Mybatis
相关概念
ResultMap 与 ResultType
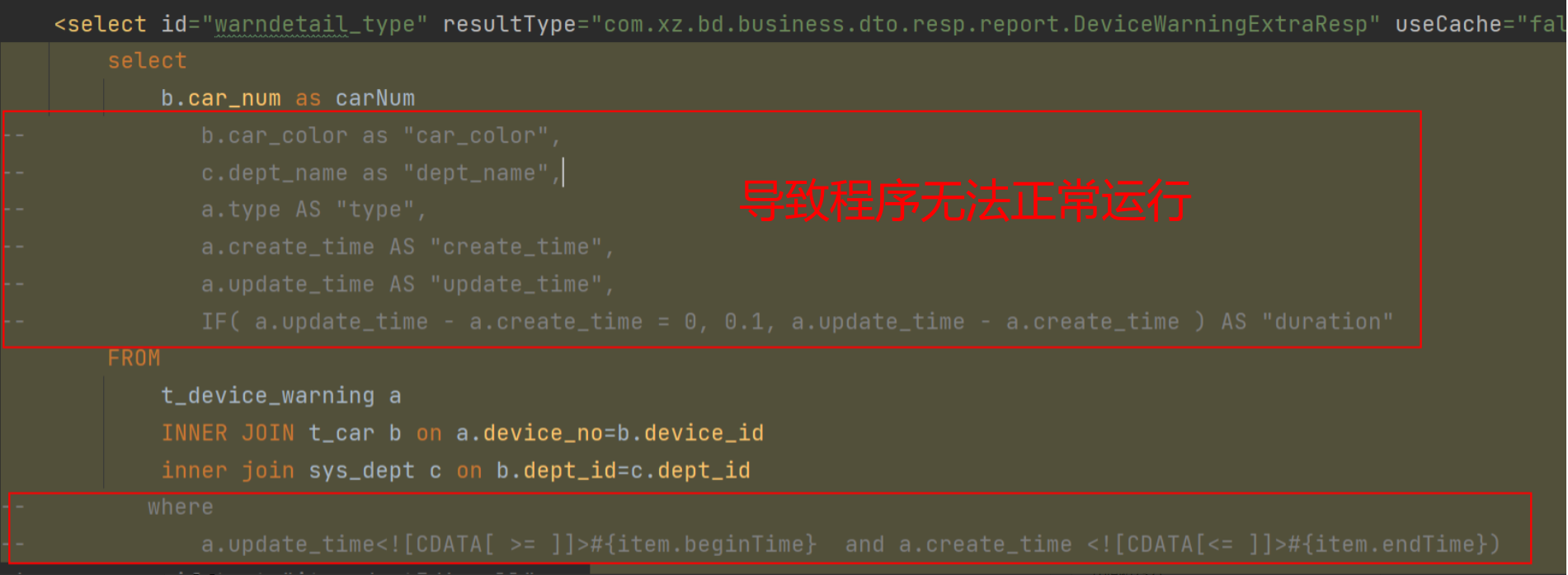
- 都表示的是一种映射关系,即只有当结果集需要映射(select)的时候才会使用;像新增、修改、删除只返回受影响行数,且框架默认会返回int类型,故可以不用显示声明ResultType="int"
- 如果数据表字段和实体类是一一对应的,就使用ResultType,否则就使用ResultMap,因此两者是不能共存的
- 实际开发中,对于一张表的映射其实通过驼峰命名等配置就可以实现,故ResultMap更多的是用在多张表的联合查询上
#{} 取参和 ${} 取参的区别
- #{} 会将内容先替换为?占位符,并且自动进行参数类型转化;能够防止SQL注入,安全性更高
- ${} 只是简单的字符串拼接
SELECT * FROM ${tableName}
SELECT * FROM user WHERE username = #{username}
配置文件
虽然有两种配置方式:mybatis-config.xml、application.yml, 两者有相同配置时,以mybatis-config.xml 文件为主(实践似乎并不是这样)。
推荐做法是两者结合使用:
- 核心配置(MyBatis 原生功能):建议放在 mybatis-config.xml
- Spring Boot 整合配置:建议放在 application.yml 中
application.yml
# MyBatis 配置
mybatis:
# Mapper XML 文件的路径(可以是多个路径)
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
# MyBatis 配置文件(如果需要使用 mybatis-config.xml)
config-location: classpath:mybatis-config.xml
# 指定实体类包路径,避免每次都配置全限定名
type-aliases-package: com.example.project.model
# 自动映射行为(PARTIAL 或 FULL)
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true # 开启驼峰命名自动映射
cache-enabled: true # 启用二级缓存
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl # 控制台打印日志mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 全局配置 -->
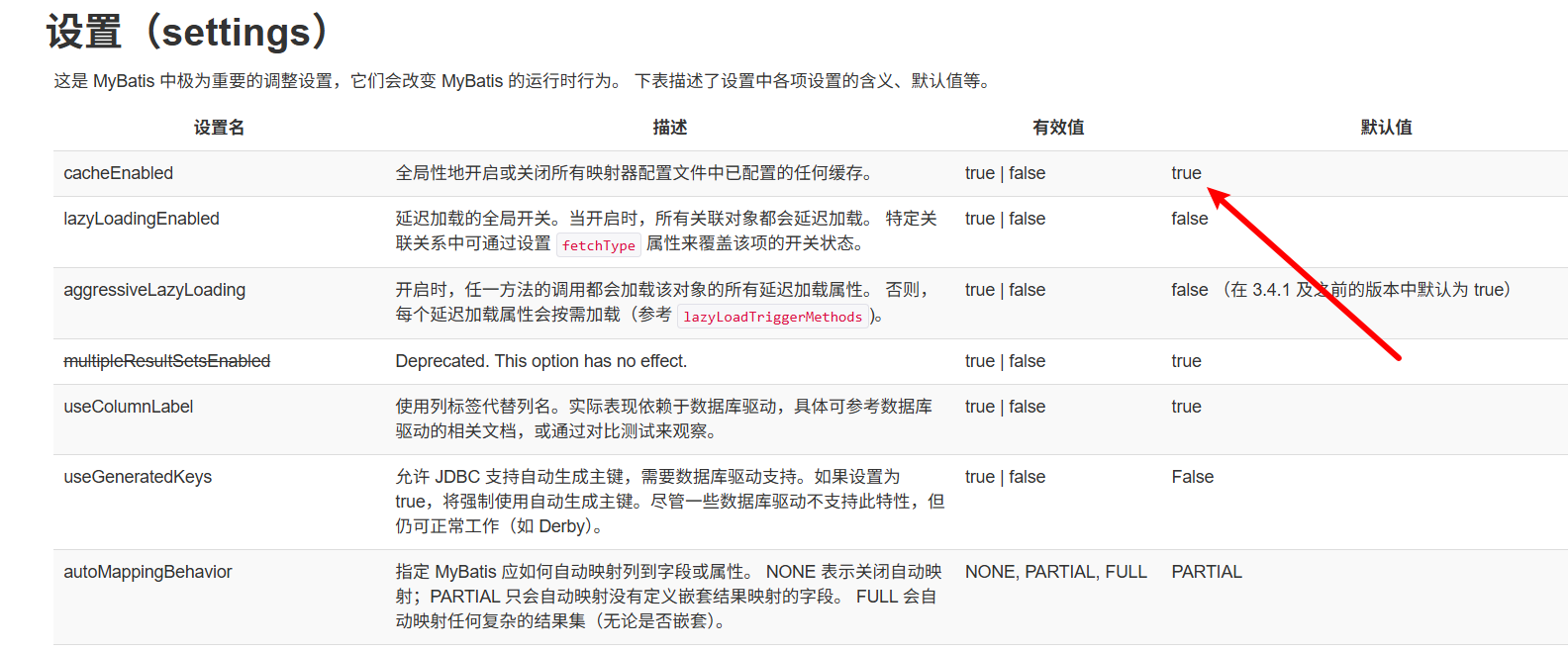
<settings>
