[算法学习记录] [更新中]最短路
顾名思义,最短路算法,就是求一个图中所有的点距某一个点的最短距离,常见的有Dijkstra算法、Bellman-Ford算法、Johnson算法与Floyd算法。
Dijkstra
Dijistra算法实际上是一种由贪心与动态规划结合的算法,我们每次都贪心地选择到某个点的最近距离,又动态地更新着距离数组d的数据,直到完成对每一个点的操作。
但它也存在着缺陷,Dijkstra算法并不能处理负权图,因为这与其核心算法贪心相悖,因为如果存在负权边,按照贪心的写法就只能选择那条负权边,从而陷入死循环。
- 算法拆解
为了减少时间复杂度,我们把每一个父节点及其邻接表存入堆(小根堆)中,这样堆顶的元素就始终是该节点的子节点中权值最小的,为了实现小根堆,我们还需要重载小于号,代码如下:
struct Edge
{
int x, w;
//x是节点的编号,w是节点的权值
bool operator < (const Edge&u)const
{
if(w != u.w) return w > u.w;
//升序排列
}
}
为了避免重复操作,我们可以创建一个bool数组(或创建bitset,两者的作用在这儿是相同的,不过bitset更快一点),来标记已操作过的父节点;由于我们要得到的是最短路,为了避免出错,我们应该把d距离数组的值都初始化为当前使用的数据类型的最大值。示例代码如下:
void dijkstra(int st)
{
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) d[i] = inf;
//首先对d(每个点到起点的距离)数组进行初始化,其中inf是long long的近似最大值
priority_queue<Edge> pq;
pg.push({st, d[st] = 0});
bitset<N> vis;
//N,是点个数的上限
while(pq.size())
{
int x = pq.top(),pq.pop();
if(vis[x])continue;
//操作过的节点,直接跳过
for(auto &t : g[x])
{
int v = t.x, w = t.w;
if(d[x] + w < d[v])
{
d[v] = d[x] + w;
//找到更小的路径,更新
pq.push({v,d[v]});
//把子节点放入堆中
}
}
}
//如果堆非空,也就是说没有遍历所有点,就继续操作
}
例题1 星码Starrycoding P70 【模板】最短路(2)
本题是dijkstra算法的模版题,依照上文所说的思路写出代码即可,代码如下:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
const ll inf = 2e18;
int n, m;
ll d[N];
//用一个数组存储各个点到起点的距离
struct edge
{
ll x, w;//x是某一个点所连接的点,w是权值
bool operator < (const edge& u)const
{
if (w != u.w)return w > u.w;
//生、序排列
}
//重载<以实现小根堆,最短路的核心思想就是贪心和dp,既然求最短路,那么就需要选权值(距离)最小的
};
vector<edge> g[N];
//创建邻接表,存储每个点的子节点与每条边的权值
void dijkstra(int st)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) d[i] = inf;
//首先将所有节点距起点的距离为(ll的)最大值,默认除起点外的点都无法到达
priority_queue<edge>pq;
//使用堆(小根堆)来实现权值最小点的快速寻找
bitset<N>vis;
//标记以处理过的父节点
pq.push({ st,d[st] = 0 });
//把起点放入堆中
while (pq.size())
{
int x = pq.top().x; pq.pop();
if (vis[x])continue;
//跳过已经入堆的节点,防止重复
vis[x] = true;
//将该点标记为已走过
for (const auto &t : g[x])
{
int v = t.x, w = t.w;
if (d[x] + w < d[v])
{
d[v] = d[x] + w;
pq.push(edge{v, d[v]});
}
//遍历x这一点的所有子节点,如果有一个子节点可以让距离缩短,那么就更新距离,并把更新后的点放入堆中
}
}
//如果堆非空就一直进行
