第一部分:面向对象
面向对象复习
类和对象
1.什么是面向对象?一种分析问题的方式(增强了程序的可扩展性)。
2.面向对象三大特性:封装、继承、多态。
3..什么是类?什么是对象?类和对象的区别?
类:类是模子,确定对象将会拥有的特征(属性)和行为(方法)
对象是一个你能够看得到、摸得着的具体实体—万物皆对象
类是模具,创建对象的模具,抽象的。
类是一种数据类型,用户自定义的数据类型
类决定了对象将要拥有的属性和行为。
对象是具体的,是类的具体实例。对象具有属性(特征)和方法(行为)
类中包含了数据(用字段表示)与行为(用方法(函数、功能)表示,方法为一块具有名称的代码)
this ,当前对象,base
类组成:字段、属性、函数、构造函数、索引器。。。
【字段:存储数据
属性:保护字段 get set
函数:描述对象的行为
构造函数:初始化对象,给对象的每个属性进行赋值
构造函数是一个特殊的方法:
1)、构造函数没有返回值,连void也不能写。
2)、构造函数的名称必须跟类名一样。
索引器:通过索引访问对象

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //int[] nums = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; //Console.WriteLine(nums[2]); Person p = new Person(); //p.Numbers = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; p[0] = 1; p[1] = 2; p[2] = 3; p[3] = 4; Console.WriteLine(p[0]); Console.WriteLine(p[1]); p["张三"] = "一个好人"; p["大黄"] = "汪汪汪"; p["春生"] = "哈哈哈"; Console.ReadKey(); } } class Person { private int[] numbers = new int[5]; public int[] Numbers { get { return numbers; } set { numbers = value; } } //索引器 让对象以索引的方式操作数组 public int this[int index] { get { return numbers[index]; } set { numbers[index] = value; } } Dictionary<string, string> dic = new Dictionary<string, string>(); public string this[string index] { get { return dic[index]; } set { dic[index] = value; } } Dictionary<int, string> dic2 = new Dictionary<int, string>(); }
】
结构和类的区别
1、类当中写了一个新的构造函数之后,默认的无参数的就被干掉了。
但是在结构中,写了一个新的构造函数之后,默认的那个无参数的还在。
在结构的构造函数当中,必须给所有的字段赋值,这样也就限制了结构中最多
只能有两个构造函数,一个是默认的无参数的构造函数,一个是全参数的构造函数。
2、结构的new关键字只干了一件事儿,就是调用结构的构造函数。
3、结构不能继承于类,而类也不能继承于结构。
结构不具备面向对象的特征。
而类才是面向对象的产物。
4、如果不给结构创建对象的话,不允许调用结构中的非静态方法。
enum

namespace 枚举 { enum Gender { 男, 女 } enum Direction { East, West, North, South } enum QQStatus { online, offline, hidden, Qme } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //Gender zsGender = Gender.男; //Gender lsGender = Gender.女; //Direction dir = Direction.East; //dir = Direction.South; //QQStatus qqstatus = QQStatus.Qme; ////qqstatus = QQStatus.offline; //整数强转成枚举 ////qqstatus = (QQStatus)1; //枚举强转成整数 //int num = (int)qqstatus; //Console.WriteLine(num); //枚举转字符串 //Console.WriteLine(qqstatus.ToString()); //如何将字符串转换成枚举 //会用就行 //(Gender)(Enum.Parse( typeof(Gender),“male”)); //(枚举类型)(Enum.Parse(typeof(枚举类型),"字符串")); Console.WriteLine("请输入你QQ的状态"); string input= Console.ReadLine(); QQStatus qq = (QQStatus)(Enum.Parse(typeof(QQStatus), input)); Console.WriteLine(qq.ToString()); Console.ReadKey(); } } }

namespace 三元表达式 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // int score = 70; //if (score > 80) //{ // Console.WriteLine("给你100!"); //} //else //{ // Console.WriteLine("跪方便面去!"); //} //表达式1的值,如果为ture,则取表达式2的值为整个表达式的值,为为false则去表达式3的值为整个表达式的值。 //string str= score > 80 ? "给你100" : "跪方便面!"; //Console.WriteLine(str); Console.WriteLine("请输入用户名:"); string userName = Console.ReadLine(); Console.WriteLine("亲输入密码:"); string passwrod = Console.ReadLine(); string result=(userName=="admin"&&passwrod=="888888")?"登录成功":"账户或密码错误!"; Console.WriteLine(result); Console.ReadKey(); } }
占位符
只是改变了输出数据的样子,值本身没有变化
{"占位符编号:格式控制字符}"

