Hadoop复习(2)MapReduce
核心思想(理解)

工作流程(理解)
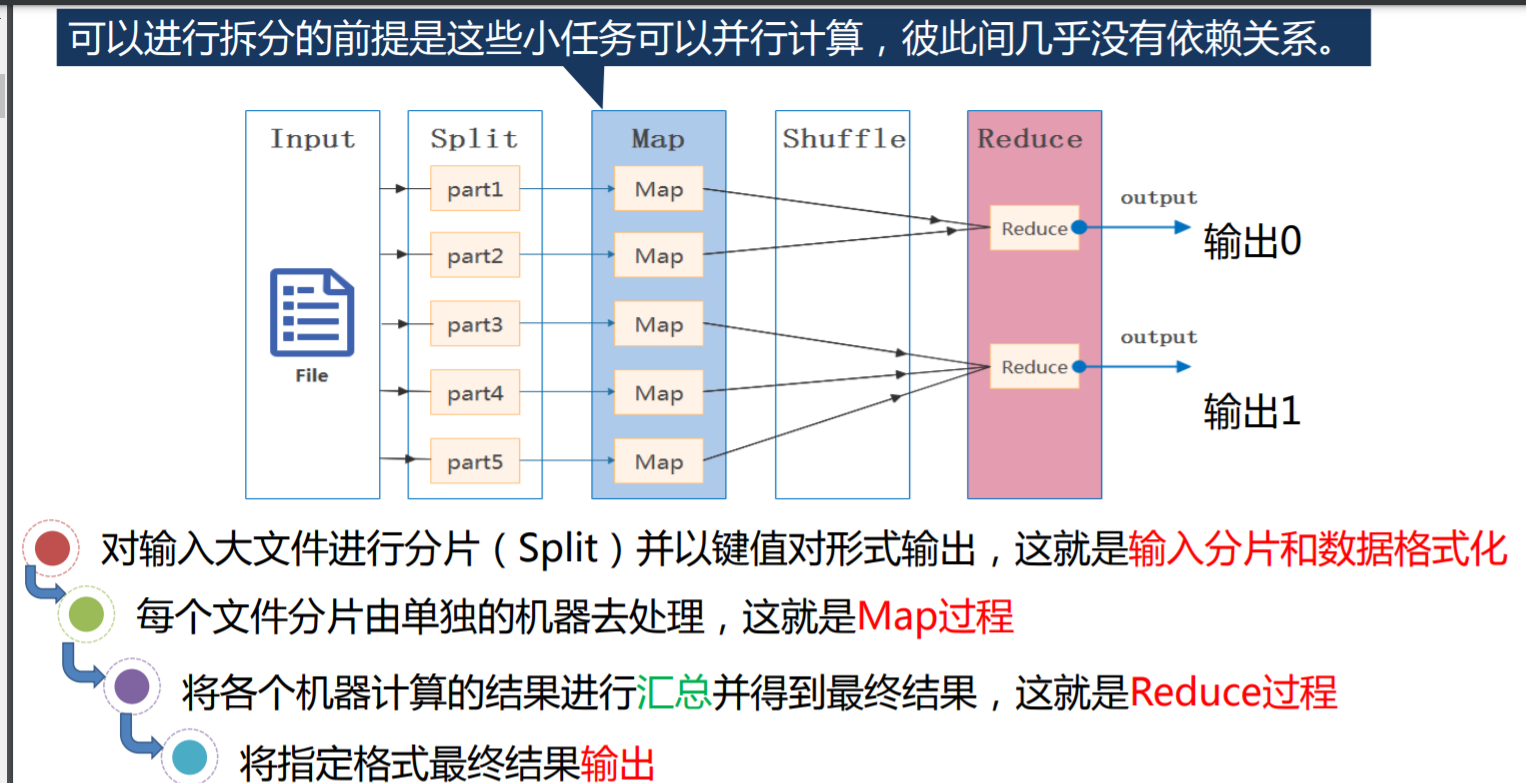
MapReduce 的 Shuffle 过程


Map端
1.写入缓存区,map函数的输出会先写入一个缓冲区,默认大小为100mb
2.溢写
一旦缓存内容达到阈值(默认为80%),一个后台线程便开始吧内容溢写入磁盘.
