字符串
字符串太菜了,补一补。
哈希
P8819 [CSP-S 2022] 星战
首先如果保证了每个点出度都为 \(1\),那每个点一定可以走到一个环(原因显然)。
暴力维护时 \(O(nq)\) 的。考虑出度不好维护,我们维护入度。每个点随机一个权值 \(w_u\),每个点的入度哈希函数 \(s_u\) 为其入边的 \(w_u\) 之和 以及 所有点的 \(s_u\) 之和。四个操作如下:
-
废除 \(u \to v\):\(s_v \leftarrow s_v - w_u\);
-
废除点 \(u\):\(s_u \leftarrow 0\);
-
加入 \(u \to v\):\(s_v \leftarrow s_v + w_u\);
-
加入点 \(u\):\(s_u \leftarrow t_u\)(\(t_u\) 是一开始的 \(s_u\));
然后你会发现合法当且仅当 \(S = \sum_{i = 1}^n t_u\)。正确性是比较显然的。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e5 + 5;
int n, m, q; vector<int> G[N]; ll S, p, w[N], s[N], a[N]; mt19937 R(time(0));
signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m; int op, u, v;
_for (i, 1, n) p += w[i] = R();
_for (i, 1, m) cin >> u >> v, a[v] += w[u], s[v] += w[u], S += w[u]; cin >> q;
while (q -- ) {
cin >> op >> u;
if (op == 1) cin >> v, s[v] -= w[u], S -= w[u];
else if (op == 2) S -= s[u], s[u] = 0;
else if (op == 3) cin >> v, s[v] += w[u], S += w[u];
else S += a[u] - s[u], s[u] = a[u]; cout << (S == p ? "YES" : "NO") << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
P4503 [CTSC2014] 企鹅 QQ
由于每个字符串的长度只有 \(200\),枚举每一位,然后用哈希枚举字符串判断即可。复杂度 \(O(nL)\)。
注意一下枚举顺序,如果先枚举串再枚举位的话会荣获 TLE / MLE(也有可能是我实现太劣了)。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 3e4 + 5, M = 205, B = 917120411;
int n, L, S; char s[N][M]; ll ans; ull H[N], pw[M]; unordered_map<ull, int> cnt[65], sum;
inline int id(char c) { return 'a' <= c && c <= 'z' ? c - 'a' + 1 : ('A' <= c && c <= 'Z' ? c - 'A' + 27 : ('0' <= c && c <= '9' ? c - '0' + 53 : (c == '_' ? 63 : 64))); }
signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> L >> S; pw[0] = 1;
_for (i, 1, M - 1) pw[i] = pw[i - 1] * B;
_for (i, 1, n) {
cin >> (s[i] + 1);
_for (j, 1, L) H[i] += pw[j] * id(s[i][j]);
} _for (j, 1, L) {
_for (i, 1, n) ans += sum[H[i] - pw[j] * id(s[i][j])] - cnt[id(s[i][j])][H[i] - pw[j] * id(s[i][j])], cnt[id(s[i][j])][H[i] - pw[j] * id(s[i][j])] ++ , sum[H[i] - pw[j] * id(s[i][j])] ++ ; sum.clear();
_for (i, 1, 64) cnt[i].clear();
} cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
} sder
AT_abc312_h [ABC312Ex] snukesnuke
对于每个串记录他上一次枚举到的 \(k\) 和哈希值,直接从上一次的地方开始枚举即可。
不会证明复杂度,但是最慢点不到 \(100\) 毫秒。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define ull unsigned long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 4e5 + 5, B = 917120411;
int T, n; unordered_map<ull, int> lst, vis; unordered_map<ull, ull> lstH; char s[N]; ull H, cur, pw[N];
signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> T, pw[0] = 1;
_for (i, 1, N - 1) pw[i] = pw[i - 1] * B;
_for (_, 1, T) {
cin >> (s + 1), n = strlen(s + 1), H = 0;
_for (i, 1, n) H = H * B + (s[i] - 'a' + 1); cur = lstH[H] * pw[n] + H;
while (vis[cur]) lst[H] ++ , cur = cur * pw[n] + H; vis[cur] = 1, lst[H] ++ , lstH[H] = cur; cout << lst[H] << " ";
}
return 0;
}=
回文自动机(PAM)
求以每个位置结尾的回文串个数。
考虑将字符依次加入。以 \(i\) 结尾的回文串有若干个,把长度较小的对长度最长的对称一下,发现这些回文串都会在之前出现过。所以一个串的不同回文串只有 \(O(n)\) 个。
考虑建 Trie。不同于之前的 Trie,一个节点表示的字符串是他到根再到他路径上所组成的串。由于回文串分为奇数和偶数,建两个源点分别表示奇数的根,偶数的根。对于每个 Trie 上的节点,记录 \(len_i\) 表示 \(i\) 节点代表的回文串的长度。
考虑类似 ACAM 求出 fail 数组,指向每个串的最长后缀回文串。求 fail 和父亲时,只需不断跳 \(i - 1\) 的 fail 直到回文串前面的字符和 \(s_i\) 相等,这样可以再之前的回文串两段加一个相同字符组成一个新的回文串。
上面证明过复杂度 \(O(n)\)。
警告:strlen() 复杂度是 \(o(n)\),不要在循环里面用 strlen()!!!
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e6 + 5;
int n; char s[N];
struct Palindrom_Automation {
int ncnt, fail[N], len[N], tot[N], tr[N][26];
inline int gfail(int x, int i) { while (s[i - len[x] - 1] ^ s[i]) x = fail[x]; return x; }
inline void init() { fail[0] = ncnt = 1, len[1] = - 1; }
inline void insert() {
int pos, cur = 0, c;
_for (i, 1, n) {
s[i] = (s[i] - 97 + tot[cur]) % 26 + 97, pos = gfail(cur, i), c = s[i] - 'a';
if ( ! tr[pos][c]) fail[ ++ ncnt] = tr[gfail(fail[pos], i)][c], tr[pos][c] = ncnt, len[ncnt] = len[pos] + 2, tot[ncnt] = tot[fail[ncnt]] + 1; cur = tr[pos][c], cout << tot[cur] << " ";
} cout << "\n";
}
} PAM;
signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> (s + 1), n = strlen(s + 1), PAM.init(), PAM.insert();
return 0;
}
P5496 【模板】回文自动机(PAM)
板子题。
P3649 [APIO2014] 回文串
简单题。考虑先建出 PAM,然后在 fail 树上倒着(从叶子到根)求出每个串的出现次数。复杂度 \(O(n)\)。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define _all(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i >= (b); i -- )
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 3e5 + 5;
int n; char s[N];
inline void chkmax(ll & x, ll y) { x = x > y ? x : y; }
struct Palindrom_Automation {
int ncnt, fail[N], sz[N], len[N], tr[N][26]; ll ans;
inline void init() { ncnt = fail[0] = 1, len[1] = - 1; }
inline int gfail(int x, int i) { while (s[i - len[x] - 1] ^ s[i]) x = fail[x]; return x; }
inline void build() {
int pos, cur = 0, c; init();
_for (i, 1, n) {
pos = gfail(cur, i), c = s[i] - 'a';
if ( ! tr[pos][c]) fail[ ++ ncnt] = tr[gfail(fail[pos], i)][c], tr[pos][c] = ncnt, len[ncnt] = len[pos] + 2; cur = tr[pos][c], sz[cur] ++ ;
}
} inline ll gans() { _all (i, ncnt, 1) sz[fail[i]] += sz[i], chkmax(ans, 1ll * len[i] * sz[i]); return ans; }
} PAM;
signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> (s + 1), n = strlen(s + 1), PAM.build(), cout << PAM.gans() << "\n";
return 0;
}
P5555 秩序魔咒
建两个 PAM,在两棵 Trie 树上 dfs,如果有相同的儿子节点就往下走,并更新答案。
注意奇数点和偶数点都要 dfs。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
using namespace std;
const int N = 4e5 + 5;
int n[2], ans1, ans2; char s[2][N];
struct Palindrom_Automation {
int o, ncnt, fail[N], len[N], tot[N], tr[N][26];
inline void init(int t) { o = t, fail[0] = ncnt = 1, len[1] = - 1; }
inline int gfail(int x, int i) { while (s[o][i - len[x] - 1] ^ s[o][i]) x = fail[x]; return x; }
inline void build(int t) {
int pos, cur = 0, c; init(t);