int num = 201258; int d=18.81818181 //Console.WriteLine("{0:0.0000}",d); //保留小数位 18.8182 //Console.WriteLine(d); //Console.WriteLine("{0:####-#-#}",num);//2012-5-8 Console.WriteLine(num+1);
return:
1、立即结束本次方法
2、在方法中返回要返回的值
break
跳出当前循环
continue
结束本次循环,回到循环条件进行判断
关键字
new
1、创建对象
--->在堆中开辟空间
--->在开辟的堆空间中创建对象
--->调用对象的构造函数
2、隐藏父类的成员
this
1、代表当前类的对象
2、显示的调用本类的构造函数 :this
base
1、显示调用父类的构造函数
2、调用父类的成员
访问修饰符
public private internal protected protected internal
private 当前类中可以访问,类中成员的默认访问修饰符。
protected 当前类及子类中可以访问(在继承中用。)
internal 当前程序集内部可以访问
protected internal当前程序集或子类中(不同程序集也可以访问)。
public 任何地方
注意点:
1、能够修饰类的访问修饰符只有两个:public internal(默认就是internal)。
2、在同一个项目中,public的权限跟internal是一样的。
3、子类的访问权限不能高于父类。
导入命名空间
命名空间就是类的"文件夹"。类就是"文件夹"中的文件。需要导入命名空间
添加引用:
如果我需要在一个项目中,访问另一个项目中的某一个类
--->添加对另一个项目的引用
--->导入命名空间
静态和非静态
静态成员:被static修饰
实例成员:不被static修饰
静态成员先于实例成员被加载到内存中,只有创建了对象,才有实例成员=》静态类中只能存在静态成员调用
静态成员调用:类名.静态成员名;
实例成员调用:实例名.实例成员;(实例就是我们的对象)
静态和非静态的区别
1)、在非静态类中,既可以有实例成员,也可以有静态成员。
2)、在调用实例成员的时候,需要使用对象名.实例成员;
在调用静态成员的时候,需要使用类名.静态成员名;
总结:静态成员必须使用类名去调用,而实例成员使用对象名调用。
静态函数中,只能访问静态成员,不允许访问实例成员。
实例函数中,既可以使用静态成员,也可以使用实例成员。
静态类中只允许有静态成员,不允许出现实例成员。
什么时候使用静态?
---->作为工具类
---->在整个项目中资源共享,正因为它是资源共享的,所以静态成员必须要等到整个项目都结束的时候才会被资源释放。
在我们的项目中应该尽可能的少使用静态成员。
继承是创建对象的过程。
partial部分类
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { } } public partial class Person { private string _name; public void Test() { } } public partial class Person { public void Test(string name) { // _name } }
sealed密封类
不能够被其他类继承,但是可以继承于其他类。
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { } } public sealed class Person:Test { } public class Test { }
设计模式
---->单例设计模式
在整个程序中,我们要保证对象必须是唯一的。
实现:
---->第一步:构造函数私有化
---->第二步:声明一个静态字段,作为全局唯一的单例对象
---->第三步:声明一个静态函数,返回全局唯一的对象

//Form2 public partial class Form2 : Form { //第一步:构造函数私有化 private Form2() { InitializeComponent(); } //第二部:声明一个静态的字段用来存储全局唯一的窗体对象 private static Form2 _single = null; //第三步:通过一个静态函数返回一个全局唯一的对象 public static Form2 GetSingle() { if (_single == null) { _single = new Form2(); } return _single; } private void Form2_FormClosing(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e) { //当你关闭窗体的时候 让窗体2的资源不被释放 _single = new Form2(); } } //Form1 private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { Form2 frm2 = Form2.GetSingle();//new Form2(); frm2.Show(); }
---->简单工厂设计模式
核心:把所有的子类都当做父类来看待
练习:
提示用户分别的输入两个数字:
再输入运算符:返回一个计算的父类,并调用方法得到结果。
Add Sub Cheng Chu
建筑行业最早应用到设计模式这个概念
1、注册一个公司
2、招兵买马
3、投标买地
4、安排施工队开始施工
5、卖楼
设计模式就是用来专门解决一些特定的问题。

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("请输入你想要的笔记本品牌"); string brand = Console.ReadLine(); //整个简单工厂的核心 工厂 //根据用户的输入 返回相应的笔记本 父类 NoteBook nb = GetNoteBook(brand); if (nb != null) { nb.SayHello(); } else { Console.WriteLine("没有你想要的电脑品牌!!!!"); } Console.ReadKey(); } static NoteBook GetNoteBook(string brand) { NoteBook nb = null; switch (brand) { case "IBM": nb = new IBM(); break; case "Acer": nb = new Acer(); break; case "Lenovo": nb = new Lenovo(); break; case "Dell": nb = new Dell(); break; } return nb; } } abstract class NoteBook { public abstract void SayHello(); } class IBM : NoteBook { public override void SayHello() { Console.WriteLine("我是IBM笔记本"); } } class Lenovo : NoteBook { public override void SayHello() { Console.WriteLine("我是联想笔记本"); } } class Dell : NoteBook { public override void SayHello() { Console.WriteLine("我是戴尔笔记本"); } } class Acer : NoteBook { public override void SayHello() { Console.WriteLine("我是鸿基笔记本"); } }
类库
.dll文件,我们使用类库来帮助我们封装一些常用的功能
面向对象三大特征
封装
方法封装了常用的代码
类 封装了常用的方法
好处:
-->减少了大量的冗余代码
-->封装将一坨很难理解的功能封装起来,但是对外提供了一个很简单的使用接口。我们会使用就OK。
继承
解决了类与类之间代码的冗余
子类 ---->父类 属性、方法 。私有字段,构造函数。
--->减少了类中的冗余代码
--->让类与类产生了关系,为多态打下了基础。
特性:
单根性:一个子类只能有一个父类
传递性:爷爷类 爹类 儿子类
里氏转换:
1、子类可以赋值给父类
2、如果父类中装的是子类对象,则可以将这个父类转换为对应的子类对象
---->关键字
1、is:返回bool类型,指示是否可以做这个转换
2、as:如果转换成功,则返回对象,否则返回null
is:表示类型转换,如果能够转换成功,则返回一个true,否则返回一个false
as:表示类型转换,如果能够转换则返回对应的对象,否则返回一个null
作用:我们可以将所有的子类都当做是父类来看,针对父类进行编程,写出通用的代码,适应需求的不断改变

