代码随想录算法训练营第52天 | 图论基础1
图论理论基础
https://www.programmercarl.com/kamacoder/图论理论基础.html#图的基本概念
深度优先搜索理论基础
https://www.programmercarl.com/kamacoder/图论深搜理论基础.html#深搜三部曲
98.所有可达路径
https://kamacoder.com/problempage.php?pid=1170
代码随想录
https://www.programmercarl.com/kamacoder/0098.所有可达路径.html
广度优先搜索理论基础
https://www.programmercarl.com/kamacoder/图论广搜理论基础.html
图论基础
-
图种类
- 有向图和无向图;
- 加权无向图和加权有向图;
-
度
- 无向图:边的个数
- 有向图:入度(指向该节点的个数) 和 出入 (从该节点出发的个数)
-
连通性
- 无向图-连通图:任何节点都可以达到;
- 有向图- 强连通图:任何两个节点可以互相达到;
-
连通分量
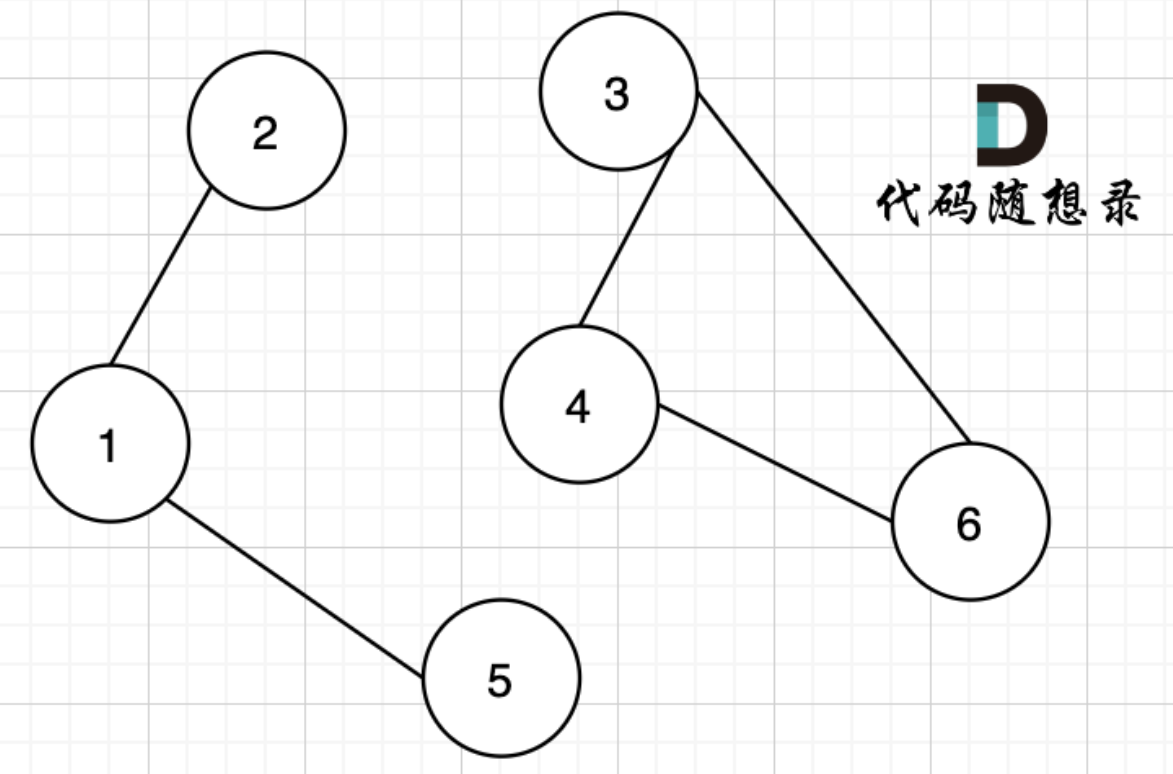
- 在无向图中:极大连通子图就是该图的连通分量;如下图的(1,2,5)节点和(3,4,6)节点;
![image]()
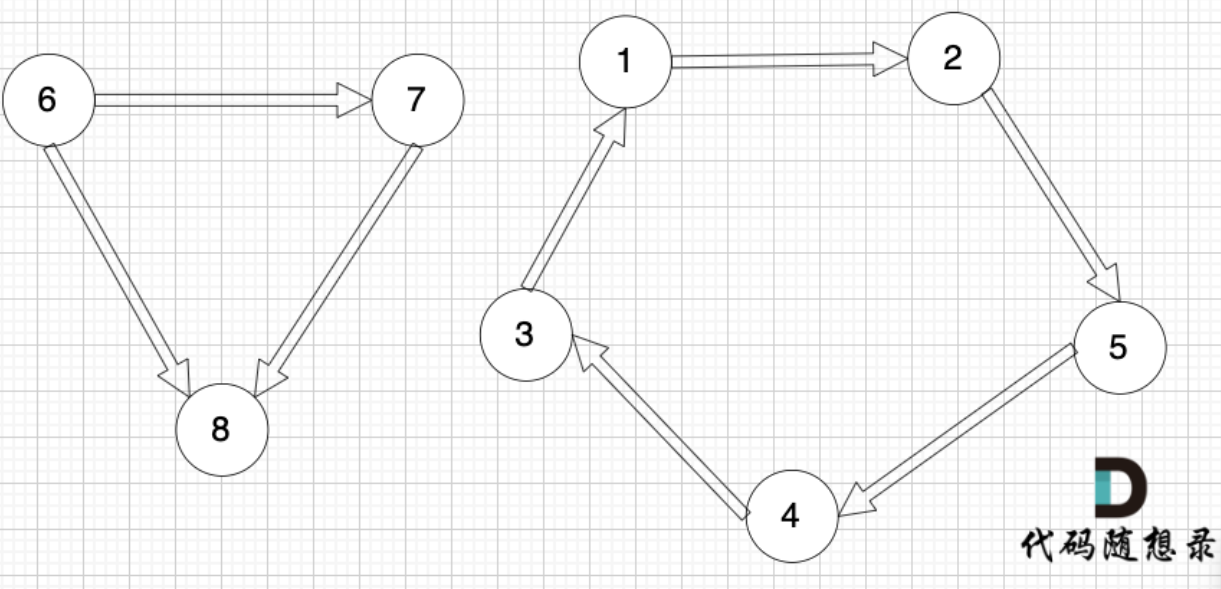
- 强连通分量:有向图中,极大强连通子图称之为该图的强连通分量;如下图(6,7,8)和(1,2,3,4,5)的图;
![image]()
- 在无向图中:极大连通子图就是该图的连通分量;如下图的(1,2,5)节点和(3,4,6)节点;
-
图的构造
- 邻接表;邻接矩阵;类;
- 朴素存储;邻接表;邻居矩阵;
-
邻接矩阵
- 二维数组表示图结构;
- 节点表示图
- grid[2][5]=6 grid[5][2]=6 说明grid中2和5节点中有一边;
-
