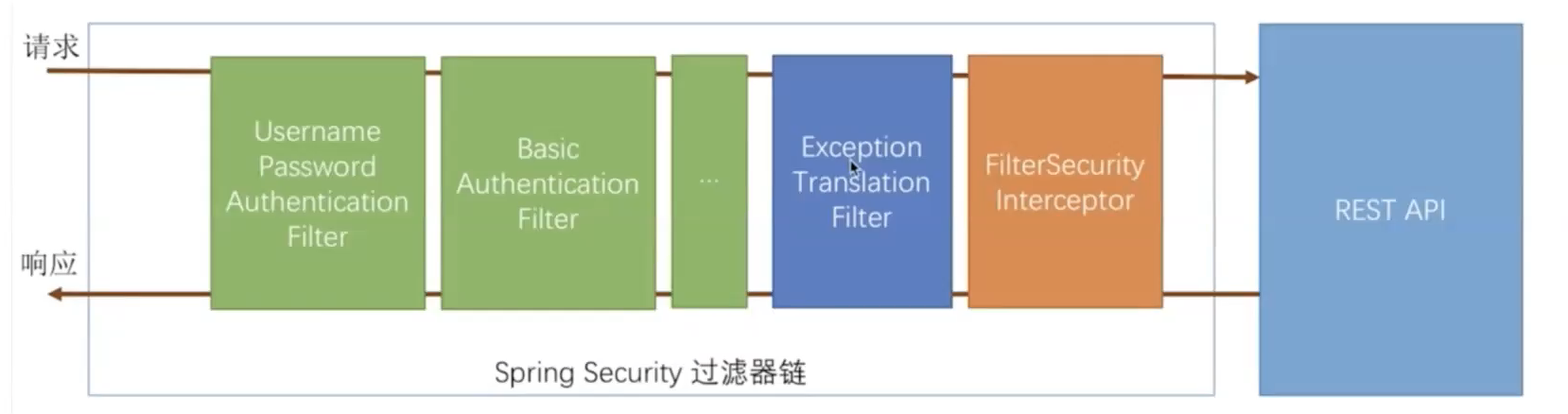
how to get user information:
-
storage with in-memory authentication
-
JDBC, put in database
-
custom data stores with UserDetailsService (important : implement get from database or form a third-part authentication system)
-
LDAP (OOS)
5. UserDetailService
what we need is to add a security filter as mentioned above;
-
Firstly, to take user information, asume story user information format as
User class, and we have a third-part service "FakeClient" which will
give a user back ;(our user type) -
CustomUserDetailService will implement UserDetailService, loadUserByUsername() will take a String username, from FakeClient got the user we need, change user's rolesAndAuthrity to what spring understand. (Stirng---> SimpleGrantedAuthority);and then, return the UserDetails back.
-
SecurityConfiguration will be scanned by spring, and will be added in spring security filter chain; and it extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter. authenticationManagerBuilder have many methods, support inmemory authentication, by jdbc and by userDetailsService.
The SecurityConfiguration also need a bean: PasswordEncoder, which transfer password encrypted or not ;
5.1 create a fake client for user information
it will be the fake database which contains username, password, roles and authority.
User is:
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class User {
private String name;
private String password;
private List<String> rolesAndAuthority;
}
fake user client is:
@Component//will be autowired to spring containers
public class FakeClient {
private static final List<User> users = List.of(
User.builder().name("first").password("123").rolesAndAuthority(List.of("ROLES_ADMIN", "read")).build(),
User.builder().name("second").password("123").rolesAndAuthority(List.of("ROLES_ADMIN")).build()
);
public Optional<User> findByUserName(String username) {
return users.stream().filter(user -> user.getName().equals(username)).findFirst();
}
}
CustomUserDetailService is :
@Component
public class CustomUserDetailService implements UserDetailsService {
private final FakeClient fakeClient;
public CustomUserDetailService(FakeClient fakeClient) {
this.fakeClient = fakeClient;
}
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
// query database, find out the user by username;
final var userDetailsOption = fakeClient.findByUserName(username);
User user = userDetailsOption.orElseThrow(() -> new UsernameNotFoundException("User not found"));
// change rolesAndAuthority to what spring security can understand(change to another type)
List<SimpleGrantedAuthority> auths = user.getRolesAndAuthority().stream()
.map(SimpleGrantedAuthority::new)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// put query information to UserDetails and return
return org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User
.withUsername(user.getName())
.password(user.getPassword())
.authorities(auths)
.build();
}
}
SecurityConfiguration is:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
private final UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
public SecurityConfiguration(UserDetailsService userDetailsService) {
this.userDetailsService = userDetailsService;
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder authenticationManagerBuilder) throws Exception {
authenticationManagerBuilder.userDetailsService(userDetailsService);
}
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
// must have
return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();//which means when password transferred to filter, it's without encrypted
// return PasswordEncoderFactories.createDelegatingPasswordEncoder();
}
}
6. Authorization
6.1 HttpSecurity config:
write a configure() in Class SecurityConfiguration:
config(AuthenticationManagerBuilder) focus on authentication
config(HttpSecurity) focus on authorization
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity httpSecurity) throws Exception {
httpSecurity.authorizeRequests()
.mvcMatchers(HttpMethod.GET, "/cars").hasRole("ADMIN")// 允许某个角色访问
.mvcMatchers(HttpMethod.GET, "/car/*").hasAuthority("read")// 允许有某个权限的访问
.mvcMatchers("/public").anonymous()//只允许匿名用户访问
.mvcMatchers(HttpMethod.GET, "/afterLogin").permitAll()//登录后都可以访问
.anyRequest().authenticated()//其他都需要认证
.and().formLogin()//支持表单
.and().httpBasic();//支持basic
}
Expression: if there have some relationship
.mvcMatchers(HttpMethod.GET, "/cars").access("hasRole('ADMIN') or hasAuthority('read')")// permit or
6.2 In controller
-
as a param, Authorization, by getAuthorities(), and compared with expected authorities, then determine if the user can access or not;
-
in controller, by SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication(), the controller can have authentication data, use the same method to do such things.
6.3 Annotation
when use annotation, remenber enable the methodsecurity:
put on security configuration class : @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
on controller: add
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN') or hasAuthority('read')")
and
@PostFilter(filterObject..... === authentication....),
filterObject will be the collector of method return, and will compare with authentication.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号