Java集合综述
Java集合图,虚线框为接口,实线框是具体的类
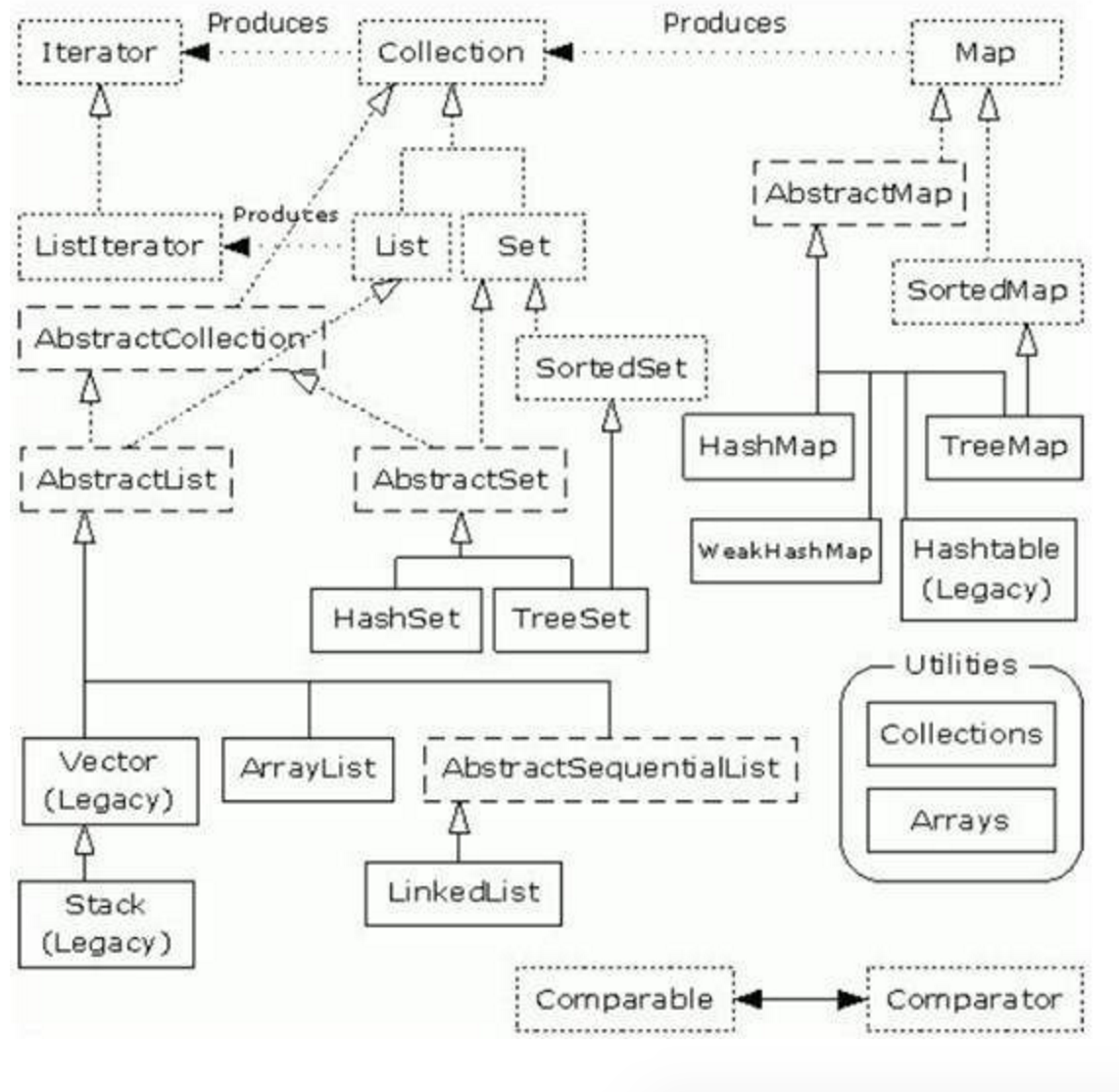
具体实现类
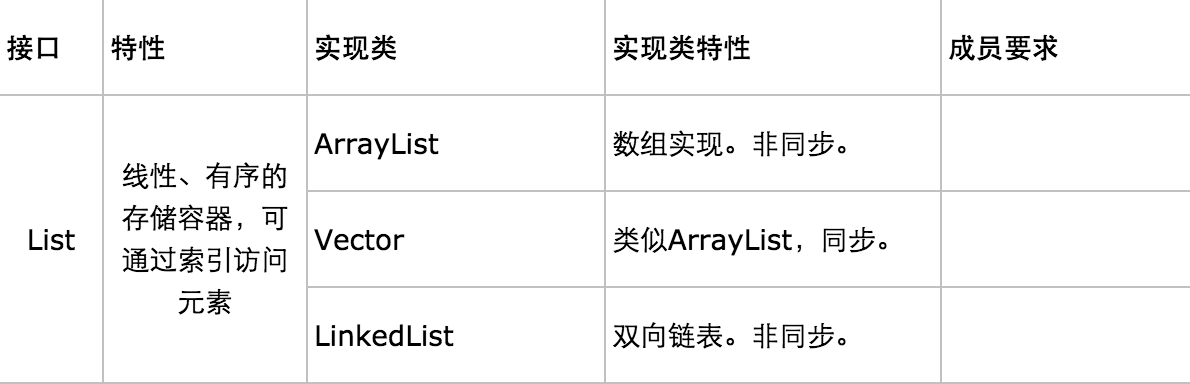
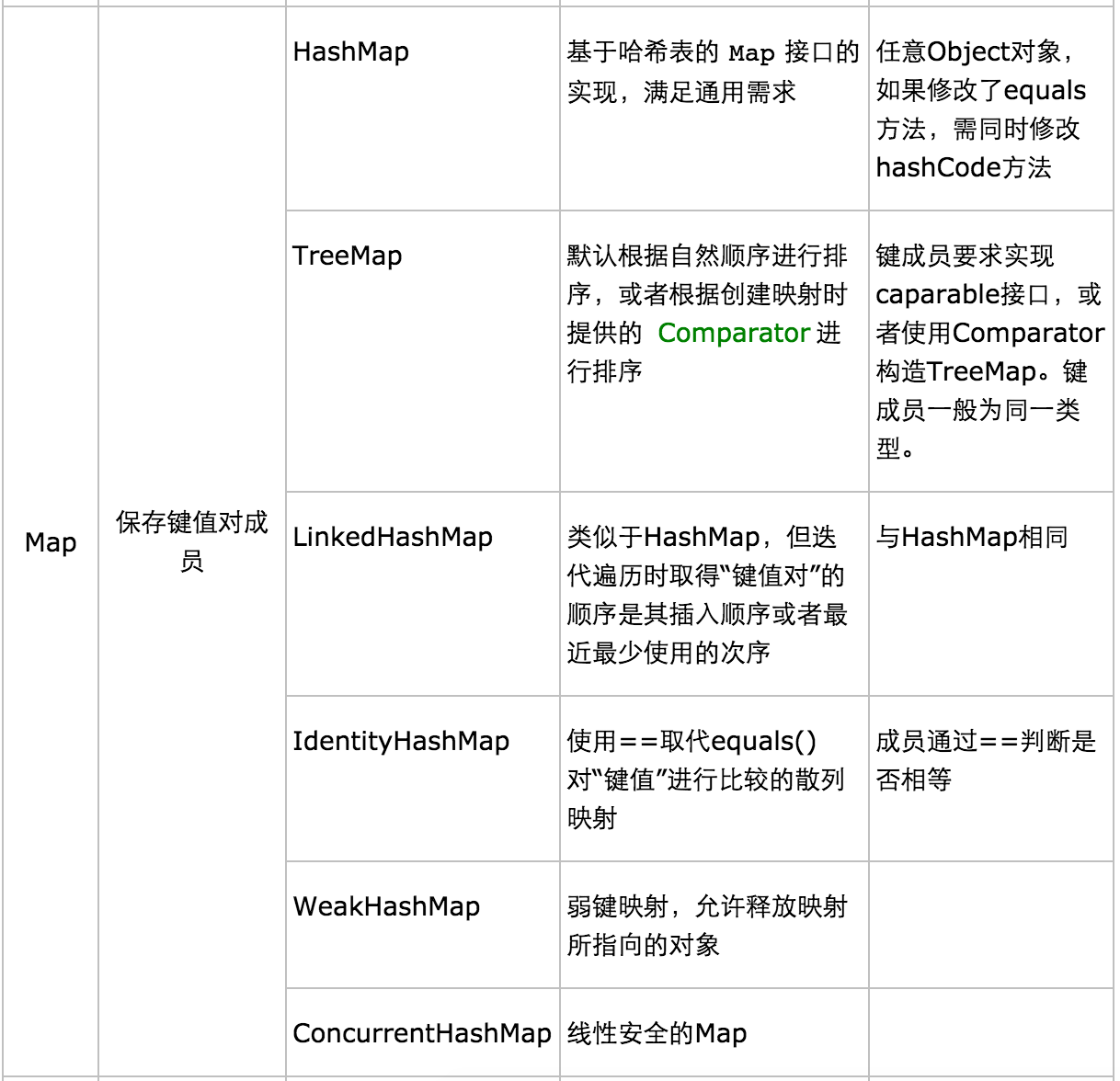

基本使用
(1)List:
List基本操作
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<String>();
arrayList.add("Tom");
arrayList.add("Jerry");
arrayList.add("Micky");
// 使用Iterator遍历元素
Iterator<String> it = arrayList.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
String str = it.next();
System.out.println(str);
}
// 在指定位置插入元素
arrayList.add(2, "Kate");
// 通过索引直接访问元素
for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(arrayList.get(i));
}
List<String> subList = new ArrayList<String>();
subList.add("Mike");
// addAll(Collection<? extends String> c)添加所给集合中的所有元素
arrayList.addAll(subList);
// 判断是否包含某个元素
if (arrayList.contains("Mike")) {
System.out.println("Mike is include in the list");
}
LinkedList<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<String>();
linkedList.addAll(arrayList);
// 获取指定元素
System.out.println(linkedList.get(4));
// 获取第一个元素
System.out.println(linkedList.getFirst());
// 获取最后一个元素
System.out.println(linkedList.getLast());
// 获取并删除第一个元素
System.out.println(linkedList.pollFirst());
// 获取,但不移除第一个元素
System.out.println(linkedList.peekFirst());
(2)Map:
Map基本操作
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