3.分区
在写磁盘前,首先根据数据划分相应的分区,如果有一个Combiner,它就在排序后的输出运行.
4.合并,排序
每次内容缓冲区达到溢出阈值,就会新建一个溢出文件(Spill File),以此在Map任务写完前,可能会有多个溢出文件.在任务完成之前,溢出文件被合并成一个已分区且已排序的输出文件。
注意点:
排序结束后,用户可根据实际需求选择是否要执行合并操作,只有预先定义了 Combine()函数,才会执行合并操作即合并操作并不是必须的
排序默认按key排序
最后一步:归并(merge)

整体流程图:注意这里merge应该改成归并
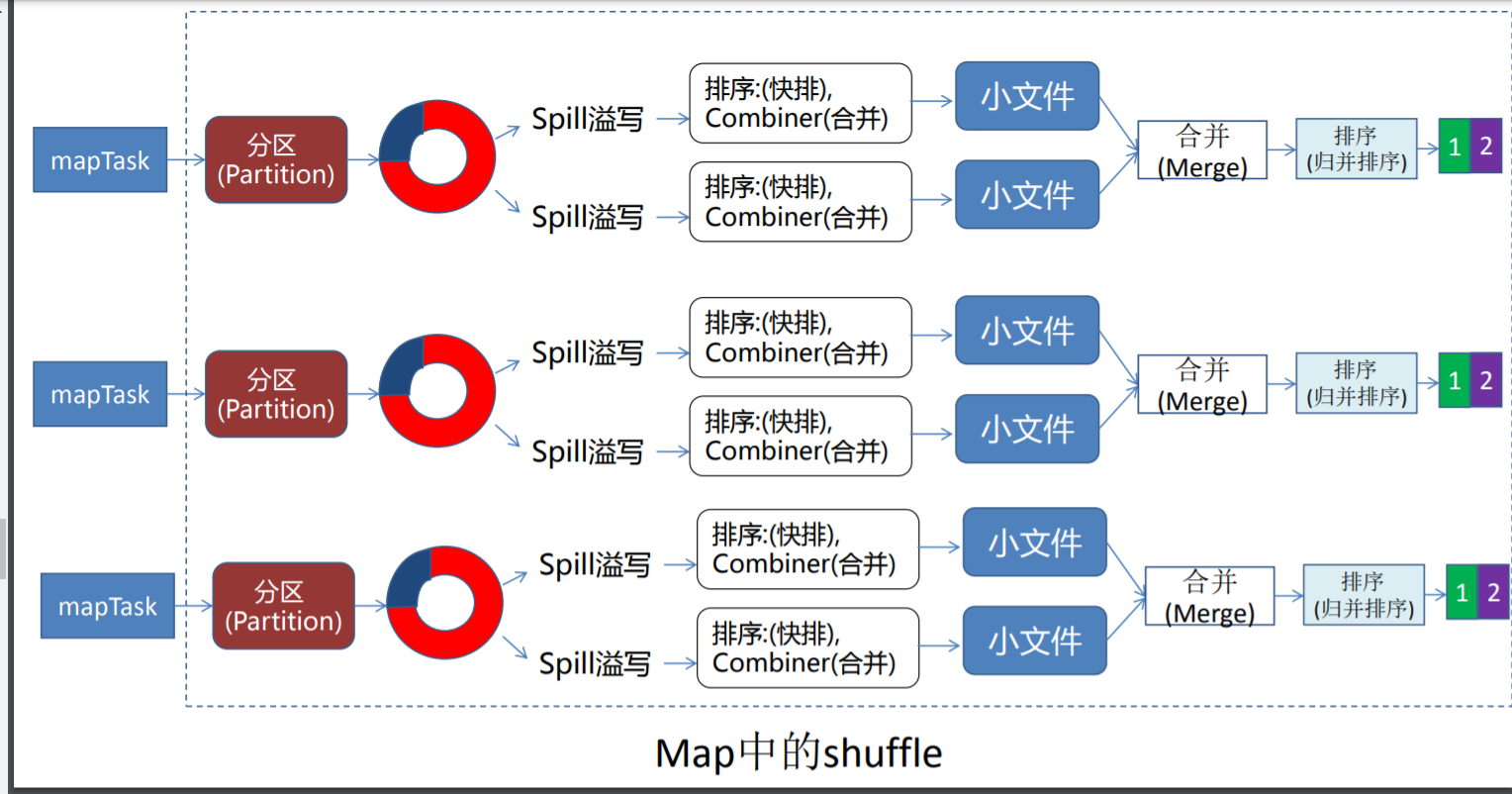
Rdeuce端

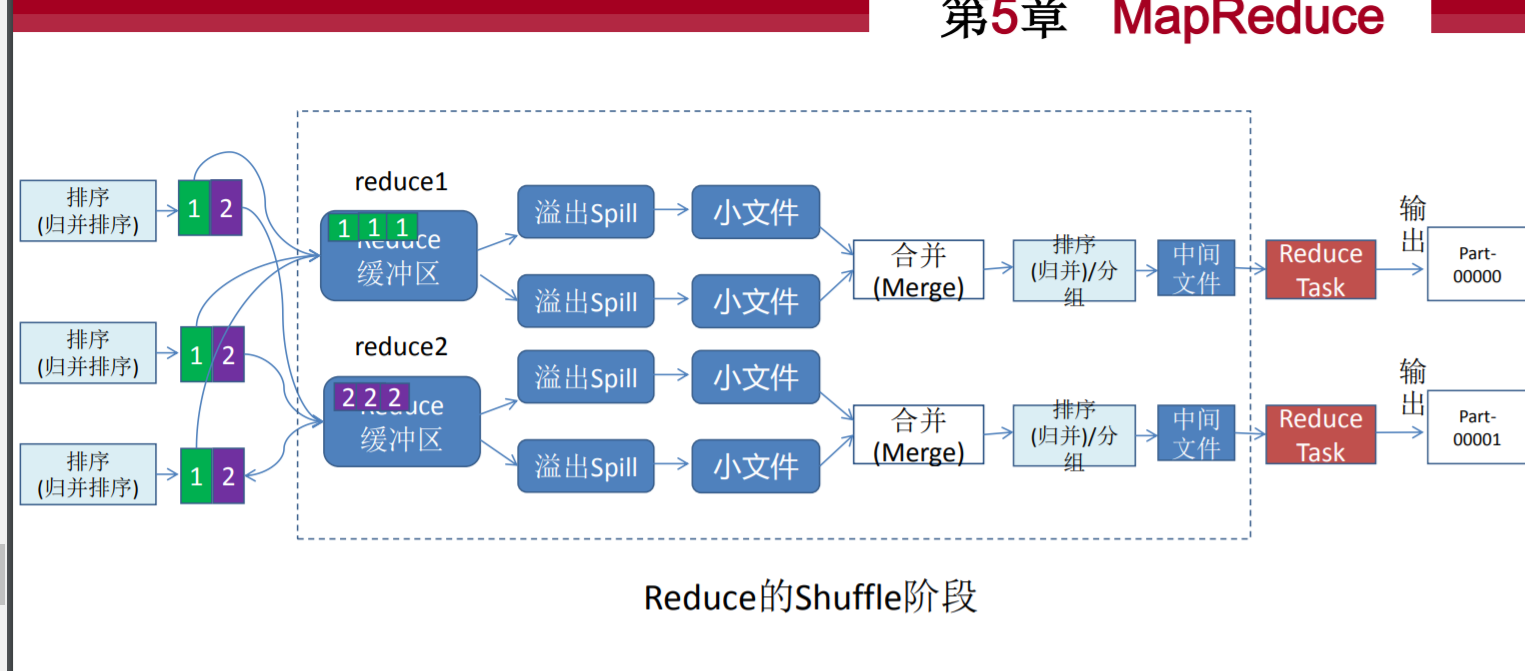
MapReduce 体系结构主要包含哪四个部分,这四个部分的主要作用

简单代码分析
词频统计
Mapper函数:
public static class WordCountMapper extends
Mapper<LongWritable,Text,Text,LongWritable> {//对应v1,k1,v2,k2类型
//通常来说v1规定为LongWritable k1,v2,k2则需要根据题目去规定类型
@Override
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws
IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString(); //获取value中的值
String[] split = line.split(","); //分词 通过逗号分割单词
//如果输入的是 hello,jie 那么就返回一个数组内容是 [hello] [jie]
for (String word : split) {
context.write(new Text(word),new LongWritable(1)); //输出
//构造出一种映射关系
//如上面的例子最后结果就是 {hello,1} {jie,1}
//这样后续吧 key 相同的 value加上去就是词频统计
}
}