_for (i, 1, n[o]) {
pos = gfail(cur, i), c = s[o][i] - 'a';
if ( ! tr[pos][c]) fail[ ++ ncnt] = tr[gfail(fail[pos], i)][c], tr[pos][c] = ncnt, len[ncnt] = len[pos] + 2, tot[ncnt] = tot[fail[ncnt]] + 1; cur = tr[pos][c];
}
}
} PAM1, PAM2;
void dfs(int u, int v) {
if (PAM1.len[u] > ans1) ans1 = PAM1.len[u], ans2 = 1;
else if (PAM1.len[u] == ans1) ans2 ++ ;
_for (i, 0, 25) if (PAM1.tr[u][i] && PAM2.tr[v][i]) dfs(PAM1.tr[u][i], PAM2.tr[v][i]);
}
signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n[0] >> n[1] >> (s[0] + 1) >> (s[1] + 1), PAM1.build(0), PAM2.build(1), dfs(0, 0), dfs(1, 1), cout << ans1 << " " << ans2 << "\n";
return 0;
}
P5685 [JSOI2013] 快乐的 JYY
和 P5555 非常像。建两个 PAM,求出每个回文串的出现次数,然后 dfs 两棵树计算答案即可(每个串的贡献是两个串的出现次数乘积)。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define _all(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i >= (b); i -- )
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 4e5 + 5;
int n[2]; char s[2][N]; ll ans;
string ztysb;
struct Palindrom_Automation {
int o, ncnt, fail[N], len[N], sz[N], tr[N][26];
inline int gfail(int x, int i) { while (s[o][i - len[x] - 1] ^ s[o][i]) x = fail[x]; return x; }
inline void build(int t) {
int pos, cur = 0, c; o = t, fail[0] = ncnt = 1, len[1] = - 1;
_for (i, 1, n[o]) {
pos = gfail(cur, i), c = s[o][i] - 'A';
if ( ! tr[pos][c]) fail[ ++ ncnt] = tr[gfail(fail[pos], i)][c], tr[pos][c] = ncnt, len[ncnt] = len[pos] + 2; sz[cur = tr[pos][c]] ++ ;
} _all (i, ncnt, 1) sz[fail[i]] += sz[i];
}
} PAM[2];
void dfs(int u, int v) {
if (u >= 2 && v >= 2) ans += 1ll * PAM[0].sz[u] * PAM[1].sz[v];
_for (i, 0, 25) if (PAM[0].tr[u][i] && PAM[1].tr[v][i]) dfs(PAM[0].tr[u][i], PAM[1].tr[v][i]);
} signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> (s[0] + 1) >> (s[1] + 1), n[0] = strlen(s[0] + 1), n[1] = strlen(s[1] + 1), PAM[0].build(0), PAM[1].build(1), dfs(0, 0), dfs(1, 1), cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
}
CF17E Palisection
糖糖题。相交的回文串对数不好做,考虑反过来求不交的回文串数。
用 PAM 似乎不太好做,考虑 manacher,我们可以快速求出以 \(i\) 开头 / 结尾的回文串个数和。
然后算贡献是简单的。复杂度 \(O(n)\),区间加可以通过差分实现。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define _all(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i >= (b); i -- )
#define ll long long
#define ld long double
#define PII pair<int, int>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define mp make_pair
#define pb push_back
using namespace std;
const int N = 4e6 + 5, P = 51123987;
int n, m, sum, ans, pal[N], f[N], g[N]; char s[N], t[N];
inline int mul(int x, int y) { return 1ll * x * y % P; }
inline void Add(int & x, int y) { x = x + y >= P ? x + y - P : x + y; }
signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> (t + 1); int l = 1, r = - 1, k;
_for (i, 1, n) s[ ++ m] = '#', s[ ++ m] = t[i]; s[ ++ m] = '#';
_for (i, 1, m) {
k = i > r ? 1 : min(pal[l + r - i], r - i + 1);
while (1 <= i - k && i + k <= m && s[i - k] == s[i + k]) k ++ ; pal[i] = k -- ;
if (i + k > r) l = i - k, r = i + k;
} _for (i, 1, m) if (i - pal[i] + 2 <= i + pal[i] - 2) f[(i - pal[i] + 2) / 2 - 1] -- , f[i / 2] ++ , g[i / 2 - (s[i] != '#') + 1] ++ , g[(i + pal[i] - 2) / 2 + 1] -- , Add(sum, pal[i] / 2);
_for (i, 1, n) Add(g[i], g[i - 1]);
_all (i, n, 1) Add(f[i], f[i + 1]);
_all (i, n, 1) Add(f[i], f[i + 1]);
_for (i, 1, n - 1) Add(ans, mul(g[i], f[i + 1])); cout << ((1ll * sum * (sum - 1) / 2) % P - ans + P) % P << "\n";
return 0;
}
CF932G Palindrome Partition
有点牛的 *2900。
考虑将序列转化成:\(s_1s_ns_2s_{n - 1} \cdots s_{\frac{n}{2}}s_{\frac{n}{2} + 1}\)。
这样你会发现原问题的要求转化为了:将序列划分成若干个长度为偶数的回文串,求方案数(证明是简单的)。
考虑 DP:设 \(f_i\) 表示已经划分了前 \(i\) 个字符的方案数。转移 \(f_i \leftarrow \sum_{s_{[j + 1, i]} \text{ is palindrome}} f_j\)。
暴力在 PAM 的 fail 树上跳,复杂度最高可达 \(O(n^2)\),考虑优化。
有结论:PAM 的 fail 树上每个节点到根的路径上的 \(len\) 之差序列一定是一些等差数列,且个数不超过 \(\log n\)。
证明和 border 有关,不难推出。这里略了。
于是可以考虑将一个等差数列的贡献放到一起计算。设 \(g_u\) 表示 fail 树上节点 \(u\) 到他所在等差数列的顶端(记为 \(top_u\))的 \(f\) 值之和。
然后你考虑从 \(g_{fail_u}\) 推到 \(g_u\)(当 \(u\) 和 \(fail_u\) 处于同一个等差数列之中时)。你会发现,关于最长回文串对称后,\(g_u\) 只比 \(g_{fail_u}\) 多出了起始位置为 \(i - len_{top_u} - (len_u - len_{fail_u})\) 的贡献。
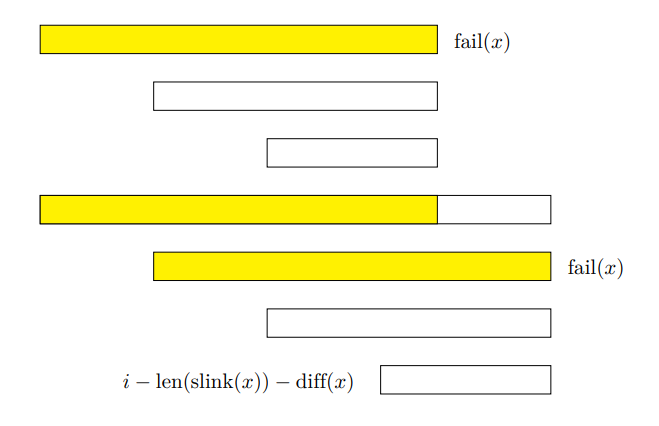
所以我们可以在建 SAM 的时候 \(O(1)\) 维护每个节点的 \(g\) 值,然后将连续一段等差数列集体贡献给当前加入的位置 \(i\)。这个过程在每个 \(i\) 只会做 \(\log n\) 次,因为只会向上跳 \(\log n\) 个等差数列。
总复杂度 \(O(n \log n)\)。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 5, P = 1e9 + 7;
int n, f[N]; char s[N], t[N];
inline void Add(int & x, int y) { x = x + y >= P ? x + y - P : x + y; }
struct Palindrome_Automation {
int ncnt, f[N], g[N], fail[N], len[N], diff[N], top[N], tr[N][26];
inline int gfail(int x, int i) { while (s[i - len[x] - 1] ^ s[i]) x = fail[x]; return x; }
inline void build() {
int pos, cur = 0, c, now; fail[0] = ncnt = f[0] = top[0] = 1, len[1] = - 1;
_for (i, 1, n) {
pos = gfail(cur, i), c = s[i] - 'a';
if ( ! tr[pos][c]) fail[ ++ ncnt] = tr[gfail(fail[pos], i)][c], tr[pos][c] = ncnt, len[ncnt] = len[pos] + 2, diff[ncnt] = len[ncnt] - len[fail[ncnt]], top[ncnt] = diff[ncnt] == diff[fail[ncnt]] ? top[fail[ncnt]] : fail[ncnt]; cur = now = tr[pos][c];
while (now >= 2) {
g[now] = f[i - len[top[now]] - diff[now]];
if (top[now] ^ fail[now]) Add(g[now], g[fail[now]]);
if ( ! (i & 1)) Add(f[i], g[now]); now = top[now];
}
}
}
} PAM;
signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> (t + 1), n = strlen(t + 1);
_for (i, 1, n / 2) s[i * 2 - 1] = t[i];
_for (i, n / 2 + 1, n) s[(i - n / 2) * 2] = t[n + n / 2 + 1 - i]; PAM.build(), cout << PAM.f[n] << "\n";
return 0;
}
CF906E Reverses
略难于 CF932G,主播不想输方案。
类似上题把序列变为 \(a_1b_1a_2b_2 \cdots a_nb_n\),转化为了最小偶回文划分(长度为 \(2\) 不需计数)。
输出方案的话就记录一下转移点即可。也是 \(O(n \log n)\)。
后缀数组(SA)
P3809 【模板】后缀排序
后缀排序板子。
考虑暴力做是 \(O(n ^ 2 \log n)\) 的。如何优化呢?
