软件工程第一次编程作业
| 软件工程 | 班级链接 |
|---|---|
| 作业要求 | 作业要求链接 |
| 作业要求目标 | 实现论文查重功能 |
PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 60 | 30 |
| Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 1860 | 1865 |
| Development | 开发 | 600 | 480 |
| Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 600 | 600 |
| Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 120 | 180 |
| Design Review | 设计复审 | 30 | 60 |
| Coding Standard | 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 30 | 15 |
| Design | 具体设计 | 60 | 80 |
| Coding | 具体编码 | 600 | 480 |
| Code Review | 代码复审 | 30 | 65 |
| Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 120 | 180 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 60 | 15 |
| Test Report | 测试报告 | 60 | 30 |
| Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 60 | 120 |
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 60 | 10 |
| 合计 | 1860 | 1865 |
设计过程
需求分析
-
一开始觉得要实现一个论文查重系统有很多的功能需要实现,不过搜索了一下资料发现其实很多功能调用已有的接口就可以实现。
研究了几个方法,一个是用SimHash算法然后算海明距离。SiMHash主要有分词、Hash、加权、合并、降维几个步骤,然后用海明距离算相似度。不过后面选择了比较多人用的通过jieba分词然后用余弦相似度来算相似度。搜索资料过程中发现Gensim库是一个比较擅于处理自然语言的工具包,同时Gensim支持文档的流式处理,可优化内存于是决定使用。但是实际运用过程中发现调用的接口对于我来说还是比较难学习。。。
设计文档
我先是了解了下Gensim的原理
- 主要参考文章 What is Gensim?
- 安装Gensim
pip install gensim
- 预处理语料:使用gensim提供的预处理函数来对文本进行预处理。这些预处理函数可以删除标点符号、停用词和数字,将文本转换为小写,并使用词干提取器将单词转换为其基本形式。
def preprocess(text):
return preprocess_string(text)
original_preprocessed = preprocess(original_text)
plagiarized_preprocessed = preprocess(plagiarized_text)
实际使用发现这个功能并没有很好的处理好,也是导致论文查重率结果异常的模块
- 创建文档对象:使用gensim的corpora.Dictionary类创建文档对象。将预处理的文本作为输入,并使用字典的add_documents()方法将其添加到文档对象中。