Reducer函数:
public static class WordCountReducer extends Reducer<Text,LongWritable,Text,LongWritable>//对应k3,v3 k4,v4
{
/**
* 自定义我们的reduce逻辑
* 所有的key都是我们的单词,所有的values都是我们单词出现的次数
* @param key ,@param values ,@param context
*/
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<LongWritable> values,//这里Iterable<LongWritable>类型 是因为map后经过shuffle过程的归并
Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {//比如出现了3次jie 那么在map后会有3个{jie,1},shuffle会将key相同的进行归并
//最后变成{jie,1,1,1} 我们只需要遍历循环加上value就完成词频统计了
long count = 0;
for (LongWritable value : values) {
count += value.get(); //统计
}
context.write(key,new LongWritable(count));
}
}
大数据例题
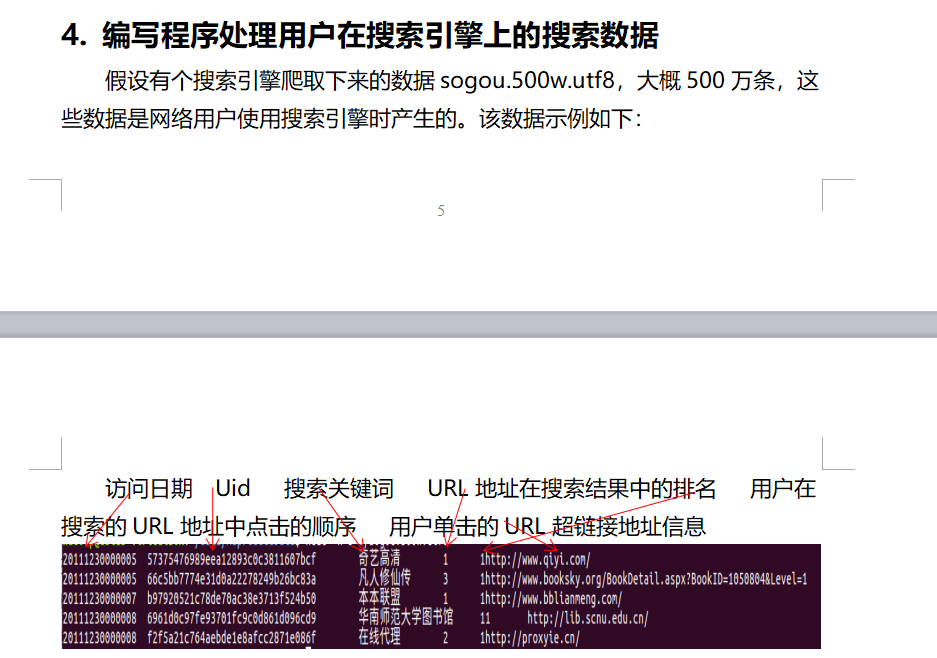
请编写程序实现统计出搜索关键词出现次数大于7000次的搜索关键词。
其实就是磁频统计,在reduce阶段计算出次数,如果超过7000才写入context
map函数:
public static class TokenizerMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
public TokenizerMapper() {
}
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper< LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException
{
String data=value.toString();
String[] words=data.split("\\s+");
//获取关键词 \\s+代表分割一到多个空格
//数组下标为2时对应关键词
context.write(new Text(words[2]), new IntWritable(1));
}
}
reduce函数:
public static class IntSumReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
public IntSumReducer() {
}
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException
{
int total=0;
for(IntWritable v:values) {
total+=v.get();
}
if(total>7000) {
context.write(key, new IntWritable(total));
}
}
}
}
请编写程序实现获取URL排名第二、用户点击顺序第一的日志
这个比较简单就不说了。
薪水分区
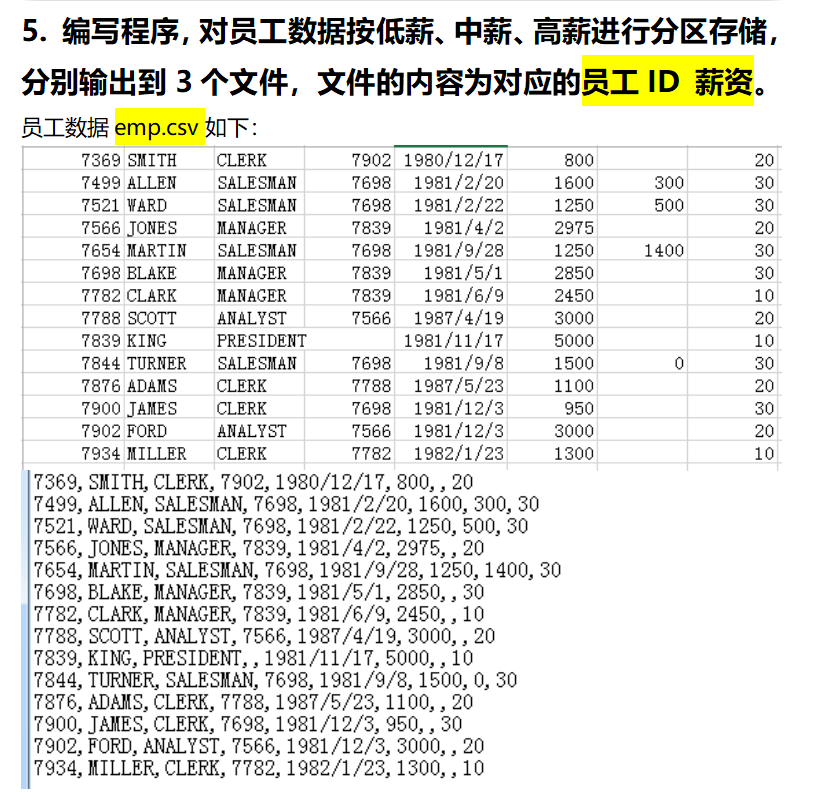
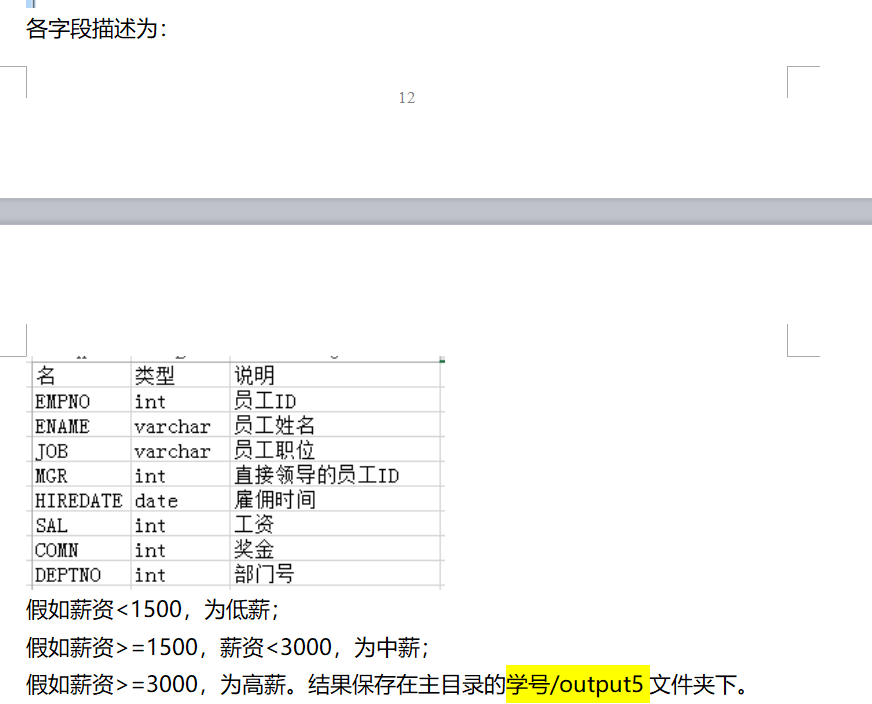
满足要求就必须去自定义一个分区规则
map函数:
public static class TokenizerMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
public TokenizerMapper() {
}
//这一大串就是写一个判断有无奖金方法 不是重点
public static boolean isNumeric(final String str) {
// null or empty
if (str == null || str.length() == 0) {
return false;
}
try {
Integer.parseInt(str);
return true;
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