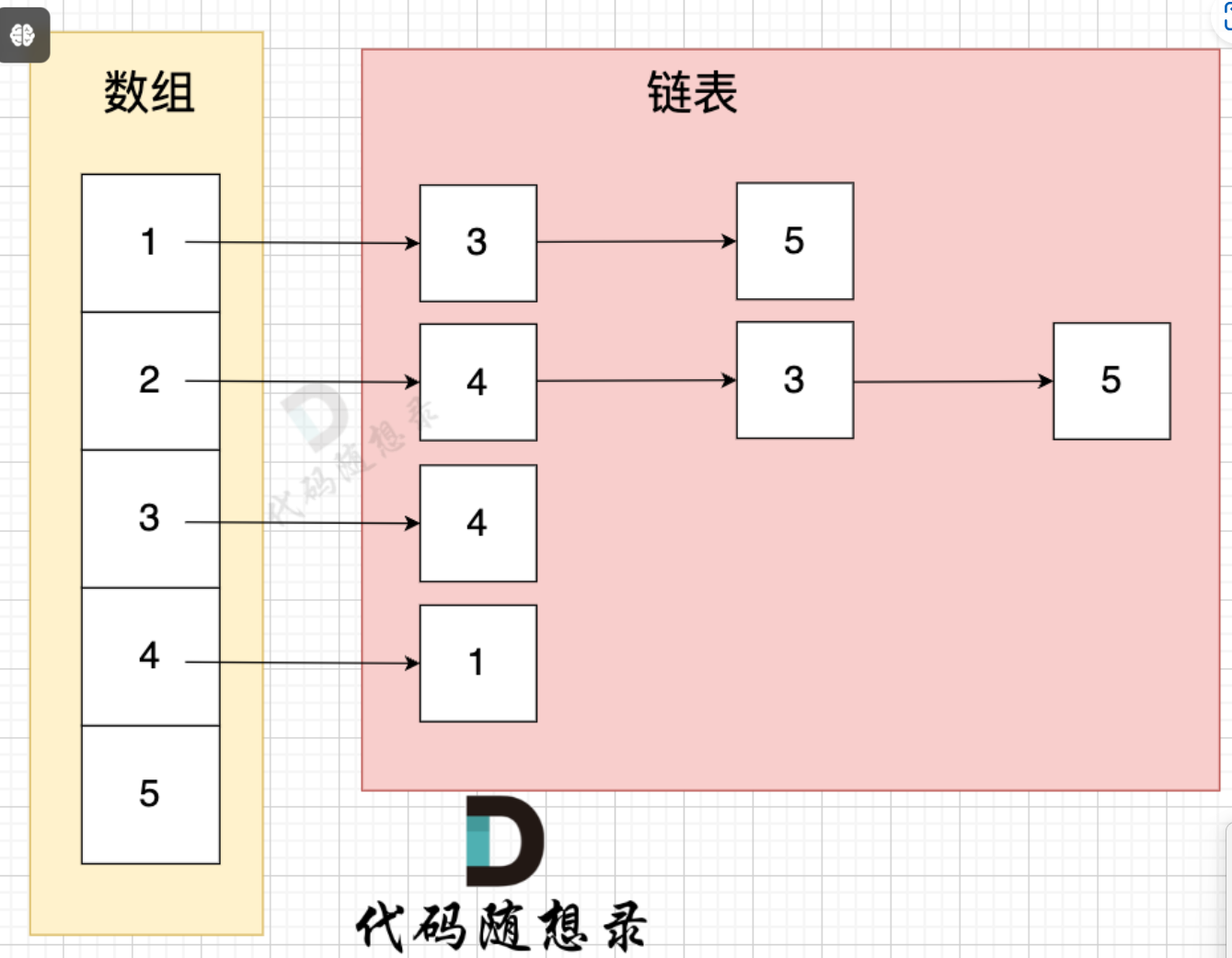
邻接表
- 数组+链表;
- 从边的角度存储图
![image]()
图的遍历方式
- 深度优先搜索(dfs)
- 广度优先搜索(bfs)
深度优先搜索理论基础
概念
- 向一个方向搜索,遇到绝境就回溯,继续;
代码框架
- 因为有路径回溯和路径选择;
- 所以是递归+回溯的过程;
void dfs(参数) {
if (终止条件) {
存放结果;
return;
}
for (选择:本节点所连接的其他节点) {
处理节点;
dfs(图,选择的节点); // 递归
回溯,撤销处理结果
}
}
深搜三部曲
- 确认递归函数、参数;
void dfs(参数)
- 二维数组保存所有路径;路径以一维数组保持;
- 全局变量保存
- 确认终止条件;
if (终止条件) {
存放结果;
return;
}
- 处理目前搜索节点出发的路径;
for (选择:本节点所连接的其他节点) {
处理节点;
dfs(图,选择的节点); // 递归
回溯,撤销处理结果
}
98. 所有可达路径
题解
采用邻接矩阵方式
- 该方式采用邻接矩阵方式存储数据
- 严格按照模版进行遍历
点击查看代码
```python
def dfs(graph,x,n,res,path):
if x==n:
res.append(path.copy())
return
for i in range(1,n+1):
if graph[x][i]==1:
path.append(i)
dfs(graph,i,n,res,path)
path.pop()
def main():
n,m = map(int,input().split())
graph =[[0]*(n+1) for _ in range(n+1)]
for i in range(m):
s,t = map(int,input().split())
graph[s][t] = 1
path = [1]
res = []
dfs(graph,1,n,res,path)