}
void solve()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
ll x, y, w; cin >> x >> y >> w;
g[x].push_back({ y,w });
}
dijkstra(1);
cout << (d[n] == inf ? -1 : d[n]) << "\n";
//如果最后一个点的值仍是最大值,说明不存在从1到n的最短路径
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int _ = 1;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
例题2 星码Starrycoding P113 小鱼吃虾米
本题仍是一个明显的最短路问题,但不一样的是我们需要求的是其它点到某一点的距离,与dijkstra算法正好想反,如果直接对每一点进行求解,时间复杂度将会非常之大,所以我们不妨把思路逆转过来,我们仍然把它看做一个从某一点到其它所有点的最短距离的题,为了做到这一点,我们需要把图的指向全都翻转过来(只需要在读入邻接表时倒转一下即可),代码如下。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
const ll N = 1e4+5,inf = LLONG_MAX;
ll v[N],d[N],n,m,k;
struct Edge
{
ll x,w;
bool operator < (const Edge&u)const
{
if(w != u.w)return w > u.w;
}
};//重载小于号,实现小根堆
vector<Edge> g[N];
//邻接表
void dijkstra(int st)
{
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)d[i] = inf;
bitset<N> vis;
priority_queue<Edge> pq;
pq.push({st,d[st] = 0});
while(pq.size())
{
int x = pq.top().x;pq.pop();
if(vis[x])continue;
vis[x] = true;
for(auto &t : g[x])
{
int v = t.x,w = t.w;
if(d[x] + w < d[v])
{
d[v] = d[x] + w;
pq.push({v,d[v]});
}
}
}
}
void solve()
{
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for(int i = 1;i<=k;i++)cin >> v[i];
for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++) g[i].clear();
//测试样例不止一个,所以别忘了清空邻接表。
while(m--)
{
int a, b, c;cin >> a >> b >> c;
g[b].push_back({a,c});
}
dijkstra(1);
ll ans = inf;
for(int i = 1;i <= k;i++) ans = min(ans, d[v[i]]);
//求所有路径中的最小值
cout << (ans==inf ? -1 : ans) << "\n";
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int _;cin >> _;
while(_--)solve();
return 0;
}
Bellman-Ford
相比于Dijkstra算法,Bellman-Ford算法的最大优点就是能够处理存在负权的图,它能够在求得最短路的同时检测出负权环。
Bellman-Ford算法的核心思想就是“松弛”,比如下面这样。
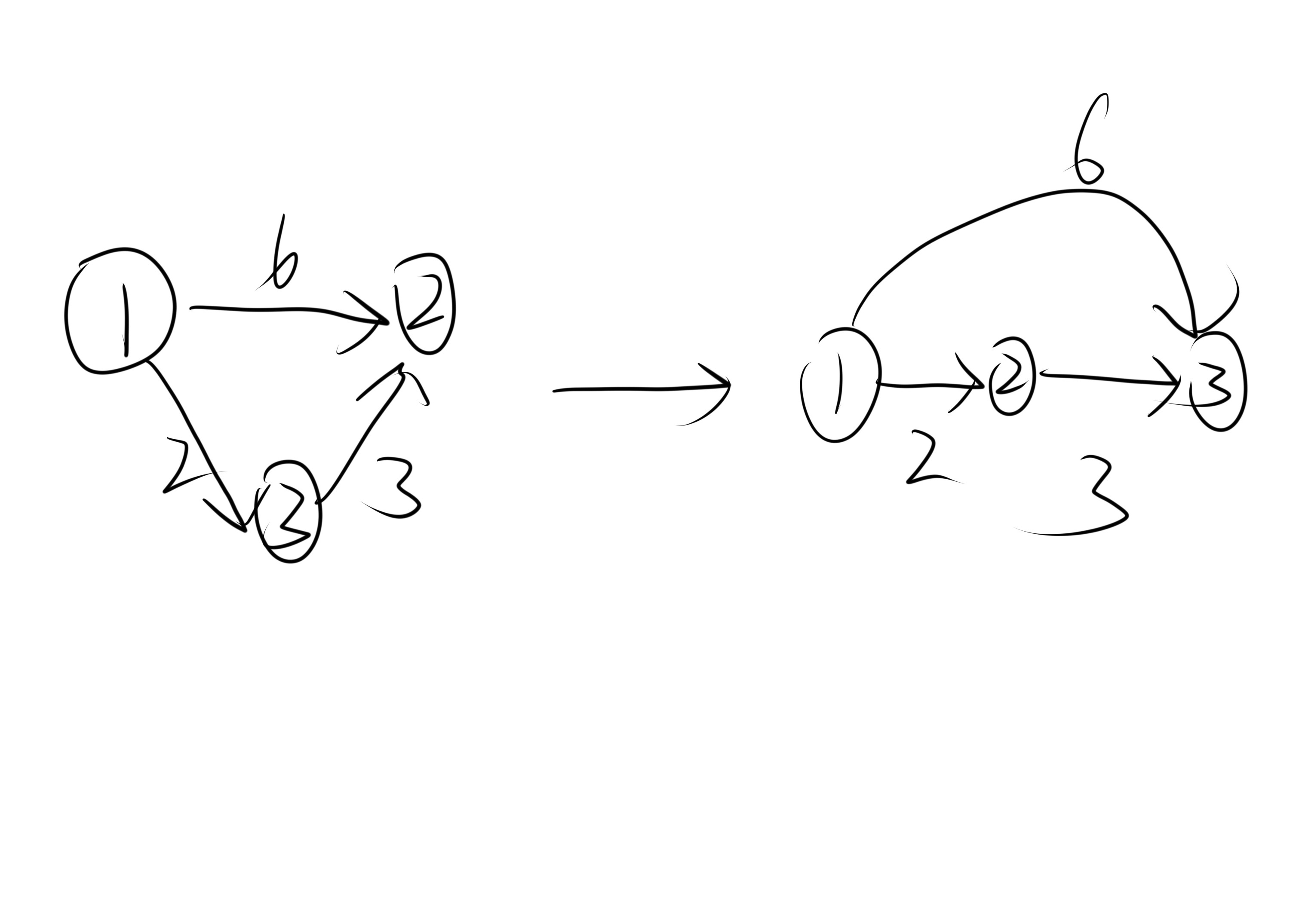
所以,如果一个图在进行n-1次松弛操作后仍然可以进行松弛操作,说明该图一定存在负权环,代码实现如下:
星码Starrycoding P97
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
const ll N = 1e4+5,inf = LLONG_MAX;
ll d[N], n, m;
//d数组就是每个点到起点的距离
struct Edge
{
ll x,w;
};
vector<Edge> g[N];
