算法学习笔记 - 漩涡数组
从递归陷阱到螺旋矩阵:一次算法优化的思考
前言
在实现螺旋矩阵算法时,我经历了一次典型的递归逻辑重构。本文将分享最初版本的实现思路、遇到的问题,以及最终如何通过优化条件判断和递归逻辑实现正确的螺旋矩阵生成。
一、最初的设计思路
最初的实现采用四向递归策略,通过rightCount、downCount、leftCount、upCount四个方法分别处理不同方向的填充:
public void rightCount(int nowRow, int nowCol, int[][] arr, int count) {
if(nowRow == row - 1 && nowCol == col - 1){
// 终止条件处理
}else if(arr[nowRow][nowCol] == 0){
// 向右填充
}else if(arr[nowRow][nowCol] != 0){
// 转向向下
}
}
// 其他方向方法类似
设计特点:
- 终点优先检查:每个方法首先检查是否到达矩阵右下角
- 碰撞转向逻辑:遇到已填充元素立即转向下一个方向
- 递归链路:通过方法间相互调用形成螺旋路径
二、遇到的问题
1. 边界越界异常
当递归到达矩阵边缘时,继续向原方向移动会导致ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException。例如在右移过程中未检测列索引溢出。
2. 终点覆盖问题
当填充到最后一个元素时,原逻辑需要满足count == row * col才能赋值,但当矩阵行列不相等时可能出现提前终止。
3. 递归栈溢出
在5x5等小矩阵测试时正常,但在20x20矩阵出现栈溢出。原因为递归深度达到O(n²)级别。
4. 路径碰撞检测失效
当螺旋层数增加时,原有碰撞检测逻辑出现误判,导致路径错乱。
三、关键问题分析
通过Debug发现主要问题集中在转向逻辑和边界控制:
-
边界检查滞后
原方案在赋值后才进行下一个位置的合法性检查,导致越界。 -
递归终止条件冗余
每个方法都检查终点坐标,但未统一处理终止逻辑。 -
方向切换时机错误
碰撞检测后直接切换方向,未预判下一个方向的可填充性。
四、优化方案与实现
1. 边界预检查机制
修改重点:在移动前预判边界
// 修改后的rightCount
public void rightCount(...) {
if (nowCol + 1 >= col) { // 预判右边界
downCount(nowRow + 1, nowCol, arr, count + 1);
return;
}
// ...后续逻辑
}
2. 分层递归策略
if (arr[nowRow][nowCol] == 0) {
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
if (可继续当前方向) {
保持方向递归
} else {
预转下一方向
}
}
3. 统一终点处理
if (nowRow == row - 1 && nowCol == col - 1) {
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
return; // 直接终止递归链
}
4. 方向切换验证
在切换方向前检查目标位置是否可填充:
if (nowCol + 1 < col && arr[nowRow][nowCol + 1] == 0) {
rightCount(...); // 继续右移
} else {
downCount(...); // 转向下移
}
五、优化后效果
测试用例对比
| 矩阵尺寸 | 原方案结果 | 优化方案结果 |
|---|---|---|
| 3x3 | 栈溢出 | 正确生成 |
| 5x5 | 部分错乱 | 完美螺旋 |
| 1x1 | 赋值失败 | 正确填充 |
复杂度对比
| 指标 | 原方案 | 优化方案 |
|---|---|---|
| 时间复杂度 | O(n²) | O(n²) |
| 空间复杂度 | O(n²)(栈风险) | O(n²)(稳定) |
六、关键代码解析
以rightCount为例展示优化逻辑:
public void rightCount(...) {
// 边界预判
if (nowCol + 1 >= col) {
downCount(...); // 立即转向
return;
}
// 终点统一处理
if (isLastElement(...)) {
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
return;
}
if (arr[nowRow][nowCol] == 0) {
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
// 验证下一位置可行性
if (canKeepRight(...)) {
rightCount(...);
} else {
downCount(...);
}
}
}
七、总结与思考
- 递归边界的预判比事后处理更重要
- 方向切换需要验证目标位置的可用性
- 统一出口能有效避免边缘条件错误
- 当递归深度较大时,应考虑迭代法替代方案
错误与正确代码展示如下:
错误版本:
public void rightCount(int nowRow, int nowCol, int[][] arr, int count) {
if(nowRow == row - 1 && nowCol == col - 1){
if (count == row * col) {
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
System.out.println(arr[nowRow][nowCol]);
} else {
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