dictionary = corpora.Dictionary()
dictionary.add_documents([original_preprocessed, plagiarized_preprocessed])
- 创建语料库,将文本转换为稀疏向量:使用字典的doc2bow()方法将预处理的文本转换为词袋表示法。这将创建一个稀疏矩阵,其中每行代表一个文档,每列代表一个单词。每个单元格的值表示相应单词在相应文档中出现的次数。
plagiarized_corpus = [dictionary.doc2bow(doc) for doc in [plagiarized_preprocessed]]
doc2bow函数将文本转换为词袋模型,还需使用TF-IDF模型将其转换为向量。:
tfidf = models.TfidfModel(corpus)
- 计算相似度
index = similarities.Similarity('index', [original_corpus], num_features=len(dictionary))
similarities = index[plagiarized_corpus][0]
具体设计
- 文件的预处理还是使用了jieba分词,一个preprocessed的接口比较麻烦,另一个是处理出来的结果比较异常
![img]()
def preprocessed(text):
text = jieba.lcut(text)
preprocessed = []
for word in text:
if (re.match(u"[a-zA-Z0-9\u4e00-\u9fa5]", word)):
preprocessed.append(word)
else:
pass
return preprocessed
注释:re.match(pattern,string,flags=0)
从一个字符串的开始位置起匹配正则表达式返回match对象
pattern,表示正则中的模式字符串
string,即表示要被处理的字符串
- 计算相似度部分在代码中注释了,原理和前面介绍的差不多,但是没有用TF-IDF模型,接口还需要研究一下
texts=[original_preprocessed,plagiarized_preprocessed]
dictionary = corpora.Dictionary(texts)
