搭建注册中心
服务治理
RPC远程调用框架的核心技术思想:在于注册中心,使用注册中心管理每个服务与服务之间的依赖关系叫做服务治理
为什么需要服务治理:
如下图:
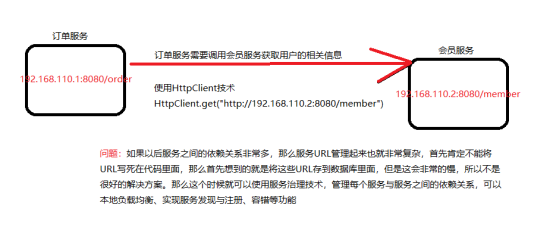
服务注册与发现
我们知道任何rpc远程框架中,都会有一个注册中心,SpringCloud支持三种注册中心:Eureka, Consul(go语言编写), Zookeeper;Dubbo支持常用两种注册中心:Zookeeper跟Redis,那么什么是注册中心呢?
注册中心
存放服务地址相关信息(接口地址),如下图
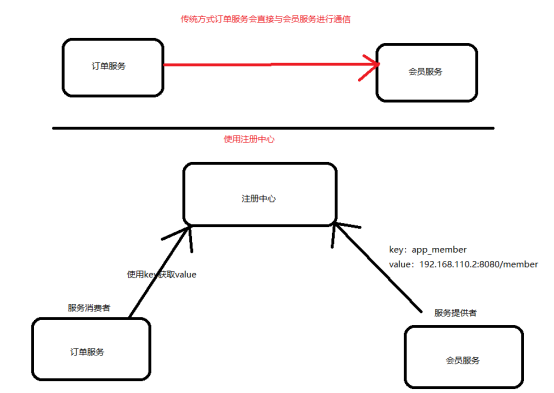
上图使用注册中心的步骤:
- 首先启动注册中心
- 启动会员服务,下面有几个概念
- 服务提供者:提供服务接口
- 服务消费者:调用别人接口进行使用
- 会员服务在启动的时候,会把当前服务的基本信息(比如服务地址和端口)以别名的形式注册到注册中心上
- 订单服务在调用远程接口的时候,使用服务别名也就是key去注册中心获取实际的rpc远程调用地址
- 一旦获取到rpc远程调用地址后,在本地使用HttpClient技术实现调用
总结:什么是服务注册,什么是服务发现
服务注册:将服务信息注册到注册中心上
服务发现:从注册中心上获取服务信息
搭建Eureka注册中心
导入Maven依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId> </dependency>
配置application.yml
server:
port: 8100 # 服务端口号
eureka:
instance:
hostname: 127.0.0.1 # 注册中心ip地址
client:
serviceUrl:
# 注册中心地址
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka
# 因为自己是注册中心,所以不需要把自己注册到注册中心(集群的时候需要注册)
register-with-eureka: false
# 因为自己是注册中心,所以不需要再检索服务信息
fetch-registry: false
在启动类中添加@EnableEurekaServer注解
@EnableEurekaServer
@SpringBootApplication
public class EurekaServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerApplication.class, args);
}
}
然后访问127.0.0.1:8100即可
搭建服务提供者注册到Eureka
导入Maven依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId> </dependency>
配置application.yml
server:
port: 8001
spring:
application:
name: jx-member # 服务注册到服务中心的名称 serviceId
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8100/eureka/ # 当前服务注册到eureka服务中心的地址
# 无需配置,因为默认是true
register-with-eureka: true # 需要将服务注册到eureka上
fetch-registry: true # 检索服务
在启动类上配置上@EnableEurekaClient
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient // 将当前的服务注册到eureka上
public class ProvideTicketApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ProvideTicketApplication.class, args);
}
}
在api.controller包下写返回的数据
一般会在controller上套一层api包,因为有些服务是没有页面的,套一层api包加以区分
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class MemberApiController {
@GetMapping("/getMember")
public String getMapper() {
return "this is member";
}
}
此时启动项目,再去注册中心就可以看到我们注册的服务了

搭建服务消费者
导入Maven依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId> </dependency>
配置application.yml
server:
port: 8200
spring:
application:
name: consumer-user # 注册到服务中心的名字
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8100/eureka # 将服务注册到服务中心
在主配置类上加上@EnableDiscoveryClient注解
注意,如果使用了RestTemplate获取远程接口,还需要将RestTemplate加到容器里面,以便使用单例模式
@EnableDiscoveryClient // 开启发现服务功能
@SpringBootApplication
public class ConsumerUserApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConsumerUserApplication.class, args);
}
@LoadBalanced // 启用负载均衡机制,如果有多个服务提供者,会轮询着访问
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
然后远程调用接口
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@RestController
public class OrderApp {
// RestTemplate是由SpringBoot Web组件提供的,默认整合ribbon负载均衡器
// rest方式底层采用HttpClient技术
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
/**
* 在SpringCloud中有两种方式调用其他服务提供的接口
* rest(SpringBoot Web)跟fegin(SpringCloud)
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/getOrder")
public String getMember() {
// 有两种方式调用:一种是采用服务别名方式调用,一种是直接通过地址调用(不会走注册中心)
String forObject = restTemplate.getForObject("http://jx-member/getMember", String.class);
return "这是:" + forObject;
}
}
搭建Eureka注册中心集群
首先,为什么要搭建集群,微服务rpc远程调用框架最核心的点在于服务治理,也就是注册中心,如果因为某种原因,注册中心出故障了,可能会导致整个微服务环境不可用,那解决这一问题的办法就是搭建注册中心集群
搭建eureka集群环境的思路:采用互相注册的原理,形成一组相互注册的注册中心,从而实现数据的相互同步,达到高可用效果
那么如何搭建呢?
