Date 2025.10.27
在 Print 之前
到现在还是想不明白为什么不骗那显眼的 80pts。
赛时 420/500pts,T5放了道紫。
A - 玩数字
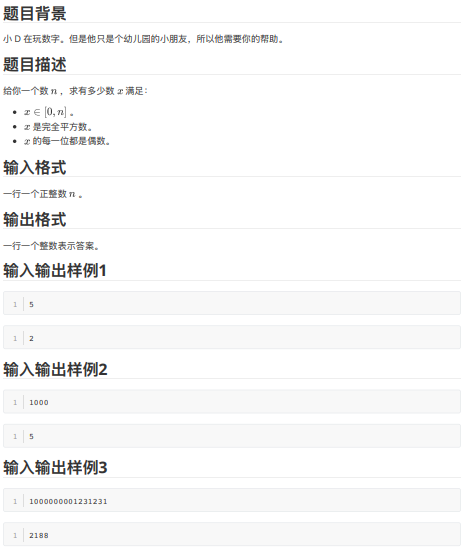
P.S. \(n \le 10^{15}\)
唐题,可以 \(O(\sqrt n)\) 解决,中间进行数位分离即可,当然你也可以打表。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define pll pair<ll,ll>
#define pld pair<ld,ld>
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef int praise_long_long;
namespace io {
using namespace std;
inline ll read() {
char x=getchar();
ll ans=0,f=1;
while(x<'0'||x>'9') {
if(x=='-') {
f*=(-1);
}
x=getchar();
}
while(x>='0'&&x<='9') {
ans*=10;
ans+=(x-'0');
x=getchar();
}
return ans*f;
}
inline void print(ll x) {
if(x<0) {
putchar('-');
x=-x;
}
if(x>=10) {
print(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
else {
putchar(x+'0');
}
}
}
using namespace io;
const ll N=2e5+5,mod=1e9+7,inf=2e18;
const ld eps=1e-6;
ll n,ans;
inline void ck(ll x) {
while(x) {
ll num=x%10;
if(num&1) {
return ;
}
x/=10;
}
ans++;
}
inline void solve() {
n=read();
for(ll i=0;i<=sqrt(n);i++) {
ck(i*i);
}
print(ans);
}
praise_long_long main() {
// freopen("num.in","r",stdin);
// freopen("num.out","w",stdout);
ll T=1;
// T=read();
while(T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
/**/
B - 课程

P.S. \(1 \le n \le 5 \times 10^{5} \ \ \ 1 \le a_i,b_i \le 10^9\)
又是一道唐题,需要注意的是输入进来 \(2 \times n\) 个数,所以空间开到 \(10^6\) 即可。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define pll pair<ll,ll>
#define pld pair<ld,ld>
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef int praise_long_long;
namespace io {
using namespace std;
inline ll read() {
char x=getchar();
ll ans=0,f=1;
while(x<'0'||x>'9') {
if(x=='-') {
f*=(-1);
}
x=getchar();
}
while(x>='0'&&x<='9') {
ans*=10;
ans+=(x-'0');
x=getchar();
}
return ans*f;
}
inline void print(ll x) {
if(x<0) {
putchar('-');
x=-x;
}
if(x>=10) {
print(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
else {
putchar(x+'0');
}
}
}
using namespace io;
const ll N=1e6+5,mod=1e9+7,inf=2e18;
const ld eps=1e-6;
struct node {
ll al,bl,pos;
} a[N];
ll n,ans;
inline void solve() {
n=read();
for(ll i=1;i<=2*n;i++) {
a[i]={read(),read(),i};
}
sort(a+1,a+1+2*n,[](node a,node b) {
return a.al-a.bl>b.al-b.bl;
});
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++) {
ans+=a[i].al;
// cout<<a[i].pos<<' ';
}
// puts("");
for(ll i=n+1;i<=2*n;i++) {
ans+=a[i].bl;
}
print(ans);
}
praise_long_long main() {
// freopen("course.in","r",stdin);
// freopen("course.out","w",stdout);
ll T=1;
// T=read();
while(T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
/**/
C - 卡牌