// 向Map中添加元素
map.put("Tom", 26);
map.put("Jack", 18);
map.put("Micky", 17);
map.put("Kate", 15);
// 根据Key获取Value
System.out.println("Jack is " + map.get("Jack") + " years old");
// 移除
map.remove("Micky");
// 遍历Map
for (Entry<String, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("name:" + entry.getKey() + " age:"
+ entry.getValue());
}
// Key相同的元素将被覆盖
map.put("Jack", 19);
// 根据Key获取Value
System.out.println("Jack is " + map.get("Jack") + " years old");
// 判断是否包含某个Key
if (map.containsKey("Tom")) {
System.out.println(map.get("Tom"));
}
// 判断是否包含某个Value
if (map.containsValue(26)) {
System.out.println("The map include the value 26");
}
// 判断map是否为空
if (!map.isEmpty()) {
// 获取map大小
System.out.println("The map's size=" + map.size());
}
// 获取Key的集合
for (String str : map.keySet()) {
System.out.println(str);
}
TreeMap<String, Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<String, Integer>();
treeMap.putAll(map);
// 输出内容按照key值排序
for (Entry<String, Integer> entry : treeMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("name:" + entry.getKey() + " age:"
+ entry.getValue());
// name:Jack age:19
// name:Kate age:15
// name:Tom age:26
}
LinkedHashMap<String, Integer> linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap<String, Integer>();
// 向Map中添加元素
linkedHashMap.put("Tom", 26);