corpus = [dictionary.doc2bow(text) for text in texts]
similarity = similarities.Similarity('-Similarity-index', corpus, num_features=len(dictionary))
test_corpus_1 = dictionary.doc2bow(original_preprocessed)
cosine_sim = similarity[test_corpus_1][1]
return cosine_sim
-
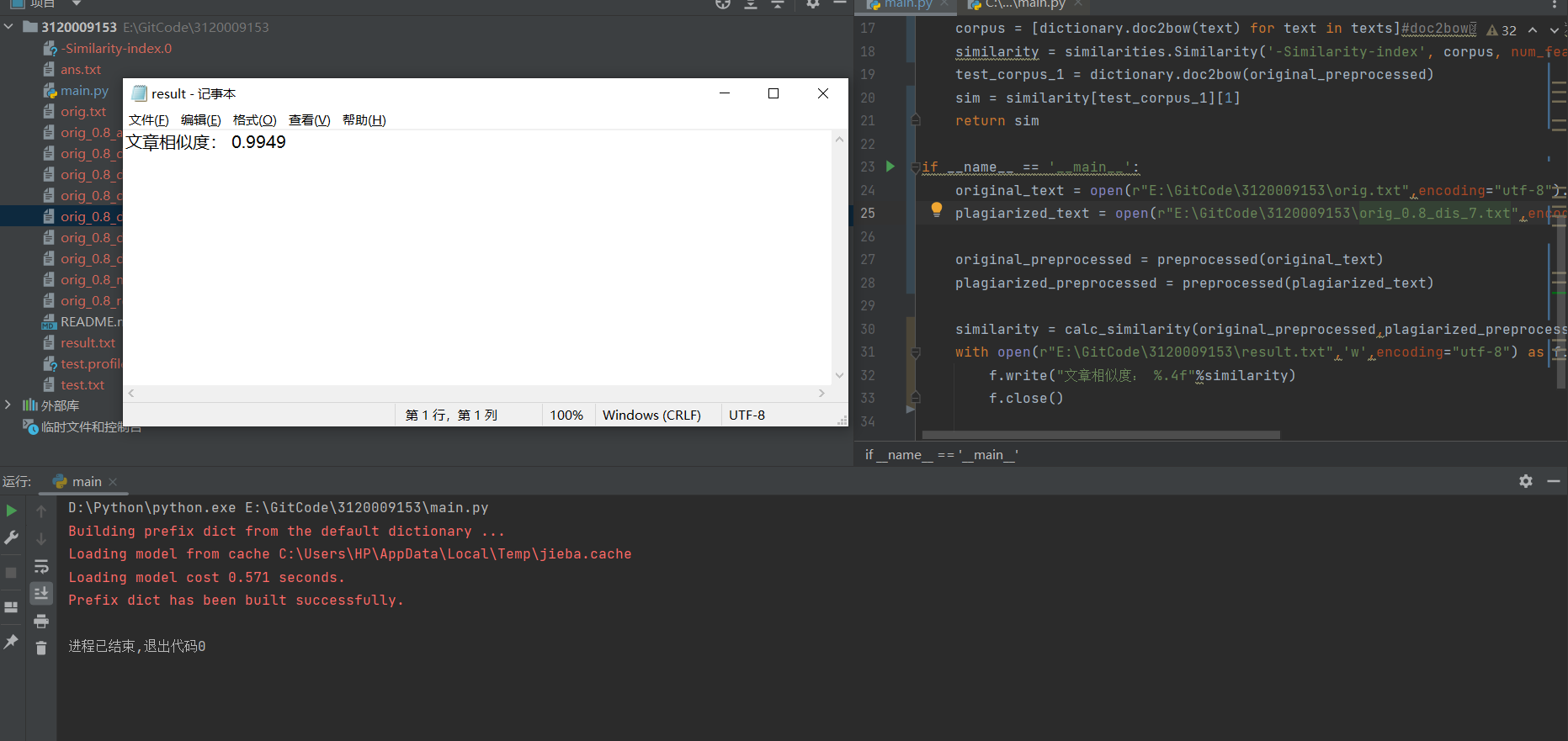
部分结果
与orig_0.8_dis_7.txt
![img]()
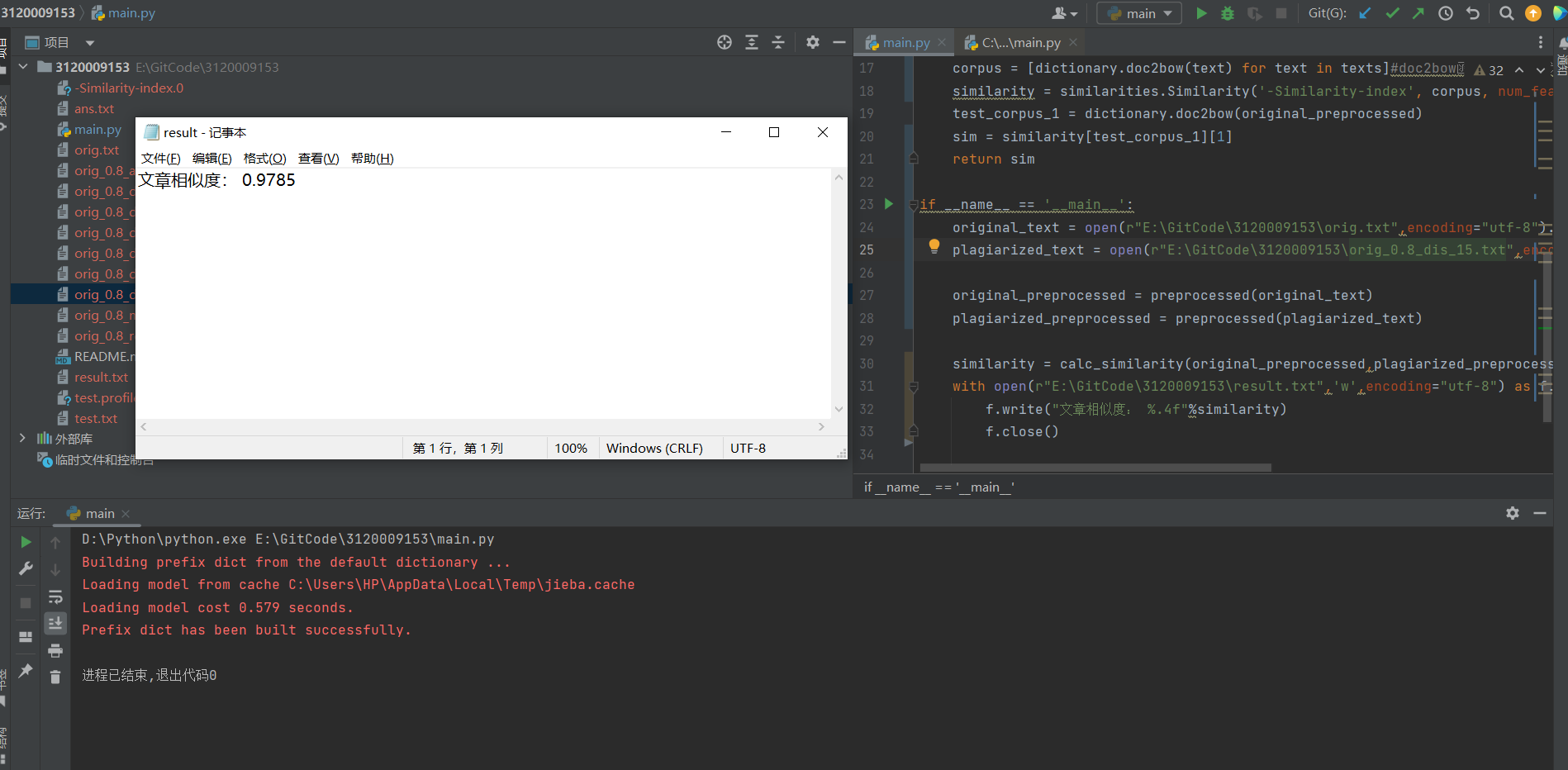
与orig_0.8_dis_15.txt
![img]()
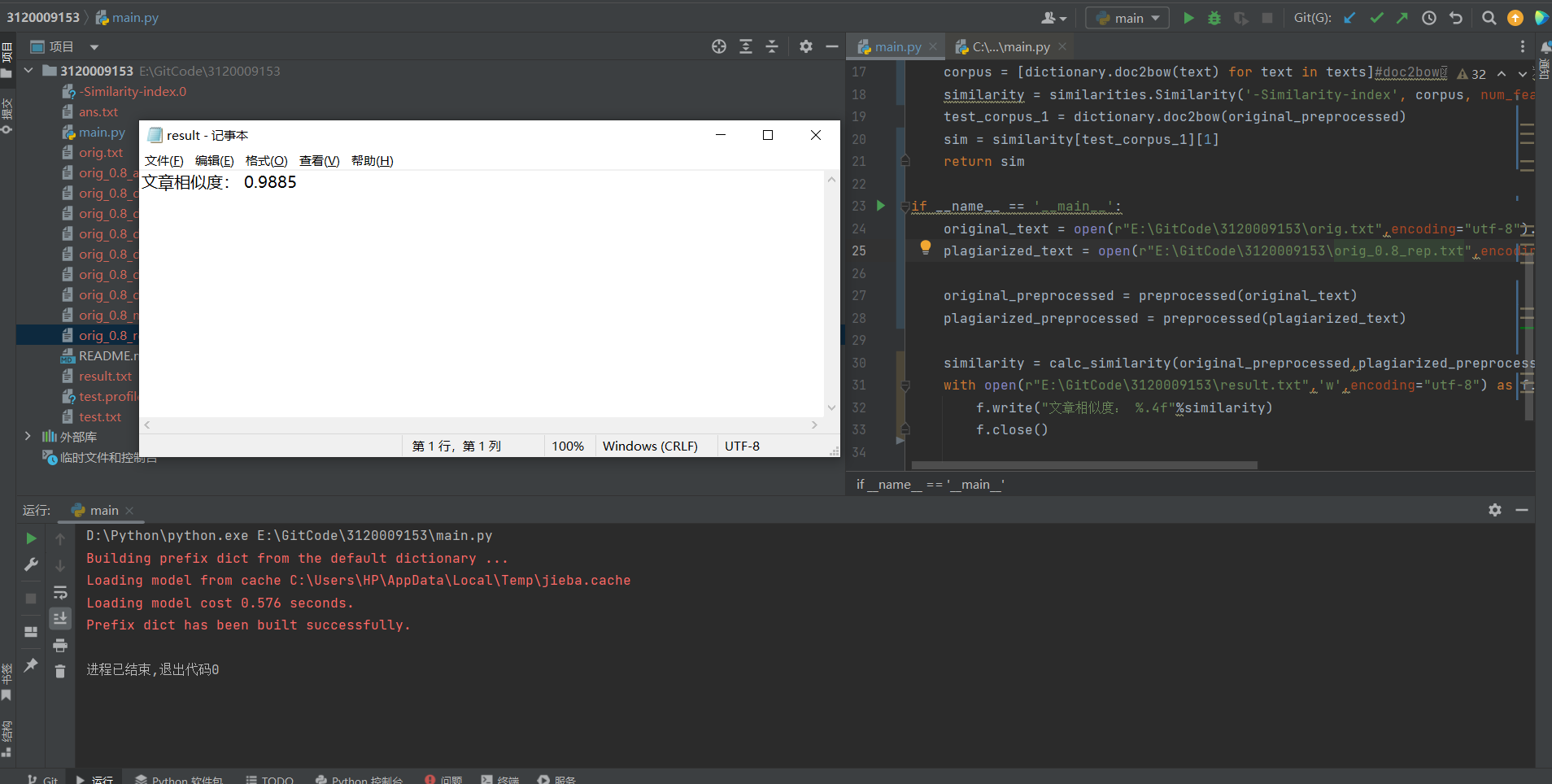
与orig_0.8_rep.txt
![img]()
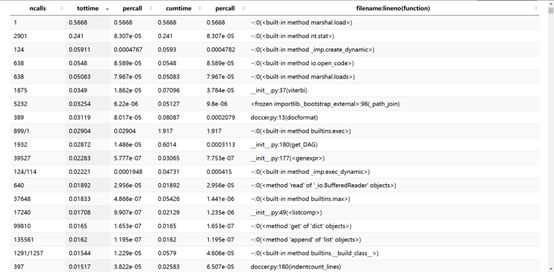