其实很简单,我们发现只要位数短的肯定没有位数长的大,所以优先考虑数的数量,然后从小往大排序即可。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define pll pair<ll,ll>
#define pld pair<ld,ld>
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef int praise_long_long;
namespace io {
using namespace std;
inline ll read() {
char x=getchar();
ll ans=0,f=1;
while(x<'0'||x>'9') {
if(x=='-') {
f*=(-1);
}
x=getchar();
}
while(x>='0'&&x<='9') {
ans*=10;
ans+=(x-'0');
x=getchar();
}
return ans*f;
}
inline void print(ll x) {
if(x<0) {
putchar('-');
x=-x;
}
if(x>=10) {
print(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
else {
putchar(x+'0');
}
}
}
using namespace io;
const ll N=1e6+5,mod=1e9+7,inf=2e18;
const ld eps=1e-6;
ll n,q,a[N],num,sum[N];
inline void solve() {
n=read(),q=read();
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++) {
a[i]=read();
num+=a[i]*i;
}
if(num%(n-1)) {
a[num%(n-1)]--;
}
sum[0]=a[0];
for(ll i=1;i<n;i++) {
sum[i]=sum[i-1]+a[i];
}
while(q--) {
ll kl=read();
ll l=0,r=n-1,cnt=-1;
while(l<=r) {
ll mid=(l+r>>1);
if(sum[mid]>kl) {
cnt=mid;
r=mid-1;
}
else {
l=mid+1;
}
}
print(cnt);
puts("");
}
}
praise_long_long main() {
// freopen("card.in","r",stdin);
// freopen("card.out","w",stdout);
ll T=1;
// T=read();
while(T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
/**/
D - 排队

事实上不知为何,我甚至还推了一个小时的杨辉三角
听说有人用 Catalan 数写了,但很明显,我没推出来,所以可以推规律。
我们可以讨论 \(1\) 在 \(j\) 号位的方案数:
\[1:1
\\
2:1 \ 1
\\
3:1 \ 2 \ 2
\\
4:1 \ 3 \ 5 \ 5
\\
5:1 \ 4 \ 8 \ 14 \ 14
\]
我们可以定义 \(f_{i,j}\) 表示当 \(n=i\) 时 \(1\) 在 \(j\) 号位的方案数。
不难发现,\(f_{i,j}=f_{i-1,j}+sum_{j-1}\) 其中 \(sum_j\) 表示上一次操作 \(j\) 及之前的贡献和。
答案就是 \(\sum_{i=1}^{n} f_{n,i}\)。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define pll pair<ll,ll>
#define pld pair<ld,ld>
typedef int ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef int praise_long_long;
namespace io {
using namespace std;
inline ll read() {
char x=getchar();
ll ans=0,f=1;
while(x<'0'||x>'9') {
if(x=='-') {
f*=(-1);
}
x=getchar();
}
while(x>='0'&&x<='9') {
ans*=10;
ans+=(x-'0');
x=getchar();
}
return ans*f;
}
inline void print(ll x) {
if(x<0) {
putchar('-');
x=-x;
}
if(x>=10) {
print(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
else {
putchar(x+'0');
}
}
}
using namespace io;
const ll N=5e3+5,mod=1e7+7,inf=2e9;
const ld eps=1e-6;
ll n,f[N][N],sum[N];
inline void solve() {
n=read();
f[1][1]=1,sum[1]=1;
for(ll i=2;i<=n;i++) {
for(ll j=1;j<=i;j++) {
f[i][j]=f[i-1][j]+sum[j-1];
f[i][j]%=mod;
}
for(ll j=1;j<=i;j++) {
sum[j]=sum[j-1]+f[i][j];
sum[j]%=mod;
}
}
print(sum[n]);
}
praise_long_long main() {
// freopen("eat.in","r",stdin);
// freopen("eat.out","w",stdout);
ll T=1;
// T=read();
while(T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
/**/



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号