考虑第一次把 \(s_{[i, i]}\) 排序,第二次把 \(s_{[i, i + 1]}\) 排序,第三次把 \(s_{[i, i + 3]}\) 排序。换句话说,我们以倍增长度的方式将每个后缀排序。比如你已经排序了长度 \(2^k\),你可以按照 \(s_{[i, i + 2^k - 1]}\) 为第一关键字,\(s_{[i + 2^k, i + 2^{k + 1} - 1]}\) 为第二关键字排序,这样就能排序长度 \(2^{k + 1}\) 了。
于是复杂度就变成了 \(O(n \log^2 n)\),瓶颈在于每一次都要 sort。把 sort 换成计数排序即可,先按照第二关键字记排,再按第一关键字记排,复杂度降到了 \(O(n \log n)\)。
但你会发现这个东西常数非常大,以下有一些常数优化:
-
倍增的过程中,记录本质不同的串个数(是递增的),不用每次枚举值域都枚举到 \(n\)。
-
如果你已经把所有后缀排好了(也就是说本质不同串个数已经达到了 \(n\)),你可以直接结束过程(实测 3s \(\to\) 0.7s)。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define _all(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i >= (b); i -- )
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e6 + 5;
int n, lim = 'z', id[N], sa[N], rnk[N], old_rnk[N], cnt[N]; char s[N];
signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> (s + 1), n = strlen(s + 1); int tot;
_for (i, 1, n) sa[i] = i, rnk[i] = s[i];
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
iota(id + 1, id + n + 1, 1), fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0), memcpy(old_rnk, rnk, sizeof(rnk));
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[i + k]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) id[cnt[rnk[i + k]] -- ] = i; fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0);
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[id[i]]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) sa[cnt[rnk[id[i]]] -- ] = id[i]; tot = 0;
_for (i, 1, n) {
if (old_rnk[sa[i]] == old_rnk[sa[i - 1]] && old_rnk[sa[i] + k] == old_rnk[sa[i - 1] + k]) rnk[sa[i]] = tot;
else rnk[sa[i]] = ++ tot;
} if (tot == n) break; lim = tot;
} _for (i, 1, n) cout << sa[i] << " "; cout << "\n";
return 0;
}
P4051 [JSOI2007] 字符加密
对于这种类似串循环的问题,考虑把串复制一遍。就变成后缀排序板子了。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define _all(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i >= (b); i -- )
using namespace std;
const int N = 4e5 + 5;
int n, tot, num, lim = 300, sa[N], rnk[N], id[N], cnt[N], old_rnk[N]; char s[N];
signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> (s + 1), n = strlen(s + 1);
_for (i, 1, n) s[i + n] = s[i]; n <<= 1;
_for (i, 1, n) sa[i] = i, rnk[i] = s[i];
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
iota(id + 1, id + n + 1, 1), fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0), memcpy(old_rnk, rnk, sizeof(old_rnk)), tot = 0;
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[i + k]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) id[cnt[rnk[i + k]] -- ] = i; fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0);
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[id[i]]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) sa[cnt[rnk[id[i]]] -- ] = id[i];
_for (i, 1, n) rnk[sa[i]] = old_rnk[sa[i]] == old_rnk[sa[i - 1]] && old_rnk[sa[i] + k] == old_rnk[sa[i - 1] + k] ? tot : ( ++ tot);
if (tot == n) break; lim = tot;
} _for (i, 1, n) if (sa[i] <= n / 2 && num < n / 2) num ++ , cout << s[sa[i] + (n / 2) - 1]; cout << "\n";
return 0;
}
P2870 [USACO07DEC] Best Cow Line G
设当前剩下的区间为 \([l, r]\),考虑策略:
-
如果 \(s_l < s_r\),选择 \(l\);
-
如果 \(s_l > s_r\),选择 \(r\);
-
如果 \(s_l = s_r\),那么我们比较 \(s_ls_{l + 1}s_{l + 2} \cdots s_n\) 和 \(s_rs_{r - 1}s_{r - 2}\cdots s_1\),选择较小的即可。
如何快速比较一段前缀和后缀的大小呢?
考虑把原串翻转过来并拼在原串后面,问题就变成比较两个后缀了。后缀排序即可。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define _all(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i >= (b); i -- )
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e6 + 5;
int n, tot, lim = 'Z', l, r, cur, cnt[N], sa[N], rnk[N], id[N], old[N]; char s[N], ans[N];
signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n, l = 1, r = n;
_for (i, 1, n) cin >> s[i], s[n * 2 + 1 - i] = s[i]; n <<= 1;
_for (i, 1, n) rnk[i] = s[i], sa[i] = i;
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
iota(id + 1, id + n + 1, 1), fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0), memcpy(old, rnk, sizeof(rnk)), tot = 0;
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[i + k]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) id[cnt[rnk[i + k]] -- ] = i; fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0);
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[id[i]]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) sa[cnt[rnk[id[i]]] -- ] = id[i];
_for (i, 1, n) rnk[sa[i]] = old[sa[i]] == old[sa[i - 1]] && old[sa[i] + k] == old[sa[i - 1] + k] ? tot : ( ++ tot);
if (tot == n) break; lim = tot;
} while (l <= r) {
if (s[l] < s[r]) ans[ ++ cur] = s[l ++ ];
else if (s[l] > s[r]) ans[ ++ cur] = s[r -- ];
else ans[ ++ cur] = rnk[l] < rnk[n + 1 - r] ? s[l ++ ] : s[r -- ];
} _for (i, 1, n / 80) _for (j, 1, 80) cout << ans[(i - 1) * 80 + j] << (j == 80 ? "\n" : "");
_for (i, n / 80 * 80 + 1, n) cout << ans[i]; cout << "\n";
return 0;
}
P2408 不同子串个数
利用 SA 求 \(height\) 数组:\(height_i = \text{LCP}(sa_i, sa_{i - 1})\)。
将子串想象成后缀的前缀。考虑所有子串 \(\frac{n(n + 1)}{2}\) 减去重复的子串。
后缀排序,相邻两个串的重复子串个数可以通过 \(height\) 求出。答案即为 \(\frac{n(n + 1)}{2} - \sum_{i = 2}^n height_i\)。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define _all(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i >= (b); i -- )
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 4e5 + 5;
int n, tot, cur, lim = 'z', sa[N], rnk[N], cnt[N], id[N], height[N], old[N]; char s[N]; ll ans;
inline void chkmin(int & x, int y) { x = x < y ? x : y; }
inline void chkmax(int & x, int y) { x = x > y ? x : y; }
signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> (s + 1), ans = 1ll * n * (n + 1) / 2;
_for (i, 1, n) sa[i] = i, rnk[i] = s[i];
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
iota(id + 1, id + n + 1, 1), fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0), memcpy(old, rnk, sizeof(rnk)), tot = 0;
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[i + k]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) id[cnt[rnk[i + k]] -- ] = i; fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0);
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[id[i]]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) sa[cnt[rnk[id[i]]] -- ] = id[i];
_for (i, 1, n) rnk[sa[i]] = old[sa[i]] == old[sa[i - 1]] && old[sa[i] + k] == old[sa[i - 1] + k] ? tot : ( ++ tot);
if (tot == n) break; lim = tot;
} _for (i, 1, n) if (rnk[i]) {
if (cur) cur -- ;
while (s[i + cur] == s[sa[rnk[i] - 1] + cur]) cur ++ ; height[rnk[i]] = cur;
} _for (i, 2, n) ans -= height[i]; cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
}
P1117 [NOI2016] 优秀的拆分
好题啊。
你考虑求出 \(f_i, g_i\) 分别表示以 \(i\) 结尾 / 开头的形如 \(\text{AA}\) 的串的个数。答案即为 \(\sum_{i = 1}^n f_ig_{i + 1}\)。