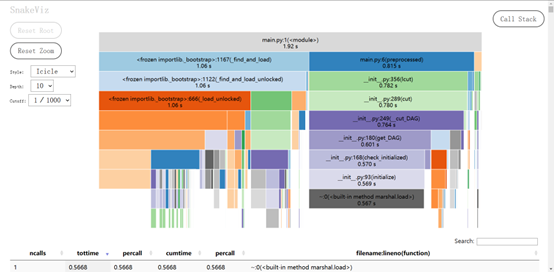
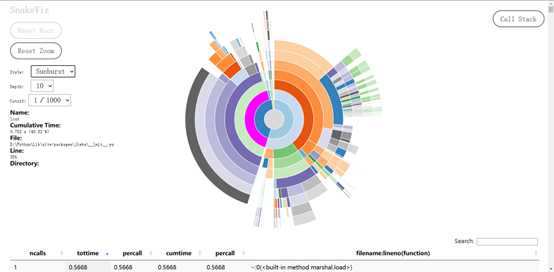
计算模块接口部分的性能
使用了SnakeViz
使用 cProfile 生成统计文件
python -m cProfile -o test.profile main.py
用 SnakeViz 对 cProfile 进行可视化
snakeviz test.profile
测试用例
测试了一下主要功能,输入了两篇一样的文本,测试similarity的值是否为1
python -m unittest

OK
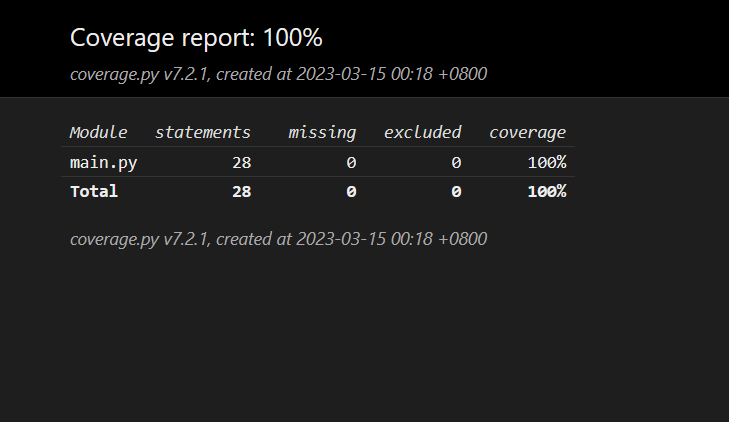
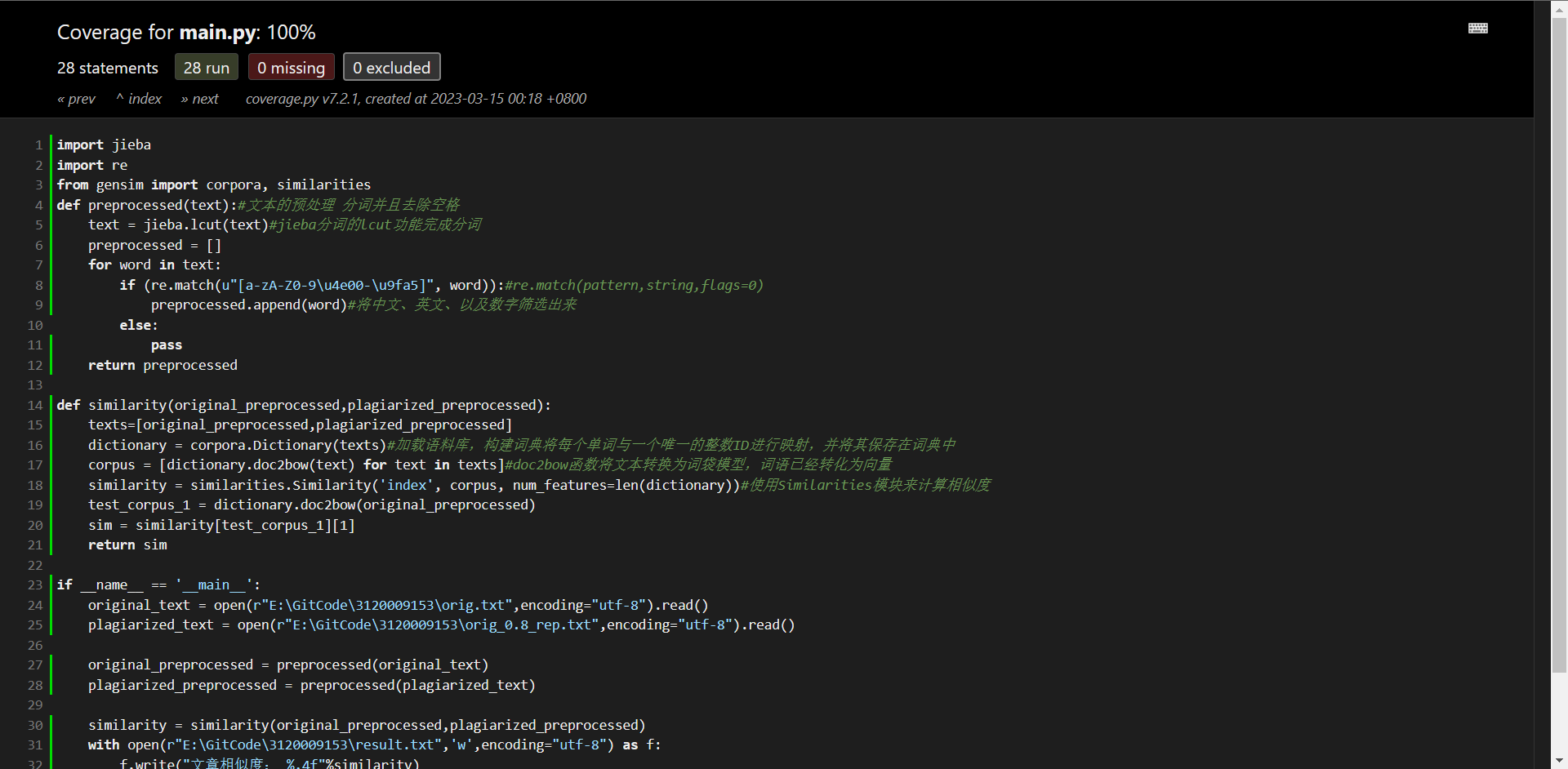
代码覆盖率
coverage run test.py
coverage report
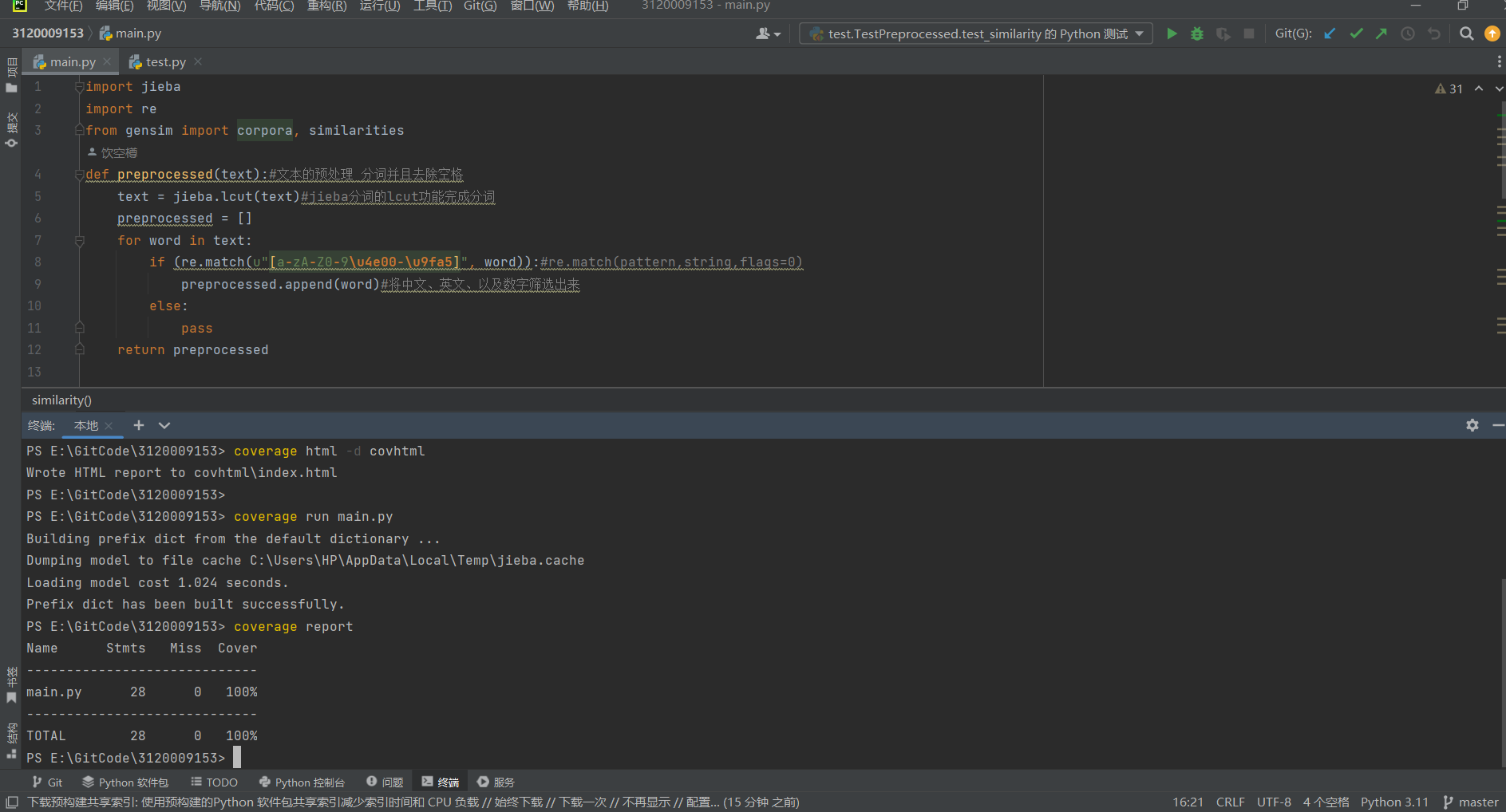
coverage html -d covhtml



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号