linkedHashMap.put("Jack", 18);
linkedHashMap.put("Micky", 17);
linkedHashMap.put("Kate", 15);
// 保持了插入的顺序
for (Entry<String, Integer> entry : linkedHashMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("name:" + entry.getKey() + " age:"
+ entry.getValue());
// name:Tom age:26
// name:Jack age:18
// name:Micky age:17
// name:Kate age:15
}
(3)Set:
Set基础操作
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
HashSet<Integer> hashSet = new HashSet<Integer>();
hashSet.add(1);
hashSet.add(3);
hashSet.add(2);
hashSet.add(6);
// 重复元素将不能被添加
hashSet.add(3);
// 只要有元素被添加就返回true
if (hashSet.addAll(list)) {
System.out.println("Add success");
}
// 判断是否存在某个集合
if (hashSet.containsAll(list)) {
System.out.println("The hashSet is contain 3 and 4");
}
Iterator<Integer> it = hashSet.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(it.next() + " ");
// 1 2 3 4 6
// 看结果是被排序了,HashSet按照Hash函数排序,Integer值的HashCode就是其int值
}
// 换转成数组
Object[] integers = hashSet.toArray();
for (int i = 0; i < integers.length; i++) {
System.out.print((Integer) integers[i]);
}
//移除元素
hashSet.remove(3);
TreeSet<String> treeSet = new TreeSet<String>();
treeSet.add("C");
treeSet.add("A");
treeSet.add("D");
treeSet.add("B");
for (Iterator<String> strIt = treeSet.iterator(); strIt.hasNext();) {
System.out.print(strIt.next());