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Person person = new Student(); //if (person is Teacher) //{ // ((Teacher)person).TeacherSayHello(); //} //else //{ // Console.WriteLine("转换失败"); //} Student s = person as Student;//将person转换为student对象 if (s != null) { s.StudentSayHello(); } else { Console.WriteLine("转换失败"); } Console.ReadKey(); //is as } } class Person { public void PersonSayHello() { Console.WriteLine("我是父类"); } } class Student : Person { public void StudentSayHello() { Console.WriteLine("我是学生"); } } class Teacher : Person { public void TeacherSayHello() { Console.WriteLine("我是老师"); } }
多态
多态就是指不同对象收到相同消息时,会产生不同行为,同一个类在不同的场合下表现出不同的行为特征
多态的作用:把不同的子类对象都当作父类来看,可以屏蔽不同子类对象之间的差异,写出通用的代码,做出通用的编程,以适应需求的不断变化。
--->虚方法virtual override

//员工类、部门经理类(部门经理也是员工,所以要继承自员工类。员工有上班打卡的方法。用类来模拟。 class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //员工九点打卡 经理11点打卡 程序猿不打卡 // Employee emp = new Employee(); //// emp.DaKa(); // Manager m = new Manager(); // //m.DaKa(); // Programmer p = new Programmer(); // //p.DaKa(); // Employee e = m; //Employee[] emps = { emp, m, p }; //for (int i = 0; i < emps.Length; i++) //{ // //if (emps[i] is Manager) // //{ // // ((Manager)emps[i]).DaKa(); // //} // //else if (emps[i] is Programmer) // //{ // // ((Programmer)emps[i]).DaKa(); // //} // //else // //{ // // emps[i].DaKa(); // //} // emps[i].DaKa(); //} Employee emp = new Programmer();//new Manager(); //new Employee(); emp.DaKa(); Console.ReadKey(); } } class Employee { public virtual void DaKa() { Console.WriteLine("员工九点打卡"); } } class Manager : Employee { public override void DaKa() { Console.WriteLine("经理11点打卡"); } } class Programmer : Employee { public override void DaKa() { Console.WriteLine("程序猿不打卡"); } }
--->抽象类abstract override
抽象类的特点:
1.抽象成员必须标记为abstract,并且不能有任何实现。
2.抽象成员必须在抽象类中。
3.抽象类不能被实例化
4.子类继承抽象类后,必须把父类中的所有抽象成员都重写。(除非子类也是一个抽象类,则可以不重写)
5.抽象成员的访问修饰符不能是private
6.在抽象类中可以包含实例成员。并且抽象类的实例成员可以不被子类实现
7.抽象类是有构造函数的。虽然不能被实例化。
8、如果父类的抽象方法中有参数,那么。继承这个抽象父类的子类在重写父类的方法的时候必须传入对应的参数。
如果抽象父类的抽象方法中有返回值,那么子类在重写这个抽象方法的时候 也必须要传入返回值。
=====
如果父类中的方法有默认的实现,并且父类需要被实例化,这时可以考虑将父类定义成一个普通类,用虚方法来实现多态。
如果父类中的方法没有默认实现,父类也不需要被实例化,则可以将该类定义为抽象类。