首先需要新建一个注册中心,也就是一个项目,然后修改两个项目的配置文件
- 端口:两个注册中心设置不同的端口
- 名称:两个注册中心必须有名称,也就是spring.application.name
- 服务注册:将那两个注册服务相关的属性设置为true
- 注册中心地址:注册中心地址写上另外一个的(其实只需要改一下端口号即可),如果有多个注册中心,就用逗号隔开
eureka-server1
server:
port: 8100 # 服务端口号
eureka:
instance:
hostname: 127.0.0.1 # 注册中心ip地址
client:
serviceUrl:
# 注册中心地址
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:9100/eureka
# 因为自己是注册中心,所以不需要把自己注册到注册中心(集群的时候需要注册)
register-with-eureka: true
# 因为自己是注册中心,所以不需要再检索服务信息
fetch-registry: true
spring:
application:
name: eureka-server1
eureka-server2
server:
port: 9100 # 服务端口号
eureka:
instance:
hostname: 127.0.0.1 # 注册中心ip地址
client:
serviceUrl:
# 注册中心地址
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:8100/eureka
register-with-eureka: true
fetch-registry: true
spring:
application:
name: eureka-server2
然后访问8100跟9100两个端口,可以看到两个服务都已经互相注册好了

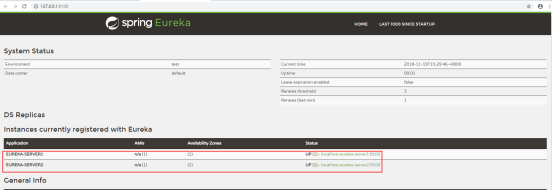
客户端调用Eureka集群
因为此时有多个注册中心了,所以服务提供者和消费者要将这几个注册中心的地址都带上
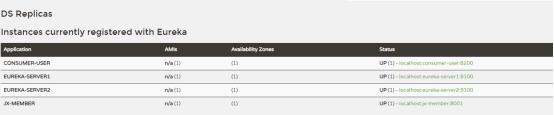
9100:
8100:
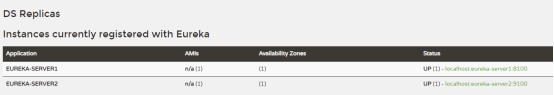
可以看到只有9100上有服务信息,8100上没有,这是因为,在注册过程中只会保证有一个注册中心有相应的服务数据,当9100宕机后,数据会自动同步到8100上
Eureka自我保护机制
Eureka分为两种角色
EurekaClient(注册客户端)
EurekaServer(注册中心服务端)
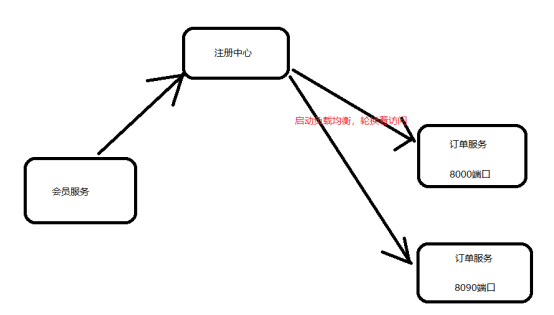
首先会有这么一个现象:由于订单服务开启了两台,一台8000,后面叫它8000,一台8090,后面叫它8090,那么现在会员服务去访问订单服务,会先去到注册中心,然后基于负载均衡机制轮换着访问8000跟8090,但是如果此时8000宕机了,那么就不能访问了,就得从注册中心剔除掉,否则仍旧会轮换着访问,而此时8000已经不能用了,再去访问就会出问题
为什么需要Eureka自我保护机制:基于上面的现象,我们知道,当8000宕机后,就会从注册中心剔除,但是有这么一种情况,如果8000并没有宕机,只是跟注册中心的网络不通畅,那么为了防止这种情况下误将8000从注册中心剔除掉,就得使用Eureka的自我保护机制了
自我保护机制:默认情况下EurekaClient会定时向EurekaServer端发送心跳包,来告诉EurekaServer自己是存活状态。相反,如果EurekaServer在一定时间(默认90s)内没有收到EurekaClient发送的心跳包,就会直接从注册中心中剔除该EurekaClient。但是在短时间内丢失了大量的服务实例心跳,这时候EurekaServer会开启自我保护机制,不会去剔除该服务
什么时候开启自我保护机制
建议在本地开发环境禁止自我保护机制,在生产环境下开启自我保护机制
那么怎样禁止自我保护呢?