然后你考虑如何求出 \(f\) 和 \(g\)。考虑枚举 \(len\) 表示 \(\text{AA}\) 中 \(\text{A}\) 的长度。将序列中提取出若干个关键点:\(len, 2len, \cdots\)。而显然一个符合条件的 \(\text{AA}\) 必须覆盖恰好两个关键点。
枚举每个关键点的复杂度只有 \(O(n \ln n)\),所以考虑对相邻两个点 \(i, j\) 计算贡献。
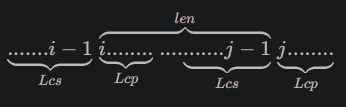
我们求出 \(\text{Lcp} = \text{lcp}(suf_i, suf_j)\) 和 \(\text{Lcs} = \text{lcs}(pre_{i - 1}, pre_{j - 1})\)。那么 \([i, i + Lcp - 1]\) 和 \([j - Lcs, j]\) 的公共部分就可以作为两个 \(\text{A}\) 的分界点(手摸可知)。
这里就可以通过二分 + 哈希做到 \(O(T n \ln n \log n)\) 的复杂度了。
继续优化。考虑将原串和反串求 SA,可以 \(O(1)\) 求出 \(\text{Lcp}\) 和 \(\text{Lcs}\)。总复杂度 \(O(T n \log n)\)。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define _all(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i >= (b); i -- )
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 4e5 + 5;
int n, f[N], g[N]; char s[N]; ll ans;
struct Suffix_Array {
int tot, lim, cur, cnt[N], sa[N], id[N], old[N], height[N], Log[N], ST[20][N], rnk[N];
inline void clear() {
lim = 'z', cur = 0;
_for (i, 0, n << 1) {
cnt[i] = sa[i] = id[i] = old[i] = height[i] = Log[i] = rnk[i] = 0;
_for (j, 0, 19) ST[j][i] = 0;
}
} inline void build_ST(int * a) {
Log[0] = - 1;
_for (i, 1, n) Log[i] = Log[i >> 1] + 1, ST[0][i] = a[i];
_for (k, 1, Log[n]) _for (i, 1, n - (1 << k) + 1) ST[k][i] = min(ST[k - 1][i], ST[k - 1][i + (1 << (k - 1))]);
} inline int query(int i, int j) { int l = min(rnk[i], rnk[j]) + 1, r = max(rnk[i], rnk[j]), k = Log[r - l + 1]; return l <= r ? min(ST[k][l], ST[k][r - (1 << k) + 1]) : 0; }
inline void build() {
_for (i, 1, n) sa[i] = i, rnk[i] = s[i]; lim = 'z', cur = 0;
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
iota(id + 1, id + n + 1, 1), fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0), memcpy(old, rnk, sizeof(rnk)), tot = 0;
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[i + k]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) id[cnt[rnk[i + k]] -- ] = i; fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0);
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[id[i]]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) sa[cnt[rnk[id[i]]] -- ] = id[i];
_for (i, 1, n) rnk[sa[i]] = old[sa[i]] == old[sa[i - 1]] && old[sa[i] + k] == old[sa[i - 1] + k] ? tot : ( ++ tot);
if (tot == n) break; lim = tot;
} _for (i, 1, n) if (rnk[i]) {
if (cur) cur -- ;
while (s[i + cur] == s[sa[rnk[i] - 1] + cur]) cur ++ ; height[rnk[i]] = cur;
} build_ST(height);
}
} SA[2];
inline void solve() {
cin >> (s + 1), n = strlen(s + 1), SA[0].clear(), SA[1].clear();
_for (i, 0, n << 1) f[i] = g[i] = 0; SA[0].build(), reverse(s + 1, s + n + 1), SA[1].build(), ans = 0; int lcs, lcp, x;
_for (len, 1, n / 2) for (int i = len, j = len * 2; j <= n; i += len, j += len) {
lcp = min(len, SA[0].query(i, j)), lcs = min(len - 1, SA[1].query(n - i + 2, n - j + 2)), x = lcp + lcs - len + 1; // x - number of possible position of the first A
if (lcp + lcs >= len) f[j + lcp - x] ++ , f[j + lcp] -- , g[i - lcs] ++ , g[i - lcs + x] -- ;
} _for (i, 1, n) f[i] += f[i - 1], g[i] += g[i - 1];
_for (i, 1, n - 1) ans += 1ll * f[i] * g[i + 1]; cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int T; cin >> T; while (T -- ) solve();
return 0;
}
P2178 [NOI2015] 品酒大会
独立切出来了,尽管调了很久。
题面写的很绕,“\(r\) 相似” 其实是 LCP 长度为 \(r\)。由于 “\(r\) 相似” 也是 “\(< r\) 相似” 的,考虑先求出 LCP \(= r\),再做后缀和 / 后缀 max。
然后就变成了:有多少对后缀串,使得 LCP 长度为 \(r\)。
显然的 SA,求出 height,然后再变成:有多少个区间的 \(\min\) 为 \(r\)。这个乱维护一下即可。
我用了二分(单调栈也是可以的),复杂度是 \(O(n \log n)\) 的。要注意边界。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define _all(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i >= (b); i -- )
#define ll long long
#define PII pair<int, int>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define mp make_pair
using namespace std;
const int N = 6e5 + 5, INF = 2e9 + 5;
int n, tot, lim = 'z', cur, A[N], a[N], cnt[N], sa[N], id[N], rnk[N], old[N], height[N], Log[N], lst[N]; char s[N]; ll ans1[N], ans2[N];
inline void chkmax(ll & x, ll y) { x = x > y ? x : y; }
struct Sparse_Table {
int ST[20][N];
inline void build(int * a) {
_for (i, 1, n) ST[0][i] = a[i];
_for (k, 1, Log[n]) _for (i, 1, n - (1 << k) + 1) ST[k][i] = min(ST[k - 1][i], ST[k - 1][i + (1 << (k - 1))]);
} inline int query(int l, int r) { int k = Log[r - l + 1]; return min(ST[k][l], ST[k][r - (1 << k) + 1]); }
} ST;
inline PII operator + (PII u, PII v) {
PII res; res.fi = max(u.fi, v.fi);
if (u.fi > v.fi) res.se = max(u.se, v.fi);
else if (u.fi < v.fi) res.se = max(u.fi, v.se);
else res.se = u.fi; return res;
} struct Segment_Tree {
#define lc (p << 1)
#define rc (p << 1 | 1)
#define mid ((tr[p].l + tr[p].r) >> 1)
struct Tree { int l, r; PII val; } tr[N << 2];
inline int len(int p) { return tr[p].r - tr[p].l + 1; }
inline bool In(int p, int l, int r) { return l <= tr[p].l && tr[p].r <= r; }
inline void push_up(int p) { tr[p].val = tr[lc].val + tr[rc].val; }
void build(int p, int l, int r) {
tr[p].l = l, tr[p].r = r;
if (l == r) return tr[p].val = mp(A[l], - INF), void(); build(lc, l, mid), build(rc, mid + 1, r), push_up(p);
} PII query(int p, int l, int r) {
if (l > r) return mp( - INF, - INF);
if (In(p, l, r)) return tr[p].val;
if (r <= mid) return query(lc, l, r);
if (l > mid) return query(rc, l, r); return query(lc, l, r) + query(rc, l, r);
}
#undef lc
#undef rc
#undef mid
} SGT[2];
signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> (s + 1), Log[0] = - 1; int l, r, mid, posl, posr; PII x, y;
_for (i, 1, n) cin >> a[i], rnk[i] = s[i], sa[i] = i, Log[i] = Log[i >> 1] + 1, ans2[i] = - (ll)1e18 + 5;
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
iota(id + 1, id + n + 1, 1), fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0), memcpy(old, rnk, sizeof(rnk)), tot = 0;
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[i + k]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) id[cnt[rnk[i + k]] -- ] = i; fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0);
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[id[i]]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) sa[cnt[rnk[id[i]]] -- ] = id[i];
_for (i, 1, n) rnk[sa[i]] = old[sa[i]] == old[sa[i - 1]] && old[sa[i] + k] == old[sa[i - 1] + k] ? tot : ( ++ tot);
if (tot == n) break; lim = tot;
} _for (i, 1, n) if (rnk[i]) {
if (cur) cur -- ;
while (s[i + cur] == s[sa[rnk[i] - 1] + cur]) cur ++ ; height[rnk[i]] = cur;
} ST.build(height);
_for (i, 1, n) A[rnk[i]] = a[i]; SGT[0].build(1, 1, n);
_for (i, 1, n) A[i] = - A[i]; SGT[1].build(1, 1, n);
_for (i, 1, n) {
if (i >= 2) {
l = lst[height[i]] + 1, r = i, posl = i;
while (l <= r) {
mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (ST.query(mid, i) == height[i]) posl = mid, r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
} l = i, r = n, posr = i;