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //抽象类不允许创建对象 Animal a = new Cat(); //new Dog(); a.Bark(); Console.ReadKey(); } } abstract class Animal { public abstract void Bark(); private string _name; public string Name { get { return _name; } set { _name = value; } } int _age; public int Age { get { return _age; } set { _age = value; } } public Animal(string name, int age) { this.Name = name; this.Age = age; } } class Dog : Animal { public override void Bark() { Console.WriteLine("狗狗旺旺的叫"); } } class Cat : Animal { public override void Bark() { Console.WriteLine("猫咪喵喵的叫"); } }
--->接口interface
接口(interface I开头...able结尾)
---->接口是一种能力
---->接口也是一种规范
---->如果你继承了这个接口,就必须按照接口的要求来实现这个接口。
接口特点:
接口是一种规范。也是一种能力。
只要一个类继承了一个接口,这个类就必须实现这个接口中所有的成员
接口的功能要单一
为了多态。
接口不能被实例化。也就是说,接口不能new(不能创建对象),跟抽象类是一样的,因为创建对象也没意义。
接口中的成员不能加“访问修饰符”,接口中的成员访问修饰符为public,不能修改。
类中的成员默认的访问修饰符是private ,而接口中默认的访问修饰符是public
(默认为public)
接口中的成员不能有任何实现(“光说不做”,只是定义了一组未实现的成员)。
接口中只能有方法、属性、索引器、事件,不能有“字段”和构造函数。
接口与接口之间可以继承
接口并不能去继承一个类,而类可以继承接口 (接口只能继承于接口,而类既可以继承接口,也可以继承类)
实现接口的子类必须实现该接口的全部成员。
一个类可以同时继承一个类并实现多个接口,如果一个子类同时继承了父类A,并实现了接口IA,那么语法上A必须写在IA的前面。
class MyClass:A,IA{},因为类是单继承的。

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //实现多态 IKouLan kl = new Driver();//new Teacher();//new Student(); kl.KouLan(); Console.ReadKey(); } } class Person { public void CHLSS() { Console.WriteLine("人类可以吃喝拉撒睡"); } } class NoTuiPerson : Person { } class Student : Person, IKouLan { public void KouLan() { Console.WriteLine("学生可以扣篮"); } } class Teacher : Person, IKouLan { public void KouLan() { Console.WriteLine("老师也可以扣篮"); } } class Driver : Person, IKouLan { public void KouLan() { Console.WriteLine("司机也可以扣篮"); } } interface IKouLan { void KouLan(); } class NBAPlayer : Person { public void KouLan() { Console.WriteLine("NBA球员可以扣篮"); } }

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //麻雀 会飞 企鹅不会飞 鸵鸟不会飞 鹦鹉会飞 飞机 会飞 IFly[] flys = { new MaBird(), new YingWu(), new Plane() }; for (int i = 0; i < flys.Length; i++) { flys[i].Fly(); } Console.ReadKey(); } } class Bird { public void CHLSS() { Console.WriteLine("鸟都会吃喝拉撒睡"); } } interface IFly { void Fly(); // void DownEggs(); } class MaBird : Bird, IFly { public void Fly() { Console.WriteLine("麻雀会飞"); } } class TuoBird : Bird { } class YingWu : Bird, IFly { public void Fly() { Console.WriteLine("鹦鹉也会飞"); } } class QQ : Bird { } class Plane : IFly { public void Fly() { Console.WriteLine("飞机也会飞"); } } interface IStrong { void Strong(); } interface NKWC { void NKWC(); } interface ISupperMan : IFly, IStrong, NKWC { } class Student : ISupperMan { public void Fly() { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public void Strong() { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public void NKWC() { throw new NotImplementedException(); } }
显示实现接口的目的:解决方法的重名问题
什么时候显示的去实现接口:
当继承的接口中的方法和参数一摸一样的时候,要是用显示的实现接口

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { I1 i = new Person(); i.Test(); Console.ReadKey(); } } class Person:I1 { public void Test() { Console.WriteLine("这个Test函数是属于Person的"); } //显示实现接口:告诉编译器 这个函数才是接口的 不是类的 void I1.Test() { Console.WriteLine("显示实现接口的Test函数"); } } interface I1 { void Test(); }
当一个抽象类实现接口的时候,需要子类去实现接口。

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { I1 i = new PersonDaughter();//new PersonSon(); //new Person(); i.Test(); Console.ReadKey(); } } abstract class Person:I1 { public void Test() { Console.WriteLine("抽象类实现接口"); } } class PersonSon : Person { } class PersonDaughter : Person { } interface I1 { void Test(); }
案例:
---->使用多态的思想计算圆形、矩形的面积和周长。
---->真鸭子嘎嘎叫,橡皮鸭子唧唧叫,木头鸭子不会叫。 但是他们都会游泳。