需要在Server端的yml加上下面的配置
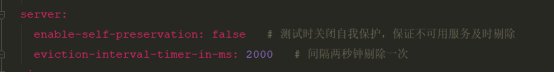
即如下配置
server:
port: 8100 # 服务端口号
eureka:
instance:
hostname: 127.0.0.1 # 注册中心ip地址
client:
serviceUrl:
# 注册中心地址
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:9100/eureka
# 因为自己是注册中心,所以不需要把自己注册到注册中心(集群的时候需要注册)
register-with-eureka: true
# 因为自己是注册中心,所以不需要再检索服务信息
fetch-registry: true
server:
enable-self-preservation: false # 测试时关闭自我保护,保证不可用服务及时剔除
eviction-interval-timer-in-ms: 2000 # 间隔两秒钟剔除一次
spring:
application:
name: eureka-server1
然后还要在服务端配置如下信息
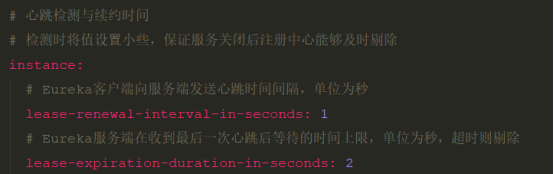
即如下配置
server:
port: 8001
spring:
application:
name: jx-member # 服务注册到服务中心的名称 serviceId
eureka:
# 心跳检测与续约时间
# 检测时将值设置小些,保证服务关闭后注册中心能够及时剔除
instance:
# Eureka客户端向服务端发送心跳时间间隔,单位为秒
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 1
# Eureka服务端在收到最后一次心跳后等待的时间上限,单位为秒,超时则剔除
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 2
prefer-ip-address: true
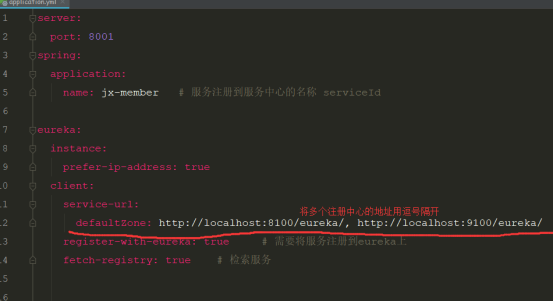
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8100/eureka/, http://localhost:9100/eureka/ # 当前服务注册到eureka服务中心的地址
register-with-eureka: true # 需要将服务注册到eureka上
fetch-registry: true # 检索服务
使用zookeeper作为注册中心
首先配置yml文件
server:
port: 8002
spring:
application:
name: zk-member
cloud:
zookeeper:
# 注册到zookeeper地址
connect-string: 192.168.253.132:2181
然后在入口类上标注上@EnableDiscoveryClient注解
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class ZkpServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ZkpServerApplication.class, args);
}
}
然后启动程序即可将该服务注册到zookeeper
当注册到了zookeeper注册中心后,其余的操作----使用会员服务调用订单服务的过程和Eureka做注册中心的时候是一样的,其实只是将一个注册中心变化了而已,其他的都不变
使用Consul搭建注册中心
安装
Consul是一套开源的分布式服务发现和配置管理系统,由Go语言开发
安装Consul,只需要把consul.exe放到一个英文目录下即可
然后打开cmd来到这个目录,执行命令consul agent -dev -ui -node=cy 即可启动consul
-dev:开发服务器模式启动
-node:结点名为cy
-ui:可以用界面访问,默认能访问
测试访问地址:http://localhost:8500
上面就是consul的界面,还是很漂亮的呢
实现服务注册与发现
首先导入Maven依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-consul-discovery</artifactId> </dependency>
然后配置yml
server:
port: 8501 # 服务端口号
spring:
application:
name: consul-member # 服务名称
cloud:
consul:
host: localhost # consul地址
port: 8500 # consul端口号
discovery:
# 默认情况下,服务注册到注册中心的地址是随机生成的英文:PC-jinxin
# 指定服务注册到注册中心的地址为下面的ip地址
hostname: 192.168.10.220