<!-- 是否启用二级缓存 -->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true" />
<!-- 延迟加载 -->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true" />
<!-- 多结果集是否允许延迟加载 -->
<setting name="multipleResultSetsEnabled" value="true" />
<!-- 使用列别名 -->
<setting name="useColumnLabel" value="true" />
<!-- 自动映射行为(NONE, PARTIAL, FULL) -->
<setting name="autoMappingBehavior" value="PARTIAL" />
<!-- 自动生成主键 -->
<setting name="useGeneratedKeys" value="true" />
<!-- 数据库字段与 Java 属性的映射是否使用驼峰命名法 -->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true" />
<!-- 查询超时时间(秒) -->
<setting name="defaultStatementTimeout" value="30" />
<!-- 默认抓取大小 -->
<setting name="defaultFetchSize" value="100" />
</settings>
<!-- 类型别名 -->
<typeAliases>
<!-- 为包中的所有类定义别名 -->
<package name="com.example.project.model" />
<!-- 为特定类定义别名 -->
<typeAlias alias="User" type="com.example.project.model.User" />
</typeAliases>
</configuration>
缓存
sqlSession
Spring 管理的事务
@Service
public class MyService {
@Transactional
public void myMethod() {
myMapper.method1(); // 第一次 SQL 执行,SqlSession 开始
myMapper.method2(); // 第二次 SQL 执行,使用相同的 SqlSession
myMapper.method3(); // 第三次 SQL 执行,仍然使用相同的 SqlSession
} // 事务提交,SqlSession 生命周期结束
}手动管理 SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
MyMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(MyMapper.class);