//橡皮rubber鸭子、木wood鸭子、真实的鸭子realduck。三个鸭子都会游泳,而橡皮鸭子和真实的鸭子都会叫,只是叫声不一样,橡皮鸭子“唧唧”叫,真实地鸭子“嘎嘎”叫,木鸭子不会叫. IBark bark = new XPDuck();//new RealDuck();//new MuDuck(); bark.Bark(); Console.ReadKey(); public class Duck { public void Swim() { Console.WriteLine("鸭子们都会游泳,旱鸭子不会~~~~"); } } interface IBark { void Bark(); } class XPDuck : Duck, IBark { public void Bark() { Console.WriteLine("橡皮鸭子唧唧叫"); } } class RealDuck : Duck, IBark { public void Bark() { Console.WriteLine("真是的鸭子嘎嘎叫"); } } class MuDuck : Duck { }
简单工厂设计模式:
案例:银行卡、饭卡、门卡、胸卡
虚方法,抽象方法
关于虚方法需要注意的几点:
1.父类中如果有方法需要让子类重写,则可以将该方法标记为virtual
2.虚方法在父类中必须有实现,哪怕是空实现。
3.虚方法子类可以重写(override),也可以不重写
关于抽象方法注意的几点:
1.需要用abstract关键字标记
2.抽象方法不能有任何方法实现。
3.抽象成员必须包含在抽象类中。
4.由于抽象成员没有任何实现,所以子类必须将抽象成员重写。
5.抽象类不能实例化,
抽象类的作用:抽象类的作用就是为了让子类继承。
6.抽象类中可以包括抽象成员,可以包括有具体代码的成员。
7. 还有抽象方法不能用static修饰
什么时候用虚方法和抽象类
父类能不能创建对象,父类的函数有木有意义==》虚方法
父类没有必要创建对象,这里的成员也没有意义==》抽象类
接口
1.接口中只能包含方法(属性、事件、索引器也都是方法)
2.接口中的成员都不能有任何实现。
3.接口不能被实例化。
4.接口中的成员不能有任何访问修饰符。(默认为public)
5.实现接口的子类必须将接口中的所有成员全都实现。
6.子类实现接口的方法时,不需要任何关键字,直接实现即可。
7.接口存在的意义就是为了多态。
8.多态的意义:程序可扩展性。最终→节省成本,提高效率。
9.接口解决了类的多继承的问题以及体积庞大的问题、接口之间可以实现多继承、显示实现接口
面向对象五大原则
--->1.单一职责原则
--->一个对象应该只包含一个单一的职责,并且该职责被完整的封装在一个类中。
如果一个类中封装了过多的职责,这些职责在并发执行的时候会相互干扰。
案例:宿舍和图书馆
--->2.开放封闭原则
--->对扩展开放,对修改代码封闭。
修改容易出现bug
案例:把自己变的好看一些
买好看的衣服、眼睛、鞋子。
整容的时候
--->3.依赖倒转原则
--->高层(high level)模块不该直接依赖低层(low level)模块。它们两个应该依赖抽象(abstraction)。
案例:数据库调用
--->4.里氏替换原则
--->子类能够替换掉他们的父类
--->5.接口隔离原则
--->客户端不应该依赖那些它不需要的接口。
代码冗余、臃肿