while (l <= r) {
mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (ST.query(i, mid) == height[i]) posr = mid, l = mid + 1;
else r = mid - 1;
} x = SGT[0].query(1, max(1, posl - 1), posr), y = SGT[1].query(1, max(1, posl - 1), posr), y = mp( - y.fi, - y.se), ans1[height[i]] += 1ll * (i - posl + 1) * (posr - i + 1), chkmax(ans2[height[i]], max(max(1ll * x.fi * x.se, 1ll * x.fi * y.fi), max(1ll * y.fi * y.se, 1ll * y.fi * x.fi)));
} lst[height[i]] = i;
} _all (i, n - 1, 0) ans1[i] += ans1[i + 1], chkmax(ans2[i], ans2[i + 1]);
_for (i, 0, n - 1) cout << ans1[i] << " " << (ans1[i] ? ans2[i] : 0) << "\n";
return 0;
}
P4248 [AHOI2013] 差异
和上一道题本质相同。
考虑把式子拆开,前面每个后缀的 \(len\) 会贡献 \(n - 1\) 次,后面的 LCP 用 height 计算贡献即可。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define _all(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i >= (b); i -- )
#define ll long long
#define ld long double
#define PII pair<int, int>
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
int n, tot, cur, lim = 'z', cnt[N], rnk[N], sa[N], id[N], old[N], height[N], lst[N], Log[N]; char s[N]; ll ans;
inline void chkmin(int & x, int y) { x = x < y ? x : y; }
inline void chkmax(int & x, int y) { x = x > y ? x : y; }
struct Sparse_Table {
int ST[20][N];
inline void build(int * a) {
_for (i, 1, n) ST[0][i] = a[i];
_for (k, 1, Log[n]) _for (i, 1, n - (1 << k) + 1) ST[k][i] = min(ST[k - 1][i], ST[k - 1][i + (1 << (k - 1))]);
} inline int query(int l, int r) { int k = Log[r - l + 1]; return min(ST[k][l], ST[k][r - (1 << k) + 1]); }
} ST;
signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> (s + 1), n = strlen(s + 1); int l, r, mid, posl, posr; Log[0] = - 1;
_for (i, 1, n) sa[i] = i, rnk[i] = s[i], ans += 1ll * (n - i + 1) * (n - 1), Log[i] = Log[i >> 1] + 1;
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
iota(id + 1, id + n + 1, 1), fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0), memcpy(old, rnk, sizeof(old)), tot = 0;
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[i + k]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) id[cnt[rnk[i + k]] -- ] = i; fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0);
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[id[i]]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) sa[cnt[rnk[id[i]]] -- ] = id[i];
_for (i, 1, n) rnk[sa[i]] = old[sa[i]] == old[sa[i - 1]] && old[sa[i] + k] == old[sa[i - 1] + k] ? tot : ( ++ tot);
if (tot == n) break; lim = tot;
} _for (i, 1, n) if (rnk[i]) {
if (cur) cur -- ;
while (s[i + cur] == s[sa[rnk[i] - 1] + cur]) cur ++ ; height[rnk[i]] = cur;
} ST.build(height);
_for (i, 1, n) {
if (i >= 2) {
l = lst[height[i]] + 1, r = i, posl = i;
while (l <= r) {
mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (ST.query(mid, i) == height[i]) posl = mid, r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
} l = i, r = n, posr = i;
while (l <= r) {
mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (ST.query(i, mid) == height[i]) posr = mid, l = mid + 1;
else r = mid - 1;
} ans -= 2ll * (i - posl + 1) * (posr - i + 1) * height[i];
} lst[height[i]] = i;
} cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
}
P3181 [HAOI2016] 找相同字符
如果是一个串,和上面两题一模一样了。
但是有两个串,于是考虑把他俩拼起来(中间接一个非小写字母字符)算一遍答案,然后减去两个串分别的答案即可。
这样显然是对的。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define _all(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i >= (b); i -- )
#define ll long long
#define ld long double
#define PII pair<int, int>
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
int n1, n2, tot, cur, lim, sa[N], rnk[N], id[N], cnt[N], old[N], height[N], lst[N], Log[N]; char s1[N], s2[N], s3[N];
inline void chkmin(int & x, int y) { x = x < y ? x : y; }
inline void chkmax(int & x, int y) { x = x > y ? x : y; }
struct Sparse_Table {
int ST[20][N];
inline void build(int * a, int n) {
_for (i, 1, n) ST[0][i] = a[i];
_for (k, 1, Log[n]) _for (i, 1, n - (1 << k) + 1) ST[k][i] = min(ST[k - 1][i], ST[k - 1][i + (1 << (k - 1))]);
} inline int query(int l, int r) { int k = Log[r - l + 1]; return min(ST[k][l], ST[k][r - (1 << k) + 1]); }
} ST;
inline ll gans(char * s, int n) {
_for (i, 0, N - 1) sa[i] = rnk[i] = id[i] = cnt[i] = old[i] = height[i] = lst[i] = 0; cur = tot = 0, lim = 'z';
_for (i, 1, n) sa[i] = i, rnk[i] = s[i]; ll res = 0; int l, r, mid, posl, posr;
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
iota(id + 1, id + n + 1, 1), fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0), memcpy(old, rnk, sizeof(old)), tot = 0;
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[i + k]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) id[cnt[rnk[i + k]] -- ] = i; fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0);
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[id[i]]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) sa[cnt[rnk[id[i]]] -- ] = id[i];
_for (i, 1, n) rnk[sa[i]] = old[sa[i]] == old[sa[i - 1]] && old[sa[i] + k] == old[sa[i - 1] + k] ? tot : ( ++ tot);
if (tot == n) break; lim = tot;
} _for (i, 1, n) if (rnk[i]) {
if (cur) cur -- ;
while (s[i + cur] == s[sa[rnk[i] - 1] + cur]) cur ++ ; height[rnk[i]] = cur;
} ST.build(height, n);
_for (i, 1, n) {
if (i >= 2) {
l = lst[height[i]] + 1, r = i, posl = i;
while (l <= r) {
mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (ST.query(mid, i) == height[i]) posl = mid, r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
} l = i, r = n, posr = i;
while (l <= r) {
mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (ST.query(i, mid) == height[i]) posr = mid, l = mid + 1;
else r = mid - 1;
} res += 1ll * (i - posl + 1) * (posr - i + 1) * height[i];
} lst[height[i]] = i;
} return res;
} signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> (s1 + 1) >> (s2 + 1), n1 = strlen(s1 + 1), n2 = strlen(s2 + 1), s3[n1 + 1] = '#', Log[0] = - 1;
_for (i, 1, N - 1) Log[i] = Log[i >> 1] + 1;
_for (i, 1, n1) s3[i] = s1[i];
_for (i, 1, n2) s3[n1 + 1 + i] = s2[i]; cout << gans(s3, n1 + n2 + 1) - gans(s1, n1) - gans(s2, n2) << "\n";
return 0;
}
P5546 [POI 2000] 公共串
UVA760 DNA Sequencing
SP1811 LCS - Longest Common Substring
SP1812 LCS2 - Longest Common Substring II
SP10570 LONGCS - Longest Common Substring
SP32577 ADAPHOTO - Ada and Terramorphing
全是给一车串,让你求最长公共子串(除此之外还有若干道类似题目,没有列举了)。
把所有串拼在一起,然后建 SA,取一个包含所有串的区间 chkmax 即可。复杂度是 \(O(n \log n)\),\(\log\) 来自 sort 和 ST 表。
这里放一下 UVA760 的代码,这题不仅要输出答案还要要求输出所有位置。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define _all(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i >= (b); i -- )
using namespace std;
const int N = 1205;