try {
Double.parseDouble(str);
return true;
} catch (NumberFormatException ex) {
try {
Float.parseFloat(str);
return true;
} catch (NumberFormatException exx) {
return false;
}
}
}
}
@Override
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper< LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException
{
String data=value.toString();
String[] words=data.split(",");
//获取关键词
int temp=0;
if(isNumeric(words[6])) {//判断有无奖金
temp=Integer.parseInt(words[6]);
}
System.out.println(temp);
//建立 员工姓名和金钱对应关系
context.write(new Text(words[1]), new IntWritable(Integer.parseInt(words[5])+temp));
}
}
reduce函数 老老实实吧value加上去就好 没什么要干的
public static class IntSumReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
public IntSumReducer() {
}
@Override
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException
{
int total=0;
for(IntWritable v:values) {
total+=v.get();
}
context.write(key, new IntWritable(total));
}
}
}
分区规则,记住语法怎么写就好
Partitioner<Text,IntWritable>{
public int getPartition(Text key,IntWritable value,int
numPartitions) {
final int money=value.get();
if(money<1500)
return 0%numPartitions;
else if(money>=1500 && money<3000)
return 1%numPartitions;
else
return 2%numPartitions;
}
}
比较复杂的题目(重要在于理解shuffle过程)
文件合并和去重操作

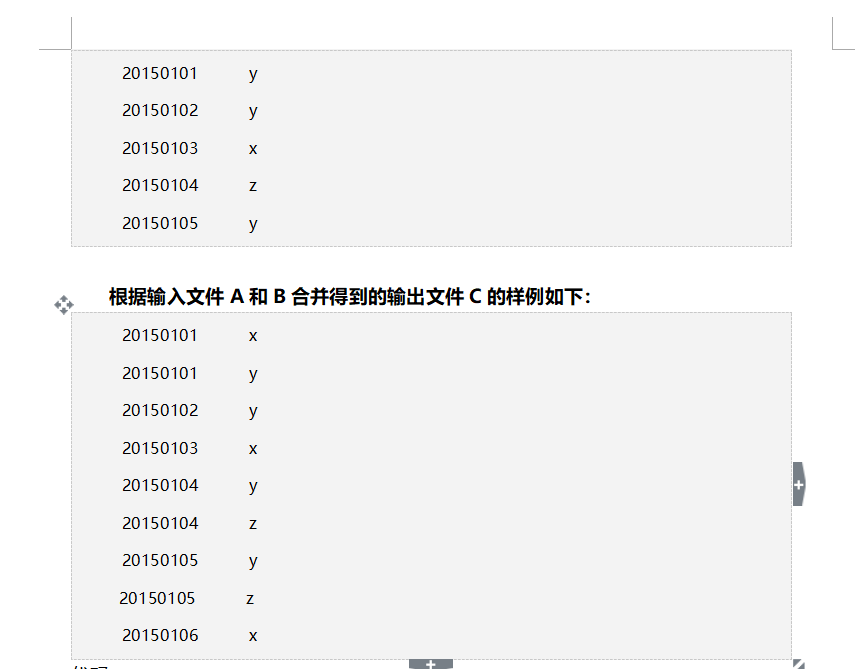
思路:
啥都不用干! 吧文本内容当成key,value设置成空
shuffle过程的归并会吧key相同的value归并起来 这里我们设置value为空 这样就实现了去重操作
map函数
public static class TokenizerMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable> {
public TokenizerMapper() {
}
@Override
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper< LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException
{
context.write(value, NullWritable.get());
}
}
reduce函数
public static class IntSumReducer extends Reducer<Text, NullWritable, Text, NullWritable> {
public IntSumReducer() {
}
@Override
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<NullWritable> values,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException
{
context.write(key,NullWritable.get());
}
}
}
文件的排序
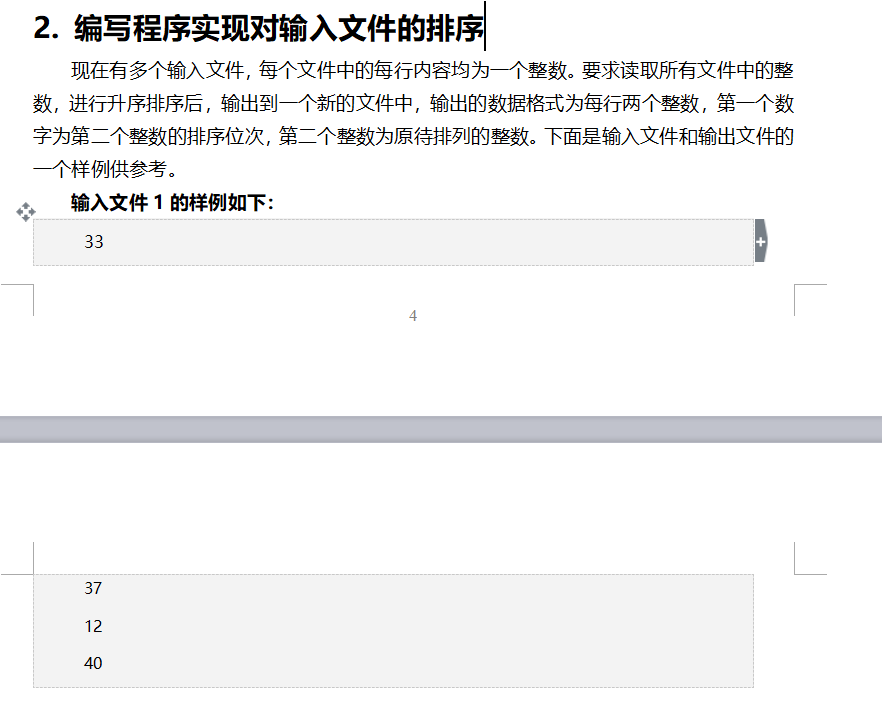

shuffle过程会根据key进行排序,所以吧文本的数字提取出来当做key就实现了排序
map函数
public static class TokenizerMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, IntWritable, Text> {
public TokenizerMapper() {
}
private Text val = new Text("");//和value设置成null 本质一样的操作
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
if(line.trim().length()>0){
context.write(new IntWritable(Integer.valueOf(line.trim())), val);
}
}
}
reduce函数
设置num为1 然后每次写入num+1 就实现了要求的前面那个数字
public static class IntSumReducer extends Reducer<IntWritable, Text, IntWritable, IntWritable> {
public IntSumReducer() {
}
private IntWritable num = new IntWritable(1);
@Override
public void reduce(IntWritable key, Iterable<Text> values,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for(Text val:values){
context.write(num, key);
num = new IntWritable(num.get()+1);
}
}
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号