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //作业:定义父亲类Father(姓lastName,财产property,血型bloodType),儿子Son类(玩游戏PlayGame方法),女儿Daughter类(跳舞Dance方法),调用父类构造函数(:base())给子类字段赋值 //作业:定义汽车类Vehicle属性(brand(品牌),color(颜色))方法run,子类卡车(Truck) 属性weight载重 方法拉货,轿车 (Car) 属性passenger载客数量 方法载客 //Truck t = new Truck("解放牌卡车", VehicalColor.Red, 10000000); //t.LaHuo(); //Car c = new Car("红旗轿车", VehicalColor.Black, 5); //c.LaRen(); //作业:计算形状Shape(圆Circle,矩形Square ,正方形Rectangle)的面积、周长 //Shape shape = new Square(5, 8);//new Circle(5); //double area = shape.GetArea(); //double perimeter = shape.Getperimeter(); //Console.WriteLine("这个形状的面积是{0:0.00},周长是{1:0.00}",area,perimeter); //Console.ReadKey(); //业:橡皮rubber鸭子、木wood鸭子、真实的鸭子realduck。三个鸭子都会游泳,而橡皮鸭子和真实的鸭子都会叫,只是叫声不一样,橡皮鸭子“唧唧”叫,真实地鸭子“嘎嘎”叫,木鸭子不会叫. IBark bark = new XPDuck();//new RealDuck();//new MuDuck(); bark.Bark(); Console.ReadKey(); } } public class Duck { public void Swim() { Console.WriteLine("鸭子们都会游泳,旱鸭子不会~~~~"); } } interface IBark { void Bark(); } class XPDuck : Duck, IBark { public void Bark() { Console.WriteLine("橡皮鸭子唧唧叫"); } } class RealDuck : Duck, IBark { public void Bark() { Console.WriteLine("真是的鸭子嘎嘎叫"); } } class MuDuck : Duck { } abstract class Shape { public abstract double GetArea(); public abstract double Getperimeter(); } class Circle : Shape { public double R { get; set; } public Circle(double r) { this.R = r; } public override double GetArea() { return Math.PI * this.R * this.R; } public override double Getperimeter() { return 2 * Math.PI * this.R; } } class Square : Shape { public double Height { get; set; } public double Width { get; set; } public Square(double height, double width) { this.Height = height; this.Width = width; } public override double GetArea() { return this.Height * this.Width; } public override double Getperimeter() { return (this.Height + this.Width) * 2; } } enum VehicalColor { Black, Red, White, Blue, Yellow } class Vehicle { public string Brand { get; set; } public VehicalColor Color { get; set; } public void Run() { Console.WriteLine("是车都会跑"); } public Vehicle(string brand, VehicalColor color) { this.Brand = brand; this.Color = color; } } class Truck : Vehicle { public double Weight { get; set; } public Truck(string brand, VehicalColor color, double weight) : base(brand, color) { this.Weight = weight; } public void LaHuo() { Console.WriteLine("卡车可以最多拉{0}KG的货物", this.Weight); } } class Car : Vehicle { public int Passenger { get; set; } public Car(string brand, VehicalColor color, int passenger) : base(brand, color) { this.Passenger = passenger; } public void LaRen() { Console.WriteLine("轿车最多可以拉{0}个人", this.Passenger); } } class Father { public string LastName { get; set; } public double Property { get; set; } public string BloodType { get; set; } public Father(string lastName, double property, string bloodType) { this.LastName = lastName; this.Property = property; this.BloodType = bloodType; } } class Son : Father { public Son(string lastName, double property, string bloodType) : base(lastName, property, bloodType) { } public void PlayGame() { Console.WriteLine("儿子可以玩游戏"); } } class Daughter : Father { public Daughter(string lastName, double property, string bloodType) : base(lastName, property, bloodType) { } public void Dance() { Console.WriteLine("女儿会跳舞"); } }
进程 :一个应用程序就是一个进程,而一个进程又是由多个线程组成的。
进程帮助我们在内存中分配应用程序执行所需要的空间。
---->我们可以通过进程来直接操作应用程序。
//存储着我们当前正在运行的进程
Process[] pro = Process.GetProcesses();
foreach (var item in pro)
{
//item.Kill();不试的不是爷们
Console.WriteLine(item.ProcessName);
}
//使用进程来打开应用程序
Process.Start("notepad");//打开记事本
Process.Start("mspaint");//打开画图工具
Process.Start("iexplore", "http://www.baidu.com");
Process.Start("calc");//打开计算器
//使用进程来打开文件
//封装我们要打开的文件 但是并不去打开这个文件
ProcessStartInfo psi = new ProcessStartInfo(@"C:\Users\SpringRain\Desktop\打开文件练习.exe");
//创建进程对象
Process pro2 = new Process();
//告诉进程要打开的文件信息
pro2.StartInfo = psi;
//调用函数打开
pro2.Start();
Console.ReadKey();
案例
动物类继承
猜拳游戏
面向对象计算器
外部设备(抽象方法)
登记案例(接口)
打开文件案例
磁盘上有不同的文件,比如:.txt文本文件、.avi视频文件、.xls电子表格。
要求:编写一个控制台程序,用户输入一个带后缀名的文件,将该文件名传递到一个方法中,该方法中根据用户输入的文件名后缀,返回一个对应的文件对象。提示:编写不同的类模拟不同的文件、为不同的文件类创建统一的父类、使用简单工厂实现。
效果如图:

打开文件案例

//磁盘上有不同的文件,比如:.txt文本文件、.avi视频文件、.xls电子表格。要求:编写一个控制台程序,用户输入一个带后缀名的文件,将该文件名传递到一个方法中,该方法中根据用户输入的文件名后缀,返回一个对应的文件对象。提示:编写不同的类模拟不同的文件、为不同的文件类创建统一的父类、使用简单工厂实现 class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("请输入要打开的文件所在的路径"); string filePath = Console.ReadLine(); Console.WriteLine("请输入要打开的文件的名字"); string fileName = Console.ReadLine(); //通过简单工厂设计模式返回父类 BaseFile bf = GetFile(filePath, fileName); if (bf != null) { bf.OpenFile(); } Console.ReadKey(); } static BaseFile GetFile(string filePath,string fileName) { BaseFile bf = null; string strExtension = Path.GetExtension(fileName);//3.txt switch (strExtension) { case ".txt": bf = new TxtFile(filePath, fileName); break; case ".avi": bf = new AviFile(filePath, fileName); break; case ".mp4": bf = new MP4File(filePath, fileName); break; } return bf; } } class BaseFile { //字段、属性、构造函数、函数、索引器 private string _filePath; public string FilePath//ctrl+R+E { get { return _filePath; } set { _filePath = value; } } //自动属性 prop+两下tab public string FileName { get; set; } public BaseFile(string filePath, string fileName) { this.FilePath = filePath; this.FileName = fileName; } //设计一个函数 用来打开指定的文件 public void OpenFile() { ProcessStartInfo psi = new ProcessStartInfo(this.FilePath + "\\" + this.FileName); Process pro = new Process(); pro.StartInfo = psi; pro.Start(); } } class TxtFile : BaseFile { //子类会默认调用父类无参数的构造函数(如果父类写了一个有参的构造函数,父类中默认的无参的构造函数将被干掉了,那么子类就拿不到初始化后的数据了) //子类为什么会默认调用父类无参数的构造函数??? =》假如父类对属性值进行初始化,它有可能会在无参的构造函数里进行初始化 public TxtFile(string filePath, string fileName) : base(filePath, fileName) { } } class MP4File : BaseFile { public MP4File(string filePath, string fileName) : base(filePath, fileName) { } } class AviFile : BaseFile { public AviFile(string filePath, string fileName) : base(filePath, fileName) { } } 打开文件练习
动物类继承案例