int n, n1, n2, anslen, anscnt, Case, tot, cur, lim = 'z', op[N], ans[N], cnt[N], sa[N], id[N], rnk[N], old[N], height[N], lst[N], pre[N], nxt[N], Log[N], vis[N]; char s1[N], s2[N], s[N];
struct Sparse_Table {
int ST[15][N];
inline void build(int * a) {
_for (i, 1, n) ST[0][i] = a[i];
_for (k, 1, Log[n]) _for (i, 1, n - (1 << k) + 1) ST[k][i] = min(ST[k - 1][i], ST[k - 1][i + (1 << (k - 1))]);
} inline int query(int l, int r) { int k = Log[r - l + 1]; return min(ST[k][l], ST[k][r - (1 << k) + 1]); }
} ST;
inline void solve() {
n1 = strlen(s1 + 1), n2 = strlen(s2 + 1), Case ++ , anslen = anscnt = 0, Log[0] = - 1; int flag = 0;
_for (i, 1, n1) s[i] = s1[i]; s[n1 + 1] = '#';
_for (i, 1, n2) s[n1 + 1 + i] = s2[i]; n = n1 + n2 + 1;
if (Case > 1) cout << "\n";
_for (i, 0, N - 1) cnt[i] = sa[i] = id[i] = rnk[i] = old[i] = height[i] = lst[i & 1] = pre[i] = nxt[i] = vis[i] = op[i] = 0;
_for (i, 1, n) sa[i] = i, rnk[i] = s[i], Log[i] = Log[i >> 1] + 1; tot = cur = 0, lim = 'z';
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
iota(id + 1, id + n + 1, 1), fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0), memcpy(old, rnk, sizeof(old)), tot = 0;
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[i + k]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) id[cnt[rnk[i + k]] -- ] = i; fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0);
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[id[i]]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) sa[cnt[rnk[id[i]]] -- ] = id[i];
_for (i, 1, n) rnk[sa[i]] = old[sa[i]] == old[sa[i - 1]] && old[sa[i] + k] == old[sa[i - 1] + k] ? tot : ( ++ tot);
if (tot == n) break; lim = tot;
} _for (i, 1, n) if (rnk[i]) {
if (cur) cur -- ;
while (s[i + cur] == s[sa[rnk[i] - 1] + cur]) cur ++ ; height[rnk[i]] = cur;
} ST.build(height);
_for (i, 1, n) if (sa[i] ^ (n1 + 1)) pre[i] = lst[sa[i] > n1], lst[sa[i] <= n1] = i; lst[0] = lst[1] = 0;
_all (i, n, 1) if (sa[i] ^ (n1 + 1)) nxt[i] = lst[sa[i] > n1], lst[sa[i] <= n1] = i;
_for (i, 1, n) if (sa[i] <= n1) {
if (pre[i]) {
if (ST.query(pre[i] + 1, i) > anslen) anslen = ST.query(pre[i] + 1, i), anscnt = 0;
if (ST.query(pre[i] + 1, i) == anslen) ans[ ++ anscnt] = sa[i], op[anscnt] = 1;
} if (nxt[i]) {
if (ST.query(i + 1, nxt[i]) > anslen) anslen = ST.query(i + 1, nxt[i]), anscnt = 0;
if (ST.query(i + 1, nxt[i]) == anslen) ans[ ++ anscnt] = sa[i], op[anscnt] = 2;
}
} sort(ans + 1, ans + anscnt + 1), anscnt = unique(ans + 1, ans + anscnt + 1) - ans - 1, sort(ans + 1, ans + anscnt + 1, [&] (int x, int y) { return rnk[x] < rnk[y]; });
if ( ! anslen) cout << "No common sequence.\n";
else {
_for (i, 2, anscnt) if (ST.query(rnk[ans[i - 1]] + 1, rnk[ans[i]]) >= anslen) vis[i] = 1;
_for (i, 1, anscnt) if ( ! vis[i]) {
assert(ans[i] + anslen - 1 <= n1);
_for (j, ans[i], ans[i] + anslen - 1) cout << s[j]; flag = 1; cout << "\n";
} if ( ! flag) cout << "No common sequence.\n";
} _for (i, 0, N - 1) s1[i] = s2[i] = s[i] = '\0';
} signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
while (cin >> (s1 + 1) >> (s2 + 1)) solve();
return 0;
}
P2463 [SDOI2008] Sandy 的卡片
子串相同的定义是全部加上一个数之后相等。就是差分之后相等。
UVA1223 Editor
SA 的 height 数组板子。\(\max_{i = 2}^n height_i\) 即为答案。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define _all(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i >= (b); i -- )
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e4 + 5;
int n, cur, tot, lim, ans, sa[N], rnk[N], id[N], cnt[N], old[N], height[N]; char s[N];
inline void chkmax(int & x, int y) { x = x > y ? x : y; }
inline void solve() {
cin >> (s + 1), n = strlen(s + 1), cur = tot = ans = 0, lim = 'z';
_for (i, 0, N - 1) sa[i] = rnk[i] = id[i] = cnt[i] = old[i] = height[i] = 0;
_for (i, 1, n) sa[i] = i, rnk[i] = s[i];
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
iota(id + 1, id + n + 1, 1), fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0), memcpy(old, rnk, sizeof(rnk)), tot = 0;
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[i + k]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) id[cnt[rnk[i + k]] -- ] = i; fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0);
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[id[i]]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) sa[cnt[rnk[id[i]]] -- ] = id[i];
_for (i, 1, n) rnk[sa[i]] = old[sa[i]] == old[sa[i - 1]] && old[sa[i] + k] == old[sa[i - 1] + k] ? tot : ( ++ tot);
if (tot == n) break; lim = tot;
} _for (i, 1, n) if (rnk[i]) {
if (cur) cur -- ;
while (s[i + cur] == s[sa[rnk[i] - 1] + cur]) cur ++ ; chkmax(ans, height[rnk[i]] = cur);
} cout << ans << "\n";
} signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int T; cin >> T; while (T -- ) solve();
return 0;
}
CF149E Martian Strings
正反求 SA,然后记录 \(st_i, ed_i\) 表示以 \(i\) 开头 / 结尾能匹配上的最长前缀 / 后缀。
然后随便判断即可。复杂度是 \(O(nm \log n)\),CF 上被卡常了。
Code (TLE on #22)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define _all(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i >= (b); i -- )
using namespace std;
const int N = 2.1e5 + 5, INF = 1e9 + 5;
int n1, n2, n, q, ans, cur, tot, lim, sa[N], rnk[N], id[N], cnt[N], old[N], height[N], st[N], ed[N]; char s1[N], s2[N], s[N];
inline void chkmin(int & x, int y) { x = x < y ? x : y; }
inline void chkmax(int & x, int y) { x = x > y ? x : y; }
inline void SA() {
_for (i, 0, n << 1) sa[i] = rnk[i] = id[i] = cnt[i] = old[i] = height[i] = 0;
_for (i, 1, n) sa[i] = i, rnk[i] = s[i]; cur = tot = 0, lim = 'Z';
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
iota(id + 1, id + n + 1, 1), fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0), tot = 0;
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[i + k]] ++ , old[i] = rnk[i];
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) id[cnt[rnk[i + k]] -- ] = i; fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0);
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[id[i]]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) sa[cnt[rnk[id[i]]] -- ] = id[i];
_for (i, 1, n) rnk[sa[i]] = old[sa[i]] == old[sa[i - 1]] && old[sa[i] + k] == old[sa[i - 1] + k] ? tot : ( ++ tot);
if (tot == n) break; lim = tot;
} _for (i, 1, n) if (rnk[i]) {
if (cur) cur -- ;
while (s[i + cur] == s[sa[rnk[i] - 1] + cur]) cur ++ ; height[rnk[i]] = cur;
}
} inline int solve() {
_for (i, 1, n1) s[i] = s1[i]; s[n1 + 1] = '#', scanf("%s", s2 + 1), n2 = strlen(s2 + 1); int t, flag = 0;
if (n2 <= 1 || n2 > n1) return 0;
_for (i, 1, n2) s[n1 + 1 + i] = s2[i]; n = n1 + n2 + 1, SA(), t = INF;
_all (i, rnk[n1 + 2] - 1, 1) { chkmin(t, height[i + 1]); if (sa[i] <= n1) st[sa[i]] = t; } t = INF;
_for (i, rnk[n1 + 2] + 1, n) { chkmin(t, height[i]); if (sa[i] <= n1) st[sa[i]] = t; } reverse(s + 1, s + n + 1), SA(), t = INF;