//存储子节点以及其权值的邻接表
void solve()
{
cin >> n >> m;
while(m--)
{
int x,y,z;cin >> x >> y >> z;
g[x].push_back({y,z});
//读取邻接表
}
for(int i = 2;i <= n;i++)d[i] = inf;
//将除第一个点外的其它点到第一个点的距离设为ll的最大值,以防止后续出错
bool circle = false;
//负权的判断
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
circle = false;
for(int j = 1;j<=n;j++)
{
for(const auto &t : g[j])
{
int u = t.x,w = t.w;
if(d[j] + w < d[u])
{
d[u] = d[j] + w;
circle = true;
}
}
}
}
//有n个点的图有n-1条边,所以如果无负权环,在n-1次松弛操作后,就不能再进行松弛操作了。
if(circle) cout << -1 <<"\n";
else
{
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)cout << d[i] <<" ";
cout << "\n";
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int _ = 1;
while(_--)solve();
return 0;
}
松弛过程中的暴力枚举会导致时间复杂度较高,我们可以考虑进行队列优化,以便降低时间复杂度。
SPFA算法(Bellman-Ford算法的路径优化版本)
SPFA算法可以显著改善Bellman-Ford算法的时间复杂度,与Dijkstra算法的优化版本类似,SPFA算法是利用队列来减少冗余操作的。代码实现如下:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
const int N = 1e5+5,inf = 2e18;
ll n, m, d[N], cnt[N];
struct Edge
{
int x,w;
};
vector<Edge> g[N];
//创建邻接表
bool SPFA(int st)
{
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) d[i] = inf;
queue<int> q;
bitset<N> inq;
//标记顶点是否在队列中
d[st] = 0;
q.push(st);
while(q.size())
{
int x = q.front().x;
q.pop();inq[x] = false;
//弹出队列元素,并将该节点标记为false;
for(const auto &t : g[x])
{
int u = t.x,w = t.w;
if(d[x]+w<d[u])
{
d[u] = d[x] + w;
cnt[u] = cnt[x] + 1;
//cnt是记录到i的路径边数,如果要经过超过n-1条边(n个顶点,n-1条边)才能到达,说明存在负权环
if(cnt[u]>=n) return false;
if(!inq[u])q.push(u),inq[u] = true;
//将未操作过的节点放入队列中
}
}
//遍历该节点的子节点并进行松弛操作
}
return true;
}
//SPFA算法实现返回true说明无负权环,否则有负权环
void solve()
{
cin >> n >> m;
while(m--)
{
int x, y, z;cin >> x >> y >> z;
g[x].push_back({y, z});
}
if(SPFA(1)) for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) cout << d[i] << " ";
else cout << -1 << " ";
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int _ = 1;
while(_--)solve();
return 0;
}
Johnson最短路径
Floyd
Floyd算法与Dijkstra算法的不同之处就在于Floyd算法可以求任意两点间的最短路,相比Dijkstra算法更加灵活。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号