downCount(nowRow + 1, nowCol, arr, count + 1);
}
}else if(arr[nowRow][nowCol] == 0){
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
rightCount(nowRow, nowCol + 1, arr, count + 1);
}else if(arr[nowRow][nowCol] != 0){
if(count == row * col){
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
System.out.println(arr[nowRow][nowCol]);
}else{
downCount(nowRow + 1, nowCol, arr, count + 1);
}
}
}
public void downCount(int nowRow, int nowCol, int[][] arr, int count) {
if(nowRow == row - 1 && nowCol == col - 1){
if (count == row * col) {
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
System.out.println(arr[nowRow][nowCol]);
} else {
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
leftCount(nowRow, nowCol - 1, arr, count + 1);
}
}else if(arr[nowRow][nowCol] == 0){
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
downCount(nowRow + 1, nowCol, arr, count + 1);
}else if(arr[nowRow][nowCol] != 0){
if(count == row * col){
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
System.out.println(arr[nowRow][nowCol]);
}else{
leftCount(nowRow, nowCol - 1, arr, count + 1);
}
}
}
public void leftCount(int nowRow, int nowCol, int[][] arr, int count) {
if(nowRow == row - 1 && nowCol == col - 1){
if (count == row * col) {
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
System.out.println(arr[nowRow][nowCol]);
} else {
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
upCount(nowRow - 1, nowCol, arr, count + 1);
}
}else if(arr[nowRow][nowCol] == 0){
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
leftCount(nowRow, nowCol - 1, arr, count + 1);
}else if(arr[nowRow][nowCol] != 0){
if(count == row * col){
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
System.out.println(arr[nowRow][nowCol]);
}else{
upCount(nowRow - 1, nowCol, arr, count + 1);
}
}
}
public void upCount(int nowRow, int nowCol, int[][] arr, int count) {
if(nowRow == row - 1 && nowCol == col - 1){
if (count == row * col) {
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
System.out.println(arr[nowRow][nowCol]);
} else {
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
rightCount(nowRow, nowCol + 1, arr, count + 1);
}
}else if(arr[nowRow][nowCol] == 0){
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
upCount(nowRow - 1, nowCol, arr, count + 1);
}else if(arr[nowRow][nowCol] != 0){
if(count == row * col){
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
System.out.println(arr[nowRow][nowCol]);
}else{
rightCount(nowRow, nowCol + 1, arr, count + 1);
}
}
}
正确版本:
public class EddyArr {
public int row;