_all (i, rnk[1] - 1, 1) { chkmin(t, height[i + 1]); if (sa[i] >= n2 + 2) ed[n - sa[i] + 1] = t; } t = INF;
_for (i, rnk[1] + 1, n) { chkmin(t, height[i]); if (sa[i] >= n2 + 2) ed[n - sa[i] + 1] = t; } t = 0;
_all (i, n1 - n2 + 1, 1) { chkmax(t, ed[i + n2 - 1]); if (st[i] && t && t + st[i] >= n2) { flag = 1; break; } }
_for (i, 0, n << 1) st[i] = ed[i] = 0, s[i] = s2[i] = '\0'; return flag;
} signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
scanf("%s %d", s1 + 1, & q), n1 = strlen(s1 + 1);
while (q -- ) ans += solve(); cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
}
CF204E Little Elephant and Strings
考虑把所有串拼在一起。由于必须要 \(\ge k\) 个串包含,考虑对于每个起始位置 \(l\) 求出最小的 \(r\) 使得 \([l, r]\) 恰好包含 \(k\) 个串,记为 \(r_l\)。
容易双指针扫一遍维护出 \(O(n)\) 个区间 \([i, r_i]\),权值为这一段的 \(height\) 最小值(即 LCP 长度)。
然后每一位的贡献即包含他的区间的权值取 \(\max\)。使用 ST 表即可。
P9482 [NOI2023] 字符串
调了一天 /tuu。
首先把原串反过来拼在后面,建 SA,转化为一个二维偏序问题。
但是存在一个问题,就是说如果一个后缀字典序比另一个大,但并不一定能成为答案,因为在规定的长度 \(r\) 内他俩可能是相等的。考虑把这些多算的东西减掉。
观察性质,发现此时 \(s[i, i + l - 1]\) 和 \(s[i + l, i + 2l - 1]\) 构成一个回文串。跑 Manacher,转化为斜线加,竖线求和。转化一下坐标系即可。
复杂度是 \(O(Tn \log n)\) 的。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define _all(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i >= (b); i -- )
#define pb push_back
using namespace std;
const int N = 4e5 + 5;
int n, q, m, tot, cur, lim, rt, ans[N], Log[N], cnt[N], old[N], sa[N], rnk[N], id[N], f[N]; char s[N], t[N];
inline void chkmin(int & x, int y) { x = x < y ? x : y; }
inline void chkmax(int & x, int y) { x = x > y ? x : y; }
struct Node { int x, id, op; }; vector<Node> qry[3][N], upd[N];
struct Fenwick_Tree {
int tr[N];
inline void clear() { _for (i, 0, n + 5) tr[i] = 0; }
inline int lowbit(int x) { return (x & ( - x)); }
inline void update(int x, int k) { for (int i = x; i <= n; i += lowbit(i)) tr[i] += k; }
inline int query(int x) { int res = 0; for (int i = x; i; i -= lowbit(i)) res += tr[i]; return res; }
inline int query(int l, int r) { return l <= r ? (l ? query(r) - query(l - 1) : query(r)) : 0; }
} BIT[3];
inline void SA() {
lim = 'z', cur = 0;
_for (i, 1, n) sa[i] = i, rnk[i] = s[i], Log[i] = Log[i >> 1] + 1;
for (int k = 1; k < n; k <<= 1) {
iota(id + 1, id + n + 1, 1), fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0), tot = 0;
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[i + k]] ++ , old[i] = rnk[i];
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) id[cnt[rnk[i + k]] -- ] = i; fill(cnt, cnt + lim + 1, 0);
_for (i, 1, n) cnt[rnk[id[i]]] ++ ;
_for (i, 1, lim) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
_all (i, n, 1) sa[cnt[rnk[id[i]]] -- ] = id[i];
_for (i, 1, n) rnk[sa[i]] = old[sa[i]] == old[sa[i - 1]] && old[sa[i] + k] == old[sa[i - 1] + k] ? tot : ( ++ tot);
if (tot == n) break; lim = tot;
}
} inline void Manacher() {
int l = 1, r = - 1, k;
_for (i, 1, m) {
k = i > r ? 1 : min(f[l + r - i], r - i + 1);
while (1 <= i - k && i + k <= m && t[i - k] == t[i + k]) k ++ ; f[i] = k -- ;
if (r < i + k) l = i - k, r = i + k;
} _for (i, 1, n / 2) {
k = f[i << 1 | 1] >> 1;
if (k && k < i && s[i - k] > s[i + k + 1]) upd[i - k + 1].pb((Node){i + 1, 0, 1}), upd[i + 1].pb((Node){i + 1, 0, - 1});
}
} inline void solve() {
cin >> n >> q >> (s + 1), m = 0; int x, y; Log[0] = - 1;
_for (i, 1, n) s[n * 2 + 2 - i] = s[i]; s[n + 1] = '#', n = n * 2 + 1;
_for (i, 1, n) t[ ++ m] = '@', t[ ++ m] = s[i]; t[ ++ m] = '@'; Manacher(), SA();
_for (i, 1, q) cin >> x >> y, qry[(x & 1) ^ 1][n - x].pb((Node){rnk[x] + 1, i, 1}), qry[(x & 1) ^ 1][n + 1 - x - 2 * y].pb((Node){rnk[x] + 1, i, - 1}), qry[2][x].pb((Node){x + y, i, - 1});
_for (i, 1, n) {
if (s[i] ^ '#') BIT[i & 1].update(rnk[i], 1);
for (Node j : upd[i]) BIT[2].update(j.x, j.op);
_for (k, 0, 2) for (Node j : qry[k][i]) ans[j.id] += j.op * (k <= 1 ? BIT[k].query(j.x, n) : BIT[k].query(1, j.x));
} _for (i, 1, q) cout << ans[i] << "\n";
_for (i, 0, max({n, m, q}) + 5) cnt[i] = old[i] = sa[i] = rnk[i] = id[i] = s[i] = ans[i] = f[i] = 0, qry[0][i].clear(), qry[1][i].clear(), qry[2][i].clear(), upd[i].clear(); BIT[0].clear(), BIT[1].clear(), BIT[2].clear();
} signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int T; cin >> T >> T; while (T -- ) solve();
return 0;
}
后缀自动机(SAM)
SAM 可以理解为把一个字符串的所有子串压缩起来的一个结构,总点数和边数都是线性的。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define ll long long
#define pb push_back
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e6 + 5;
int n; char s[N]; vector<int> Tr[N]; ll ans;
inline void chkmax(ll & x, ll y) { x = x > y ? x : y; }
struct Suffix_Automation {
int ncnt, lst, cur, val[N]; struct Node { int fa, len, ch[26]; } tr[N];
inline int cre(int x) { tr[ ++ ncnt].fa = - 1, tr[ncnt].len = x; return ncnt; }
inline void init() { ncnt = - 1, lst = cre(0); }
inline int clone(int x) { return tr[ ++ ncnt] = tr[x], ncnt; }
inline void ins(int c) {
int p = lst, cur = cre(tr[lst].len + 1), q, nq; val[cur] = 1;
while ( ~ p && ! tr[p].ch[c]) tr[p].ch[c] = cur, p = tr[p].fa;
if ( ! ~ p) tr[cur].fa = 0;
else {
q = tr[p].ch[c];
if (tr[q].len == tr[p].len + 1) tr[cur].fa = q;
else {
nq = clone(q), tr[nq].len = tr[p].len + 1, tr[cur].fa = tr[q].fa = nq;
while ( ~ p && tr[p].ch[c] == q) tr[p].ch[c] = nq, p = tr[p].fa;
}
} lst = cur;
}
} SAM;
inline void dfs(int u) { for (int v : Tr[u]) dfs(v), SAM.val[u] += SAM.val[v]; chkmax(ans, SAM.val[u] == 1 ? 0 : 1ll * SAM.val[u] * SAM.tr[u].len); }
signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> (s + 1), n = strlen(s + 1), SAM.init();
_for (i, 1, n) SAM.ins(s[i] - 'a');
_for (i, 1, SAM.ncnt) Tr[SAM.tr[i].fa].pb(i); dfs(0), cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
}
P3975 [TJOI2015] 弦论 / SP7258 SUBLEX - Lexicographical Substring Search
第一遍在 fa 树上 dfs 后可以求出 \(f_i\) 表示以节点 \(i\) 代表的串的出现次数。
然后进行第二轮在 DAG 上 DP。注意要分 \(t = 0 / 1\) 讨论。
求答案的话就是在 DAG 上 dfs。复杂度是线性的。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define ll long long
#define pb push_back
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
int n, type, vis[N]; char s[N]; vector<int> Tr[N]; ll k, f[N], g[N];
struct Suffix_Automation {
int ncnt, cur, lst; struct Node { int len, fa, ch[26]; } tr[N];
inline int cre(int x) { tr[ ++ ncnt].fa = - 1, tr[ncnt].len = x; return ncnt; }
inline void init() { ncnt = - 1, lst = cre(0); }
inline int clone(int x) { return tr[ ++ ncnt] = tr[x], ncnt; }
inline void ins(int c) {
int p = lst, cur = cre(tr[lst].len + 1), q, nq; f[cur] = 1;
while ( ~ p && ! tr[p].ch[c]) tr[p].ch[c] = cur, p = tr[p].fa;
if ( ! ~ p) tr[cur].fa = 0;
else {
q = tr[p].ch[c];
if (tr[q].len == tr[p].len + 1) tr[cur].fa = q;
else {