if not res:
print(-1)
return
for path in res:
print(" ".join(map(str,path)))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
```
</details>
采用邻接列表方式
-
采用 from collections import defaultdict方式
点击查看代码
from collections import defaultdict def dfs(graph,x,n,path,res): if x==n: res.append(path.copy()) return for i in graph[x]: path.append(i) dfs(graph,i,n,path,res) path.pop() def main(): n,m = map(int,input().split()) graph = defaultdict(list) for i in range(m): s,t = map(int,input().split()) graph[s].append(t) # print(graph) res = [] path = [1] dfs(graph,1,n,[1],res) if not res: print(-1) else: for path in res: print(" ".join(map(str,path))) if __name__ == '__main__': main()
广度优先搜索理论基础
使用场景
- 解决两点之间的最短路径问题
- 不涉及具体遍历方式,只要把相邻和相同属性的节点标记上即可;
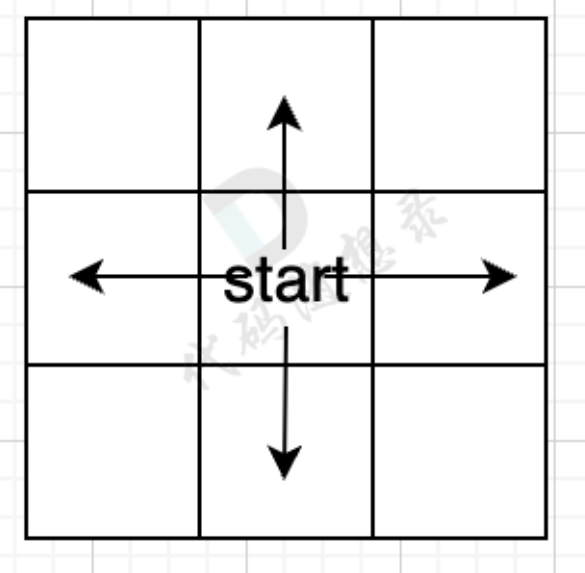
广搜过程
- 一圈一圈搜索
![image]()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号