然后启动项目即可在consul中找到该服务

DiscoveryClient使用
有时我们希望能够在本地服务中获取一些注册中心的相关的信息,就可以调用这个API来获取相关信息
DiscoveryClient实际上是一个接口,想要使用只需要让Spring替我们自动注入即可
@RestController
public class ConsulMemberController {
@Autowired
private DiscoveryClient discoveryClient;
@RequestMapping("/discoveryClient")
public List<ServiceInstance> discoveryClient() {
/**
* getInstances:里面传入想要获取的服务的serverId
* 返回一个集合,因为有可能做集群,所以要用集合接收
*/
List<ServiceInstance> instances = discoveryClient.getInstances("consul-member");
instances.forEach((e) -> {
URI uri = e.getUri();// 获取url
System.out.println("url:" + uri);
});
return instances;
}
}

其他的一些api不做赘述
Spring Cloud客户端负载均衡
本地负载均衡与服务器端负载均衡的区别
Ribbon是Spring Cloud本地(客户端)的负载均衡器
那么它是如何实现的?
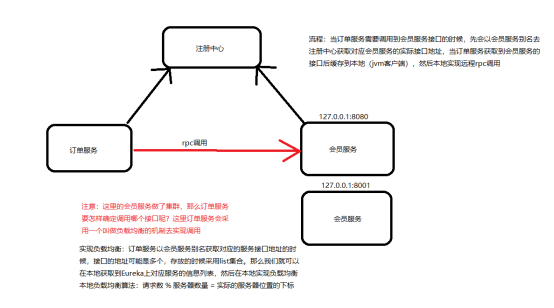
本地负载均衡实现算法:请求数 % 服务器数量,就可以得到对应服务器位置的下标
例:
List[0] ---> 127.0.0.1:8000
List[1] ---> 127.0.0.1:8001
假设总请求数为1 (总请求数为1:订单服务调用了一次会员服务)
会员服务器集群2台
那么 1 % 2 = 1,即下标是1,取List[1]
如果 2 % 2 = 0,即下标是0,取List[0]
如果 3 % 2 = 1,即下标是1,取List[1]
如果 4 % 2 = 0,。。。。。。
纯手写类似于Ribbon本地客户端负载均衡效果
@RestController
public class ExtRibbonController {
@Autowired
private DiscoveryClient discoveryClient;
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
// 请求总数
private int reqCount = 1;
@RequestMapping("/ribbonMember")
public String ribbonMember() {
// 1. 获取对应服务器远程调用地址
String instance = getInstance();
if (null == instance) {
return null;
}
String serverUri = instance + "/getOrder";
// 2. 使用rest方式发送请求
return restTemplate.getForObject(serverUri, String.class);
}
/**
* 获取当前要调用的服务的uri
* @return
*/
private String getInstance() {
List<ServiceInstance> instances = discoveryClient.getInstances("consul-order");
if ((null == instances) || (instances.size() <= 0)) {
return null;
}
// 算法:下标数 = 请求总数 % 服务集群数
int serverCount = instances.size();
int serverIndex = reqCount++ % serverCount;
return instances.get(serverIndex).getUri().toString();
}
}
Ribbon本地负载均衡与Nginx服务器端负载均衡区别
Ribbon本地负载均衡原理:在调用接口的时候,会在eureka注册中心上获取注册信息服务列表,获取到之后,缓存在jvm,然后本地实现rpc远程调用技术进行调用,就是客户端实现负载均衡
Nginx实现服务器端负载均衡原理:客户端的请求都会交给Nginx,然后由nginx实现转发请求,即负载均衡在服务器端实现
应用场景:本地负载均衡适合在微服务rpc远程调用,比如dubbo、springcloud;
服务器端负载均衡适合于针对于服务器端的,比如Tomcat、jetty



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号