nq = clone(q), tr[nq].len = tr[p].len + 1, tr[cur].fa = tr[q].fa = nq;
while ( ~ p && tr[p].ch[c] == q) tr[p].ch[c] = nq, p = tr[p].fa;
}
} lst = cur;
}
} SAM;
void dfs1(int u) { for (int v : Tr[u]) dfs1(v), f[u] += f[v]; }
void dfs2(int u) {
if (vis[u]) return ; vis[u] = 1; int v;
_for (i, 0, 25) if ((v = SAM.tr[u].ch[i])) dfs2(v), g[u] += g[v];
} void dfs3(int u, ll k) {
if (k <= f[u]) return ; k -= f[u]; int v;
_for (i, 0, 25) if ((v = SAM.tr[u].ch[i])) {
if (k > g[v]) k -= g[v];
else return cout << (char)(i + 'a'), dfs3(v, k);
}
} signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> (s + 1) >> type >> k, n = strlen(s + 1), SAM.init();
_for (i, 1, n) SAM.ins(s[i] - 'a');
_for (i, 1, SAM.ncnt) if ( ~ SAM.tr[i].fa) Tr[SAM.tr[i].fa].pb(i); dfs1(0);
_for (i, 0, SAM.ncnt) g[i] = type ? f[i] : (f[i] = 1); f[0] = g[0] = 0, dfs2(0);
if (k > g[0]) cout << - 1 << "\n";
else dfs3(0, k), cout << "\n";
return 0;
}
P4070 [SDOI2016] 生成魔咒
SAM 性质:每个节点的等价类字符串的长度是一段区间。
而没新增一个节点就代表多出了那么多个不同的子串。于是答案为 \(\sum_p len_p - len_{fa_p}\)。
值域较大,离散化后开 umap 存储即可。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
int n, t, a[N], b[N]; ll ans;
struct Suffix_Automation {
int ncnt, cur, lst; struct Node { int len, fa; unordered_map<int, int> ch; } tr[N];
inline int cre(int x) { tr[ ++ ncnt].fa = - 1, tr[ncnt].len = x; return ncnt; }
inline void init() { ncnt = - 1, cre(0); }
inline int clone(int x) { return tr[ ++ ncnt] = tr[x], ncnt; }
inline void ins(int x) {
int p = lst, cur = cre(tr[lst].len + 1), q, nq;
while ( ~ p && ! tr[p].ch[x]) tr[p].ch[x] = cur, p = tr[p].fa;
if ( ! ~ p) tr[cur].fa = 0;
else {
q = tr[p].ch[x];
if (tr[q].len == tr[p].len + 1) tr[cur].fa = q;
else {
nq = clone(q), tr[nq].len = tr[p].len + 1, tr[cur].fa = tr[q].fa = nq;
while ( ~ p && tr[p].ch[x] == q) tr[p].ch[x] = nq, p = tr[p].fa;
}
} lst = cur, ans += tr[cur].len - tr[tr[cur].fa].len;
}
} SAM;
signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n, SAM.init();
_for (i, 1, n) cin >> a[i], b[i] = a[i]; sort(b + 1, b + n + 1), t = unique(b + 1, b + n + 1) - a - 1;
_for (i, 1, n) SAM.ins(lower_bound(b + 1, b + n + 1, a[i]) - b), cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
}
P5341 [TJOI2019] 甲苯先生和大中锋的字符串
也是板子题,求答案是一个区间加后求全局 \(\max\),直接差分即可。
复杂度是 \(O(n)\)。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define _all(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i >= (b); i -- )
#define ll long long
#define pb push_back
using namespace std;
const int N = 4e5 + 5;
int n, res, ans, cnt[N]; ll k, f[N]; char s[N]; vector<int> Tr[N];
struct Suffix_Automation {
int ncnt, lst, cur; struct Node { int len, fa, ch[26]; } tr[N];
inline int cre(int x) { tr[ ++ ncnt].fa = - 1, tr[ncnt].len = x; return ncnt; }
inline void init() { ncnt = - 1, cre(0); }
inline int clone(int x) { return tr[ ++ ncnt] = tr[x], ncnt; }
inline void ins(int x) {
int p = lst, cur = cre(tr[lst].len + 1), q, nq; f[cur] = 1;
while ( ~ p && ! tr[p].ch[x]) tr[p].ch[x] = cur, p = tr[p].fa;
if ( ! ~ p) tr[cur].fa = 0;
else {
q = tr[p].ch[x];
if (tr[q].len == tr[p].len + 1) tr[cur].fa = q;
else {
nq = clone(q), tr[nq].len = tr[p].len + 1, tr[cur].fa = tr[q].fa = nq;
while ( ~ p && tr[p].ch[x] == q) tr[p].ch[x] = nq, p = tr[p].fa;
}
} lst = cur;
} inline void clear() {
lst = cur = 0;
_for (i, 0, n) cnt[i] = 0;
_for (i, 0, ncnt) {
tr[i].len = tr[i].fa = f[i] = 0, Tr[i].clear();
_for (j, 0, 25) tr[i].ch[j] = 0;
} ncnt = 0;
}
} SAM;
void dfs(int u) { for (int v : Tr[u]) dfs(v), f[u] += f[v]; }
inline void solve() {
cin >> (s + 1) >> k, n = strlen(s + 1), ans = res = 0, SAM.init();
_for (i, 1, n) SAM.ins(s[i] - 'a');
_for (i, 1, SAM.ncnt) if ( ~ SAM.tr[i].fa) Tr[SAM.tr[i].fa].pb(i); dfs(0);
_for (i, 1, SAM.ncnt) if (f[i] == k) cnt[SAM.tr[i].len] ++ , cnt[SAM.tr[SAM.tr[i].fa].len] -- ;
_all (i, n, 1) if ((cnt[i] += cnt[i + 1]) > res) res = cnt[i], ans = i; cout << (ans ? ans : - 1) << "\n", SAM.clear();
} signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int T; cin >> T; while (T -- ) solve();
return 0;
}
P6640 [BJOI2020] 封印
考虑对 \(s\) 串的每个位置求出 \(len_i\) 表示 \(s[i - len_i + 1, i]\) 是 \(t\) 串的子串的最大的 \(len_i\)。
如何求呢?对 \(t\) 串建 SAM,\(s\) 每加入一个字符就在 SAM 上跳 fa,跳到一个含有当前出边的节点并过去,最后节点的 \(len\) 就是所求(原因是显然的)。
预处理可以 \(O(n)\) 完成。
现在查询变成了:\(\max_{i = l}^r \min(len_i, i - l + 1)\)。
考虑二分答案,设为 \(mid\),显然 \(l \le i \le l + mid - 2\) 的 \(i\) 已经不可能成为答案了,所以只需保证 \(\max_{i = l + mid - 1}^r len_i \ge mid\) 即可。
复杂度是 \(O(n \log n)\)。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i <= (b); i ++ )
#define _all(i, a, b) for (int i = (a); i >= (b); i -- )
#define ll long long
#define ld long double
#define PII pair<int, int>
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
using namespace std;
const int N = 4e5 + 5;
int n, m, q, ans, len[N]; char s[N], t[N];
inline void chkmin(int & x, int y) { x = x < y ? x : y; }
inline void chkmax(int & x, int y) { x = x > y ? x : y; }
struct Sparse_Table {
int Log[N], ST[20][N];
inline void init(int * a) {
Log[0] = - 1;
_for (i, 1, n) Log[i] = Log[i >> 1] + 1, ST[0][i] = a[i];
_for (k, 1, Log[n]) _for (i, 1, n - (1 << k) + 1) ST[k][i] = max(ST[k - 1][i], ST[k - 1][i + (1 << (k - 1))]);
} inline int query(int l, int r) { int k = Log[r - l + 1]; return max(ST[k][l], ST[k][r - (1 << k) + 1]); }
} ST;
struct Suffix_Automation {
int ncnt, lst; struct Node { int len, fa, ch[26]; } tr[N];
inline int cre(int x) { tr[ ++ ncnt].fa = - 1, tr[ncnt].len = x; return ncnt; }
inline void init() { ncnt = - 1, cre(0); }
inline int clone(int x) { return tr[ ++ ncnt] = tr[x], ncnt; }
inline void ins(int x) {
int p = lst, cur = cre(tr[lst].len + 1), q, nq;
while ( ~ p && ! tr[p].ch[x]) tr[p].ch[x] = cur, p = tr[p].fa;
if ( ! ~ p) tr[cur].fa = 0;
else {
q = tr[p].ch[x];
if (tr[q].len == tr[p].len + 1) tr[cur].fa = q;
else {
nq = clone(q), tr[nq].len = tr[p].len + 1, tr[cur].fa = tr[q].fa = nq;
while ( ~ p && tr[p].ch[x] == q) tr[p].ch[x] = nq, p = tr[p].fa;
}
} lst = cur;
}
} SAM;
signed main() {
ios :: sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> (s + 1) >> (t + 1) >> q, n = strlen(s + 1), m = strlen(t + 1), SAM.init(); int p = 0, curlen = 0, l, r, L, R, mid;
_for (i, 1, m) SAM.ins(t[i] - 'a');
_for (i, 1, n) {
while (p && ! SAM.tr[p].ch[s[i] - 'a']) curlen = SAM.tr[p = SAM.tr[p].fa].len;
if (SAM.tr[p].ch[s[i] - 'a']) p = SAM.tr[p].ch[s[i] - 'a'], curlen ++ ; len[i] = curlen;
} ST.init(len);
while (q -- ) {
cin >> l >> r, L = 1, R = r - l + 1, ans = 0;
while (L <= R) mid = (L + R) >> 1, ST.query(l + mid - 1, r) >= mid ? (ans = mid, L = mid + 1) : (R = mid - 1); cout << ans << "\n";
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号