// ABCD 按照字母顺序
}
LinkedHashSet<String> linkedHashSet = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
linkedHashSet.add("C");
linkedHashSet.add("A");
linkedHashSet.add("D");
linkedHashSet.add("B");
for (Iterator<String> linkedIt = linkedHashSet.iterator(); linkedIt
.hasNext();) {
System.out.print(linkedIt.next());
// CADB 按照插入顺序
}
(1)使用集合类时需要指定范型参数,否则是按Object类型存储的,取出时需要强制类型转换,并且通过范型可以在编译器进行验证
(2)Object的toString()方法返回类名+hashCode()
(3)所有基本类型都不能放入容器,自动包装机制会进行双向转换
(4)类库两个根类接口Collection、Map
一、List:像数组一样,List也建立与数字索引与对象间的关联
ArrayList:长于随机访问
LinkedList:长于插入删除元素,有使其可以作为栈、队列、双端队列的方法
Interator:迭代器,是一个对象,作用是遍历并返回序列中的对象,Java中迭代器只能单向移动,编码时可以使用interator摆脱对容器类型编码
(1)interator()要求容器返回一个interator
(2)next()返回下一个元素
(3)hasNext()检查是否还有下一个元素
(4)remove()返回最近元素
ListInterator:可以双向移动,但只能由List返回
二、Set:不保存重复元素,(除了TreeSet)与Collection具有完全相同的接口,必须为放入集合的类型创建equals()方法
HashSet(默认该选择):对速度进行了优化
TreeSet:保持次序,底层使用红黑树
LinkedList:使用了散列,但维护了插入顺序
三、Map:HashMap用来快速访问,TreeMap保持了键处于排序状态,LinkedHashMap保持元素插入状态,但是也通过散列加快访问速度
四、优先队列:声明下一个弹出对象具有最高优先级
Collection和Interator:
AbstractCollection抽象类实现了Collection接口,除了size()和interacor()如果想要遍历自己建立的类可以
继承AbstractCollection:实现两个方法
实现Collcetion:实现很多方法
生成interactor:只需创建interator()方法(类中四个方法)
Foreach迭代器:任何继承了Iterable接口的类都可以使用foreach





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号