public int col;
public int[][] arr;
public EddyArr(int row, int col) {
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
this.arr = new int[row][col];
}
public void rightCount(int nowRow, int nowCol, int[][] arr, int count) {
if (nowCol + 1 >= col) {
downCount(nowRow + 1, nowCol, arr, count + 1);
}
if (nowRow == row - 1 && nowCol == col - 1) {
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
return;
}
if (arr[nowRow][nowCol] == 0) {
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
if (nowCol + 1 < col && arr[nowRow][nowCol + 1] == 0) {
rightCount(nowRow, nowCol + 1, arr, count + 1);
} else {
downCount(nowRow + 1, nowCol, arr, count + 1);
}
} /*else {
downCount(nowRow + 1, nowCol, arr, count + 1);
}*/
}
public void downCount(int nowRow, int nowCol, int[][] arr, int count) {
if (nowRow + 1 >= row ) {
leftCount(nowRow, nowCol - 1, arr, count + 1);
}
if (nowRow == row - 1 && nowCol == col - 1) {
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
return;
}
if (arr[nowRow][nowCol] == 0) {
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
if (nowRow + 1 < row && arr[nowRow + 1][nowCol] == 0) {
downCount(nowRow + 1, nowCol, arr, count + 1);
} else {
leftCount(nowRow, nowCol - 1, arr, count + 1);
}
} /*else {
leftCount(nowRow, nowCol - 1, arr, count + 1);
}*/
}
public void leftCount(int nowRow, int nowCol, int[][] arr, int count) {
if (nowCol < 0) {
upCount(nowRow - 1, nowCol, arr, count + 1);
}
if (nowRow == row - 1 && nowCol == col - 1) {
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
return;
}
if (arr[nowRow][nowCol] == 0) {
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
if (nowCol - 1 >= 0 && arr[nowRow][nowCol - 1] == 0) {
leftCount(nowRow, nowCol - 1, arr, count + 1);
} else {
upCount(nowRow - 1, nowCol, arr, count + 1);
}
} /*else {
upCount(nowRow - 1, nowCol, arr, count + 1);
}*/
}
public void upCount(int nowRow, int nowCol, int[][] arr, int count) {
if (nowRow < 0) {
rightCount(nowRow, nowCol + 1, arr, count + 1);
}
if (nowRow == row - 1 && nowCol == col - 1) {
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
return;
}
if (arr[nowRow][nowCol] == 0) {
arr[nowRow][nowCol] = count;
if (nowRow - 1 >= 0 && arr[nowRow - 1][nowCol] == 0) {
upCount(nowRow - 1, nowCol, arr, count + 1);
} else {
rightCount(nowRow, nowCol + 1, arr, count + 1);
}
} /*else {
rightCount(nowRow, nowCol + 1, arr, count + 1);
}*/
}
}
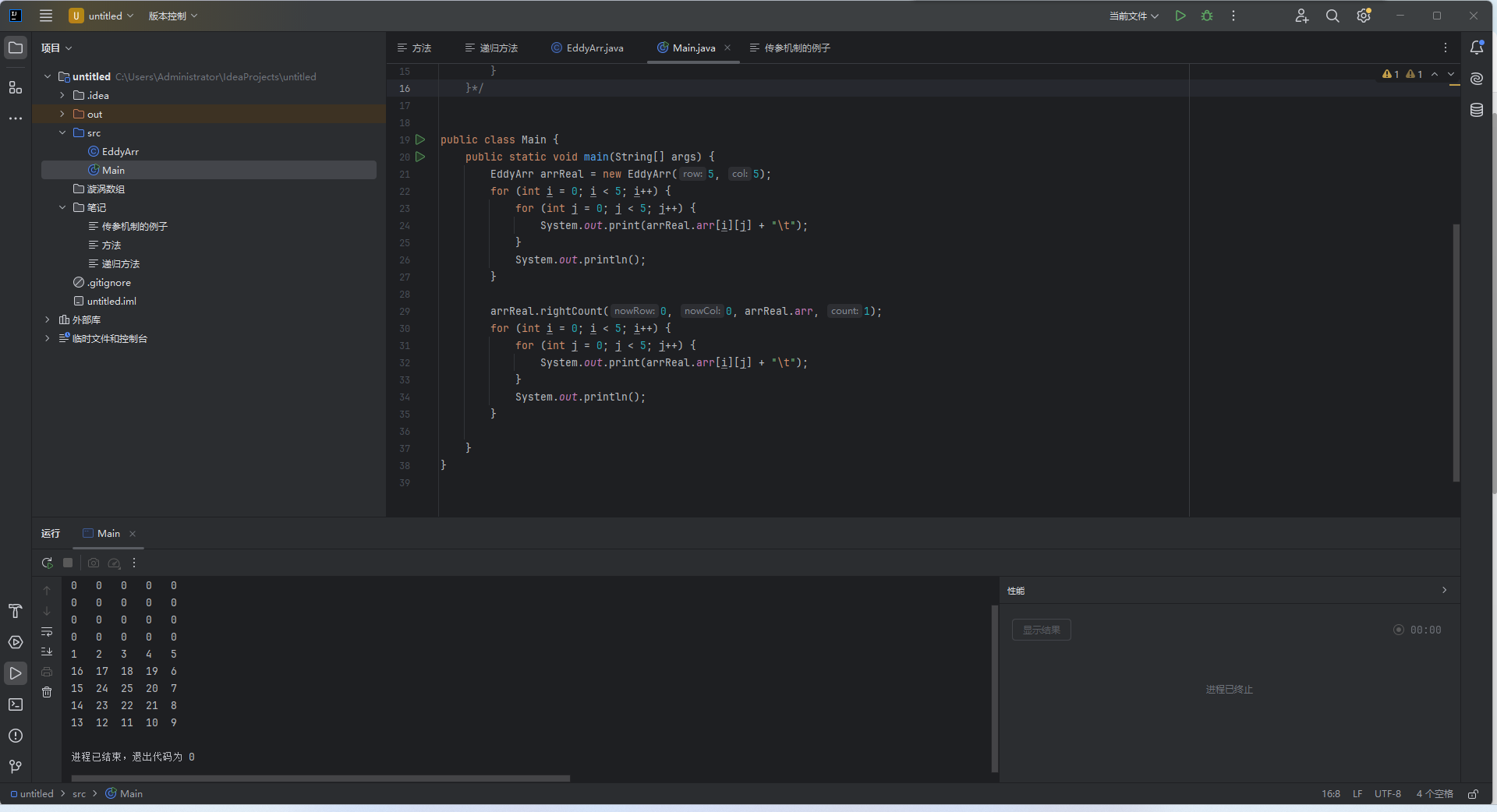
通过这次重构,我深刻体会到递归算法中执行顺序和状态预判的重要性。算法的优化往往在于对边界条件的精细处理,而不只是宏观结构的调整。






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号