mapper.method1(); // 第一次 SQL 执行
mapper.method2(); // 第二次 SQL 执行
mapper.method3(); // 第三次 SQL 执行
sqlSession.commit(); // 提交
} finally {
sqlSession.close(); // SqlSession 生命周期结束
}无事务支持(每次调用单独管理)
myMapper.method1(); // 第一次调用,SqlSession 生命周期开始和结束
myMapper.method2(); // 第二次调用,新的 SqlSession 开始和结束
myMapper.method3(); // 第三次调用,新创建的 SqlSession 生命周期开始和结束
一级缓存
默认开启,作用范围是同一个sqlSession对象下的相同sql查询
关闭方式:配置中localCacheScope设置为:STATEMENT。 即:<setting name="localCacheScope" value="STATEMENT"/>
二级缓存
作用范围:多个SqlSession之间需要共享缓存,其共享范围为Namespace
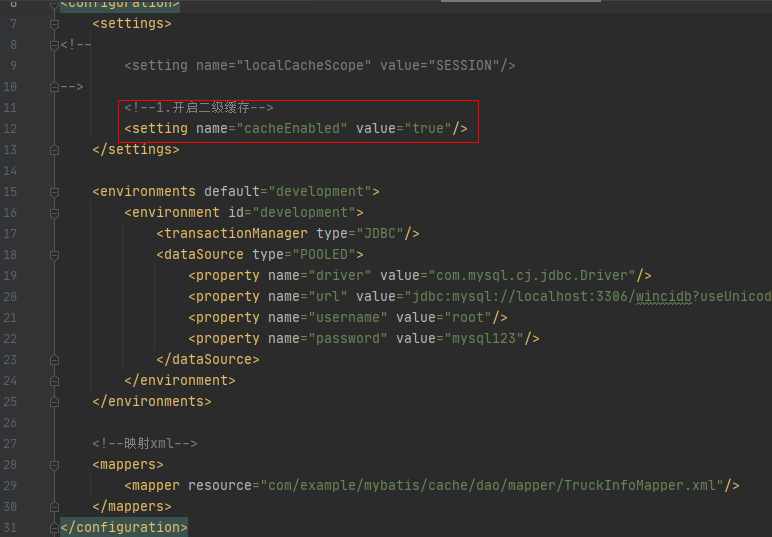
开启方式:
- 步骤一:配置setting,即:<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
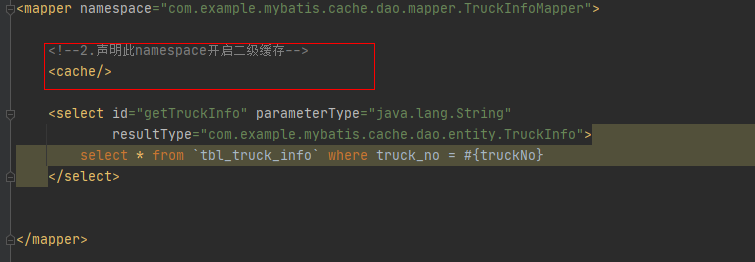
- 步骤二:指定namespace配置开启,即:<cache/>
传递实体参数
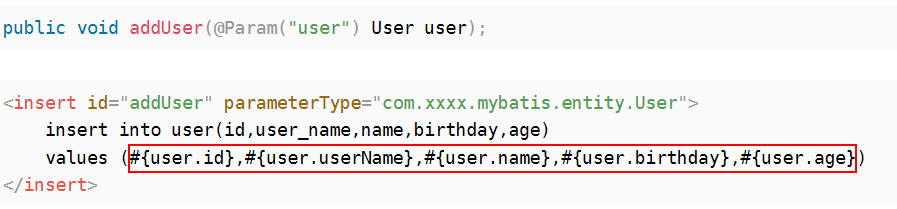
不加@Param注解,取值的时候直接写属性

加了@Param注解,取值必须使用对象.属性的方式
动态SQL
trim标签
insert into t_car
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="vin != null">vin,</if>
<if test="deviceId != null">device_id,</if>
<if test="fenceId != null">fence_id,</if>
</trim>
<trim prefix="values (" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="vin != null">#{vin},</if>
<if test="deviceId != null">#{deviceId},</if>
<if test="fenceId != null">#{fenceId},</if>
</trim>
</insert>
foreach标签