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //实现多态:声明父类去指向子类对象 Animal[] a = { new Cat(), new Dog(), new Pig() }; for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++) { a[i].Bark(); a[i].Drink(); a[i].Eat(); } Console.ReadKey(); } } abstract class Animal { //抽象成员只能存在于抽象类中 public abstract void Bark();//父类没有办法确定子类如何去实现 public void Eat() { Console.WriteLine("动物可以舔着吃"); } public void Drink() { Console.WriteLine("动物可以舔着喝"); } } //一个子类继承了一个抽象的父类,那么这个子类必须重写这个抽象父类中的所有抽象成员,除非该子类是抽象类 class Cat : Animal { public override void Bark() { Console.WriteLine("猫咪喵喵的叫"); } } class Dog : Animal { public override void Bark() { Console.WriteLine("狗狗旺旺的叫"); } } class Pig : Animal { public override void Bark() { Console.WriteLine("猪猪哼哼的叫"); } }


class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { MobileDisk md = new MobileDisk(); MP3 mp3 = new MP3(); UDisk u = new UDisk(); Computer cpu = new Computer(); Telphone tel = new Telphone(); cpu.MS = tel;//u;//mp3;//将MP3插到了电脑上 cpu.CpuWrite(); cpu.CpuRead(); // mp3.PlayMusic(); Console.ReadKey(); } } abstract class MobileStorage { /// <summary> /// 方法,类,属性上面,外部设备的读 /// </summary> public abstract void Read(); /// <summary> /// 外部设备的写 /// </summary> public abstract void Write(); } class Telphone : MobileStorage { public override void Read() { Console.WriteLine("手机在读取数据"); } public override void Write() { Console.WriteLine("手机在写入数据"); } } class MobileDisk : MobileStorage { public override void Read() { Console.WriteLine("移动硬盘在读取数据"); } public override void Write() { Console.WriteLine("移动硬盘在写入数据"); } } class UDisk : MobileStorage { public override void Read() { Console.WriteLine("U盘在读取数据"); } public override void Write() { Console.WriteLine("U盘在写入数据"); } } class MP3 : MobileStorage { public override void Read() { Console.WriteLine("Mp3在读取数据"); } public override void Write() { Console.WriteLine("Mp3在写入数据"); } public void PlayMusic() { Console.WriteLine("Mp3可以自己播放音乐"); } } class Computer { public MobileStorage MS { get; set; } public void CpuRead() { this.MS.Read(); } public void CpuWrite() { this.MS.Write(); } }

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //Person需要登记 //House房子也需要登记 //汽车也需要登记 //财产登记 //最后写一个函数 来实现以上物品的登记 DengJi(new Person()); DengJi(new House()); DengJi(new Car()); DengJi(new Money()); Console.ReadKey(); } static void DengJi(IDengJi dj) { dj.DengJi(); } } //接口中的方法不能有任何的大括号(不能有任何的实现) //接口中的成员默认的访问修饰符就是public /// <summary> /// 登记的方法 /// </summary> interface IDengJi { void DengJi(); } class Person : IDengJi { public void DengJi() { Console.WriteLine("人出生就要登记"); } } class House : IDengJi { public void DengJi() { Console.WriteLine("买房子也要登记"); } } class Car : IDengJi { public void DengJi() { Console.WriteLine("买汽车也要登记"); } } class Money : IDengJi { public void DengJi() { Console.WriteLine("财产也要登记"); } }
石头剪刀布案例
玩家
--->出拳的方法,是我们指定的
电脑
--->出拳的方法,随机的
裁判
--->判断输赢或者平手
石头1 剪刀2 布3
玩家赢:石头1 剪刀2 =-1 剪刀2 布3 =-1 布3 石头1=2
平手:玩家-电脑=0;
电脑赢:

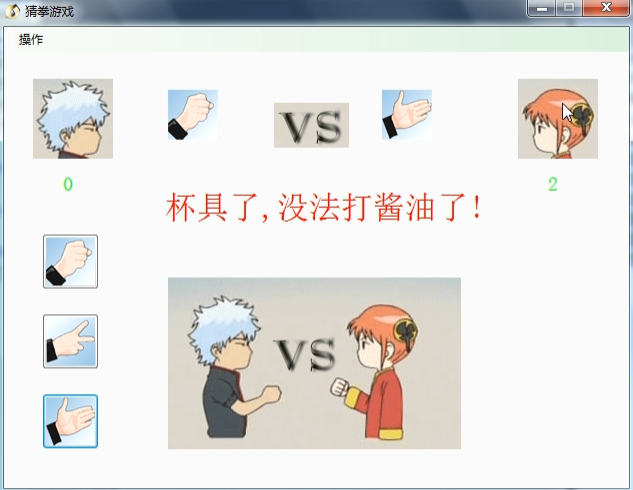

class CaiPan { /// <summary> /// 判断玩家和电脑输赢 /// </summary> /// <param name="playNum">玩家出拳的数字结果</param> /// <param name="computerNum">电脑出拳的数字结果</param> /// <returns></returns> public string Win(int playNum,int computerNum) { if (playNum-computerNum==-1||playNum-computerNum==2) { return "玩家赢了"; } else if (playNum-computerNum==1||playNum-computerNum==-2) { return "电脑赢了"; } else { return "平手了"; } } } public class Computer { /// <summary> /// 存储出拳内容的属性 /// </summary> public string FistName { get; set; } public int Play() { //伪随机数 Random r = new Random(); int num= r.Next(1,4); switch (num) { case 1: this.FistName = "石头"; break; case 2: this.FistName = "剪刀"; break; case 3: this.FistName = "布"; break; } return num; } } public class Player { /// <summary> /// 存储出拳的内容 /// </summary> public string FistName { get; set; } public int Play(string name) { //把内容存起来 this.FistName = name;//出拳的内容存起来 int num=0; switch (this.FistName) { case "石头": num = 1; break; case "剪刀": num = 2; break; case "布": num = 3; break; } return num; } } //石头按钮的单击事件 private void btnShiTou_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { Button btn = (Button)sender; StartPlay(btn.Text); } private void StartPlay( string name) { //玩家 Player p = new Player(); //出拳并获取该出拳内容的数字结果 int playerNum = p.Play(name); lblPlay.Text = p.FistName;//出拳内容显示出来 //电脑 Computer c = new Computer(); //出拳并获取该出拳内容的数字结果 int computerNum = c.Play(); lblComputer.Text = c.FistName;//显示出拳的内容 //裁判 CaiPan cp = new CaiPan(); //把输赢的结果显示出来 lblResult.Text = cp.Win(playerNum, computerNum); } //剪刀 //private void btnJianDao_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) //{ // StartPlay(); //}
简单工厂设计模式之计算器练习案例

namespace ProOperation { public abstract class Operation { public int NumberOne { get; set; } public int NumberTwo { get; set; } public Operation(int n1, int n2) { this.NumberOne = n1; this.NumberTwo = n2; } public abstract int GetResult(); } public class Add : Operation { public Add(int n1, int n2) : base(n1, n2) { } public override int GetResult() { return this.NumberOne + this.NumberTwo; } } public class Sub : Operation { public Sub(int n1, int n2) : base(n1, n2) { } public override int GetResult() { return this.NumberOne - this.NumberTwo; } } public class Chu : Operation { public Chu(int n1, int n2) : base(n1, n2) { } public override int GetResult() { return this.NumberOne / this.NumberTwo; } } public class Cheng : Operation { public Cheng(int n1, int n2) : base(n1, n2) { } public override int GetResult() { return this.NumberOne * this.NumberTwo; } } }

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using ProOperation;//引入 namespace 简单工厂设计模式之计算器练习 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("请输入第一个数字"); int n1 = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine()); Console.WriteLine("请输入第二个数字"); int n2 = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine()); Console.WriteLine("请输入操作符"); string oper = Console.ReadLine(); //根据用户输入的操作符 返回算符的父类 Operation operation = GetOperation(oper, n1, n2); if (operation != null) { int result = operation.GetResult(); Console.WriteLine("{0}{1}{2}={3}", n1, oper, n2, result); } else { Console.WriteLine("没有你想要的运算符"); } Console.ReadKey(); } static Operation GetOperation(string oper, int n1, int n2) { Operation operation = null; switch (oper) { case "+": operation = new Add(n1, n2); break; case "-": operation = new Sub(n1, n2); break; case "*": operation = new Cheng(n1, n2); break; case "/": operation = new Chu(n1, n2); break; } return operation; } } }
知识点总结
什么是面向对象?
面向对象三大特性:封装、继承、多态。
什么是类?什么是对象?类和对象的区别?
提问:大家觉得什么是封装?
类和对象本身就是封装的体现。
1.属性封装了字段、2.方法的多个
参数封装成了一个对象、3.将一堆代码封装到了一个方法中、4.将
一些功能封装到了几个类中、5.将一些具有相同功能的代码封装到
了一个程序集中(dll、exe),并且对外提供统一的访问接口。(
属性名、方法名等。)
继承(是指类与类之间的关系。)
为什么要继承?继承带给我们的好处?
代码重用
LSP里氏替换原则(通过代码说明一下,声明父类类型变
量,指向子类类型对象,以及调用方法时的一些问题)、多态。
类的单根继承性、传递性、继承时构造函数的问题(:this() ,
:base())。构造函数不能被继承。
所有的类都直接或间接的继承
自object。查看IL代码。
继承中的访问修饰符问题:(提一
下protected即可。)
virtual、abstract、接口区别与联系,总结。举例。
小总结
封装,继承,多态.
五个访问修饰符,
字段和属性及索引器,
里氏替换
添加引用和导入命名空间








 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号