<foreach item="id" collection="array" open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{id}
</foreach>属性介绍
- item:集合中元素迭代时的别名(必选)
- collection:要做foreach的对象类型(必选)
- index:用于表示在迭代过程中,每次迭代到的位置(可选)
- open:开始符号,一般是(和close=")"合用。常用在in(),values()时(可选)
- separator:元素之间的分隔符,在in()的时候,separator=","会自动在元素中间用“,“隔开,如in(1,2,)(可选)
- close:关闭符号,一般是)和open="("合用。常用在in(),values()时(可选)
where标签
注:and关键字必须存在,且where标签只能去除第一个条件中出现的前置and关键字
<where>
<if test="simNo != null and simNo != ''"> and sim_no = #{simNo}</if>
<if test="deptId != null "> and dept_id = #{deptId}</if>
<if test="status != null "> and status = #{status}</if>
</where>
异常处理
MyBatis框架自定义了一个异常基类,叫做PersistenceException, 而PersistenceException是RuntimeException的子类
故Mybatis没有的异常都是非检查异常,会自动向上抛出,所以直接使用全局异常处理器捕获即可
注释写法
使用 <!-- 注释 -->,千万别用 --(pgsql) 或者 #(mysql) 之类的
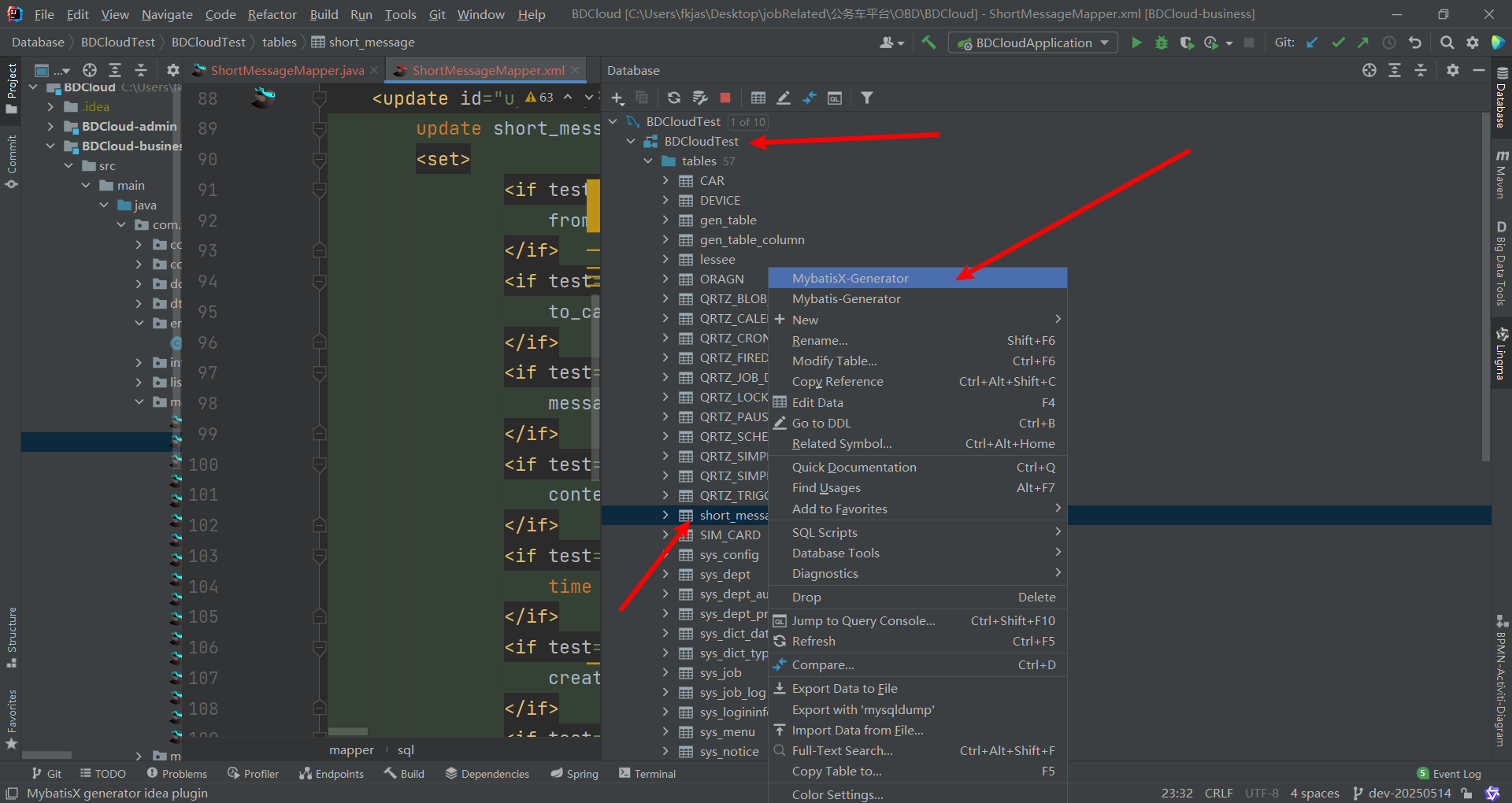
MybatisX 插件
拦截器
注:@Signature注解中的参数都是使用Mybatis中自定义好的值,与我们自定义的目标方法无关
package com.xz.bd.business.interceptor;
import com.xz.bd.business.entity.BaseEntity;
import com.xz.bd.common.utils.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.ibatis.executor.Executor;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Interceptor;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Intercepts;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Invocation;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Signature;
import java.util.Date;
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "update", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class})
})
public class MybatisInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Object[] args = invocation.getArgs();
MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) args[0];
Object parameter = args[1];
// 只处理实体参数
if (parameter instanceof BaseEntity) {
BaseEntity entity = (BaseEntity) parameter;
String operation = ms.getSqlCommandType().name();
Date now = new Date();
if ("INSERT".equals(operation)) {
entity.setCreateTime(now);
entity.setUpdateTime(now);
} else if ("UPDATE".equals(operation)) {
entity.setUpdateTime(now);
}
}
// 执行原方法
Object result = invocation.proceed();
return result;
}
}参考链接 :Mybatis拦截器(Interceptor)的理解与实践
踩过的坑
Mybatis拦截器注册失败
问题描述
# 使用配置类的是否注册拦截器失败
@Configuration
public class MybatisConfig {
@Bean
public ConfigurationCustomizer mybatisConfigurationCustomizer() {
return configuration -> {
// 创建并添加拦截器实例到配置中
configuration.addInterceptor(new MybatisInterceptor());
};
}
}
问题解决
项目中存在mybatis-config.xml文件,导致mybatis配置类失效,故强烈推荐只用一种配置方式
参考文章
【1】控制台打印SQL语句



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号